Інтегрований урок біології та англійської мови
UNICELLULAR ANIMAL-LIKE ORGANISMS WHICH ARE PATHOGENS
OF HUMAN DISEASES
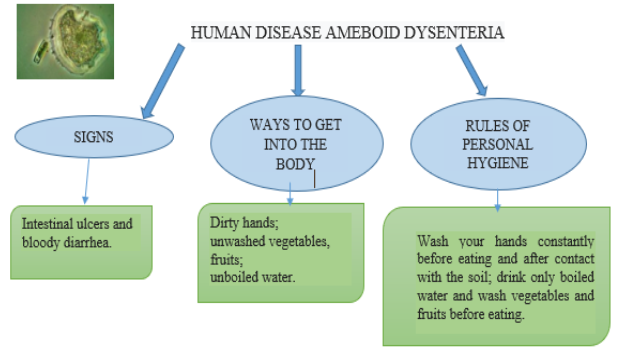
Today we learn about parasitic unicellular animal-like organisms: dysenteric amoeba and
Plasmodium falciparum. Parasites are organisms that live inside or on the surface of other
creatures, feed for a long time at their expense.
General characteristics of unicellular animal-like organisms
|
|
Sign |
|
|
1 |
Habitat |
human intestine |
|
2 |
Body shape |
does not have a constant body shape |
|
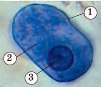
3 |
Physique |
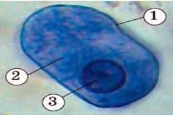
2 - cytoplasm; 3 - core |
|
4 |
Movement |
moves and captures food with the help of fake legs |
|
5 |
Breath |
breathes all over the body |
|
6 |
Nutrition |
it feeds on the cells of bacteria that live in the intestines and leftover food |
|
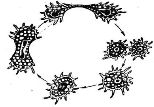
7 |
Reproduction |
|
|
8 |
Adaptation to adverse conditions |
forms cysts |
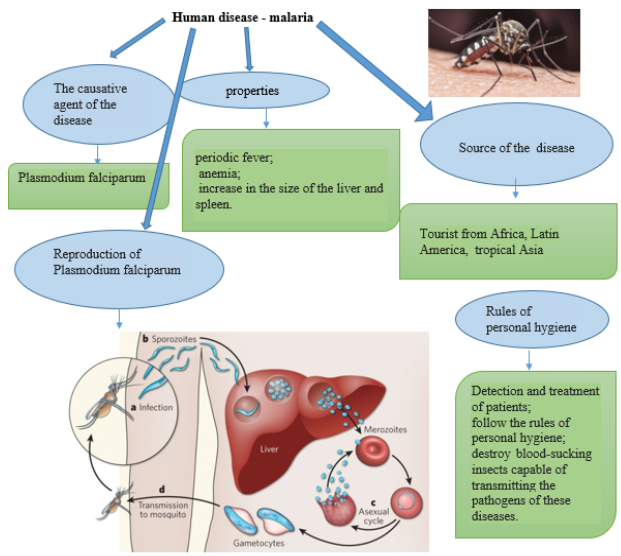
Malaria infection
Due to the bite of a female malaria mosquito, Plasmodium falciparum cells enter human blood. The parasites enter the liver cells of an infected person and multiply there. When a liver cell is destroyed, parasites are released. Then the cells of Plasmodium falciparum enter the human blood and multiply many times. When a female mosquito bites a person, it gets infected and carry the diseases to another human.

- Fill in the table.
|
Word |
Transcription |
Translation |
|
|
/ˈʌl.sər/ |
|
|
|
/ˈpæθ.ə.dʒən/ |
|
|
|
/ɪnˈtes·tənz/ |
|
|
|
/ˈkæp.tʃər/ |
|
|
|
/ˈdɪs.ən.tər.i/ |
|
|
|
/ˌdaɪ.əˈriː.ə/ |
|
|
|
/ˈhaɪ.dʒiːn/ |
|
|
|
/plazˈməʊdɪəm / |
|
|
|
/ˈlɪv.ər/ |
|
|
|
/ˈhen.ə/ |
|
- Match the words with their definitions:
|
1 |
ulcers |
a) |
a long tube through which food travels while it is being digested after leaving the stomach |
|
2 |
pathogen |
b) |
a break in the skin, or on the surface of an organ inside the body, that does not heal naturally |
|
3 |
intestines |
c) |
any small organism, such as a virus or a bacterium that can cause disease |
|
4 |
captures |
d) |
to take something into your possession, especially by force |
|
5 |
dysentery |
e) |
a disease that causes the contents to be passed out of the body much more often and sometimes with blood |
|
6 |
diarrhea |
f) |
the degree to which people keep themselves or their environment clean |
|
7 |
hygiene |
j) |
an illness in which the body's solid waste is more liquid than usual and comes out of the body more often |
|
8 |
plasmodium |
h) |
a unicellular parasite of humans that causes malaria |
|
9 |
liver |
i) |
a reddish-brown substance made from the leaves of a bush and used for colouring hair or skin |
|
10 |
henna |
j) |
- Indicate which statement is true and which is false.
1) Parasites can photosynthesize.
2) Parasitic organisms are exclusively heterotrophs and receive nutrients from the host organism.
3) Dysenteric amoeba is able to form cysts.
4) To protect against dysentery it is necessary to follow the rules of personal hygiene.
5) Parasitic Plasmodium can infect humans through unwashed hands.
6) The carrier of Plasmodium falciparum is a mosquito.
5. Define the following concepts:
1. Parasite.
2. Amoeboid dysentery.
3. Malaria.
6. Sign the structure of the dysenteric amoeba:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку