Презентація до теми "DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH" (form 10-th )


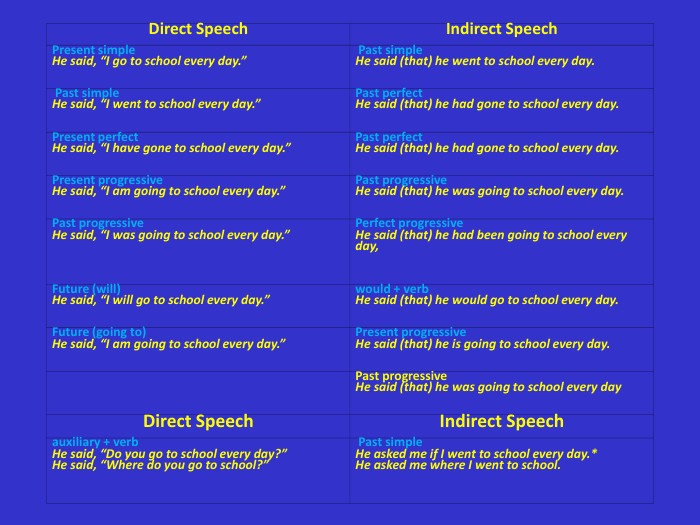















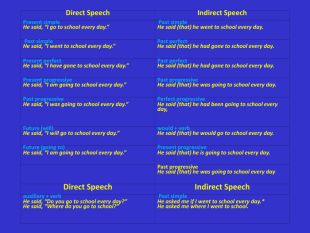
Direct Speech Indirect Speech Present simple He said, “I go to school every day.” Past simple He said (that) he went to school every day. Past simple He said, “I went to school every day.” Past perfect He said (that) he had gone to school every day. Present perfect He said, “I have gone to school every day.” Past perfect He said (that) he had gone to school every day. Present progressive He said, “I am going to school every day.” Past progressive He said (that) he was going to school every day. Past progressive He said, “I was going to school every day.” Perfect progressive He said (that) he had been going to school every day, Future (will) He said, “I will go to school every day.” would + verb He said (that) he would go to school every day. Future (going to) He said, “I am going to school every day.” Present progressive He said (that) he is going to school every day. Past progressive He said (that) he was going to school every day Direct Speech Indirect Speech auxiliary + verb He said, “Do you go to school every day?” He said, “Where do you go to school?” Past simple He asked me if I went to school every day.* He asked me where I went to school.
The situation changes if instead of the common said another part of the very to say is used. In that case the verb tenses usually remain the same. Some examples of this situation are given below. Direct Speech Indirect Speech Present simple + present simple He says, “I go to school every day.” present simple + present simple He says (that) he goes to school every day. present perfect + present simple He has said, “I go to school every day.” present perfect + present simple He has said (that) he goes to school every day. past progressive + past simple He was saying, “I went to school every day.” past progressive + past simple He was saying (that) he went to school every day. past progressive + past perfect He was saying (that) he had gone to school every day. future + present simple He will say, “I go to school every day.” future + present simple He will say (that) he goes to school every day.
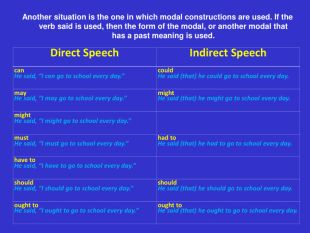
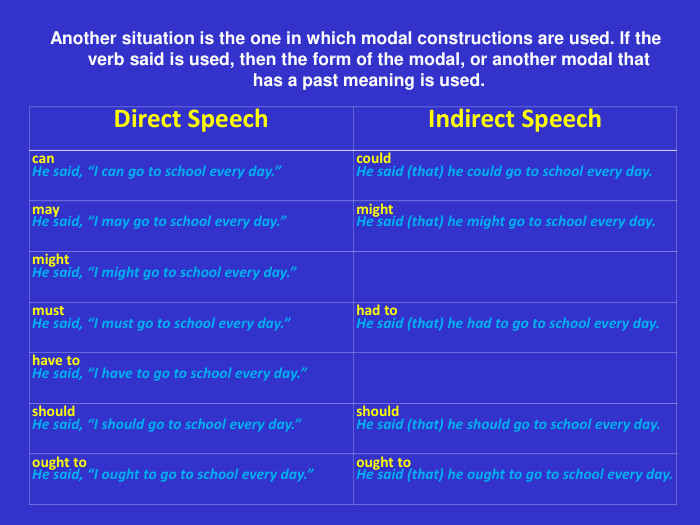
Another situation is the one in which modal constructions are used. If the verb said is used, then the form of the modal, or another modal that has a past meaning is used. Direct Speech Indirect Speech can He said, “I can go to school every day.” could He said (that) he could go to school every day. may He said, “I may go to school every day.” might He said (that) he might go to school every day. might He said, “I might go to school every day.” must He said, “I must go to school every day.” had to He said (that) he had to go to school every day. have to He said, “I have to go to school every day.” should He said, “I should go to school every day.” should He said (that) he should go to school every day. ought to He said, “I ought to go to school every day.” ought to He said (that) he ought to go to school every day.
Questions General questions Indirect Questions “Are you watching TV?” “Do you play chess?” “Does she go to school?” “Are you listening to me?” “Have you done your homework?” “Did you skate last winter?” “Will you see your friend tomorrow?” if, whether …I was watching TV. …I played chess. …she went to school. …I was listening to him. …I had done my homework. …I had skated the winter before. …I should see my friend the next day.
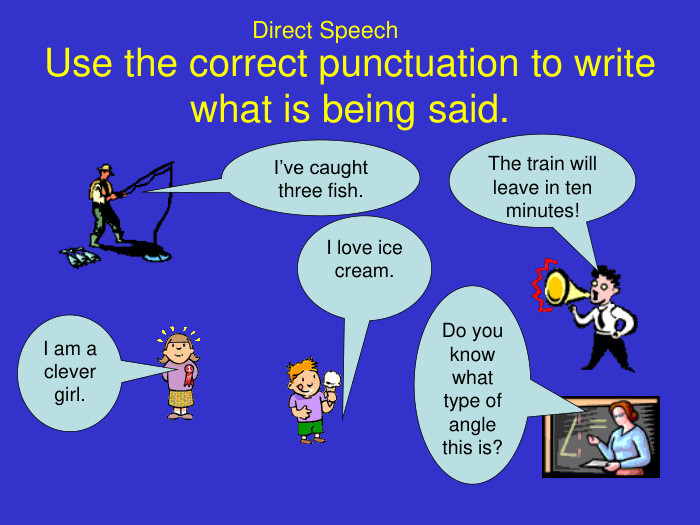
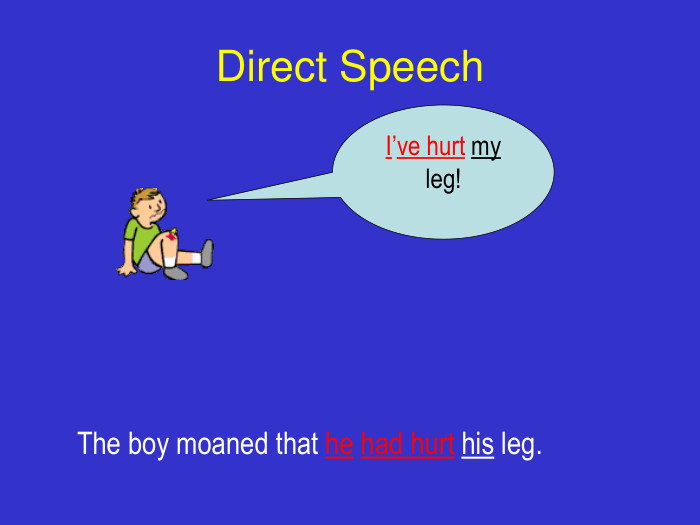
By the end of the lesson I’ll look for evidence to show that you will: Understand the difference between direct and indirect speech. Be able to apply this knowledge in your writing. Accurately punctuate direct and indirect speech Know when and how to change pronouns and verb tenses in indirect speech.


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку