Розробка уроку за професійним спрямуванням для електрослюсарів "What is electricity?"
Даний урок тісно пов'язаний з предметом "Фізика" та розглядає такі поняття, як "будова атома", "одиниці вимірювання електричного струму", "електропровідність матеріалів". Урок містить тексти для читання, аудіювання та письмові завдання для учнів.
Розробка уроку
з англійської мови
за професійним спрямуванням
для електрослюсарів
Theme: What is electricity?
Aim:
- Using the knowledge on physics to remember what is electricity, conductors, what are the types of current, units of measurement of current and connect this knowledge with English.
- Develop reading, listening and writing skills.
- Learn new lexical units.
- Bring up the respect and pride for the profession the students have chosen.
Type of the lesson: combined.
Equipment: texsts, cards, pictures.
PROCEDURE
I Preparing for the reception of foreign language
Greeting
T: Good morning children! How are you getting on?
Brain storm
T: Before starting to work answer my questions:
1)Without what you can not imagine your life? (electricity) (учні дають свої варіанти відповіді, якщо вони не вгадали продовжуємо задавати питання).
2)What do power plants produce? або With the help of what do mobile phones, computers, washing machines and other appliances work?
Aim
T: Yes, that’s right! Today we are going to talk about the electricity. We will use the knowledge on physics to remember what is electricity, conductors, what are the types of current, units of measurement of current and connect this knowledge with English.
II Main Part
Vocabulary work
The teacher reads the words that are on the blackboard and translate them, pupils repeat after the teacher and write them down in the vocabulary.
charge –заряд
coated – покритий
conductor –провідник
current flow – потік струму
impurity – домішка
insulator – ізолятор
to orbit – рухатись по орбіті
to pass through – проходити крізь
property – властивість
semiconductor – напівпровідник
shell - оболонка
halfway – частково, наполовину
steady – стійкий, міцний
to switch off - вимкнути
thickness - товщина
to name after – названий в честь к-н
valence - валентність
T: Now, to find out more about the electricity we will have to know what are all substances, solids liquids or gases composed of. Read the text attentively, please.
All substances, solids, liquids or gases, are composed of one or more of the chemical element s. Each element is composed of identical atoms.
Each atom is composed of a small central nucleus consisting of protons and neutrons around which orbit shells of electrons.
These electrons are very much smaller than protons and neutrons. The electrons in the outermost shell are called valence electrons and the electrical properties of the substance depend on the number of these electrons.
Neutrons have no electric charge, but protons have a positive charge while electrons have a negative charge. In some substances, usually metals, the valence electrons are free to move from one atom to another and this is what constitutes an electric current.
T: Here is a scheme of the atom on the blackboard. Please, draw the same scheme in your copybooks and label the picture with the name of each part according to the text.
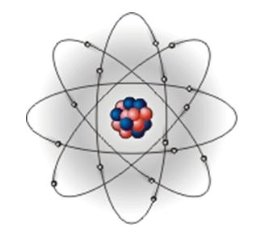
T: Well done! Now, read the text again and complete the sentences with the missing information. Write your answers in your copybooks.
1 Elements make up _____ ________________________________________
2 Identical atoms ________________________________________________
3 Atoms consist of _________,___________and_______________________
4 Inside there are ________ and___________ , while outside_____________
5 Shells________________________________________________________
6 Valence electrons ______________________________________________
7 Neutrons do not have ___________________________________________
8 Electricity is generated when _____________________________________
(Вчитель перевіряє вправу запитуючи учнів по одному)
T: Now, you can see some words on the blackboard. Listen to the text attentively and complete it with these missing words.
(Учні слухають аудіо запис та підставляють слова в текст)
|
flow |
reduce |
resistance |
few |
|
insulator |
charge |
conductors |
plastic |
Electricity consists of a (1) ______ of free electrons along a conductor. To produce this current flow, a generator is placed at the end of the conductor in order to move the (2)______
Conductors
Electricity needs a material which allows a current to pass through easily, which
offers little (3)______ to the flow and is full of free electrons. This material is called a conductor and can be in the form of a bar, tube or sheet. The most commonly used (4) _______ are wires, available in many sizes and thicknesses. They are coated with insulating materials such as plastic.
Semiconductors
Semiconductors such as silicon and germanium are used in transistors and their
conductivity is halfway in between a conductor and an (5) _______ Small quantities of other substances, called impurities, are introduced in the material to (6) _______ the conductivity.
Insulators
A material which contains very (7) __________ electrons is called an insulator. Glass, rubber, dry wood and (8) ______ _ resist the flow of electric charge, and as such they are good insulating materials.
(Вчитель перевіряє текст)
T: Good! Now, you have some cards, named “insulator”, “semiconductor” and “conductor”. Your task is to arrange the materials according to their conductivity.
(Rubber, glass, wood, dry air, silicon, germanium, water, carbon, mercury, iron, aluminium, copper, silver)
(Вчитель перевіряє завдання)
T: Now, look through the text you have already got and decide if the following statements are true (T) or false (F), then correct the false ones.
1 A flow of electrons moving inside a conductor creates an electric current.
2 A generator is used to move the charges.
3 Electrons can easily pass through any material.
4 Any material is a good conductor.
5 Conductors are coated with insulators.
6 The presence of free electrons affects the conductivity of materials.
7 Impurities are introduced to increase conductivity.
8 Insulating materials resist the flow of electrons.
T: Read the text and complete the table with the missing information.
There are two types of current: Direct current (DC) and Alternating current (AC).
Direct current is a continuous flow of electrons in one direction and it never changes its direction until the power is stopped or switched off.
