Ділова англійська мова для 10 (11) класу (повний курс)
|
|
|
Business English |
|
17 Lessons for the Secondary School English Learner |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents
Lesson 1 – Introduction to Careers
Lesson 4 – Curriculum Vitae (C.V.)
Lesson 6 – Job Interviews (Part I): Types Of Interviews and How to Prepare for Them
Lesson 7 – Job Interviews (Part II: The Interview
Lesson 8 - Stock Market and Finance
Lesson 10 – Banking and Accounting
Lesson 13 – Sales and Marketing
Lesson 15 – Business Communications: Phone and Email
Lesson 17 – Office or Sports Field?
Lesson 1 – Introduction to Careers
Vocabulary
General
- Career - Кар'єра
- Occupation - Рід занять
- Profession - Професія
- Career ladder - кар'єрні сходи
- Career opportunity - Кар'єрна можливість
- Employed - Зайнятий
- Unemployed - Безробітний
- Job - Робота
- Industry - Промисловість
- Skills - Навички
Industries
- Banking and Finance - Банки та фінанси
- Construction - Будівництво
- Education - Освіта
- Engineering - Проектування
- Energy - Енергетика
- Food and drink - Їжа та напої
- Healthcare - Охорона здоров'я
- IT (Information Technology)/Electronics - інформаційні технології / Електроніка
- Manufacturing - Виробництво
- Media & Advertising – ЗМІ(Засоби масової інформації) і Реклама
- Pharmaceutical - Фармацевтичний
- Real Estate - Нерухомість
- Retail - Роздрібний
- Telecommunications - Телекомунікації
- Tourism - Туризм
- Transportation – Транспорт
Grammar:
When we tell the specific job a person does, we use to be. For example:
- He is a doctor
- I am a banker.
- They are marketing managers.
When we describe the industry or general type of work a person does in a non-specific way, we use to work or to be and the preposition in. For example:
- He works in medicine. He’s in medicine.
- I work in banking. I’m in banking.
- They work in marketing.
Exercise 1: Industries
What industries do you know? Which industries exist in your city? In which industries do your parents, family and friends work? What jobs do they have? Write 6-8 sentences.
Exercise 2: Reading - Career Interests
The table below describes 6 types of people. Each type has different interests and skills. Read the following table and descriptions.
REALISTIC
The "Do-ers"
|
REALISTIC people are characterized by competitive/assertive behavior and by interest in activities that require motor coordination, skill, and physical strength. These people prefer situations involving "action solutions" rather than tasks involving verbal or people skills. They like to take a concrete approach to problem-solving rather than depend on abstract theory. They are usually interested in scientific or mechanical things rather than cultural and aesthetic areas. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
Mechanic Builder/Construction worker - Будівельник Police officer - Поліцейський Dental Assistant - Стоматологічний помічник Engineer Farmer – Фермер |
Firefighter - Пожежний Painter - Художник Plumber - Водопровідник Nurse - Медсестра Property Manager/Landloard – Менеджер по нерухомості Truck Driver- водій вантажівки Woodworker - Верстальник |
||
INVESTIGATIVE
The "Thinkers"
|
INVESTIGATIVE people prefer to think rather than to act, to organize and understand rather than to persuade. They are not usually "people oriented". |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
Actuary Management Consultant - Консультант з питань управління |
Marketing Research Analyst - Маркетингові дослідження аналітика
Research Analyst - Аналітик |
||
ARTISTIC
The "Creators"
|
ARTISTIC people like to express themselves and connect to other people through art. They don’t like structure. They often prefer tasks involving personal or physical skills, and often express more emotion than others. They are like investigative people but are more interested in cultural things than scientific things. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
Actor/Actress |
Drama Teacher
Graphic Designer - Графічний дизайнер |
||
SOCIAL – The "Helpers"
|
SOCIAL people seem to satisfy their needs in teaching or helping situations. In contrast to investigative and realistic people, social people like relationships with people. Thinking about theories and doing physical work is less important to them. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
City Manager |
Priest - Священик
Paralegal – Помічник юриста
Sociologist Medical Assistant - Фельдшер |
||
ENTERPRISING – The "Persuaders"
|
ENTERPRISING people are good at speaking and using words. Enterprising people use this skill to persuade others and make them believe in their ideas. Prestige, power, respect and status are important to them. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
Advertising manager - менеджер по рекламі Marketing manager
Public relations manager - - менеджер по зв'язкам з громадськістю |
Flight Attendant - Бортпровідник
Hotel Manager
Sales manager - комерційний директор |
||
CONVENTIONAL – The "Organizers"
|
CONVENTIONAL people don't mind rules and regulations and emphasize self-control. They prefer structure and order to ambiguity in work and interpersonal situations. They place value on prestige or status. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES: |
|||
|
Accountant - Бухгалтер
Financial Analyst |
Kindergarten Teacher - Вихователь дитячого садка |
||
Based on John L. Holland's MAKING VOCATIONAL CHOICES; A THEORY OF CAREERS (Englewood Cliffs, NJ; Prentice Hall, 1973). The formal validated assessment instrument using John Holland's theory is the "Self-Directed Search", available from PAR, Inc.
Exercise 4: Career Interests
What type of person are you? Using the table above, write about yourself. What professions match your interests and skills?
|
I AM: |
SKILLS I CAN: |
I LIKE TO: |
MY HOBBIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
|
|||
Exercise 5: Speaking
Work in pairs. Ask your partner these questions. Then, tell the class about your partner’s answers.
What kind of career would you like? What do you think is the most important reason to have a career? Interesting work, earn money, feel successful, etc.
Exercise 6 / Home Task 1: My Ideal Job
What kind of job would you like? What industry would you prefer to work in? Explain why you are interested in this type of job. What kind of work will you do? Write 10-12 sentences.
Home Task 2: Job Exploration
Speak with a family member, friend or relative about his/her job. What does he/she do every day? What skills does he/she use? What are the good and bad parts of the job? Write 3 questions of your own to ask. Tell the class about what you learned.
Lesson 2 – Want Ads
Vocabulary:
- Application--додаток
- To apply--застосовувати
- Resume-- резюме
- Full-time--повний робочий день
- Part-time--неповний робочий день
- Experience--досвід
- Qualified--кваліфікований
- Want ads-- Оголошення
- Computer Personnel--комп'ютер персоналу
- Drivers--драйвери
- Engineers/ Chemists—Інженери/ хіміки
- Financial/Accounting—фінансовий/ бухгалтерський обліk
- Instructors-- інструктори
- Insurance--страхування
- Managers--менеджери
- Medical--медичний
- Office/ Clerical—офіс/ канцелярський
- Restaurants/ Hotels/ Clubs--ресторани / готелі / клуби
- Sales/ Marketing--продаж / маркетинг
- Telemarketing/ Phone Skills--Телемаркетинг / навички спілкування по телефону
Exercise 1: Vocabulary Practice
Fill in the blanks. Use the following words:
applied want ads qualified resume application part-time
- Tom sent his to companies who were looking for a website manager.
- Sarah for the job she was qualified for.
- Mary got the job because she was the most person who applied.
- Jim didn’t have a lot of time for work because he was a student at the university, so he was looking for a job.
- Mark looked through the to see who was hiring.
- Kim filled out the at the cd store because she wanted to work there.
Exercise 2: Reading Want Ads
Look at the want ads from the newspaper. Answer the following questions
-
Under what number can you find jobs related to the “medical” field?
- Answer: 1460
-
Under what number can you find jobs related to “restaurants”?
- Answer: 1540
-
What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “LOCAL PIPE, valve & fitting” under “Drivers”?
- Answer: Class A CDL, TWIC card, clean driving record and forklift experience required.
-
What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “F/T BOOKKEEPER” under “Financial/Accounting”?
- Answer: Word and Excel experience
-
Where can you send your resume if you want to apply for “BLUE BAYOU DIXIE LANDIN’” under “industrial tech. skills”?
- Answer: Email it to jobbrla@gmail.com, or you can apply online at www.bluebayou.com
-
What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “PHYSICIAN” under “medical”? How much does it pay?
- Answer: Must be board certified. It pays up to $175/hour.
-
What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “FULL TIME GRILL position” under “Restaurants/Hotels/Clubs”? What is required in order to get the job?
- Answer: You must have good customer service and communication skills. In order to get the job you must take a pre-employment drug and background screening.
-
Where can you send your resume if you want to apply for “FULL TIME RETAIL COUNTER SALES PERSON” under “Sales/Marketing”?
- Answer: redstickjob@gmail.com
Lesson 3 – Resume
Vocabulary
- Resume - резюме
- Reverse chronological - у зворотному хронологічному порядку
- Functional - функціональний
- Hybrid - гібрид
Purpose of a Resume
A resume is a document highlighting specific skills, previous employment, education, and awards that employers will base a potential employee on. Different types of resumes have different purposes.
- Reverse Chronological is a style of resume where in the previous work experience most recent employment comes first and it goes down by date employed.
- Functional is a style of resume where instead of labeling a position in chronological or reverse chronological, employment experience is organized by the type of job and each employment provided with detail in a description.
- Hybrid is a style of resume that uses both functional and reverse chronological. Job descriptions are listed in reverse chronological order and given a little detail like a functional resume.
Model Resume
A resume contains different sections. Find each of these in the sample resume.
- Header-contains name, work address, home address, phone number
- Objective-goal of the resume
-
Education-list all forms education the applicant has been through
- List all awards and special skills like languages below
- Previous Work Experience-list all previous work experience with 2 sentences in detail
- Activities-list all extra activities the applicant is involved
Exercise 1: Listing Skills
Listing skills is difficult for people to do. It is not often we are given the task of writing down what we are good at and what we aren’t good at, especially when it comes to what an employer would find interesting. What skills and talents can you include on your resume? Make a list. Here are some ideas of what a good skills can be if you put it on your résumé.
- Foreign Language(s)
- Awards granted in school
- Programs or certificates completed or received in school
- Programs or certificates completed or received outside of school
- Abilities like “works well with others” or “can multi-task efficiently”.
Exercise 2
Unscramble the resume. Put the sections of the resume in the correct order to make it look like the model resume.
Exercise 3
Create your own resume including header, objective (fake job), education, previous work experience, activities. When you’re finished, present your resume to the class.
Sample Resume

 Scrambled Resume
Scrambled Resume
Lesson 4 – Curriculum Vitae (C.V.)
