Конспект заняття з англійської мови для 1 курсу студентів коледжу
Конспект заняття
Предмет Англійська мова
Група
Викладач Дерека К.О.
Вид заняття практичне заняття
Тема заняття Минулий тривалий час.
Утворення питальної та заперечної форми.
Студентське життя. Освіта в Україні і закордоном
Мета заняття
Навчальна:
1. Залучити студентів до активної мовленнєвої діяльності на занятті шляхом використання сучасних засобів навчання та різних організаційних форм роботи.
2. Розширити знання студентів про таке граматичне явище –минулий тривалий час та тренувати його у вживанні;
3.Навчити ставити запитання загального типу в Past Continuous;
4. Розширювати лексичний запас по темі.
5. Учити діставати інформацію з тексту.
6. Учити будувати аргументоване висловлювання.
7. Збагачувати мову ідіоматичними виразами.
Розвиваюча:
1. Розвивати навички читання із загальним обхватом змісту.
2. Розвивати критичне і логічне мислення при постановці проблеми, уміння аргументовано висловлюватися, переконувати співбесідників, враховуючи при цьому їх аргументи і факти;
3. Розвивати мовну здогадку та мовленнєву реакцію.
Виховна:
1. Виховувати культуру спілкування
2. Учити вести дискусію.
Лiтература, методичне та матерiальне забезпечення заняття:
- Робочий зошит з англійської мови складений викладачем
Education is what survives
when what has been learned has been forgotten.
B.F. Skinner
Хід заняття
- Органiзацiйний момент (1-2хв.)
- Контроль знань та навичок студентiв: (перевiрка домашнього завдання):
- Перевірка вивчення теорії про Прислівники. Ступені порівняння прислівників.
- Past Simple Tense
- Переказ тексту “Travelling”.
-
Вивчення нового матерiалу (75-80% основного часу заняття):
- Питання, які будуть вивчатися на занятті:
- Ознайомлення з новою темою «Студентське життя. Освіта в Україні і закордоном». Ознайомлення з новими лексичними одиницями.
- Читання та переклад нових слів до теми [3].
- Запис нових слів, фраз і виразів у зошит та словник.
Слово викладача: In Great Britain children begin to go to school at the age of five. First they study at infant schools. In these schools they learn to draw with coloured pencils and paints. They also make figures out of plasticine and work with paper and glue. They play much because
they are very young. Later they begin to learn letters and read, write and count.
At the age of seven English schoolchildren go to junior schools. They do many subjects: English and Maths, History and Music, Natural History and Drawing, Handicrafts, French and Latin. They do not go to school as early as we do, but they stay there longer. The first lesson usually starts at 9 o'clock. There are 3 lessons with short breaks of 10 minutes between them and then an hour break for lunch. After lunch they have two more lessons which are over by half past three.
If you have a look at an English pupil's school record you will see that the marks in it differ from the marks we have. Our schoolchildren get markes from 1 to 12. At English school there are marks from 1 up to 10 and at some schools from 1 up to 100.
Junior school ends at the age of 11 when pupils take the Eleven Plus examination and then secondary school begins.
At the age of 16 schoolchildren take their exams. Only 45 per cent continue with full-time education after 16. The rest go to work or join employment training schemes.
Now, let’s write the difference between 2 words: bring up and educate.
Bring up and upbringing are mostly used for the moral and social training that children receive at home.
Educate and education are used for the intellectual and cultural training that people get at school and university.
She was brought up by her grandmother and educated at the local secondary school.
His son is very badly brought up — always screaming and fighting.
Would you rather have a good upbringing and a bad education, or the opposite?
Ok. Let’s read the text about education in GB.
- Подання тексту для читання “Education in Great Britain” [3].
1) Pre-reading. Дотекстова підготовка:
T: Listen to a humorous rhyme.
The more we study, the more we know.
The more we know, the more we forget.
The more we forget, the less we know.
The less we know, the less we forget.
The less we forget, the more we know.
- Why study?
- Is education really important? What do you think?
 2) While-reading. Робота з текстом.
2) While-reading. Робота з текстом.

3) Post reading. Обговорення тексту шляхом відповідей на комунікативні запитання.
1. What does the system of secondary education in Ukraine include?
2. What age do children go to school?
3. What is the system of higher education presented by?
4. When do children begin to go to school in Britain?
5. What subjects do they study?
2. Let’s do some exercises about different types of secondary school.
Fill in the blanks with the words given in the box below.
|
independent school(s) link(s) pupil(s) education academic general slant secondary entrance attend fee(s) types ability (ies) college(s) specialist |
Different Types of Secondary School
Over 85 per cent of __________(1) school pupils go to comprehensive schools. These take children of all _____(2), and provide a wide range of secondary______(3) for all or most of the children in a district from the age 11 to 16 or 18.
There are also other _____ (4) of secondary school. Grammar schools offer a mainly _____(5) education for the 11 to 18-year age group. Children enter grammar schools on the basis of their abilities, first sitting the 11-plus or _____ (6) examination. Grammar ________ (7) cater for 4% of children in secondary education.
A small minority of children _____(8) secondary modern schools (around 4%). These schools provide a more ______ (9) and technical education for children aged 11—16.
City Technology Colleges (CTCs) aim to give boys and girls a broad secondary education with a strong technological and business ____ (10).
They are non-fee-paying _____ (11) schools, set up by the Government with the help of business sponsors who finance a large proportion of the initial capital costs and develop ____(12) with the schools. There are now 15 such ______(13) in operation in England and Wales.
Specialist schools, which only operate in England, give _____(14) a broad secondary education with a strong emphasis on technology, languages, art and sports. There are over 250 _______(15) schools. They charge no_______ (15) and any secondary school can apply for specialist school status.
- Робота з малюнком. Читання та переклад тексту про різницю у освіті Великої Британії та США на сторінці 67.
EDUCATION IN ENGLAND & WALES (TO AGE 16)
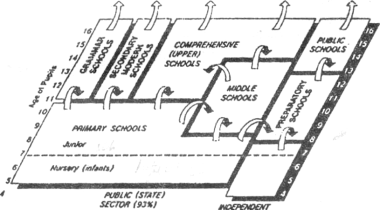
- Заповнення таблиці після тексту на сторінці 67.
- Виконання завдань на закріплення лексичних навичок.
- Match each AE word or phrase in the left-hand column with its BE equivalent from the right-hand column
1. public school ( free local authority school) a. first year student
2. student b. public school ( private fee-paying school)
3. to graduate from a school c. last year student
4. two semesters or four quarters d. time-table
5. freshman year (at college) e. essay
6. senior year (at college) f. pupil
7. sophomore year (at college) g. headmaster
8.schedule h. second year student
9. term paper i. holidays
10. school principal j. to leave school
11. vocation k. three terms (at universities)
- Робота з ідіоматичними виразами.
Memorize some idioms and idiomatic expressions dealing with the topic "Education". Make up sentences of your own using them:
- То learn smth. by heart means to learn smth. so well that it can be written or recited without thinking; to memorise smth.
Вивчити щось папам 'ять.
- То live and learn (a proverb, also informal and folksy. Usually said when one is surprised to learn smth.) means to increase one's knowledge by experience
Вік живи, вік учись. Життя коротке, мистецтво вічне.
Synonym: Art is long, life is short.
- То hit the books (Am., slang) means to begin to study; to study
Починати вчитись; вчитись.
- То cut a lecture (informal) means to skip going to class; to stay away from school without permission or explanation
Пропустити, не бути присутнім на уроці, лекції; прогулювати (уроки в школі, заняття в університеті)
Synonyms: To cut class (Am., informal)
To play hook(e)y (Am., informal)
To play the wag (informed)
To play truant (informal).
- То flunk the exam means to fail at the examination
Провалитися на іспиті.
- On paper means a) in writing; b) in theory rather than in reality
а) письмово; б) лише на папері.
- A ready tongue means to have an ability to speak fluently, to have a ready answer to any question
Добре підвішений язик
- Робота з прислів’ями.
Use the proverbs and sayings in a natural context. First make sure that you know what they mean and prove that they have sense:
- Education is life, not books.(African).
- Education is light, lack of it is darkness (Russian).
- He who has knowledge has power (Iranian).
- Knowledge comes through practice(Irish).
- Knowledge is no burden(English).
- Knowledge is power (English).
- Repetition is mother of knowledge(African).
- Never too late to learn ( Scottish)
- Soon learned, soon forgotten (English).
- We are to learn while we live ( Scottish)
- Respect your teachers more that your parents (Russian).
- A good tongue is a good weapon (English).
- Повторення граматичного матеріалу «Минулий тривалий час».
Past Continuous утворюється з допоміжного дієслова to be b Past Indefinite та дієприкметника теперішнього часу основного дієслова
I
He We
was working You were working
She They
It
У питальній формі допоміжне дієслово ставиться перед підметом:
What were you telling him? Що ви йому говорили?
У заперечній формі після допоміжного дієслова вживається частка not:
I was not working in the evening. Я не працював увечері
В усному мовленні в заперечній і питально- заперечній формах замість was not i were not вживаються переважно скорочені форми wasn't i weren't:
He wasn't working. Wasn't he working?
They weren't working. Weren't they working?
Вживання Past Continuous
- Past Continuous вживається для вираження дії, що відбувалась, тривала в певний момент у минулому. На час дії звичайно вказують також обставинні слова типу at two o'clock, at midnight, at that moment, at 5 o'clock, або підрядні речення з дієсловом-присудком y Past Indefinite:
He was working at his English at that time.
Він працював над англійською мовою в той час.
Carrie was sitting by the window when he came in.
Керрі сиділа біля вікна, коли він увійшов
- Past Continuous вживається для вираження дії, що тривала протягом якогось періоду часу в минулому:
In the spring of the year 1881 he was visiting his old schoolfellow.
Навесні 1881 року він гостював у свого старого шкільного товариша
- Автоматизація дій студентів з граматичними структурами активного граматичного мінімуму.
- Виконання завдань на закріплення граматичних навичок:
Activity 1. Розкрийте дужки, вживаючи дієслова y Present Continuous або Past Continuous.
1. I (to write) an English exercise now.
2. I (to write) an English exercise at this time yesterday.
3. My little sister (to sleep) now.
4. My little sister (to sleep) at this time yesterday.
5. My friends (not to do) their homework now. They (to play) volley-ball.
6. My friends (not to do) their homework at seven o'clock yesterday. They (to play) volley-ball.
7. She (to read) the whole evening yesterday.
8. What you (to do) now? — I (to drink) tea.
9. You (to drink) tea at this time yesterday? — No, I (not to drink) tea at this time yesterday, I (to eat) a banana.
10. My sister is fond of reading. She (to read) the whole evening yesterday, and now she (to read) again.
11. Look! My cat (to play) with a ball.
12. When I went out into the garden, the sun (to shine) and birds (to sing) in the trees.
2. Складіть речення.
1. The cat / not / drink milk.
2. The children / not / do / their homework.
3. I / not / listen / to the radio at 5.
4. You / not / watch / TV at 2 o’clock.
5. She / not / work / in the garden
6. She / watch TV.
7. They / come / out of the house.
8. Marry / write / a letter?
9. My brother / not / listen / to the radio.
10. The girls / sit / in the living room?
11. We / not / go / to the cinema.
12. Tom and Jane / sing / a song?
- Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (домашнє завдання):
- Опрацювати теоретичний матеріал про Past Continuous Tense.
- Читати та перекладати текст “Education in Ukraine”
- Переказувати текст “Education in Great Britain”.
- Вивчити нові слова та записати у словник.
- Закріплення або контроль засвоєння матеріалу (5хв.):
Переклад речень:
I was working in the field at that time.
1


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