Alternating current constantly changes its direction because of the way it is generated. The term 'frequency' is used to indicate how many times the current changes its direction in one second.
Alternating current has a great advantage over direct current because it can be transmitted over very long distances through small wires, by making energy high voltage and low current.
There are several quantities that are important when we are talking about electric current. Volts (V) - so named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta - measure the difference of electric potential between two points on a conducting wire. Amperes (A) measure the amount of current flowing through a conductor, that is to say the number of electrons passing a point in a conductor in one second. Coulomb (C) measure the quantity of charge transferred in one second by a steady current of one ampere. Power is the rate at which work is performed and it is measured in watts (W). A Kilowatt (kW), which is equal to one thousand watts, is used to measure the amount of used or available energy. The amount of electrical energy consumed in one hour at the constant rate of one kilowatt is called kilowatt-hour.
|
Unit of measurement |
What does it measure? |
|
1) |
The number of electrons passing a given point in a conductor in one second |
|
2) |
The quantity of electricity transferred by a steady current of one ampere |
|
3) |
The amount of electric energy used |
|
4) |
The difference of potential between two points on a conductor |
|
5) |
Rate at which work is done |
III Summarizing
T: Now, let’s remember, what have we talked about today?
1) What does the atom consist of?
2) Name the groups of materials according to their conductivity.
3) Name the two types of current.
4) Name the units of measurement.
Homework
Learn new words by heart.
ДОДАТОК 1
All substances, solids , liquids or gases, are composed of one or more of the chemical element s. Each element is composed of identical atoms.
Each atom is composed of a small central nucleus consisting of protons and neutrons around which orbit shells of electrons.
These electrons are very much smaller than protons and neutrons. The electrons in the outermost shell are called valence electrons and the electrical properties of the substance depend on the number of these electrons.
Neutrons have no electric charge, but protons have a positive charge while electrons have a negative charge. In some substances, usually metals, the valence electrons are free to move from one atom to another and this is what constitutes an electric current.
1 Elements make up _____ ________________________________________
2 Identical atoms ________________________________________________
3 Atoms consist of _________,___________and_______________________
4 Inside there are ________ and___________ , while outside_____________
5 Shells________________________________________________________
6 Valence electrons ______________________________________________
7 Neutrons do not have ___________________________________________
8 Electricity is generated when _____________________________________
ДОДАТОК 2
Electricity consists of a (1) ______ of free electrons along a conductor. To produce this current flow, a generator is placed at the end of the conductor in order to move the (2)______
Conductors
Electricity needs a material which allows a current to pass through easily, which
offers little (3)______ to the flow and is full of free electrons. This material is called a conductor and can be in the form of a bar, tube or sheet. The most commonly used (4) _______ are wires, available in many sizes and thicknesses. They are coated with insulating materials such as plastic.
Semiconductors
Semiconductors such as silicon and germanium are used in transistors and their
conductivity is halfway in between a conductor and an (5) _______ Small quantities of other substances, called impurities, are introduced in the material to (6) _______ the conductivity.
Insulators
A material which contains very (7) __________ electrons is called an insulator. Glass, rubber, dry wood and (8) ______ _ resist the flow of electric charge, and as such they are good insulating materials.
1 A flow of electrons moving inside a conductor creates an electric current.
2 A generator is used to move the charges.
3 Electrons can easily pass through any material.
4 Any material is a good conductor.
5 Conductors are coated with insulators.
6 The presence of free electrons affects the conductivity of materials.
7 Impurities are introduced to increase conductivity.
8 Insulating materials resist the flow of electrons.
ДОДАТОК 3
There are two types of current: Direct current (DC) and Alternating current (AC).
Direct current is a continuous flow of electrons in one direction and it never changes its direction until the power is stopped or switched off.
Alternating current constantly changes its direction because of the way it is generated. The term 'frequency' is used to indicate how many times the current changes its direction in one second.
Alternating current has a great advantage over direct current because it can be transmitted over very long distances through small wires, by making energy high voltage and low current.
There are several quantities that are important when we are talking about electric current. Volts (V) - so named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta - measure the difference of electric potential between two points on a conducting wire. Amperes (A) measure the amount of current flowing through a conductor, that is to say the number of electrons passing a point in a conductor in one second. Coulomb (C) measure the quantity of charge transferred in one second by a steady current of one ampere. Power is the rate at which work is performed and it is measured in watts (W). A Kilowatt (kW), which is equal to one thousand watts, is used to measure the amount of used or available energy. The amount of electrical energy consumed in one hour at the constant rate of one kilowatt is called kilowatt-hour.
|
Unit of measurement |
What does it measure? |
|
1) |
The number of electrons passing a given point in a conductor in one second |
|
2) |
The quantity of electricity transferred by a steady current of one ampere |
|
3) |
The amount of electric energy used |
|
4) |
The difference of potential between two points on a conductor |
|
5) |
Rate at which work is done |
ДОДАТОК 4
|
Insulator |
|
|
Semiconductor |
|
|
Conductor |
|
|
Rubber |
Water |
|
Glass |
Carbon |
|
Wood |
Mercury |
|
Dry air |
Iron |
|
Silicon |
Aluminium |
|
Germanium |
Copper |
|
|
Silver |
ДОДАТОК 5
|
flow |
|
insulator |
|
reduce |
|
charge |
|
resistance |
|
conductors |
|
few |
|
plastic |
ДОДАТОК 6
|
charge |
|
coated |
|
conductor |
|
current |
|
halfway |
|
impurity |
|
insulator |
|
to name after |
|
to orbit |
|
to pass through |
|
property |
|
Semiconductor |
|
shell |
|
steady |
|
to switch off |
|
thickness |
|
valence |
|
conductivity |


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