Vocabulary
- curriculum vitae - резюме
- profile - Профіль
- skills - навички
- interests – інтереси
Exercise 1: Reading - Definition of Curriculum Vitae
A Curriculum Vitae, or C.V. for short, is similar to a resume. Curriculum Vitae is Latin for means of life. This is the document that employers will look at before making the hiring decision. It provides an overview of a person's life and qualifications. In some countries, a CV is typically the first item that a potential employer encounters regarding the job seeker and is typically used to screen applicants, often followed by an interview, when seeking employment. C.V.s are more common in Europe, while resumes are more common in the United States.
The Profile section is the section of the C.V. where the applicant talks about themselves. In the Skills section, the applicant can discuss any skills that they think would be useful for the job. Interests is the section of the application where the applicant can discuss any interests that they think would be useful for the job.
Exercise 2: Sample C.V.
Look at the sample C.V. Can you locate all of the sections?
- What is the person’s profile?
- Where did this person study?
- What was this person first job?
- What does this person like to do?
- What skills does this person have?
Exercise 3: Scrambled C.V.
Unscramble the C.V. Put the sections of the C.V. in the correct order to make it look like the model resume.
Exercise 4: Write a C.V.
Create your own resume including header, profile, work experience, education, skills and interests.
Sample C.V.

Scramble C.V.
Lesson 5 – Cover Letter
Definition of cover letter
A letter of introduction attached to, or accompanying another document such as a résumé or curriculum vitae.. This is a way of introducing themselves to potential employers and explaining their suitability for the desired position.
Vocabulary
- Header-заголовок
- Introduction- вступ
- Body-основна частина
- Closing-заключна частина
- Header. Cover letters use standard business letter style, with the sender's address and other information, the recipient's contact information, and the date sent after either the sender's or the recipient's address.
- Introduction. The introduction briefly states the specific position desired, and should be designed to catch the employer's immediate interest.
- The body highlights or amplifies on material in the resume or job application, and explains why the job seeker is interested in the job and would be of value to the employer.
- Closing. A closing sums up the letter and indicates the next step the applicant expects to take
Exercise 1: Sample Cover Letter
Read the sample cover letter. Answer the following questions:
- Which address is put in the top right corner?
- What is a header?
- What comes after the header?
- Where is this person applying?
- Where did this person work before?
- When will this person call to hear back?
Exercise 2: Scrambled Cover Letter
Unscramble the cover letter. Put the sections of the cover letter in the correct order to make it look like the model resume.
Exercise 4: Write a Cover Letter
Think of a job you would like. Write a cover letter as part of your application. Make sure to include at least 3 sentences in each section (intro, body, conclusion).
Sample Cover Letter

Scrambled Cover Letter

Lesson 6 – Job Interviews (Part I): Types Of Interviews and How to Prepare for Them
Vocabulary:
|
|
Exercise 1: Reading
You have applied for a lot of jobs, sent out many resumes and finally you have gotten a response. Now it is time for the employer, or person looking to hire you, to meet you and for you to meet them. There are a few different ways a business may choose to meet you. Here are the most common:
- Phone Interview: If you live far from the job an employer might just want to talk to you over the phone. Even though you are not meeting them face to face they will ask you them same questions they would ask in person. Sometimes a phone interview is just a screening, or a test to see if they want to meet you in person.
- Group Interview: If you are applying for a job that has many openings you maybe be interviewed with a few other job seekers also called Candidates. You are not competing with the others. It is important to remain polite to the other people.
- First Interview: A face to face meeting with an employer. This is the most common type of interview.
- Second Interview: Some employers will want to meet you a second time to see if you are right for the position.
Exercise 2: Matching Type of Interview.
Match the vocabulary word with the definition.
- One employer, many candidates.
- Some employers will want to meet you again.
- The most common type of interview.
- Not done in person.
- People looking for jobs.
- Brief conversation to see if they would like to meet you
- People looking to hire a person.
Exercise 3: Reading – How to prepare for an interview.
No matter what type of interview you have, preparation is the same. Here is how you do it.
Step 1: Learn a lot about the employer. Find out what type of business they are. When and where were they started? Who are their biggest competitors? What is the job that you are interviewing for? What does a person in the role do? This is called background information.
Find answers to the questions
- "What is the business looking for?"
- "What would the business like in a candidate?"
Step 2: Write down a list of reasons you would be good at the job. These are your strengths. The list should include what work and activities you have done that would make you good at this job. This is called experience. What skills do you have? What education do you have?
Step 3: Write down a list of reasons you might be bad at this job. These are your weaknesses. Think of ways to get rid of these weaknesses.
Step 4: Review list of commonly asked questions. Think of answers.
Step 5: Write down a list of at least 5 questions you will ask your interviewer. Employers want you to participate in your interview to know you are interested.
Exercise 4:
Put the steps in the correct order.
A. Write down a list of strengths.
B. Write down 5 questions to ask the interviewer.
C. Review list of commonly asked questions
D. Background information
E. Write down a list of weaknesses.
Exercise 5:
Practice describing your strengths. Use the models below to write a list of what you are good at and what skills you have. Write at least 5.
- I am good at (skill). Example: I am good at playing football.
- I am able to (skill, something you can do). Example: I am able to use a computer.
- I have always been able to (skill) well. Example: I have always been able to dance well.
- One of my strengths is (skill / that I….). Example: One of my strengths is math.
Home Task 1.
Select a business and find out background information about that business. Answer these questions:
- Company name?
- Type of business?
- When and where were they founded?
- Who are their major competitors?
Example
Company name: Nike
Type of business: Sporting Goods
Founded: January 24, 1964
Major Competitors: Adidas, Puma
They might like: A candidate who likes sports.
Present your background information to the class using complete sentences.
Example: The name of my company is Nike. Their business is Sporting Goods. Nike was founded on January 25, 1964 in Washington County, Oregon. Nike's major competitors are Adidas and Puma. Nike may want a person who likes sports.
Lesson 7 – Job Interviews (Part II: The Interview
Vocabulary:
|
|
Exercise 1: Reading – What is an interview for?
A job interview is not about your strengths or experience. A job interview is about proving you are the best person for the job. Employers will already know about your strengths and experience from your resume. Employers want to meet you and get to know your personality and who you are. They need to know that you have the right attitude toward the job and that you really want to work for them. Look at the chart to see what an interview is about.
What employers want to know:
- That you know about their business.
- That you know about the job.
- That you can do the job.
- That you are able to communicate
Dress for Success.
In the business world we have two saying about what to wear at work. "Clothing makes the man" means that people judge you first by what you wear and what you wear says a lot about you. The better you dress for an Interview, the more seriously the employers will take you as a candidate.
The next saying is "Dress for the job you want, not the job you have." Always dress for the job you want, even if that is more formal than your current job. The interviewer must be able to picture you being successful at that position. The first step is to look like you already have that job.
DO NOT:
1. Wear a track suit.
2. Short Skirt.
3. Sport shoes.
4. Wrinkled clothing
5. Have messy hair.
6. Chew gum
7. Overly revealing clothing.
8. Button all the buttons on a shirt, the top one may remain unbuttoned if a tie is not worn.
Parts of the interview:
Part 1: Greeting
- When you enter the room body language is very important. Body language is what your actions say about you,
- Stand up straight and hold your head up.
- Introduce yourself in a clear voice saying "Hello, my name is (first and last name)" then "Its a pleasure to meet you"
- Extend your hand to everyone in the room, male and female, while you introduce yourself.
- Handshake should be firm. Do not grip too tight or too loosely. Shake their hand 3 times.
- Always maintain eye contact.
- Do not sit down until the interviewer offers you a seat!
Part 2: The Interview
- During the interview, sit up in your chair. Do not lean over. Remain still, do not fidgeting. Fidgeting is moving around too much.
- Look at the person who is speaking or asking questions in the eye. This shows that you are interested.
- Do not answer questions with "yes" or "no." Answer in complete sentences.
- Ask questions of the interviewer to show interest. Use notes to help if needed.
Part 3: The end and follow up
.
- -When the Interviewer asks "Do you have any questions of us?" Always say yes and ask one last question even if you already know the answer, or say "No, you have already answered all of my questions, Thank you."
- Thank the interview before you leave. "Thank you for taking the time to meet with me today"
- Shake hands again and say "It was nice meeting you, I look forward to hearing back from you, If there is anything else you need from me just let me know."
- Maintain eye contact.
- As soon as you get home from the interview write a thank you letter or email to the people that just interviewed you. Follow the model.
Exercise 2: Body Language
Stand up and practice introducing yourself to everyone else in the room. Remember to shake hands and make eye contact.
Exercise 3: Mock Interviews
Work in pairs. Interview your partner. When you are the employer, ask questions such as:
- "What are your strengths?"
- "What are you good at?"
- "Where do you live?"
- "What school do you go to?"
- "What is your weakness?"
- "Do you work well with others?"
-
When you are in the role of the person applying for the job, make sure to answer questions in complete sentences. Don’t forget to ask the interviewer questions also. Use the list of strengths and weaknesses you wrote in the last class.
Exercise 4: Writing a Thank you letter
Write a thank you letter about 5-7 sentences.
Sample Thank You Letter

Lesson 8 - Stock Market and Finance
Vocabulary:
|
|
Exercise 1: Reading – Stock Market or Bazaar, is there a difference?
A stock market functions exactly like a bazaar. The only difference is that instead of selling food and things, people sell pieces of businesses called stock. A single piece of a company is called a share. A person who owns a share is called a shareholder. Every morning, when a stock market opens, shareholders look to see what people will pay for their shares. They want to sell their shares for the highest prices. Since not every shareholder can be there to sell or buy all the time they have representatives called traders. It is the trader's job, to buy and sell stock for a person. They want to buy stock when the price is low and sell when the price is high.
Think of shares in a stock market like tomatoes in a bazaar. In August, there are a lot of people selling tomatoes. The supply of tomatoes is high. A person can buy a tomato without paying a high price because there are so many. The number of people wanting to buy tomatoes is called demand. During the winter, the supply of tomatoes is less but the demand remains the same. The tomato seller can charge more for tomatoes because there are fewer tomatoes to sell. This is called the law of supply and demand. Supply and demand sets the price for tomatoes in a bazaar in the same way share prices are set in a stock market.
The amount a trader is willing to pay for a share is called a bid. If a stock is very popular then the bid price must be high for a shareholder to sell. If a stock is not popular then the bid price will be low. If a business makes a lot of money then a lot of people want to own that business's stock and fewer shareholders are willing to sell. The number of shareholders selling their shares is called the supply of shares. The more people who want to own a share, the higher the demand for that share is. The higher the demand, the higher the bid must be for a shareholder to sell. If a business is not making money, then more shareholders want to sell their shares. This increases the number of shares up for sale at the stock market. If traders want to a buy a stock when a lot of shareholders want to sell, they can buy with a low bid.
At the end of the day, when the stock market closes, all the buying and selling that occurred that day is counted up. A market index is a summary of that count. A market index will go up if, on average, shareholders sold their shares for more than they bought them for. A market index goes down if shareholders sold their shares for less than they bought them for. When a price or a market index seems to go in one direction most of the time this is called a trend. If the stock of a company goes up 7 out of 10 days and is higher than before, its trend is up.
Why would a business sell part of itself? Selling stock is a way for a business to make money. If a business needs money quickly, then it can sell part of itself to get money. Making money by selling part of business is called Finance. When a business starts selling shares of itself to any person willing to buy, we say the business is publicly traded. Businesses can make so much money from being publicly traded that they give money to people to own their stocks. This payment is called a dividend. Stock markets offer businesses and shareholders a place to meet people looking to buy their shares, just like a bazaar offers farmers a place to sell their produce to people wanting to buy it.
Exercise 2: Reading Comprehension Questions
(True or False)
- Traders want to buy shares when the price is high and sell when the price is low.
- More shareholders selling their shares means that supply is high.
- The more traders who want to buy a share, the higher the demand.
- The law of supply and demand sets the finance of the share.
- The Market Index is the summary of all the buying and selling that occurred that day.
- Businesses do not want people to own shares of their stock.
- Dividends are what people pay to own a share of a business.
- If a business is publicly traded any person can buy a share.
- The supply of tomatoes in the winter is high.
Exercise 3: Vocabulary Matching
Match the description with the vocabulary word.
- People who buy and sell stock.
- Money paid to a shareholder.
- Making money by selling part of a business.
- Single piece of a company
- Summary of all the buys and sales.
- The direction a stock's price goes most often
- Any person can buy a share.
- What a person wants to pay for a share.
- Number of people willing to buy a share.
- Pieces of a company.
- Sets the price of a share.
- Number of people willing to sell a share
- Person who owns part of a business.
- A place to sell stock
Stock Markets from around the world
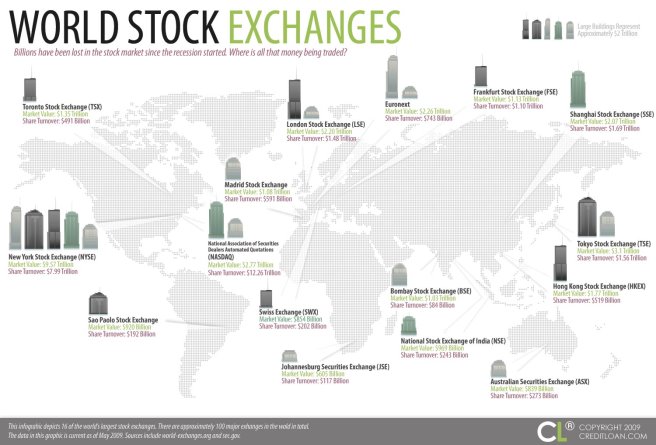
Just like there is not just one bazaar in a city, there is not just one Stock Market in the World. Here is a list of major stock Markets from around the World and the indexes that summarize them.
North America
United States
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)- Dow Jones, S&P 500
- NASDAQ
Canada
- Toronto Stock Exchange - S&P/TSX Composite
Europe
England
- London Stock Exchange - FTSE
Germany
- Deutsche Borse - DAX index
Switzerland
- 1.SIX Swiss Exchange - SMI
Spain
- BME Spanish Exchanges - IBEX 35
Russia
- MICEX - MICEX Index
Ukraine
- PFTS Ukraine Stock Exchange - PFTS Index
Asia
Japan
- Tokyo Stoke Exchange - Nikkie 225
China
- Shanghai Stock Exchange - SSE Composite
- Hong Kong Stock Exhchange - Hang Seng
- Shenzhen Stock Exchange - SZSE Component Index
South Korea
- Korea Exchange
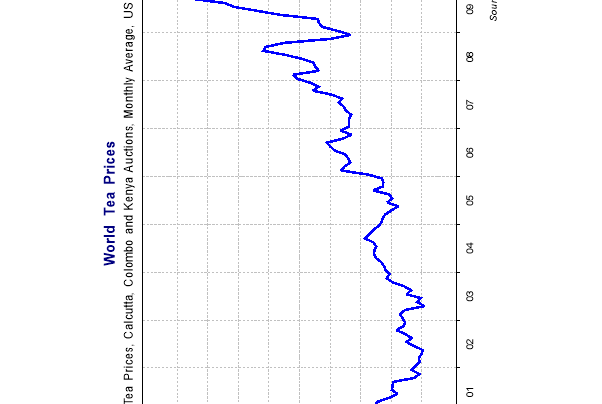
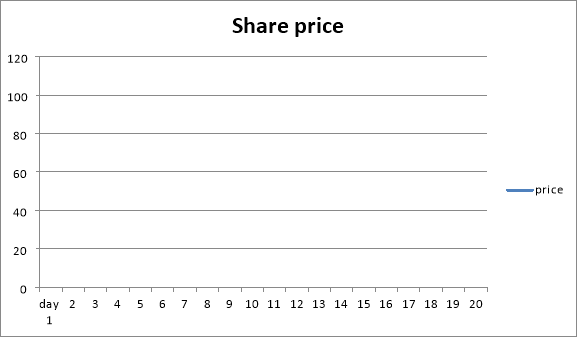
Use attached graph as an example on how to track a share price. Give the students the following handout and have the students follow the price of a stock they selected for a month.
Exercise 4: Supply and Demand
Have the students predict the share price based on the law of supply and demand.
1. Demand is high and Supply is Low, the price will be _______________
2. Demand is high and supply is high, the price will be _______________
3. Demand is low and supply is high, the price will be _______________
4. Demand is low and supply is low, the price will be_______________
Lesson 9 – Business Structure
Vocabulary
Board of Directors - Рада директорів
Executive - Виконавчий
Chief Executive Officer - Головний виконавчий директор
Manager - менеджер
Shareholder - Акціонер
Headquarters - Центральна установа
Organization chart (Org chart) - Організаційна структура
Department – Департамент, відділ
Chain of command - Підпорядкування
Departments
Marketing - маркетинг
Finance - Фінанси
Accounting /Accounts Department - Бухгалтерія
Information Technology - Інформаційні технології
Legal - Правовий відділ
Production - Виробництво
Human Resources / Personnel Department - Людські ресурси / Відділ кадрів
Sales – Відділ продажу
Exercise 1: Reading
There are many ways to organize the way people in a company work with each other. Not every company is the same. In general, there are four main types of organizational structure that companies adopt.
- Organization by function is when the company is divided into departments such as production, finance, marketing, human resources. Each department does a different type of work.
- Organization by product is when people in a company work in groups based on different kinds of products.
- Organization by customer type is when the company is organized around different sectors of the market. Large customers are called ‘key accounts’. Each group of employees works with a different kind of customer.
- Organization by geographical area means a company is organized according to regions of the world. Different executives are responsible for different countries. People work in teams that are determined by where they live in the world.
A large multinational company may use more than one kind of organization. For example a functional division initially (at an international level), then a national structure for each country, and within this some level of the other types.
The business must also decide on its management chain of command, or management hierarchy. Most companies are run by top (= senior) managers with job titles such as Chief Executive Officer (CEO), Chief Operating Officer (COO), and a series of Vice-Presidents or Directors of different departments. Top management decides on the direction for the company and tries to inspire employees with their vision for the company’s future.
The next level is middle management, where managers are in charge of a department, division, branch, etc. Middle managers develop detailed plans and procedures based on the firm’s overall strategy. Below them are the workers and regular employees.
Above everything there is the Board of Directors, which gets involved in ‘big picture’ strategic planning and meets only perhaps once a month. The CEO will be on the Board, but most Board members are not involved in running the company. They are elected by shareholders who trust them to help make sure the company stock performs well.
Exercise 2:
Look at the organization chart below. Answer the questions.
- Who are the executives at Arbor Business Company, Inc?
- Who is in charge of production? Who is his/her boss?
- Which three people work in sales?
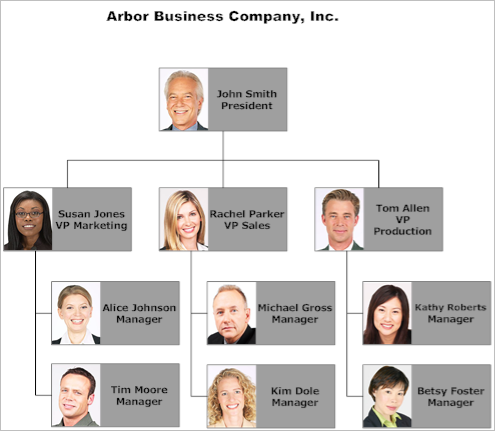
Exercise 3: Reading – Departments Within a Company
Marketing: The marketing department is responsible for developing a marketing plan (how to sell the company’s product or service to the public), setting sales goals, designing advertisements, and maintaining sales records. People in the marketing department should be confident and creative.
Finance: Companies that are publicly traded have a finance department that is responsible for selling shares, parts of the company.
Accounting / Accounts Department: The accounting, or accounts, department maintains all financial records. It creates the budget, receives bills, and makes payments to employees and vendors. Finance members should be skilled with numbers and able to maintain detailed records accurately and truthfully.
Production: The production department is responsible for organizing production, training the production staff, scheduling production activities, and monitoring production quality.
Information Technology (IT): The IT department is responsible for all technology in a company. They make sure employees’ phones and computers work and are safe from hackers and viruses. They also take care of specific software that different workers might need, for example engineering software.
Human Resources / Personnel Department
By definition, human resources are the individuals who work within your company. These individuals form your company workforce and your workforce can be considered the most important part of your organization. The Human Resources department is responsible for paying employees, finding new employees, hiring and firing of employees, motivating employees, and helping workers make progress in their careers. If an employee has a problem at work, he or she can discuss it with the human resources department.
Exercise 4:
Which department does which type of work?
- Help an employee who wants extra vacation days.
- Making a new product.
- Paying for water in the office.
- Deciding what color the package of a product should be so that people will want to buy it.
- Installing a new program on your computer.
Exercise 5:
Work in groups of 3-5 students. Each group should think of a company – it can be large or small, Ukrainian or headquartered in another country (for example, vKontakte, Roshen, Nike). Discuss the work of each department within that company. Present your ideas to the class. (Each student can present 1 or 2 departments so that all are involved.)
Exercise 6:
Look at the table of personality types and careers from Lesson 1. What types of people do you think are most likely to work in each department?
Lesson 10 – Banking and Accounting
Vocabulary:
|
Banking:
Accounting:
|
бухгалтерський облік
|
Banking
Exercise 1: Reading
Everyone knows that banks are a safe place to keep your money. A bank will protect your money from thieves and prevent you from losing it. Banks do a lot more than that. Banks give people money to keep their money in the bank. How are these two actions related? When a person opens an account in a bank they agree to certain terms. An account is where your money is kept in the bank. When you put money into your account it is called a deposit. When money is removed from your account it is called a withdrawal. Both of the actions affect the amount of money you have in your account, the amount of money is called a balance. A deposit makes your balance go up, while a withdrawal makes a balance go down.
There are different types of accounts too. A savings account is an account that allows a customer to deposit and withdraw money and earn interest on the balance. Interest is money paid to a customer based on how much money they have in the bank. The higher the balance the more money the bank will pay you to hold it. The other type of account is a checking account which is a type of account that allows a customer to deposit and withdraw money and write checks. Using a checking account can be safer and more convenient than handling cash. These accounts require a person to maintain a minimum balance which is the lowest amount a person can have in their account without being charge a fee. A fee is money a bank charges customers for services.
Why does a bank pay you to keep your money safe? Banks actually make money by lending money to people and businesses that need it. This is called a loan. Banks need your money so that they can make loans to others. Take a look at the picture below....
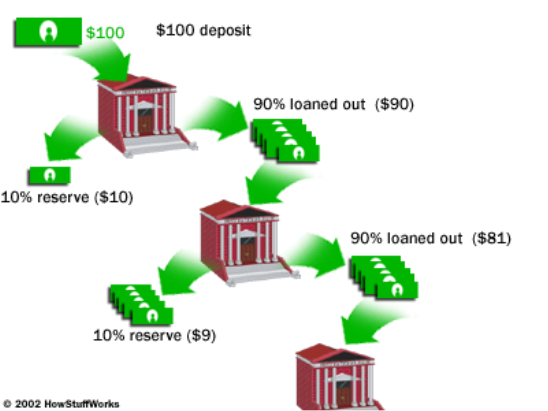
The amount of money a bank loans a person is called the principal. A person then has to re-pay the bank. This is called a payment. The amount in a payment depends on the terms of the loan. The term of a loan is the time a person has to repay and the interest they have to repay. A payment is the amount of the interest owed plus part of the principal. Banks give people a safe place to place to keep their money and even encourage people to save their money. Banks also help people make big purchases by loaning them money. Loans give people the money to start businesses when they have an idea but not enough money to turn a dream into reality. Banks help people who want to make money by saving by loaning money to people and businesses. Without banks, people and businesses would not a have a safe place to keep their money. They also provide money to people when they really need it.
Exercise 2: Fill in the Blank
1. I do not want to carry around this much money, I should make a _______________.
2. Banks offer _______________to people and businesses who need money.
3. A _______________shows how much money I have in my account.
4. A bank will pay me _______________ to keep money in my savings account.
5. Instead of carrying around a lot of money to buy a TV, I can just write a _______________.
6. My account is below the minimum balance. I will be charged a _______________.
7. I need money. I should make a _______________ to take money from my account.8. I bought a car with a loan. Now I have to make a _______________ every month.
9. The amount of my _______________ was the price of my car.
10. I don't need all this money right now, maybe I should open a _______________ account.
Accounting
Exercise 3 – Reading
Where is all that money going?
Businesses use accounting as away to know how much money they have in a bank. An accountant counts all the money and keeps track when money comes in and when it goes out. Accountants write all of this information on an Income Statement. An Income statement is a summary of a business's actions involving money. A Balance sheet tells how much a business is worth overall. An Income statement lists dates, action name, and type of action. It tells you how much cash-on-hand a business has
.
There are two types of actions, credits and debits.
- A credit is a type of action that adds money to a business. Types of credits are: deposits and interest from savings.
- A debit is a type of action that takes money from a business. Types of debits are: Withdrawals and payments.
Balance sheets also list assets and liabilities.
- An asset is a thing that is worth money to a business. Cash-on-hand is an asset.
- A liability is a thing that a costs a business money to. A loan is a liability.
All assets and credits on a balance sheet are written in black. All liabilities and debits are written in red. If a business has more debits then credits and more liabilities then assets it is "in the red" which means the business is losing money. If a business has more credits then debits and more assets then liabilities, then it is "in the black" which means the business is making money.
Exercise 4 – Credit or Debit? Asset or Liability?
Write the correct letter next to the actions below. (C- credit, D- debit, A-asset, L- liability)
1. Interest from Savings
2. Cash-on-hand
3. Loan Payment
4. Fee
5. Loan
6. Deposit
7. Withdrawal
Exercise 5:
Look at the Income Statement and Balance Sheet. Fill in the type of action (credit or Debit), find the amount of Cash-on-hand. Use the result with the Balance sheet. Is the business "in the red" or "in the black".
Lesson 11 – Business Plans I
Vocabulary
- Market research - Дослідження ринку
- risks - ризики
- evaluate - оцінювати
- consumer - споживач
- service – обслуговування
- target (n) – ціль
- target (adj) - цільовий
- target (v) - прагнути до
- market/market place - ринок
- investment - інвестиція
- start-up funds - стартові кошти
- break even point - беззбитковость
- business plan - бізнес-план
- entrepreneur - підприємець
- profits - прибуток
- profitable - вигідний
- expenses - витрати
- opportunity - можливість
- differentiate - диференціювати
- forecast - прогноз
- operating costs - експлуатаційні витрати
- fill a gap/hole in the market - заповнити пропуски в ринку
- inventory - інвентаризація
- to increase - збільшити
- to decrease – зменшувати(ся)
- prospective - перспективний
-
consignment shop – комісійний магазин
Introduction
The purpose of a business plan is to help you make a strong business strategy. First, you should describe your products and services and discuss your target market. If you wish to interest investors, you need to emphasize how the company will make a profit. You should examine customer needs and the benefits of your products and services. Evaluate the strong and weak points of any firms in competition with yours and look for market opportunities. You should explain how your products will be different in the marketplace to attract new customers.
Exercise 2: Reading
Read the example business plan below.
Description
Nine Lives, to be located in Eugene, OR will be a consignment shop for outdoor clothing and sports equipment. Nine Lives will offer used outdoor clothing and sports equipment for reasonable prices. This will allow more enjoy the outdoors. Nine Lives will sell the items on consignment. This means that when a person does not need or want their outdoor clothing or equipment, they can ask Nine Lives to sell it for them. When a customer buys the product, Nine Lives will give some money to the first owner. Usually the items on consignment will be used, or second hand. They will also consist of new manufacturers' closeouts and seconds. Occasionally, Nine Lives will purchase outright manufacturers' closeouts and seconds. This will only occur when the savings are large and the items are likely to be sold quickly. The owner, Jim Gearboy, has found a good location that is easy to travel to and near lots of people.
Nine Lives will sell a wide range of outdoor clothing and equipment for sports and outdoor recreation. Examples include track suits, sports clothing, gloves, sleeping bags, hiking backpacks, bicycles, canoes, and kayaks.
Market Analysis and Competition
The market for an outdoor clothing and gear consignment shop in Eugene is wide open. Eugene is the perfect community to support Nine Lives because many people in the town like outdoor recreation and sports. Additionally, there are no other used outdoor clothing and gear stores. For comparison, the used outdoor stores in similar towns have done very well. For these reasons the market is ready in Eugene for a store like Nine Lives.
There are three types of ideal customer:
- Outdoor and sports enthusiasts with limited financial resources – This type of customer enjoys outdoor activities and sports, but doesn’t have a lot of extra money. For them, an outdoor consignment shop is ideal because for the same amount of money it allows them to have more or better equipment than they could get through traditional retail outlets.
- “Gearheads” – These people love collecting outdoor gear and equipment. They just like to have the right piece of clothing or equipment for each individual occasion/ activity. Offering better prices than regular stores will allow them to buy more for the same amount of money.
- Bargain hunters – This group will buy things because they are cheap, not because they really need the items.
Currently there are no true direct competitors in Eugene. There are two Oregon competitors that have very similar product offerings although one is a consignment shop and the other is a normal store. However, they are both in different towns in the state of Oregon.
Nine Lives' competition is present in Eugene in the form of regular outdoor and sports stores, such as R.E.I. and Nike. These retailers have more products, but have normal, high prices and no used merchandise. Another form of competition is secondhand stores that sell used clothing and equipment. However, most general secondhand stores don’t have very much sports clothing and equipment.
Sales and Marketing Strategy
Nine Lives will be heavily promoting the store early on to drive in both buyers as well as suppliers. This will be done through advertising in the many different local outdoor magazines/ journals, at the University of Oregon generally, and through local outdoor and sports clubs. The store will request that people bring in their extra clothing and gear to sell. The business will also contact outdoor clothing and sports equipment manufacturers, and regular store to tell them they can sell extra, unwanted products to Nine Lives.
Nine Lives will be attempting to have new products frequently so people will want to come in often to find some new bargains. This will be done through reasonable prices so customers feel that they are getting a good value.
Financial Strategy
- Start-up costs will include:
- Computer system, with CD-RW, printer, Internet connection.
- Copier and fax machine
- Various office supplies.
- Office furniture (used)
- Display equipment including racks, hangers, and shelves
- Software to manage inventory of products
- Advertising- in local outdoors publications and general newspaper in the outdoor section
Jim predicts that the first month will be used to get the store ready for business and there will be no sales activity. Month two will mark when the store is officially open, and business will be slow. During month two Nine Lives will begin to build up inventory. Month four will finally have a decent amount of sales activity and it should steadily improve from there.
The business will make a profit in month six, and will grow steadily each consecutive month. The projected growth rate for Nine Lives is quite steady, with profitability estimated by month six and revenue of $45,000 by year three.
Management
Jim knows a lot about the outdoor recreation and sports equipment industry, which will help the store become profitable quickly. Jim will be working for Nine Lives full time as owner/general manager. By month two Nine Lives will bring on board one full-time sales associate. By month four Nine Lives will be in need of a second sales associate. The final employee will be another sales associate by month seven. Jim will make sure to hire employees who are enthusiastic and knowledgeable about the outdoors.
Jim’s experience includes working as the president of the University of Oregon Outdoor Club. He was responsible for the overall management of the organization. This experience was very valuable because it gave Jim some insight to, and experience in, running a company. He also worked at R.E.I, a local outdoor clothing store, for two years. This experience gave Jim the skills he needs to run Nine Lives successfully.
Exercise 3: Reading Comprehension
Answer the questions.
- Why do you think the name of the store is Nine Lives? How is the name related to the way Jim will get the products?
- What did the two other stores tell Jim about the market opportunity in his town of Eugene?
- Why will Nine Lives be different from the competition in Eugene?
- Do you think a store like this would be successful in your town? Why or why not? Discuss with the class.
Exercise 4: Identifying Needs and Opportunities
Work in groups. Brainstorm problems that exist in your city that might be solved by a new product or service. Or, are there businesses in your community you think you could improve?
For example –
- What health problems are there? What could help injured or sick people?
- What problems do students and young people have?
- Is there a store or restaurant you think you could make better? How?
Share your results with the class to develop a class list of all ideas.
Exercise 5: Planning your own business
Work in groups of 3-5 students. Each group should think of a business idea (can be from list developed in previous exercise). Imagine you are starting a small company with a product or service to solve the problem.
Use the following structure: Students may skip some questions, but should include some information for each underlined section.
-
Description of Business
- Business name and short history
- Describe your product and/or service
- Location of business (is it store-front or home-based?)
- Why is this a good location?
-
Market Analysis and Competition
-
The Industry
- Description of the overall market or industry
- Is this industry in general doing well?
- Why is it a good industry to get into?
-
Target Market (ideal customer)
- Describe your typical customer in detail.
- Name personal characteristics if your customers are individuals.
- How many potential customers do you plan to service?
- How do you plan to approach them?
-
Competition
- Who are your major competitors? (list them)
- Compare yourself with your competition.
- Describe how you are better than your competitors.
- Describe how your competitors might be better than you in some ways. What can you do about it?
-
The Industry
-
Market Strategy
-
Sales strategy
- How will you get people to buy your product/service?
-
Marketing strategy?
- How will people find out about your business?
-
Pricing
- How much will you sell this product/service for?
- How do you set your prices?
-
Inventory
- How do you plan to maintain an adequate inventory of sales goods?
-
Sales strategy
-
Management/Personnel
-
Employees
- How many employees do you need and why?
- What is each employee's job (including your own)?
- How will you find prospective employees?
- How will you pay employees? (hourly, salary, commission, etc.)
- How much will you pay employees?
-
Management (include resumes of owner and other key employees)
- Describe owner's management and industry experience
-
Employees
-
Financials
- Start-up costs
- Where will money come from? Investors/loans/personal money
- expenses
- Milestones
- Break even
Lesson 12 – Business Plans II
Vocabulary
- Partner (v) - стати партнером
- To invest - інвестувати
- Investor - Інвестор
- Pitch – a presentation, usually to try to interest someone in an idea or to get them to spend money
- To make a pitch – to present an idea, product offer or opportunity to someone in a business setting
Exercise 1: Reading
Business plans are important because they help business owners, executives and workers follow a strategy. But it is not only the people who work in a business that see a business plan. Business plans are also important to share outside a business. For example, if you would like to partner with another person or organization, it is usually important to show them your business plan. If you do not have a business plan to show them, they may think you are disorganized and it is risky to do business with you. Sometimes, you may need someone to invest in your business idea so you have enough money to start the business. Investors will examine a business plan very carefully because they want to be sure they invest their money in good opportunities. When a person presents a business plan, we say they are “making a pitch” and we sometimes call the presentation of a plan a “pitch.”
Exercise 2: Business Plans
Students should complete work on business plan started in previous lesson.
Exercise 3: Presentation of Business Plans
Imagine your classmates are investors who are willing to give money to companies that have the potential to be successful. Give a 5-7 minute presentation about your company and the opportunity. Make sure each person in your group does part of the presentation.
Exercise 4: Comprehension and Analysis
Classmates should listen carefully to each presentation. At the end of each, students should give feedback on the business plan.
- Is there a need?
- Do you think this business idea is better than the competition? Can you think of any other competitors?
- Did the group consider the costs to start the business?
Students should think of their own ideas about the business plan. At the end of all the presentations, the class may vote on the best business plan.
Lesson 13 – Sales and Marketing
Vocabulary:
|
|
Exercise 1: Warm-Up Questions
- Describe some of your favorite products. Why do you like them?
- If you could afford any product, what product would you like to own?
- Why would you like to own that product?
- What are some words you could use to describe that product to the class?
Exercise 2: Reading – The Sales Process
The First Step - The initial contact by phone
You will normally want to accomplish four things during the initial call:
- Qualify the prospect to determine whether or not you wish to pursue a relationship
- Begin a relationship with the prospect
- Establish a benefit for the prospect for continuing your relationships (find a need you can begin to fill during this first phone call)
- Confirm that you will be sending information and be in contact with them in the future with additional information.
Opener - The chief purpose of your opening is to elicit an immediate response from your prospect and to end the call quickly if the prospect is not interested. It should be short, but be sure to introduce yourself, your firm, and the purpose of your call. The opener must accomplish two things:
- Introduces you, your firm, and your service
- Probes to determine whether or not your prospects already familiar with your product.
Body of Presentation
- Determine a specific need or problem you can help with
- Build sufficient rapport and trust with your prospect to the conclusion that he or she wants to have additional contact to learn more about what your company has to offer to meet the prospect's stated needs
- Establish the mind set in your prospects that you are a professional who may be able to help them
- Determine whether your prospects are sufficiently qualified to justify making a second contact.
Close - Establish the rationale for future contact and confirm that you will be sending information and be following up to answer all questions about your factory's products. Be sure to repeat your name and the name of your firm at the end of the call.
The Second Step - Sending out the literature. In this step you follow through with your promise to provide further information. Make sure that you provide written answers to any specific questions the prospect had.
The Third Step - Presenting your product to your customers In order to be an effective sales agent, it is important that you know your customer. You are a consultant, not a salesman. Your goal is to provide the best product to your client and guide them through the buying process. Remember you are an expert on your products.
- As a sales agent, you must discover the needs of your prospect so you can determine the best combination of products to meet those needs
- Determine the priorities of those needs. Often, customers have several needs that you can meet.
- Determine the parameters of those needs-understand all the specifications of their problems.
- Educate the prospect about how you understand their needs and have the experience to solve them
Exercise 2: Reading – Marketing
In any company, marketing is a key aspect of how a company remains in business and successful. The general idea of marketing is to let your current and potential consumers know what you have to offer them. However, marketing is not only conveying what you have to offer. In its own right, marketing is also an art form. It is the art of convincing consumers that your product is the best and that they want your product versus the product of your competitors. Marketing is the art of displaying and maintaining a positive company image while getting the attention of the marketplace.
Advertising/Sales Promotions
While there are many forms and approaches to selling products, any approach will require a good command of the English language and the ability to speak to customers in a way that is convincing and appeals to their needs or desires. When attempting to sell a product, you must keep in mind the audience you are speaking to. You must remember the Who, What, and How aspects of your presentation or advertisement. You must keep in mind:
- Who will read or see what you are about to write or advertise? What point of view might they be coming from?
- What is it that you want to accomplish through your advertisement?
- What are your main points about your product? What main features are you going to concentrate on when it comes to trying to sell your product?
- How will you organize your ideas? How will you reach the customers of your target market?
Market Analysis Components
Before a company decides to launch a new product they need to analyze the market. Here are four main components that each company must look at to determine if they should move forward with their idea or improve it. It is important to analyze the market before moving too far along on a certain idea.
- The Consumers: The people who are going to buy your products
- The Company: The organization that is producing the products
- The Competitors: Other companies who produce the same kind of products that you do
- The Conditions: What the real world looks like in terms of business; do people have enough money to buy your products? Are there a lot of similar products on the market? Is now a good time to launch a new product?
The Four Steps for Market Segmentation
Once a company has a solid idea for a product they need to find out more information about their intended consumer in order to make sure that the consumer will buy their product. By finding out each of these four components, companies can design effective ad campaigns.
- Identifying product-related need sets
- Grouping customers with similar need sets
- Describing each group
- Selecting an attractive segment to serve
Marketing Strategy (The 4P’s plus Service)
- The Product
- Communications about the Product (Promotion)
- Price
- Distribution (Place)
- Service
Exercise 3:
What are the “Four P’s” of the Marketing Mix?
- P __ __ __ __ __ __
- P __ __ __ __
- P __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
- P __ __ __ __
Exercise 4:
Using the words from Exercise 3 to complete the sentences below.
- The ________ is the cost to the buyer for the goods or services they want or need.
- ___________ informs consumers about the products a company offers and persuades consumers to buy those products.
- A ________ is where goods or services are available for people to buy them.
- ___________ is the actual good or service that is sold to the consumer.
Exercise 5:
Fill in the missing vowels (a,e,i,o,u) in the words below.
- Market r_ s_ _r c h = information about what consumers want and need
- Market s _g m _n t = a group of customers of similar age, income, and social group
- Market s h _ r_ = the percentage of sales a company has
- Consumer b_ h _ v_ _ r = where and how people buy things
- Consumer p r _ f _ l _ = description of a typical consumer
- Consumer g _ _ d s = things people buy for their own use
- Product l _ _ n c h = introduction of a product into the marketplace
- Product l _ f _ c y c l _ = length of time people continue to buy a product
- Product r _ n g _ = set of products made by a company
- Sales f _ r _ c _ s t = how much a company thinks it will sell in a period
- Sales f_ g _ r _ s = how much a company has sold in a period
- Sales t _ r g _ t = how much a company wants to sell in a period
- Advertising c _ mp _ _ g n = program of advertising activities over a period of time
- Advertising b _d g _ t = the amount of money available for advertising
- Advertising _ g _ n c y = a business that advises and makes ads for other companies
Exercise 6:
Read this report, which was written by an expert on products. Each of the underlined words is incorrect. Write the correct form of the incorrect word.
“Can we have too many products?”
There are two cars in the garage. In the living room, there is a wide-screen TV with 100 channels, and first-class hi-fi equipment. Each child has a television in his or her bedroom. The kitchen (1)contain a dishwasher, an ordinary oven and a microwave oven. The cupboard in the bedroom is (2)fill with designer-label clothes. Is it possible (3)too have so many products that we don’t need any more? Some (4)economy think so. They (5)points to Japan, where demand for certain goods has been flat for 10 years now. They say that one reason for this is that Japanese people have all the material goods they want and save their money instead of buying more. Compare this with the poorest countries in the world, where there is one TV set for every 60 people!
Grammar: Compound Adjectives
A compound adjective is formed when two or more adjectives work together to modify the same noun. These terms usually have a hyphen ( - ) in between the two words to avoid confusion or ambiguity.
Examples:
- One-way street
- Long-term contract
- Kind-hearted person
Exercise 6: Compound Adjectives
Compound adjectives are also common in the advertising world. Use the words in the box to complete the sentences below.
well high best long hard high
- IBM manufactures ______-tech computer products.
- Timberland makes a range of _________-wearing footwear.
- Ferrari produces __________-quality sports cars.
- Coca-Cola and PepsiCo both developed ________-selling soft drinks.
- Duracell sells _________-lasting alkaline batteries.
- Levi jeans are a ___________-made clothing product.
Exercise 7: Marketing Verbs
The following verbs are also terms commonly used when speaking about products and when a company is advertising their products. Match the verbs on the left to their meanings on the right.
- launch a) to stop making
- test b) to build or make
- promote c) to introduce into the market
- manufacture d) to change in order to improve
- modify e) to try something in order to see how it works
- discontinue f) to make a plan or drawing
- design g) to increase sales by advertising, etc.
- distribute h) to supply to shops, companies, customers
Exercise 8
Think in more detail about how you would promote the product/service for which you developed a business plan in the previous lesson. Working in the same groups, answer the following questions.
-
What do you think the normal consumer profile is for your customers?
- Age:
- Gender:
- Job:
- Income Level:
- If you were an advertising agency what recommendations would you make to this company advertise in different ways-billboards, TV, radio, magazines, etc? And WHY does the company need to use these different ways to reach its customers?
- If you worked for this company, and had an advertising budget of $25 million, how would you try to increase their sales?
- What seems to be the target market for this company? (Children, young adults, university students, young professionals, older professionals, retired individuals, families, or any combination of the above.)
- Do you think that it would help this company to expand its advertising campaign to reach children or university students?
Lesson 14 – Daily Life
Vocabulary:
|
|
Exercise 1: Reading – Daily Life in Business: An Introduction
In the United States many different professions work in offices. A typical workweek is 40 hours, with Saturday and Sunday off. A typical workday begins at nine in the morning and ends at five in the evening. Because of this, many people refer to their jobs in offices as “the old 9-5”. Often the commute to and from work is very long and stressful due to traffic congestion. Not everyone has their own office; many people do most of their work in cubicles, small spaces without doors or high walls. It is typical for office workers to stand up and talk over their walls to their colleagues, or to decorate their own cubicles with pictures of their families and friends. During a day at the office workers are expected to attend meetings to discuss various things within the company. There are generally designated areas for employees to drink coffee and eat snacks during lunch time. Often there is a water cooler, around which many employees may stand and gossip about office goings on. It is a bit of a joke in American culture to say that you are a “slave” to your job. Quite often workers are expected to stay late at work to finish a project, or to come in on the weekends. Because it can be boring to spend so much time in the same small space doing the same thing it is very important for employers to try to keep their employees happy and motivate them to work hard.
Meetings

Many professionals - diplomats, agency representatives, and business people - have to take part in meetings which are conducted in English. The language of such meetings follows definite patterns. Even if your English is good, not all of the language of meetings is obvious. This unit presents and teaches all the language you need to participate effectively in meetings in English.
Exercise 2: Reading – Formal meetings
Business people have strong feelings for or against meetings; often meetings take up much of the workday, and sometimes accomplish very little. It is inevitable that when people are thrown together over a long period of time, personality differences show up, tempers rise, and disagreements and power struggles are common.
However, meetings are essential for international business; they are necessary in establishing relationships for future business, and in negotiating deals. You need to meet and get to know the people you will be doing business with, especially to observe foreign customs, attitudes, and behaviors. If you are in sales, meetings are often the most productive way to make those sales, or at least to get your foot in the door (make some progress.) Finally, no matter what kind of business you transact, meetings allow you to observe the behavior of others.
Since we never really know how a meeting will evolve, how can we prepare for it? Will there be arguments? Discussion? Negotiations? Disagreement? Even if we know the subject, can we control the flow of conversation? What vocabulary can we use in this situation?
There is language that deals with the purpose or function of what you want to say, such as: disagreement, doubt, suggestions, negation, or acknowledgment. We call this functional language. By learning how to approach these situations functionally, you will be able to deal with the dynamics of any meeting.
Exercise 3: Comprehension Questions
Questions:
- Why are meetings important for international business? ________________________
- What reasons are meetings organized for? ________________________
- What language do we use to run a meeting? ________________________
Exercise 4: Reading – How Motivate Employees:
Because it can be boring to spend so much time in the same small space doing the same thing it is very important for employers to try to keep their employees happy and motivate them to work hard.
- Highly value the goose - Think of each and every employee on your team as the goose that provides the golden eggs, even the ones who don’t act like it.
- If we want our employees to become top producers, we need to first treat them as such.
- We have to let them know immediately, continually and sincerely how important they are to us.
- Seeing them as your most important asset goes a long way toward creating it as a reality.
- Look for what’s right today - Most of us walk around with an unspoken question playing on a continuous loop in our head. The question sounds like this: "What’s going to go wrong today?" When we ask that question, we only pull up negative answers related to it. Consequently, we start finding a plethora of wrong things.
- Researchers tell us that we have an average of 40,000 thoughts per day, and as much as 80% of all those thoughts are negative.
- To combat this challenge, when you arrive at work tomorrow start asking, "What right things are occurring all around me that I have not noticed before." Keep asking that question and you will continue to pull up positive answers. When you do, acknowledge people for those actions.
- Reward right actions - If we want people to continue the behaviors and attitudes that are conducive to a productive, energized environment, then we must reward those actions when they occur. Acknowledging employees can be one of the most potent forms of reward and reinforcement. In fact, limited praise and lack of recognition is one of the primary reasons why employees leave jobs.
- Telling people how much you appreciate them and the contribution they make is beneficial because it meets one of their most basic needs: the need to feel important and valued. To effectively manage people we must do so in a way that builds self-esteem. Letting employees know how much we respect their good work does just that.
- Ask your employees what rewards they would like. The mistake a lot of us make is thinking that because we respond positively to a certain reward, other people will also.
- Walk your enthusiastic talk - Effective managers are basically trying to persuade employees to access their own energy, passion and enthusiasm. Accordingly, it absolutely doesn’t work to take the "do as I say, not as I do" position, because at its most basic level, persuasion is transference of feelings. If we don’t have those feelings, we can’t transfer them. As a result, our words ring hollow, our credibility is compromised, and people feel justified in simply marking time.
- Uncover hidden talents and interests - To make employees feel part of the group, find out what they love, what they are good at, and how they feel they might incorporate those things into their work environment.
- Send out questionnaires, hold meetings and having informal conversations with people.
- Find out what people love and let them express it through their actions. It gives people a sense of purpose to know they are contributing to others through their talents.
- Is someone really good at interior decorating? Give her a small budget and ask her to submit ideas for sprucing up the office.
- Is someone else passionate about sailing or gardening or car maintenance? Why not sponsor a brown bag "Learning Lunch" series and once a month have people sign up to teach what they know.
- Is there someone who is community minded? Let him organize a campaign to provide food for the homeless or adopt a family during the holidays.
- Keep people informed and answer all questions - To the best of your ability, give people as much information as possible about what’s going on. If you don’t have any information, let everyone know that you don’t have anything to communicate. Your silence can be misinterpreted as withholding.
- Laugh it up! - Studies show that humor promotes creativity and innovation. It also promotes a fun work environment and reduces tension. It shifts perspectives, minimizes negativity and contributes to our good health. Here are some examples of how to bring humor to the workplace:
- Create a costume day and contest on holidays.
- Sponsor a Friday karaoke contest. Upper management goes first!
- Have a pajama day.
- Hold a spontaneous ice cream party, complete with clowns and jugglers.
- Have a 50’s Day or a Weird Shoe Day.
- Sponsor a Joke Day with best joke winners receiving a prize.
- Have an employee baby picture contest.
- Publish funny stories or anecdotes about employees’ experiences in the company newsletter.
- Put a small toy (slinky, Rubik’s cube, magnet puzzles, etc.) on people’s desks. Encourage employees to play with the toys.
- Communicate one on one - Each week or two meet individually with all your people and find out what they need from you, how you can better serve them and what challenges they are facing.
- A great question to ask is, "What one thing can I do to make your job run more smoothly?"
- Listen attentively. After you have heard them and responded to their concerns, you can share what one thing they might do that would make your job run more smoothly.
- One of the most important things to remember about motivating employees is that you must employ lots of strategies and techniques—and change them often. We are all creatures of habit, and when we begin to expect a certain reward, it no longer serves to motivate us. That Christmas turkey we get every year has become a right, and as such, it no longer provides much incentive. In fact, if my turkey weights six ounces less than your turkey, there could be trouble!
Exercise 5: What’s Your Opinion?
Here are twelve opinions about meeting: put a (+) beside the ones you agree with and a minus (-) the ones you disagree with.
DO YOU AGREE?
The purpose of most meetings is to decide when the next one will take place. __
A meeting is a group of people who can decide nothing alone, and who decide together that nothing can be done. __
It's better to send everyone a memo about a new procedure than to have a meeting about it. __
Meetings help everyone to feel personally involved is decision-making. __
It's better for the boss to make a decision than to have a meeting. The most important person at a meeting is the chairperson. __
The most important piece of paper at a meeting is the agenda. __
Most meetings are unnecessary; they're just a way of making people feel important. __
It's better to talk to each person individually than to call them all together for a meeting. __
A meeting may be the only chance the members of a group actually have to see each other face-to-face. __
Meetings lead to better decisions, because of the exchange of information and ideas. __
You can never rely on the person who takes the minutes to tell the truth about what actually happened at a meeting. __
More time is wasted during meetings than during any other business activity. __
Exercise 6. Look at these problems and decide the best way of dealing with each problem. Which would be the best one? Put your variant in the table after the exercise.
A one-to-one meeting of two of the people involved,
B meeting of four or five of the people involved,
C a meeting of about ten of the people involved,
D a meeting of everyone involved,
E should just one person decide what to do and then inform everyone by phoning or sending a memo?
1. A large, influential customer continually pays late. Your sales manager and credit controller have politely and repeatedly complained but this hasn't made any difference. The time has come to decide what to do about this.
2. In a small factory the older workers are ignoring safety rules and encouraging the younger ones to do the same. Some of these rules may be excessively cautious and the older workers' production rates are very good.
3. In a medium-size factory, groups of workers operate as teams.
One group has been getting poorer results than the other teams and verbal warnings have had no effect.
4. The firm is having a bad year and it will probably be necessary to make five members of the office staff redundant. The normal policy is 'last in - first out'.
5. Someone has been leaking information about your firm's products to your competitor. It may be a member of your staff or one of your preferred suppliers.
6. The board requires a report on your department's long-term plans over the next ten years.
7. The territories covered by your sales force have been unchanged for ten years. A revision of the boundaries might make the team more efficient.
8. There is to be a company picnic next month and everything has to be planned and organized.
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise 7: Ideal Workday
Describe your ideal workday. Some questions to think about include:
- What is your job? Your position?
- How do you arrive to work? Do you drive your own car? Take public transportation? What about traffic in the morning?
- Do you work in an office or in somewhere less conventional?
- Do you work in a cubicle? Do you have your own office?
- What time do you arrive at the office? When do you leave?
- Do you get along with your boss? Your colleagues?
- How do you eat lunch?
- Do you attend meetings?
Exercise 8: Class Discussion
Read the “Laugh it up!” section in “How to Motivate employees”. Which of these activities would you think is the most effective in lifting employees’ motivation or morale? Can you think of any other activities that would uplift employees’ motivation or morale?
Lesson 15 – Business Communications: Phone and Email
Vocabulary:
To leave voice messages - залишити голосове повідомлення
To take messages - прийняти повідомлення
Voicemail message - голосове повідомлення
Confidential information (things that others should not know) - конфіденційна інформація
Hesitate, v - вагатися, затинатися
Further information - подальша інформація
Concerning - сумнівний
Regarding - що стосується
Currently, adv – поточно, в даний час
Urgent - терміновий
Colleague - колега
Sincerely - щиро
Kind regards - З найкращими побажаннями
Exercise 1: Reading – Business Communications Today
Does anyone send letters through the mail these days? In today’s business world, e-mail and phone are the most common forms of communication. Fax machines are rarely used. Some people even use text messages to communicate with their bosses. Communicating by phone and e-mail can be complicated because it can be formal or informal, depending on whom you’re speaking with.
The Semi-Formal Email:
A semi-formal email is similar to a standard business letter, but less formal and usually shorter. The ending is typically “Best wishes” rather than “Sincerely”. This style is best used when you are sending an e-mail to somebody who is outside of your company, or whom you do not know very well. The focus is on giving or asking for information quickly.
The Informal Email:
It is the most suitable for e-mails within your company and for people whom you know well. The greeting is often, “Hi”, “Hello”, or even “How are you?” Sometimes endings are omitted altogether. Sometimes the writer will type only in small letters. This style is much more similar to spoken than written English. Sometimes people use abbreviations if they want to save time.
Exercise 2:
Review the table of commonly used email phrases. Work in pairs. Student A should write an email making a request or asking for help from Student B. Student B should write a response to Student A’s email.
|
Situation |
Email phrases |
|
Starting an email
|
|
|
Telling why you are writing |
- Regarding/Concerning your budget plan, I think our calculations are incorrect for the month of June.
- In response to your e-mail yesterday, I have read the document and will order the product you requested. |
|
Requests |
|
|
Opinions |
|
|
Closing |
|
Exercise 3: Matching
There are many ways to end an email. Match the numbered definitions with the phrases that are commonly used in business communications.
- A phrase which means you will be unavailable for contact
- A formal way to say that you will be happy/excited to hear from somebody in the future
- A slightly aggressive way to ask somebody to do something
- An informal why to tell someone that they can contact you in the future
- To tell somebody that you will call or write to them in the future
- A polite way to ask somebody to do something
- A formal why to tell someone that they can contact you in the future
- An informal way to say that you will be happy/excited to hear from or see somebody in the future
- A formal why to tell someone that they can contact one of your colleagues in the future
- A polite way to say that you expect you have answered their question
- I will contact you.
- I hope this answers your question(s).
- If you have any further questions, please do not hesitate to contact me at (e-mail/phone number).
- Feel free to ring me if you have any questions / if you have any problems / if you need further information
- I will be out of the office on (date).
- Please (don’t hesitate to) contact my colleague (name) at (e-mail/phone).
- Please deal with this matter urgently.
- I would really appreciate it if you could ….
- I look forward to hearing from you.
- I’m looking forward to hearing from you.
Exercise 4: Phone Conversations
When should you use which phrases? Fill out the table by putting the following phrases in the correct section.
- One moment, please.
- Hello, this is John Block from ABC. I’m calling regarding the upcoming conference in Miami. I’ll try you again later today.
- Please ask him to call Susan when he gets in. He already has my number.
- I’m sorry, I didn’t catch what you just said.
- John has left for the day. Would you like to be put through to his voice mail?
- Good afternoon, XYZ firm. How may I help you?
- Thanks for calling. I’ll speak with you again soon.
- Let me repeat your information to make sure I got it right.
|
SITUATION |
EXAMPLES |
|
- Hi Marina, it’s John calling. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lesson 16 – Business Jargon
Objectives:
By the end of the lesson Students will be able to:
- Identify business idiom/jargon and use them appropriately in context
- Participate in mock dialogues using idioms/jargon
- Hold a discussion about the value of business jargon
Vocabulary:
- Workplace Jargon: a term used to describe the often needless and/or meaningless sentences and phrases used by both managers and colleagues in the workplace instead of plain English.
-
The bottom line: The final result (usually having to do with accounting)
- “Let’s get to the bottom line. How much is this going to cost?”
-
Hindsight is 20/20: Problems and solutions seem obvious once the event has occurred
- “Looking back, we should have seen that problem coming. Oh well, hindsight is 20/20.”
-
Catch 22: Whatever you do, it won’t work
- “If I decide to go this route I’ll lose the client, but if I choose the other route I’ll get fired. It’s a catch 22 situation.”
-
Deep pockets: Wealthy or having the ability to pay
- “Don’t worry about the cost. We have deep pockets.”
-
Dog and pony show: A financial presentation
- “All right, let’s see the dog and pony show. We need this budget.”
-
Fence mending: An apology, smoothing of bad relations
- “I have to go do some fence mending over last week’s awful meeting.”
-
Free ride: Getting something for free
- “They’ve offered us a free ride if we agree to their terms.”
-
“I needed it yesterday”: It is needed immediately
-
“When will you need this report, boss?”
“I needed it yesterday!”
“I’ll have it for you as soon as I can.”
-
“When will you need this report, boss?”
-
It will never fly: It will never work
- “You can try doing that, but it will never fly.”
-
On a roll: Doing well, moving forward
- “We’re on a roll! Let’s keep doing what we’re doing!”
-
Power lunch: Big business dealing at lunchtime
- “I’m off for a power lunch with our new clients.”
-
Lay your cards on the table: To be truthful or honest
- “Let me lay our cards on the table: we want to be your paper supplier and we’ll do anything to gain you as clients.”
-
To play hardball: To do business in a hard/tough manner
- “Those guys are playing hardball; they’re not agreeing to any of our conditions.”
-
Tongue in cheek: To say something jokingly/not truthfully
- “I’m sorry that my comment offended you, it was meant to be tongue in cheek.”
-
What makes him/her tick: What he/she is motivated by
- “I want you to go in there and find out what makes her tick!”
-
create the storyboard: outline what the solution will look like
- “We need to create a storyboard to fix this problem.”
-
cover all directions of the compass: trying to make things acceptable for all stakeholders
- “We need to cover all directions of the compass here; we can’t have anyone feeling left out.”
-
power to the elbow: getting additional backup information to make your case stronger
- “That was a good presentation, but you really need more power to the elbow to convince me this will work.”
-
blue sky thinking: Idealistic or visionary ideas - not always with practical application
- “This is blue sky thinking, there’s no way that your ideas will be practical in real life.”
-
touch base: a desire to meet up with a colleague to discuss progress
- “I’d like to touch base with you about your upcoming product launch.”
-
deep dive: getting into the detail
- “All right, now it’s time for the deep dive. Let’s get these numbers sorted out.”
-
singing from the same sheet music: showing a united front or everyone understanding and saying the same thing to customers or service users
- “Let’s make sure we’re all singing from the same sheet here, I don’t want anybody to be confused.”
-
pushing the envelope: going outside normal boundaries to achieve a target or goal (such as exceeding specifications)
- “Todd is a great employee; he’s always pushing the envelope and coming up with creative solutions.”
-
win-win solution: providing a product or service which makes everyone happy, e.g., buy-one-get-one-free
- “This is a win-win solution, we’re happy, the client’s happy!”
-
in the loop: knowing what's going on and being kept informed
- “Make sure you keep me in the loop about your newest project, I want to know what’s going on.”
-
pick the low-hanging fruit: going for the easiest option
- “We could do that, but I think it would be better in this case to pick the low hanging fruit and make our lives easier.”
-
under-pinning: the foundations of an idea, which helps another connected scheme or proposal
- “The underpinning of this idea is that we want everyone to be happy with our product.”
-
moving forward: making progress on an idea or scheme
- “We’re moving forward on the Bluth account; everything is going according to plan.”
Exercise 1: Dialogues
Work in pairs. Write dialogues using jargon. Student A should be the authority figure (boss, manager etc.) and Student B will play the role of the employee. Choose one of the following situations.
- There will be a meeting the next day, and the boss wants to “touch base” with their employee.
- Discuss the results of the last meeting.
- Discuss plans for a proposal to a new client.
Exercise 2: Reading:
The Importance of Business Jargon
In addition to companies having their own organizational designs, communication channels, and corporate cultures they also tend to have their own jargon. You have seen a listing of some of the most commonly used phrases that exist in business jargon. Companies do not expect that those outside of their company or their particular marketplace understand the jargon that exists within their company. However, they still continue to use common business jargon aside from the jargon that exists within their company and it is important to know these phrases and terms so that business communications is made easier on both parties involved.
Exercise 3: Comprehension Questions
- Why is business jargon important?
- Do companies have their own jargon particular to their company or marketplace?
- Do companies expect that everyone will understand their own particular jargon?
Exercise 4: Critical Thinking Questions
- Do you think jargon is necessary for ease of communication? Why?
- Do you think that plain English could be used instead of jargon? Why?
- Which business jargon phrases do you think are most useful? Why?
Exercise 5: Reading – Workplace jargon 'isolates staff'
Needless jargon in the workplace is baffling employees and widening the divide between management and staff, a survey suggests. Investors in People said that the proliferation of phrases such as "blue-sky thinking" and "power to the elbow" was damaging to British industry. About a third of the 3,000 workers polled said they felt inadequate when wordy terms were needlessly used. Others believed bosses were being untrustworthy, or hiding something.
Many managers used jargon without considering the impact it has on staff said Nicola Clark, a director at Investors in People, which works with firms to boost their performance.
"Bosses need to lead by example, ditch needless jargon and concentrate on communicating clearly with their employees," she added.
"If used inappropriately, jargon can be an obstacle to understanding, which ultimately can impact on an individual's performance and an organization’s productivity."
A survey of Scottish workers found that more than half were fed up with bosses using management jargon with two-thirds preferring no jargon at all in the workplace.
"Communication is one of the hardest things to get right in any organization," said Peter Russian, chief executive of Investors in People Scotland.
"Using management jargon doesn't make you a good manager. The most effective bosses recognize that one of the keys to engaging, motivating and enthusing people is to communicate in a way which everyone can easily understand."
Exercise 6: Comprehension Questions
- What does the survey cited suggest?
- True or false: The survey of Scottish workers said that they loved using jargon.
- True or False: The article suggests that jargon can be an impediment to understanding.
Exercise 7: Critical Thinking Questions
- Why would jargon be an impediment to understanding?
- Why would people feel that their bosses were untrustworthy when they used jargon?
- Can you think of an instance when jargon would be helpful?
Exercise 8: Class Discussion
Have a discussion on the importance of business jargon. Some questions that can be answered include:
- What does business jargon do?
- Why is business jargon used?
- Would it be simpler to use plain English?
- Which phrases do you think would be most useful in business setting?
- What role do you think time plays in the utility of business jargon? Do you think these phrases will be useful in five years? Ten years?
Exercise 9:
Match the term on the left the correct definition on the right.
- The “bottom line” A) What his motivation is
- 20/20 hindsight B) Getting something for free
- Catch 22 C) It will never work
- Deep pockets D) Big business dealing at lunch time
- Dog and Pony show E) Doing well, moving forward
- Fence mending F) To say something jokingly or not truthfully
- Free ride G) It is needed now or immediately
- “I needed it yesterday” H) The final result (from accounting)
- It will never fly I) Be truthful or honest
- On a roll J) Perfect knowledge but too late
- Power lunch K) Whatever you do, it won’t work
- Lay your cards on the table L) A financial presentation
- To play hardball M) An apology, smoothing of bad relations
- Tongue in cheek N) Wealthy or having the ability to pay
- What makes him tick O) To do business in a hard/tough manner
Lesson 17 – Office or Sports Field?
Working together with colleagues in a business setting and competing against other companies often feels similar to playing on a sports team. Many times, the language sounds similar also. English speakers have adopted many phrases from sports for use in the business world.
Exercise 1: Vocabulary
Read the sports definitions and examples of the terms below. Can you match each sports term with its business meaning to complete the table?
- Something is someone’s responsibility
- To start a meeting or presentation; to get something ready
- To be unsuccessful
- Action plan; strategy
- Worse than the standard/average; to be not good enough
- to be extremely successful; do a great job
- Try your best/hardest; give your best effort
- Better than the standard/average
- Undecided/unresolved until the very end
- Ready and able; prepared; organized and knowledgeable
- Reschedule (an appointment, meeting, conversation, etc) for a later time
- To be doing the right thing to succeed, to have the correct idea
|
Phrase |
Sport of Origin |
Sports Meaning |
Business Meaning |
Business Example |
|
Tee it up |
Golf |
Get ready to hit the ball |
|
I’ll tee up the presentation on the computer while we’re waiting for everyone to come in for the meeting. |
|
Below par |
Golf |
Par is number of hits a professional player should need for a specific hole |
|
Last month our performance was sub-par. Our profits were much lower than expected. |
|
Above par |
Golf |
|
Compared to the competition, we’re above par. More customers are visiting our store. |
|
|
To strike out (past: struck out) |
Baseball |
Not hit the ball |
|
We presented our business plan to three potential investors, but we completely struck out. None of them wanted to give us money. |
|
To make a pitch (v) To pitch (v) Pitch (n) |
Baseball |
To throw the ball toward the hitter |
(v)To tell someone about an idea; to make a presentation to interest someone in your products/ services/ company/ idea (n) A presentation about your products/ services/ company/ idea
|
I had lunch with a potential partner today. He is very interest in working with us. We will meet with him again next week to make a pitch formally. |
|
To hit/knock it out of the park |
Baseball |
To score a point with only one hit, often by hitting the ball farther than the edge of the field (out of the park) |
|
Sarah’s group earned double the revenue goal last year. They really hit it out of the park. |
|
To step up to the plate |
Baseball |
To get ready to hit the ball |
to take responsibility and do a good job |
Bob, thanks for stepping up to the plate while Amy was out sick. It was a big help that you did extra work. |
|
The ball is in someone’s court |
Tennis |
The ball is on one player’s side and the player must hit the ball |
|
"Do you think I should accept the job offer?" |
|
Blind-side(d) |
Many sports (football, hockey, American football) |
To hit someone from behind or when they are looking in the other direction |
Not see something coming, be very surprised by something |
I was completely blind-sided when Mr. Smith said he didn’t want to be our business partner anymore. I thought we had a good relationship. |
|
Down to the wire |
Horse racing |
When there is no clear winner in a race until the very last moment |
|
Tomorrow’s the last day of the month and I’m not sure if we’ll make our revenue goals. It’s down to the wire. |
|
Off the hook |
Fishing |
A fish on the hook is caught and will die |
To escape, to have responsibility removed |
Our meeting was cancelled, so we don’t need you to give a presentation. You’re off the hook. |
|
Off base |
Baseball |
A player who is not in the correct position |
Not fair; not true or accurate |
I think he is way off base with the budget. I calculated different numbers. |
|
To be on target |
Darts, Archery |
To hit the bullseye; to hit what you’re aiming at
|
|
We are on target to meet our budget this month. |
|
A long shot |
Hunting, soccer, basketball |
A shot from very far away |
A very difficult thing to accomplish, something that is unlikely to happen or succeed. |
I think it’s a long shot that Nike will want to buy our software. They’re a big company and they like our competitor’s product. |
|
On the ball |
Baseball |
To be ready to catch the ball |
|
The new secretary is really on the ball when it comes to answering the phone |
|
Out of/in left field |
Baseball |
A part of the field where the ball rarely goes and there is not much action |
Inaccurate; not relevant; not at all close to correct |
I don’t know where John got the numbers for the new budget. They don’t make sense. He’s out in left field. |
|
Start the ball rolling |
Various ball sports |
Make the ball begin to move |
To begin something |
Andrew will be late to the meeting, but let’s start the ball rolling before he arrives. |
|
Take a rain check |
Baseball |
Reschedule a game because of rain |
|
Sorry, I can't go to the movies today, but I'd love to take a rain check |
|
Drop the ball |
American football or basketball |
Lose possession of the ball so that the other team gets it. |
Make a serious mistake |
Ben, one of the salesmen, didn’t sell enough last month, so the company lost money. He really dropped the ball. |
|
Game plan |
American football |
Plan of what to do during the game |
|
We need to decide on a game plan for how we will introduce the new product to our customers. |
|
Give it/something your best shot |
Hunting, many sports with goals |
Try your hardest to hit the target or to score |
|
Mary, I know you haven't written a marketing plan before, but I think you can do it. Give it your best shot. |
Exercise 2: Reading
John: Hello, everyone. I'll tee it up. I think we need to bring in some new talent in sales. Unfortunately, our performance has been below par for the past six months.
Mary: Really? I think you’re off base with that statement. Obviously, we're not going to hit a home run every month. Also, it’s been difficult to do quality work because Victor has been sick for so long and hasn’t been able to work.
John: Yes, that’s true.
Mary: Scott’s really stepped up to the plate to help out with Victor’s work. And even though Sarah is new and still learning how to do her job, she’s giving it her best shot.
John: Okay, you’re right. We’re not completely striking out yet, but Bob dropped the ball with his last pitch to a new customer, so the customer decided to buy from a competitor instead of from us.
Mary: Ok, let’s come up with a new game plan for the next six months so we can do better. I agree we really need to hit it out of the park if we want to make the boss happy.
Exercise 3: Comprehension Questions
- Does John think the company’s performance has been good or bad recently?
- Does Mary agree with John? How do you know?
- Who is taking on more responsibility?
- Who made a big mistake?
- What does Mary mean when she says they need “a new game plan”?
Exercise 4
Read the text below. Substitute a sports phrase for the each group of underlined words.
I traveled to New York city last week to (1) give a presentation on our business plan to some investors. I was very nervous because I’d (2) been unsuccessful in similar meetings in the past. As a result, the other investors I spoke to previously didn’t give us any money. I didn’t want to (3) make a serious mistake this time. I did a lot of work to prepare, and when I went into the room for the meeting I just took a deep breath. All I could do was (4) try my hardest. Well, it went great! The investors loved our business plan. They said it was (5) better than average and decided to give us $2 million. My boss was extremely happy. He said I had really (6) taken on extra responsibility, and that I had (7) done a great job.
Exercise 5
Make up your own sentence using the following sports phrases
- Hit a home run
- Game plan
- Off the hook
- Long shot
- On target
Exercise 6
Write a dialogue using 5 of the sports phrases you have learned.
1


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку