ACCOUNTING методична розробка з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)» в закладах фахової передвищої освіти
Лисичанський промислово-технологічний фаховий коледж

ACCOUNTING
методична розробка
з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)»
в закладах фахової передвищої освіти
Розробник: Скиба Н.М., старший викладач, викладач вищої категорії Лисичанського промислово-технологічного фахового коледжу
2024
BСТУП
Методична розробка заняття виконана у відповідності з методичними рекомендаціями з підготовки та проведення практичних занять у закладах фахової передвищої освіти. Заняття підготовлено відповідно до робочої і навчальної програми з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)». У методичній розробці заняття подано розгорнутий план-конспект заняття у формі мовного практикуму з використанням методу критичного мислення, методики роботи з лексичним матеріалом, методу лінгвістичного квесту, рольовою грою, перелік літератури та необхідного обладнання, мету і задачі, надано чітку структуру заняття, вдало подано мотивацію пізнавальної діяльності студентів.
Розробка містить багато різноманітних форм та методів роботи (бесіду, читання, мозковий штурм, аудіювання з використанням тематичного відеоролику, роботу з мультимедійними презентаціями, групову та парну роботу,), що відповідають психофізіологічним та індивідуальним особливостям студентів і сприяють успішному досягненню мети заняття.
Методична розробка відкритого заняття відповідає теоретичному й методико-практичному розділам навчальної програми, має інноваційний характер, відповідає новітнім технологіям навчання, спрямована на формування комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців, розвиток пам'яті, уваги, фонематичного слуху студентів, сприяють зацікавленості та формуванню комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців.
Методична розробка може бути рекомендована для викладачів іноземної мови в закладах фахової передвищої освіти в якості як основного, так і довідково-дидактичного матеріалу.
МЕТОДИЧНА РОЗРОБКА ЗАНЯТТЯ
Заняття №
Предмет: Іноземна мова
Група:
Тема заняття: ACCOUNTING
Мета: формувати лексичні навички й навички вимови; вдосконалювати навички читання й усного мовлення; розвивати мовну здогадку й мовленнєву реакцію; виховувати зацікавленість у розширенні своїх знань, використовувати раніше вивчені структури, а також збагачувати словарний запас, практикуватися у перекладі речень, розвивати навички логічного викладання думок, пам'ять, виховувати свідоме ставлення до навчання, вчити раціонально використовувати свій час, прищеплювати бажання вивчати іноземну мову.
Обладнання: словники, комп’ютер, роздавальний матеріал
Тип заняття: практичне
Міжпредметні зв'язки: Економіка підприємства, Статистика, Фінанси підприємства, Економічний аналіз, Організація виробництва, Менеджмент, Маркетинг
СТРУКТУРА ЗАНЯТТЯ:
1.Організаційний момент:
1)Привітання
2) Перекличка
3)Перевірка готовності до заняття
2. Мотивація навчальної та пізнавальної діяльності студентів, оголошення теми та цілей заняття.
3.Реалізація теми за планом
4. Підсумок заняття. Оцінювання
5. Домашнє завдання
ХІД ЗАНЯТТЯ:
I. Scanning reading. Читання з повним розумінням змісту прочитаного.
I. Read the text ACCOUNTING.Use a dictionary, if necessary.
Accounting can be defined as the measuring and recording of all relevant financial data concerning a particular entity that is business, government organisation, etc.Financial reporting is the communicating of such information in appropriately summarised form. In the UK such summarised form is called "Accounts". In the USA it is called "Financial statements". These accounts or statements are communicated to interested parties both within and outside the organisation.

Financial reporting provides information that is useful to present and potential investors, creditors and other users in making rational investment, credit and other economic decisions.Accounting is often referred to as the "language of business". It is used in the business world to describe the transactions entered into by all kinds of organisations.
The actual record-making phase of accounting is usually called book-keeping. However, accounting extends far beyond the actual making of records. Accounting is concerned with the use to which these records are put, their analysis and interpretation. Accountants are therefore those individuals specialised in the "art" of capturing the correct data, and preparing the most meaningful financial reports from that data. They are "producers" of financial information, which is then made available to "consumers" such as owners and lenders.
Accountants are assisted in their work by bookkeepers, who operate some form of accounting system, usually computerised, to help capture, accumulate, categorise, summarise and report the many thousands of transactions that affect an economic entity every year.Accounting shows a financial picture of the firm. An accounting department records and measures the activity of a business. It reports on the effects of the transactions on the firm’s financial condition. Accounting records give a very important data. It is used by management, stockholders, creditors, independent analysts, banks and government.Most businesses prepare regularly the two types of records. That is the income statement and balance sheet. These statements show how money was received and spent by the company.
One major tool for the analysis of accounting records is ratio analysis. A ratio analysis is the relationship of two figures. In finance we operate with three main categories of ratios. One ratio deals with profitability, for example, the Return on Investment Ratio. It is used as a measure of a firm’s operating efficiency.The second set of ratios deals with assets and liabilities. It helps a company to evaluate its current financial position.The third set of ratios deals with the overall financial structure of the company. It analyses the value of the ownership of the firm.
The purpose of accounting is to provide the company's shareholders with a clear picture of the company's financial health. This "photograph", which is usually published once a year, can be used as a managerial tool, allowing us to see how efficient a company is, and whether it should stay in business.
II. Give English equivalents to the following:
1.продуктивність; 2. ревізування; 3. прибутковість; 4. аудит; 5. нерозподілений прибуток; 6. бухгалтерський облік; 7. бухгалтерську справу; 8. прогноз збуту; 9. періодичність обліку; 10. валовий прибуток; 11. рахунок; 12. прибуткові статті; 13. торговельна операція; 14. акціонерний капітал; 15. дебет; 16. бухгалтерський баланс; 17. кредит; 18. оприбуткування; 19. пробний баланс.
III. Give equivalents to the following:
А financial picture of the firm, an accounting department, a transaction, important data, stockholders, income statement, balance sheet, a major tool, ratio analysis, to deal with, profitability, assets and liabilities, current financial position, accounting, financial accounting, managerial accounting, product cost accounting, bookkeeping, accounting cycle, account , transaction .
IV. Read and translate the definitions of the basic accounting terms:
1. Accounting - the process of systematically collecting, analyzing, and reporting financial information.
2. Auditing - checking the accuracy of records.
3. Audit - an accountant's examination of a company's financial records to determine if it used proper procedures to prepare its financial reports.
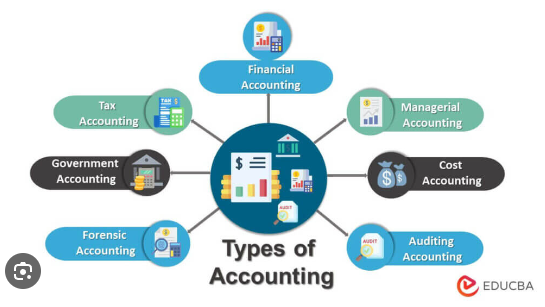
4. Financial accounting - a "scorekeeping" process that is meant to keep several interested groups (inside and outside the firm) informed of the financial condition of the firm.
5. Managerial accounting - serves the firm's managers by calling attention to problems and aiding them in planning, decision making, and controlling the firm's operations.
6. Product cost accounting - an accounting system that allocates costs to the various products made by a firm.
7. Responsibility accounting - an accounting system for classifying costs or charging them to certain responsibility centers so as to allow the performance of such centers (and their managers) to be evaluated.
8. Bookkeeping - the accurate day-to-day recording of all the financial transactions that occur in an organization; the initial step in the accounting process.
9. Accounting cycle - the sequence of accepted procedures that accountants must follow over a specific period of time.
10. Account - an individual written record for specific assets, liabilities, owners' equity, revenues, and expenses.
11. Transaction - a financially significant event that either increases or decreases the value of an account.
12. Debit — in bookkeeping, any transaction that increases assets or decreases liabilities or owner’s equity; always entered in the left column.
13. Credit — in bookkeeping, any transaction that decreases assets or increases liabilities or owner’s equity; always entered in the right column.
14. Basic accounting equation — a mathematical statement of the balance between what a firm owns, what it owes, and what its owners’ equity is.
15. Profit equation — profits equal revenue minus expenses.
16. Owners’ equity — the difference between a firm’s assets and its liabilities; what would be left over for the firm’s owners if its assets were used to pay off its liabilities.
17. Accrual — the principle in accounting that means that a firm charges off expenses only in the accounting period (usually the calendar year) and not necessarily in the period in which the actual cash payment was made.
18. Double-entry bookkeeping — a system in which each financial transaction is recorded as two separate accounting entries to maintain the balance shown in the accounting equation.
19. General journal — a book of original entry in which typical transactions are recorded in order of their occurrence.
20. General ledger — the book in which all the accounts of a business using double-entry bookkeeping are contained.
21. Posting — the process of transferring journal entries to the general ledger.
22. Trial balance — a summary of the balances of all general ledger accounts at the end of the accounting period.
23. Balance sheet (statement of financial position) — a summary of a firm’s assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity accounts at a particular time, showing the various money amounts that enter into accounting equation.
24. Accounting software package — a set of computer programs designed for solving various problems of accounting.
25. Certified public accountant (chartered accountant in BrE) — an accountant who has fulfilled the legal requirements of his or her state of knowledge in accounting theory, practice, auditing, and law and who is licensed to sign financial reports.
26. Capital stock — the original investment of the stockholderowners.
27. Revenues — are the funds received by a business, mainly from the sales of goods and services.
28. Gross profit — the difference between net sales and cost of goods sold.
29. Sales forecast — a prediction of what sales will be over a certain period of time.
30. Profit (net income, earnings) — the difference between total revenues and total expenses.
31. Retained earnings (surplus) — the amount that the firm has plowed back from profits over the years but has not paid out in dividends.
32. Return on sales (net profit margin) — a form of profitability ratio calculated as net income divided by net sales.
33. Profitability- the possibility and ability of a firm to produce a profit.
34. Productivity — the average level of output per unit of time per worker.
35. Efficiency — maximum output of a good from minimum resources used in production.
V. Agree or disagree with the statements:
1. At the end of the fiscal year a business must check out the assets and liabilities.
2. There is no difference between gross salary and net salary.
3. An employer should hire an experienced accountant for preparing a financial statement.
4. The accounting department provided data for the management.
5. The board of directors never checks out assets and liabilities a net worth.
6. Governmental corporations can not issue stock certificates.
7. The whole of financial accounting is based on the accounting equation.
8. The resources possessed by the firm are known as liabilities.
9. Credit — in bookkeeping, any transaction that increases assets or decreases liabilities or owner’s equity; always entered in the left column.
10. Most businesses prepare regularly the three types of records.
VI. Fill in the gaps using the words given:
(Business, accounting, transactions, accountants, system, financial, information, records)
1._____ is commonly defined as a comprehensive _____ for collecting, analyzing, and communicating financial _____.
2. It is the accountant’s responsibility to keep ____ of _____ transactions such as taxes, sales, incomes, and expenses.
3. Even more important is the accountant’s analysis of how those _____ will affect a particular business.
4. By sorting, analyzing, classifying, and recording thousands of transactions, _____ can determine how well a _____ is being managed and how financially strong it is.

VII. Complete as in the text:
- Accounting can be defined... the measuring and recording. . all relevant financial data.
- ... the UK such summarised form of financial reporting is called...
- ... the USA it is called...
- Financial reporting provides information that is useful to... and other users.
- Accounting is a direct result of the work of...
- Accountants specialize in the art ... capturing the correct data and preparing reports... that data.
- This financial information is made available to consumers such as...
- Accountants are assisted in their work... bookkeepers.
- Accountants report the many thousands... transactions that affect... every year.
VIII. Translate into English:
- Бухгалтерський облік - упорядкована система збору, реєстрації та узагальнення інформації про стан майна, зобов'язань організації та їх зміни (руху коштів) шляхом документального обліку всіх господарських операцій.
- Об'єктами бухгалтерського обліку є майно організацій, їх зобов'язання та господарські операції, здійснювані організаціями у процесі діяльності.
- .Однією з основних завдань бухгалтерського обліку є формування повної та достовірної інформації про діяльність організації та її майнове становище, необхідної як внутрішнім користувачам-керівникам, засновникам, учасникам та власникам майна організації, так і зовнішнім - інвесторам, кредиторам та іншим.
- .Завдання бухгалтерського обліку вирішуються з допомогою різних способів і прийомів, сукупність яких називається шляхом бухгалтерського обліку.
- Метод бухгалтерського обліку включає такі основні елементи: документування;оцінка;бухгалтерські рахунки;подвійний запис; інвентаризація; калькулювання;складання балансу та звітності.
IX. Answer some questions:
1. What is the purpose of accounting?
2. Who uses the data provided by accounting firms?
3. What are the two types of records which most businesses prepare?
4. What is the purpose of the ratio analysis?
5. What categories of ratios in finance do you know?
SUMMARIZING.
Підведення підсумків уроку. Бесіда в режимі T-P1P2.
T: What topic did we start discussing today? What did we read about? What new words and word combinations have you learned? What material was difficult/ interesting/boring? So, you all see where you need more practice and what you can do well.
Setting homework. Постановка домашнього завдання
T: Your home task is to write a table on the following topic ACCOUNTING
Use your notes from class!


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку