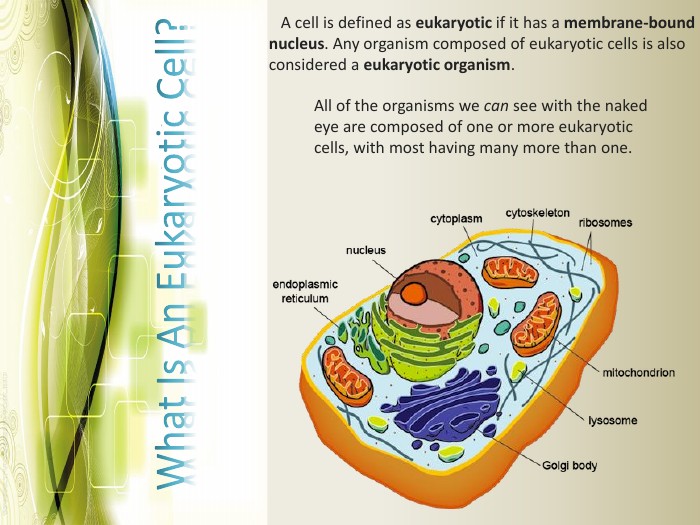
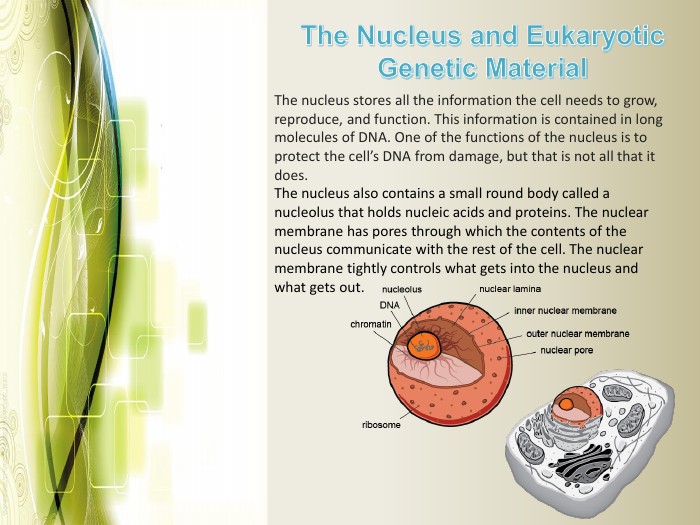
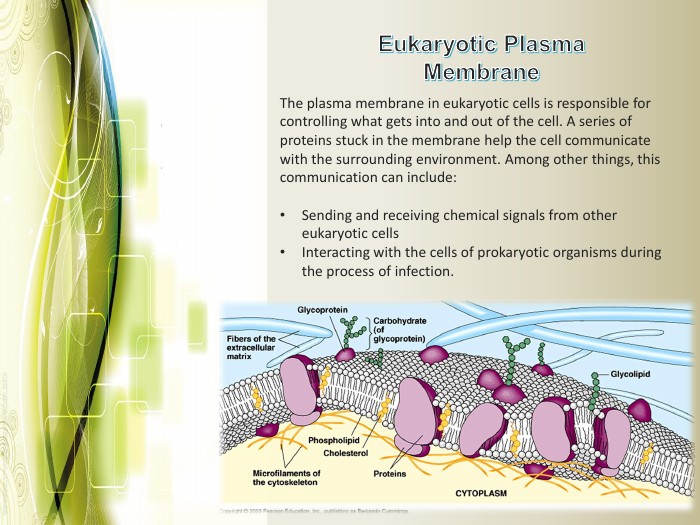
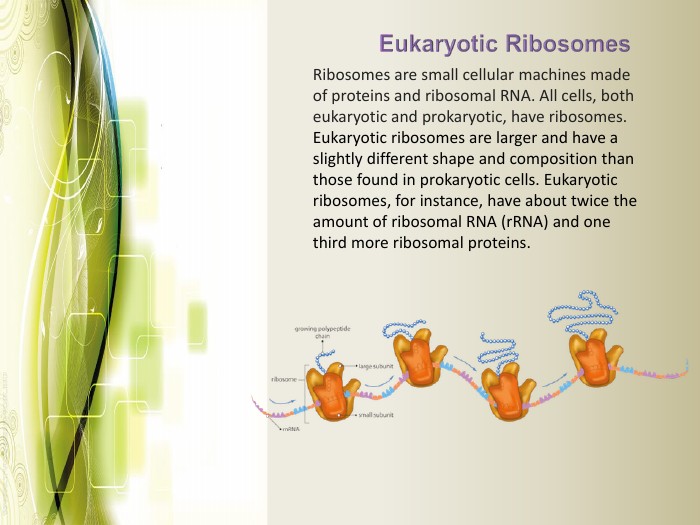
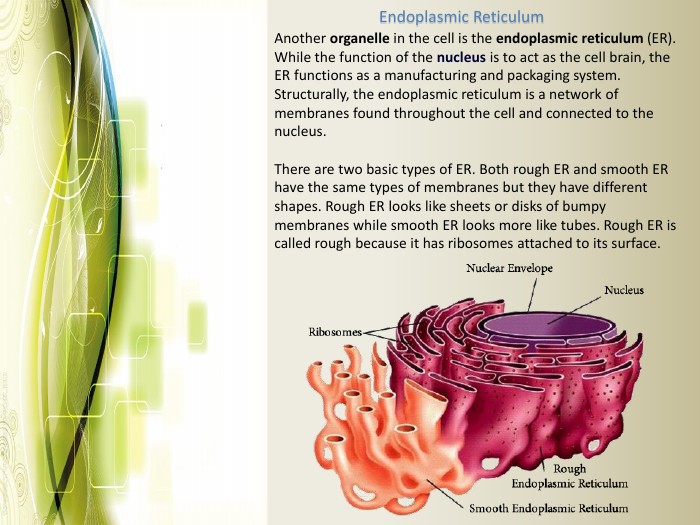
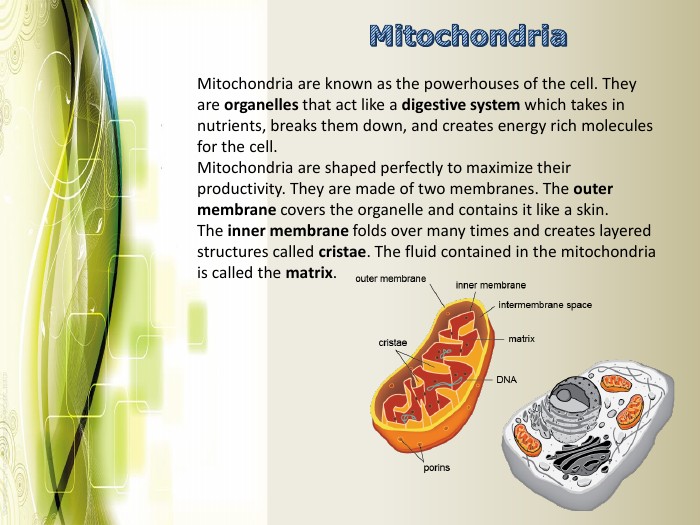
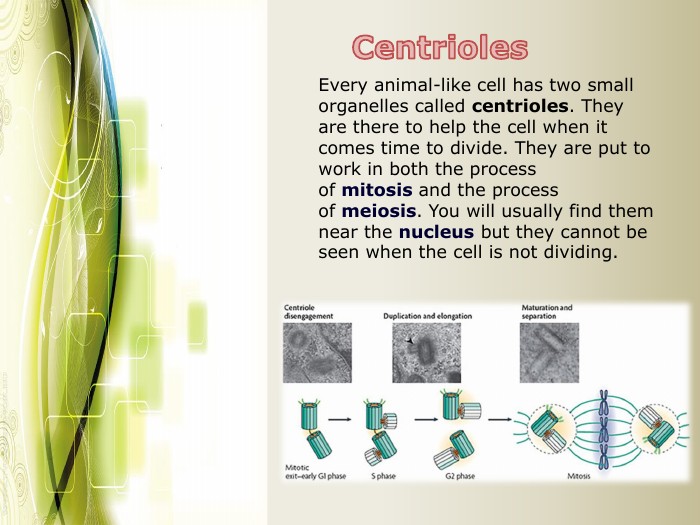
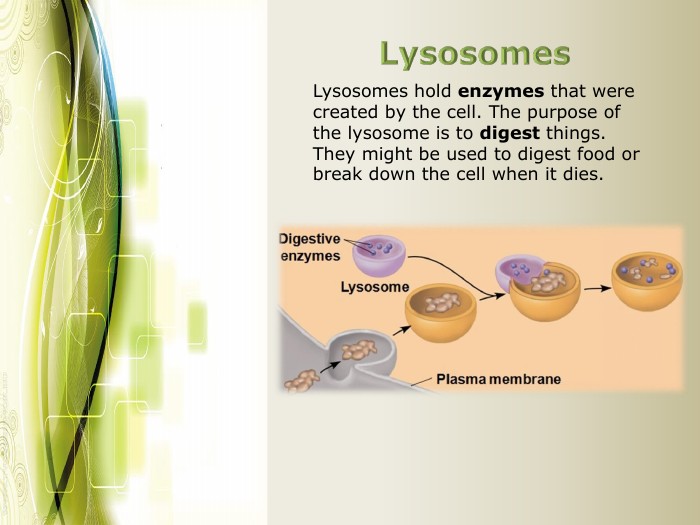
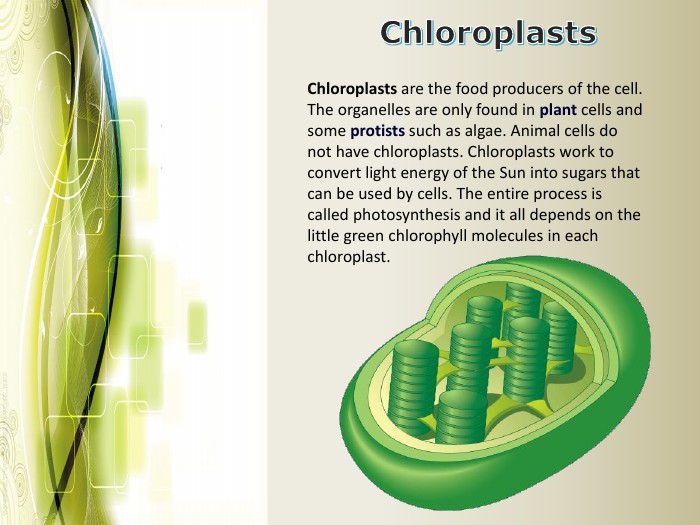
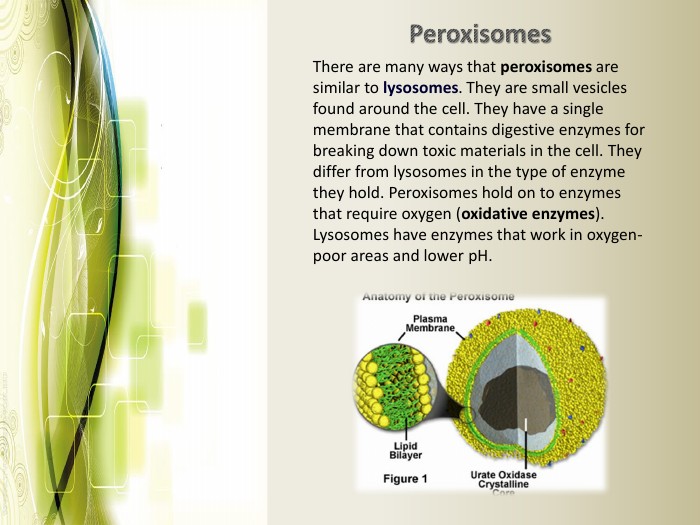
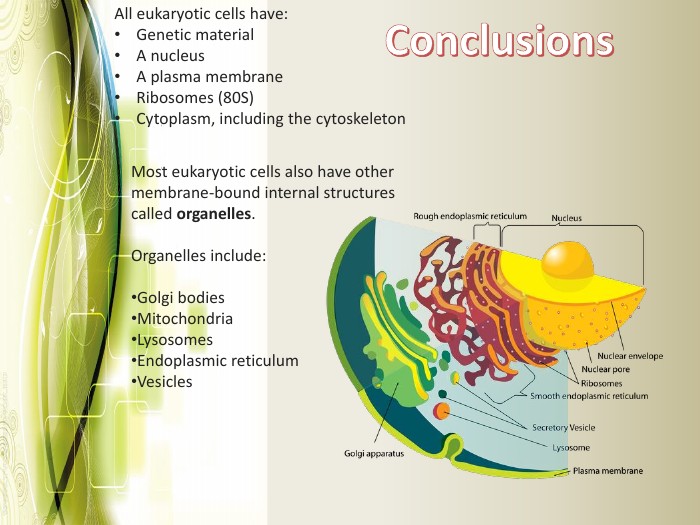
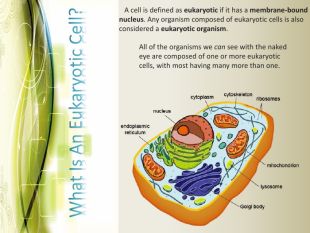
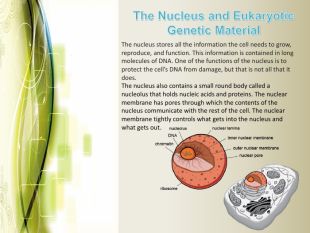
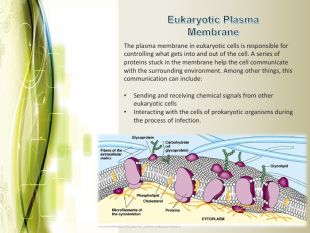
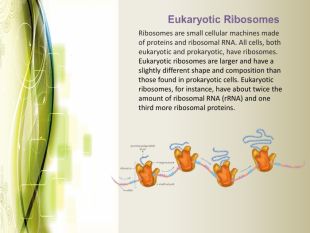
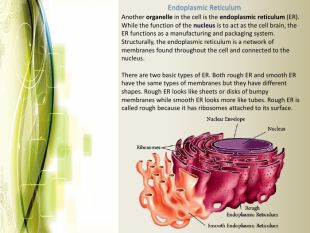
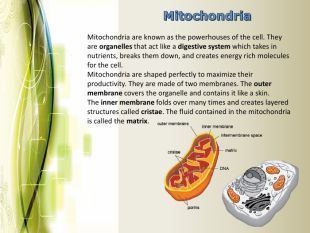
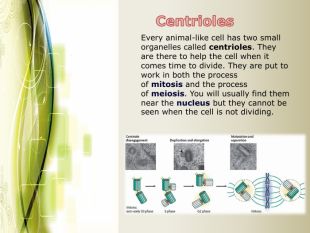
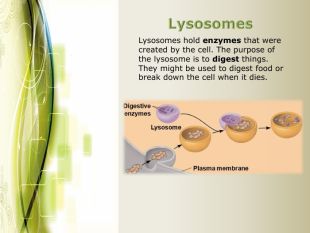
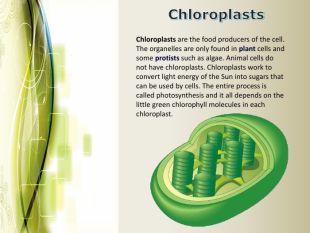
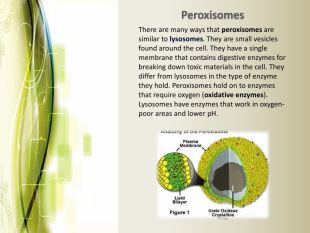
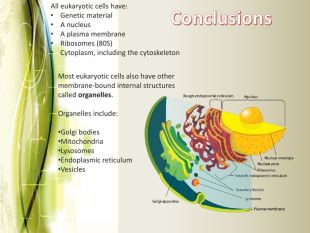
Eukaryotic cell structure
Про матеріал
Презентація підійде для інтегрованих уроків з біології та англійської під час вивчення клітин еукаріотів Перегляд файлу
Зміст слайдів


Безкоштовний сертифікат
про публікацію авторської розробки
про публікацію авторської розробки
Щоб отримати, додайте розробку
Додати розробку