Ділова англійська мова 10 (11) кл Розділ 1
Матеріал містить розробки уроків та методичні рекомендація для вчителя під час вивчення Ділової анлійської мови (Розділ 1) в старших класах
«Програма курсу «Ділова англійська мова»
для 10 (11) класів ліцеїв
Розділ 1
Підготувала
Тільна Олена Степанівна,
вчитель англійської мови
Підгірцівського ліцею
Козинської селищної ради
Зміст
Вступ……………………………………………………………………………3
- Unit 1 «Getting Started & Applying»………….…………………………6
- Teacher’s Guide «Getting Started & Applying» ………………………..34
Висновки ………………………………………………………………………47
Additional Resources (посилання на інтернет- ресурси)………………………47
ВСТУП
У сучасному світі англійська мова - найпоширеніший засіб спілкування в міжнародному масштабі: в авторитетних джерелах зазначається, що кожен четвертий житель планети (близько 1,5 мільярда людей) використовує її в одному з трьох якостей - рідна мова (first language), державна мова (second language), іноземна мова (foreign language). Визнання англійської мови як офіційної в 60 країнах світу, і її статус самої найнеобхіднішої іноземної мови, дозволяють говорити про неї як про світову мову (a world language). Підкреслюючи унікальне положення англійської мови в сучасному світі і її відмінність від інших мов міжнаціонального спілкування, деякі фахівці називають її глобальною мовою (a global or universal language). На сучасному етапі розвитку міжнародного співтовариства саме англійська мова служить засобом ділового спілкування.
Ділове спілкування - це міжособистісна міжкультурна зона професійної комунікації, яка передбачає перспективний, комунікативний та інтерактивний рівні поведінки, обумовлена прагмалінгвістичними (інформативність, регулятивного, імпліцитно, експресивність) і прагмапсихологічними (зацікавленість, конфліктність, взаєморозуміння і розуміння) характеристиками спілкування. Ділове спілкування, здійснюване з метою ефективної співпраці людей, що вступають в мовне спілкування, і спрямовані на оптимізацію того чи іншого виду діяльності, представленої у двох формах: усній і письмовій, остання включає в себе договори, накази, положення, інструкції, акти, угоди, заяви, контракти і ділову переписку.
Англійська ділова мова характеризується наявністю ряду особливостей. Так, наприклад, в англійському письмовому діловому етикеті не прийнято вживати просторічні слова і жаргони, тому що наявність їх у листі може сформувати на підсвідомому рівні негативне ставлення до відправника як до некультурної людини. Однак у комерційному вигляді ділового листа, особливо якщо справа стосується рекламної спрямованості послання, часто можна виявити і розмовні формули, і сленг.
Курс «Ділова англійська мова» призначається для учнів 10 (11) класу ліцеїв, які успішно засвоюють навчальний матеріал і виявляють бажання глибше опанувати ділову мову, докладніше освоїти ділову лексику та ознайомитися з країнознавчим матеріалом.
Головна мета курсу – активізувати в учнів їх мовні знання, сформувати навички використання термінів та особливостей ділового спілкування, розвити вміння орієнтуватися у діловій мовній інформації.
Курс охоплює 17 уроків, тобто 0,5години на тиждень. Кожний урок включає в себе повторення певного граматичного матеріалу і тематичні розробки за різними сферами і ситуаціями ділового спілкування: телефонні розмови, збори, переговори, надсилання листів, факсів та ін. На уроці проводиться робота з необхідною лексикою та кліше і розвиваються мовленнєві вміння учнів. Лінгвокомерційний та лінгвокраєзнавчий матеріал включає всебічну інформацію про англомовні країни.
При вивченні курсу учні вчаться вести листування, розмовляти по телефону, а пізніше навіть зможуть підготувати бізнес-план та вести переговори на діловій англійській мові.
Оскільки англійська мова є однією з основних у діловому світі, представлений курс викликає зацікавлення і підвищує мотивацію до вивчення англійської мови.
Матеріал подано у вигляді 17 уроків ділової англійської мови для учнів. Курс можна поділити на три основні теми:
Unit 1: Getting Started & Applying
1. Introduction to business
2. Want Ads
3. Resume
4. Curriculum Vitae
5. Cover letter
6. Job Interviews I
7. Job Interviews II
Матеріал складений з урахуванням міжпредметних зв’язків і передбачає використання на заняттях автентичного ділового мовлення зі сфери маркетингу, менеджменту та бухгалтерського обліку.
У даній роботі подано Розділ І Getting Started & Applying, також Teacher’s Guide до цього розділу.
Lesson 1 – Introduction to Careers
Vocabulary
General
- Career – кар'єра
- Occupation – рід занять
- Profession – професія
- Career ladder – кар'єрні сходи
- Career opportunity – кар'єрна можливість
- Employed – зайнятий
- Unemployed – безробітний
- Job – робота
- Industry – промисловість
- Skills – навички
Industries
- Banking and Finance – банки та фінанси
- Construction – будівництво
- Education – освіта
- Engineering – проектування
- Energy – енергетика
- Food and drink – їжа та напої
- Healthcare – охорона здоров'я
- IT (Information Technology)/Electronics – інформаційні технології/електроніка
- Manufacturing – виробництво
- Media & Advertising – ЗМІ(засоби масової інформації) і реклама
- Pharmaceutical – фармацевтичний
- Real Estate – нерухомість
- Retail – роздрібний
- Telecommunications – телекомунікації
- Tourism – туризм
- Transportation – транспорт
Grammar:
When we tell the specific job a person does, we use to be. For example:
- He is a doctor
- I am a banker.
- They are marketing managers.
When we describe the industry or general type of work a person does in a non-specific way, we use to work or to be and the preposition in. For example:
- He works in medicine. He’s in medicine.
- I work in banking. I’m in banking.
- They work in marketing.
Exercise 1: Industries
What industries do you know?
Which industries exist in your city?
In which industries do your parents, family and friends work?
What jobs do they have?
Write 6-8 sentences.
Exercise 2: Reading - Career Interests
The table below describes 6 types of people. Each type has different interests and skills. Read the following table and descriptions.
REALISTIC
The «Do-ers»
|
REALISTIC people are characterized by competitive/assertive behavior and by interest in activities that require motor coordination, skill, and physical strength. These people prefer situations involving ‘action solutions’ rather than tasks involving verbal or people skills. They like to take a concrete approach to problem-solving rather than depend on abstract theory. They are usually interested in scientific or mechanical things rather than cultural and aesthetic areas. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
- Practical - Athletic - a nature lover - stable - concrete - quiet - self-controlled - independent - systematic - persistent |
- fix electrical things - play a sport - read an architectural - plan - plant a garden - use tools and machinery |
- Work on machines/vehicles - work outdoors - build things - tend/train animals - work on electronic equipment |
- Refinishing furniture - Growing plants/flowers - Playing sports - Fishing - Woodworking - Coaching team sports - Building models - Repairing cars, equipment, etc. - Taking exercise classes |
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
Mechanic Builder/Construction worker - Будівельник Police officer - Поліцейський Dental Assistant – Помічник стоматолога Engineer Farmer – Фермер |
Firefighter - Пожежний Painter - Художник Plumber - Водопровідник Nurse - Медсестра Property Manager/Landloard – Менеджер з нерухомості Truck Driver- Водій вантажівки Woodworker - Верстальник |
||
INVESTIGATIVE
The «Thinkers»
|
INVESTIGATIVE people prefer to think rather than to act, to organize and understand rather than to persuade. They are not usually «people oriented». |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
- analytical - scientific - observant - precise a good student - cautious - quiet - interested in many things - independent - logical - curious |
- think abstractly - solve math problems - understand scientific theories - use a computer - interpret formulas |
- ask a lot of questions - explore a variety of ideas - use computers - work independently - perform lab experiments - read scientific or technical journals - analyze data - do research - be challenged |
- Book club - Crossword puzzles/board games - Computers - Visiting museums
- Collecting rocks, stamps, coins, etc. |
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
Actuary Management Consultant - Консультант з питань управління |
Marketing Research Analyst - Маркетингові дослідження й аналітика
Research Analyst - Аналітик |
||
ARTISTIC
The «Creators»
|
ARTISTIC people like to express themselves and connect to other people through art. They don’t like structure. They often prefer tasks involving personal or physical skills, and often express more emotion than others. They are like investigative people but are more interested in cultural things than scientific things. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
- Creative - Imaginative - Emotional - Independent - Expressive - Sensitive
- idealistic |
- draw, paint - play a musical instrument - write stories, poetry, music - sing, act, dance - design fashions or interiors |
- attend concerts, - theatres, art exhibits - read fiction, plays, and poetry - make art - take photographs |
- Photography - Theatre - Writing stories, poems, etc. - Sewing - Dancing - Visiting art museums - Playing a musical instrument - Painting - Speaking foreign languages |
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
Actor/Actress |
Drama Teacher
Graphic Designer – Графічний дизайнер |
||
SOCIAL
The «Helpers»
|
SOCIAL people seem to satisfy their needs in teaching or helping situations. In contrast to investigative and realistic people, social people like relationships with people. Thinking about theories and doing physical work is less important to them. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
- friendly - helpful - idealistic - understanding - generous - responsible - patient - empathic
- kind |
- teach/train others - express yourself clearly - lead a group discussion - help solve problems between people - plan and supervise an activity - work well in groups |
- work in groups - help people with their problems - participate in meetings - do volunteer work - work with young people - play team sports |
- Volunteering - Joining school or community organizations - Helping others with personal concerns - Meeting new friends - Attending sporting events - Caring for children - Religious activities - Playing team sports |
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
City Manager |
Priest – Священик
Paralegal – Помічник юриста
Sociologist Medical Assistant – Фельдшер |
||
ENTERPRISING
The «Persuaders»
|
ENTERPRISING people are good at speaking and using words. Enterprising people use this skill to persuade others and make them believe in their ideas. Prestige, power, respect and status are important to them. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
- Confident - assertive - sociable - persuasive - energetic - adventurous - popular - impulsive - ambitious - talkative - optimistic |
- initiate projects - convince people to do things your way - sell things or promote ideas - give talks or speeches - organize activities - lead a group - persuade others |
- make decisions affecting others - win a leadership or sales award - start your own service or business - meet important people - have power |
- Discussing Politics - Reading about business - Attending Meetings and Conferences - Selling Products - Leading Campus or Community Organizations |
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES |
|||
|
Advertising manager – менеджер з реклами Marketing manager
Public relations manager – менеджер зі зв'язків з громадськістю |
Flight Attendant – Бортпровідник
Hotel Manager
Sales manager – Комерційний директор |
||
CONVENTIONAL
The «Organizers»
|
CONVENTIONAL people don't mind rules and regulations and emphasize self-control. They prefer structure and order to ambiguity in work and interpersonal situations. They place value on prestige or status. |
|||
|
YOU ARE: |
YOU CAN: |
LIKE TO: |
HOBBIES: |
|
- well-organized - accurate - good at math - methodical - efficient - practical - systematic - structured - polite - persistent |
- work well within a system - do a lot of paper - work in a short time - keep accurate records - use a computer terminal - write effective business letters |
- follow clearly defined procedures - use data processing equipment - work with numbers - type or take shorthand - be responsible for details - collect or organize things |
- Arranging and organizing household or workshop, etc. - Playing computer or card games - Collecting - Keeping club or family records and files - Writing family history |
|
CAREER POSSIBILITIES: |
|||
|
Accountant – Бухгалтер
Financial Analyst |
Kindergarten Teacher – Вихователь дитячого садка |
||
Exercise 4: Career Interests
What type of person are you?
Using the table above, write about yourself.
What professions match your interests and skills?
Exercise 5: Speaking
Work in pairs. Ask your partner these questions. Then, tell the class about your partner’s answers.
What kind of career would you like?
What do you think is the most important reason to have a career? Interesting work, earn money, feel successful, etc.
Exercise 6 / Home Task 1: My Ideal Job
What kind of job would you like?
What industry would you prefer to work in?
Explain why you are interested in this type of job.
What kind of work will you do? Write 10-12 sentences.
Home Task 2: Job Exploration
Speak with a family member, friend or relative about his/her job.
What does he/she do every day?
What skills does he/she use?
What are the good and bad parts of the job?
Write 3 questions of your own to ask. Tell the class about what you learned.
Lesson 2 – Want Ads
Vocabulary:
- Application – додаток
- To apply – застосовувати
- Resume – резюме
- Full-time – повний робочий день
- Part-time – неповний робочий день
- Experience – досвід
- Qualified – кваліфікований
- Want ads – Оголошенння
- Computer Personnel – комп’ютерні фахівці
- Drivers – драйвери
- Engineers / Chemists – Інженери / хіміки
- Financial /Accounting – фінансовий / бухгалтерський обліk
- Instructors – інструктори
- Insurance – страхування
- Managers – менеджери
- Medical – медичний
- Office / Clerical – офіс / канцелярський
- Restaurants / Hotels / Clubs – ресторани / готелі / клуби
- Sales / Marketing – продаж / маркетинг
- Telemarketing / Phone Skills – Телемаркетинг / навички спілкування по телефону
Exercise 1: Vocabulary Practice
Fill in the blanks. Use the following words:
applied want ads qualified resume application part-time
- Tom sent his to companies who were looking for a website manager.
- Sarah for the job she was qualified for.
- Mary got the job because she was the most person who applied.
- Jim didn’t have a lot of time for work because he was a student at the university, so he was looking for a job.
- Mark looked through the to see who was hiring.
- Kim filled out the at the cd store because she wanted to work there.
Exercise 2: Reading Want Ads
Look at the want ads from the newspaper. Answer the following questions
- Under what number can you find jobs related to the «medical» field?
- Under what number can you find jobs related to «restaurants»?
- What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job «LOCAL PIPE, valve & fitting» under «Drivers»?
- What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “F/T BOOKKEEPER” under “Financial/Accounting”?
- Where can you send your resume if you want to apply for “BLUE BAYOU DIXIE LANDIN’” under “industrial tech. skills”?
- What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “PHYSICIAN” under “medical”? How much does it pay?
- What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “FULL TIME GRILL position” under “Restaurants/Hotels/Clubs”? What is required in order to get the job?
- Where can you send your resume if you want to apply for “FULL TIME RETAIL COUNTER SALES PERSON” under “Sales/Marketing”?
Lesson 3 – Resume
Vocabulary
- Resume - резюме
- Reverse chronological - у зворотному хронологічному порядку
- Functional - функціональний
- Hybrid - гібрид
Purpose of a Resume
A resume is a document highlighting specific skills, previous employment, education, and awards that employers will base a potential employee on. Different types of resumes have different purposes.
- Reverse Chronological is a style of resume where in the previous work experience most recent employment comes first and it goes down by date employed.
- Functional is a style of resume where instead of labeling a position in chronological or reverse chronological, employment experience is organized by the type of job and each employment provided with detail in a description.
- Hybrid is a style of resume that uses both functional and reverse chronological. Job descriptions are listed in reverse chronological order and given a little detail like a functional resume.
Model Resume
A resume contains different sections. Find each of these in the sample resume.
- Header-contains name, work address, home address, phone number
- Objective-goal of the resume
- Education-list all forms education the applicant has been through
- List all awards and special skills like languages below
- Previous Work Experience-list all previous work experience with 2 sentences in detail
- Activities-list all extra activities the applicant is involved
Exercise 1: Listing Skills
Listing skills is difficult for people to do. It is not often we are given the task of writing down what we are good at and what we aren’t good at, especially when it comes to what an employer would find interesting. What skills and talents can you include on your resume? Make a list. Here are some ideas of what a good skills can be if you put it on your résumé.
- Foreign Language(s)
- Awards granted in school
- Programs or certificates completed or received in school
- Programs or certificates completed or received outside of school
- Abilities like «works well with others» or «can multi-task efficiently».
Exercise 2
Unscramble the resume. Put the sections of the resume in the correct order to make it look like the model resume.
Exercise 3
Create your own resume including header, objective (fake job), education, previous work experience, activities. When you’re finished, present your resume to the class.
Sample Resume

 Scrambled Resume
Scrambled Resume
Lesson 4 – Curriculum Vitae (C.V.)
Vocabulary
- curriculum vitae – резюме
- profile – профіль
- skills – навички
- interests – інтереси
Exercise 1: Reading – Definition of Curriculum Vitae
A Curriculum Vitae, or C.V. for short, is similar to a resume. Curriculum Vitae is Latin for means of life. This is the document that employers will look at before making the hiring decision. It provides an overview of a person's life and qualifications. In some countries, a CV is typically the first item that a potential employer encounters regarding the job seeker and is typically used to screen applicants, often followed by an interview, when seeking employment. C.V.s are more common in Europe, while resumes are more common in the United States.
The Profile section is the section of the C.V. where the applicant talks about themselves. In the Skills section, the applicant can discuss any skills that they think would be useful for the job. Interests is the section of the application where the applicant can discuss any interests that they think would be useful for the job.
Exercise 2: Sample C.V.
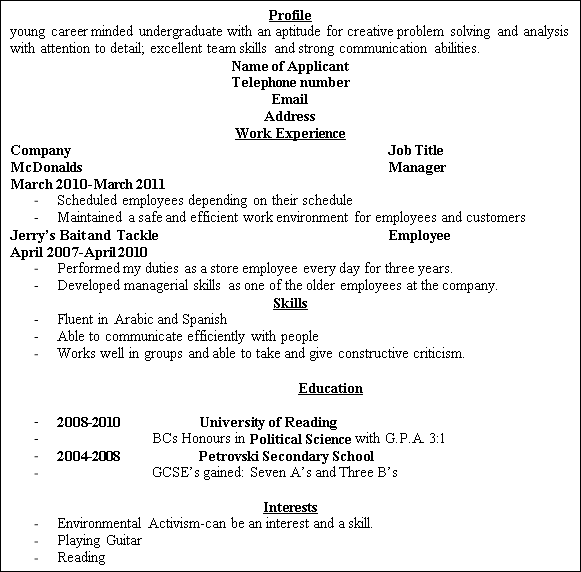
Look at the sample C.V. Can you locate all of the sections?
- What is the person’s profile?
- Where did this person study?
- What was this person first job?
- What does this person like to do?
- What skills does this person have?
Exercise 3: Scrambled C.V.
Unscramble the C.V. Put the sections of the C.V. in the correct order to make it look like the model resume.
Exercise 4: Write a C.V.
Create your own resume including header, profile, work experience, education, skills and interests.
Sample C.V.

Scramble C.V.
Lesson 5 – Cover Letter
Definition of cover letter
A letter of introduction attached to, or accompanying another document such as a résumé or curriculum vitae. This is a way of introducing themselves to potential employers and explaining their suitability for the desired position.
Vocabulary
- Header-заголовок
- Introduction- вступ
- Body-основна частина
- Closing-заключна частина
- Header. Cover letters use standard business letter style, with the sender's address and other information, the recipient's contact information, and the date sent after either the sender's or the recipient's address.
- Introduction. The introduction briefly states the specific position desired, and should be designed to catch the employer's immediate interest.
- The body highlights or amplifies on material in the resume or job application, and explains why the job seeker is interested in the job and would be of value to the employer.
- Closing. A closing sums up the letter and indicates the next step the applicant expects to take
Exercise 1: Sample Cover Letter
Read the sample cover letter. Answer the following questions:
- Which address is put in the top right corner?
- What is a header?
- What comes after the header?
- Where is this person applying?
- Where did this person work before?
- When will this person call to hear back?
Exercise 2: Scrambled Cover Letter
Unscramble the cover letter. Put the sections of the cover letter in the correct order to make it look like the model resume.
Exercise 4: Write a Cover Letter
Think of a job you would like. Write a cover letter as part of your application. Make sure to include at least 3 sentences in each section (intro, body, conclusion).
 Sample Cover Letter
Sample Cover Letter
Scrambled Cover Letter

Lesson 6 – Job Interviews (Part I): Types Of Interviews and How to Prepare for Them
Vocabulary:
|
- Strengths - Weaknesses - Experience - Background information - Phone Interview - Group Interview - First Interview - Second Interview - Screening - Candidates - Employer - Interviewer
|
- Сильні сторони - Слабкі сторони - Досвід - довідкова інформація
- Інтерв'ю по телефону - Групове Інтерв'ю - Перше інтерв'ю - Друге інтерв'ю - Скринінг - Кандидати - Роботодавець - Інтерв'юер |
Exercise 1: Reading
You have applied for a lot of jobs, sent out many resumes and finally you have gotten a response. Now it is time for the employer, or person looking to hire you, to meet you and for you to meet them. There are a few different ways a business may choose to meet you. Here are the most common:
- Phone Interview: If you live far from the job an employer might just want to talk to you over the phone. Even though you are not meeting them face to face they will ask you them same questions they would ask in person. Sometimes a phone interview is just a screening, or a test to see if they want to meet you in person.
- Group Interview: If you are applying for a job that has many openings you maybe be interviewed with a few other job seekers also called Candidates. You are not competing with the others. It is important to remain polite to the other people.
- First Interview: A face to face meeting with an employer. This is the most common type of interview.
- Second Interview: Some employers will want to meet you a second time to see if you are right for the position.
Exercise 2: Matching Type of Interview.
Match the vocabulary word with the definition.
- One employer, many candidates.
- Some employers will want to meet you again.
- The most common type of interview.
- Not done in person.
- People looking for jobs.
- Brief conversation to see if they would like to meet you
- People looking to hire a person.
Exercise 3: Reading – How to prepare for an interview.
No matter what type of interview you have, preparation is the same. Here is how you do it.
Step 1: Learn a lot about the employer. Find out what type of business they are. When and where were they started? Who are their biggest competitors? What is the job that you are interviewing for? What does a person in the role do? This is called background information.
Find answers to the questions
- "What is the business looking for?"
- "What would the business like in a candidate?"
Step 2: Write down a list of reasons you would be good at the job. These are your strengths. The list should include what work and activities you have done that would make you good at this job. This is called experience. What skills do you have? What education do you have?
Step 3: Write down a list of reasons you might be bad at this job. These are your weaknesses. Think of ways to get rid of these weaknesses.
Step 4: Review list of commonly asked questions. Think of answers.
Step 5: Write down a list of at least 5 questions you will ask your interviewer. Employers want you to participate in your interview to know you are interested.
Exercise 4:
Put the steps in the correct order.
A. Write down a list of strengths.
B. Write down 5 questions to ask the interviewer.
C. Review list of commonly asked questions
D. Background information
E. Write down a list of weaknesses.
Exercise 5:
Practice describing your strengths. Use the models below to write a list of what you are good at and what skills you have. Write at least 5.
- I am good at (skill). Example: I am good at playing football.
- I am able to (skill, something you can do). Example: I am able to use a computer.
- I have always been able to (skill) well. Example: I have always been able to dance well.
- One of my strengths is (skill / that I…). Example: One of my strengths is math.
Home Task 1.
Select a business and find out background information about that business. Answer these questions:
- Company name?
- Type of business?
- When and where were they founded?
- Who are their major competitors?
Example
Company name: Nike
Type of business: Sporting Goods
Founded: January 24, 1964
Major Competitors: Adidas, Puma
They might like: A candidate who likes sports.
Present your background information to the class using complete sentences.
Example: The name of my company is Nike. Their business is Sporting Goods. Nike was founded on January 25, 1964 in Washington County, Oregon. Nike's major competitors are Adidas and Puma. Nike may want a person who likes sports.
Lesson 7 – Job Interviews (Part II: The Interview
Vocabulary:
|
- Body Language - Eye contact - Firm handshake - Posture - Fidgeting - Business clothes - Follow up - Thank you letter - «Clothing makes the man» - «Dress for the job you want not the job you have» |
- Мова тіла - Контакт очей - Міцне рукостискання - Поза - Совання, суєта - Діловий одяг - Стежити за - Лист-подяка. |
Exercise 1: Reading – What is an interview for?
A job interview is not about your strengths or experience. A job interview is about proving you are the best person for the job. Employers will already know about your strengths and experience from your resume. Employers want to meet you and get to know your personality and who you are. They need to know that you have the right attitude toward the job and that you really want to work for them. Look at the chart to see what an interview is about.
What employers want to know:
- That you know about their business.
- That you know about the job.
- That you can do the job.
- That you are able to communicate
Dress for Success.
In the business world we have two saying about what to wear at work. «Clothing makes the man» means that people judge you first by what you wear and what you wear says a lot about you. The better you dress for an Interview, the more seriously the employers will take you as a candidate.
The next saying is «Dress for the job you want, not the job you have». Always dress for the job you want, even if that is more formal than your current job. The interviewer must be able to picture you being successful at that position. The first step is to look like you already have that job.
DO NOT:
1. Wear a track suit.
2. Short Skirt.
3. Sport shoes.
4. Wrinkled clothing
5. Have messy hair.
6. Chew gum
7. Overly revealing clothing.
8. Button all the buttons on a shirt, the top one may remain unbuttoned if a tie is not worn.
Parts of the interview:
Part 1: Greeting
- When you enter the room body language is very important. Body language is what your actions say about you.
- Stand up straight and hold your head up.
- Introduce yourself in a clear voice saying «Hello, my name is (first and last name)» then «It’s a pleasure to meet you».
- Extend your hand to everyone in the room, male and female, while you introduce yourself.
- Handshake should be firm. Do not grip too tight or too loosely. Shake their hand 3 times.
- Always maintain eye contact.
- Do not sit down until the interviewer offers you a seat!
Part 2: The Interview
- During the interview, sit up in your chair. Do not lean over. Remain still, do not fidgeting. Fidgeting is moving around too much.
- Look at the person who is speaking or asking questions in the eye. This shows that you are interested.
- Do not answer questions with «yes» or «no». Answer in complete sentences.
- Ask questions of the interviewer to show interest. Use notes to help if needed.
Part 3: The end and follow up
- When the Interviewer asks «Do you have any questions of us?» Always say yes and ask one last question even if you already know the answer, or say «No, you have already answered all of my questions, Thank you».
- Thank the interview before you leave. «Thank you for taking the time to meet with me today»
- Shake hands again and say «It was nice meeting you, I look forward to hearing back from you, If there is anything else you need from me just let me know».
- Maintain eye contact.
- As soon as you get home from the interview write a thank you letter or email to the people that just interviewed you. Follow the model.
Exercise 2: Body Language
Stand up and practice introducing yourself to everyone else in the room. Remember to shake hands and make eye contact.
Exercise 3: Mock Interviews
Work in pairs. Interview your partner. When you are the employer, ask questions such as:
- «What are your strengths?»
- «What are you good at?»
- «Where do you live?»
- «What school do you go to?»
- «What is your weakness?»
- «Do you work well with others?»
When you are in the role of the person applying for the job, make sure to answer questions in complete sentences. Don’t forget to ask the interviewer questions also. Use the list of strengths and weaknesses you wrote in the last class.
Exercise 4: Writing a Thank you letter
Write a thank you letter about 5-7 sentences.
2. Teacher’s Guide «Getting Started & Applying»
Accompanying each lesson is a Teacher’s Guide with objectives for the lesson and answers to the exercises. Also included in the Teacher’s Guides are notes to the teacher providing additional suggestions/direction for some specific exercises. There are three guides for the two lessons on interviews: one for each lesson with objectives and exercise keys as well as a more comprehensive overview of interview etiquette, procedure and questions.
General Tips and Practical Notes
• Answer keys generally include short answers. Students, however, should be strongly encouraged to write/speak answers in full sentences.
• Teachers may select which vocabulary they want to use for each lesson. They may choose to skip some words.
• Work in pairs and groups should be encouraged. Working in business involves teamwork.
• Encourage students to think creatively and analytically. These skills are just as important, if not more important than English skills in a business setting.
• Teachers should use their knowledge of and experience in the Ukrainian workplace to emphasize where cultural or practical differences exist, for example with resume/CV styles, body language in interviews, or a tendency towards more informal conversation and emails in American business, where the culture is less hierarchical.
Teacher’s Guide: Introduction to Careers
Objectives:
Students will be able to:
- Identify ~20 new vocabulary
- Understand how skills, personality and interests influence a person’s career choice
- Think critically about their own skills, personality and interests when discussing their career hopes
- Understand the different requirements needed to qualify for different jobs.
Note on vocabulary: It’s not necessary that students memorize all possible jobs. They should learn the main words as well as the names of a few jobs of interest to them.
Teacher’s Guide: Want Ads
Objectives:
Students will be able to:
- Identify new vocabulary words.
- Read and comprehend want ads.
- Understand the different requirements needed to qualify for different jobs.
Exercise 1:
-
Tom sent his to companies who were looking for a website manager.
- Answer: resume
-
Sarah for the job she was qualified for.
- Answer: applied
-
Mary got the job because she was the most person who applied.
- Answer: qualified
-
Jim didn’t have a lot of time for work because he was a student at the university, so he was looking for a job.
- Answer: part-time
-
Mark looked through the to see who was hiring.
- Answer: want ads
-
Kim filled out the at the cd store because she wanted to work there.
- Answer: application
Exercise 2:
Note: Use the included newspaper for this activity. The questions refer to the ads in it.
-
Under what number can you find jobs related to the “medical” field?
- Answer: 1460
-
Under what number can you find jobs related to “restaurants”?
- Answer: 1540
-
What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “LOCAL PIPE, valve & fitting” under “Drivers”?
- Answer: Class A CDL, TWIC card, clean driving record and forklift experience required.
-
What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “F/T BOOKKEEPER” under “Financial/Accounting”?
- Answer: Word and Excel experience
-
Where can you send your resume if you want to apply for “BLUE BAYOU DIXIE LANDIN’” under “industrial tech. skills”?
- Answer: Email it to jobbrla@gmail.com, or you can apply online at www.bluebayou.com
-
What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “PHYSICIAN” under “medical”? How much does it pay?
- Answer: Must be board certified. It pays up to $175/hour.
-
What skills are needed in order to qualify for the job “FULL TIME GRILL position” under “Restaurants/Hotels/Clubs”? What is required in order to get the job?
- Answer: You must have good customer service and communication skills. In order to get the job you must take a pre-employment drug and background screening.
-
Where can you send your resume if you want to apply for “FULL TIME RETAIL COUNTER SALES PERSON” under “Sales/Marketing”?
- Answer: redstickjob@gmail.com
Teacher’s Guide: Resume
Objectives
- Students will understand the purpose of a Resume
- Students will understand resume vocabulary (resume, reverse chronological, functional, hybrid)
- Students will understand the structure of a resume
- Students will be able to construct their own resume
Model Resume
Note: Teacher should present format of resume and explain sections.
Exercise 1: Listing Skills
Teacher should make sure model resume is visible and point out the sections discussed earlier in the lesson.
Teacher’s Guide: Curriculum Vitae (C.V.)
Objectives
- Students will understand the purpose of a C.V.
- Students will understand the definition of the structure of a C.V.
- Students will understand the vocabulary (profile, curriculum vitae, skills, interests).
- Students will be able to create their own model C.V.
Presentation
Note: Teacher should present format. Point out each section (header, profile, education, work experience, skills, and interests).
Exercise 2: Sample C.V.
Look at the sample C.V. Can you locate all of the sections?
-
What is the person’s profile?
- young career minded undergraduate with an aptitude for creative problem solving and analysis with attention to detail; excellent team skills and strong communication abilities.
-
Where did this person study?
- University of Reading, Petrovsky Secondary School
-
What was this person first job?
- Employee at Jerry’s Bait and Tackle
-
What does this person like to do?
- He is interested in environmental activism, playing guitar, and reading
-
What skills does this person have?
- Fluent in Arabic and Spanish
- Able to communicate efficiently with people
- Works well in groups and able to take and give constructive criticism.
Exercise 4:
Note: Teacher should keep up sample C.V. for students to see. Review sections. Brainstorm with students what information they could put in each section.
Тeacher’s Guide: Cover Letter
Objectives
- Students will understand the purpose of a cover letter
- Students will understand the vocabulary in a cover letter (header, introduction, the body, closing).
- Students will understand the structure of a cover letter
- Students will be able to create their own cover letter
Exercise 1: Sample Cover Letter
Note: Teacher should show sample cover letter (with handouts or big enough so everyone can see, e.g. maybe on a computer and projector). Teacher should Show the structure and vocabulary inserted in the cover letter. Teacher should emphasize the importance of customization. In a cover letter the applicant should specifically address the requirements of the job he/she is applying for and demonstrate a knowledge of the company and/or position.
Read the sample cover letter. Answer the following questions:
- Which address is put in the top right corner?
- What is a header?
- What comes after the header?
- What job is this person applying for?
- Where did this person work before?
- When will this person call to hear back?
Exercise 2:
-Scrambled information activity
- Students are given many different bits of a cover letter
- Students must individually put the pieces on the board making the cover letter
Exercise 3
Students create their own cover letter (give sample job offer)
- Leave up sample cover letter
- Show where each piece of information is located
-
They put their own information in each spot.
- 3 sentences in each section (intro, body, conclusion).
Teacher’s Guide to Interview Lessons
Objectives:
Teachers will be able to
- Understand that preparation and body language are the most important part of a business interview.
- Simulate the behaviors of employers and interviewers.
- Aid students in improving their body language by observing them.
- Prepare students for interviews
What an Interview Is Really About
Interviews are not about qualifications and experience; they are about attitude and communication skills. An employer already knows the candidate's qualifications from their resume. An interview is looking at how the candidate holds him/herself. It is impossible to teach students how to answer every question in every interview. Each interview is different. Interviewers are looking for different things depending on what the job is. Teachers can give the students the ability to anticipate these questions and give excellent answers.
The first lesson is designed to help students know what a business is looking for in a candidate by learning about the business. Background information can tell what a business wants and by writing about their own strengths and weaknesses they will be able to tell a company why they are the best candidate for the job.
The second lesson is designed to teach students how to act in each interview. All interviews pay attention to body language. The right body language always improves a candidate’s chances at getting a job. Students are often unaware of bad body language. By observing them and grading them, a teacher can teach them to stop bad behavior and encourage good body language. A thank you letter is a very important part of an interview even though it is done after the interview. A thank you letter shows an interviewer that a candidate is polite.
Acting Like An Interviewer
- Teachers already command the respect of their students, which is the first step in simulating and interview. Interviewers hold a place of authority over candidates. A candidate should be a little nervous in the interview because they want to do well, just as a student wants to perform well in front of a teacher.
- Evaluate the students’ clothes and appearance. Are they dressed appropriately for an interview? They should not be dressed to play football or to go to the disco.
- Greet the student by maintaining eye contact and extending your hand. In the business world, men and women all shake hands. Offer the student a seat, the student should not sit until a seat is offered. A student who sits down too soon should be marked down.
- During the interview, students should maintain eye contact, especially when answering questions. It is okay for them to look away when thinking of answer.
- The student should speak more than the interviewer. Ask questions that require long answers. Students should answer in complete sentences. Mark them down for answering just "yes" or "no." Use list of suggested questions to help. These questions are commonly asked, and it will help students to get used to answering them.
- Mark students down if they move too much during an interview or if they lean forward. They should not be constantly moving and should sit straight up.
- Use the attached sheet to grade the students on their performance and help them get better in weak areas.
- An interview should be 5-10 minutes long.
Mock Interview Evaluation
INTERVIEWER: _____________________________
STUDENT: _____________________________
DATE OF INTERVIEW: _____________________________
Rate the student interviewee on a scale of 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest) in the following areas of interviewing skill.
|
NONVERBAL BEHAVIORS |
|||||
|
1. Dressed appropriately |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
2. Firmly shook hands of interviewer before and after |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
3. Maintained eye contact with interviewer |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
4. Maintained good posture |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
5. Did not fidget |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
6. Used hands for emphasis where appropriate |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
VERBAL BEHAVIORS |
|||||
|
1. Listened closely to questions |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
2. Answered questions completely, yet briefly |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
3. Greeted interviewer by name |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
4. Thanked interviewer |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
5. Displayed enthusiasm |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
6. Focused on strengths; avoided weaknesses |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
7. Acted in polite manner |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
8. Stayed calm |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
9. Responded to questions promptly, but not hurriedly |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
10. Asked appropriate questions of the interviewer |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
11. Spoke clearly and at a reasonable volume |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
12. Avoided use of phrases such as “um” & “you know” |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
Interview Questions to Think About
Questions Often Asked By Employers
- Tell me about yourself.
- What are your short-range and long-range career goals, and how are you preparing to achieve them?
- Why did you choose this career?
- What do you consider to be your greatest strengths? Weaknesses?
- How would you describe yourself? How would a friend or professor describe you?
- How has your college experience prepared you for your career?
- Why should I hire you?
- How do you determine or evaluate success?
- In what ways do you think you can make a contribution to our company?
- Describe the relationship that should exist between a supervisor and those reporting to him/her.
- Describe your most rewarding high school/college experience.
- If you were hiring for this position, what qualities would you look for?
- What led you to choose your field or major?
- What have you learned from participation in extracurricular activities?
- How do you work under pressure?
- Describe the ideal job/college.
- Why did you decide to seek a position with this organization and what do you know about us?
- What major problems have you encountered and how did you deal with it?
- What criteria are you using to evaluate the company/college for which you hope to work/attend?
- What salary do you want?
Questions Often Asked By Applicants
- What are the strengths of the organization or department?
- What are the career opportunities for someone entering this position?
- What kind of orientation and training is available to new employees?
- How large is the company/college? How large is this particular department/major?
- To whom would I be reporting and what kind of communication channels are there?
- What are the long-range plans for this organization?
- How long was my predecessor in this position? Why did he/she leave?
- How will I be evaluated? How often?
- Is there an opportunity to transfer from one division to another?
- What are the prospects for promotion in the future? What are some of the qualities or accomplishments you would consider important for promotion?
- What is the management philosophy of this organization? What is the general philosophy?
- In what areas of the organization do you expect growth?
- Is continuing education encouraged? Is tuition reimbursement offered?
- Can you tell me about the history of this position, and changes anticipated?
- What are your expectations of the person in this position?
- Is overtime the norm in this office?
- What kind of support staff is available? What is the ratio of support staff to professionals, and how is work distributed?
- Generally, what percentage of time will be devoted to each of my responsibilities?
- Do you work with daily, weekly, monthly, or annual deadlines?
- Does the organization have a process for sharing creative ideas?
Teacher’s Guide: Job Interviews (Part I)
Objectives:
Students will be able to....
- To prepare for common interview questions
- Identify several different types of interviews
- Understand the purpose of an interview
Exercise 2: Matching type of Interview.
Match the vocabulary word with the definition.
- One employer, many candidates.
- Some employers will want to meet you again.
- The most common type of interview.
- Not done in person.
- People looking for jobs.
- Brief conversation to see if they would like to meet you
- People looking to hire a person.
Answers:
- Group interview
- Second interview
- First interview
- Phone interview
- Candidates
- Screening interview
- Employer
Exercise 5:
Note: This can be a class activity. Use these models and have the students plug their skills in. Have the students read their statements out loud. Ask them individually,
-What are you good at?
-What are your strengths?
Teacher’s Guide: Job Interviews (Part II)
Objectives:
Students will be able to...
- Gain experience for interviewing by conducting a mock interview
- Use appropriate body language for an interview.
- Respond appropriately to commonly asked interview questions
- Ask questions of interviewer to demonstrate appropriate attitude.
Exercise 2: Practicing body language.
- Demonstrate the proper introduction with a volunteer. All behaviors.
- Students will stand up and practice introducing themselves to everyone else in the room.
- Walk around the room and make sure to meet with all the students.
Exercise 3: Mock Interviews
Mock interview
- Interview a student in front of the class.
- Ask simple questions. The most important thing is body language.
ex. "What are your strengths?"
"What are you good at?"
"Where do you live?"
"What school do you go to?"
"What is your weakness?"
- "Do you work well with others?"
- Allow the student to use the list of strengths and weaknesses they wrote in the last class.
- Make sure the student asks you at least one question.
Exercise 4: Writing a Thank you letter.
- Have the students write a thank you letter about 5-7 sentences
Висновки
Підводячи підсумки, можна сказати наступне. У сучасному діловому світі неможливо обійтися без знань англійської мови. Особливості володіння діловою англійською стосуються багатьох типів діяльності стосовно до різних галузей економіки. Величезну важливість освоєння цих особливостей підкреслюють численні програми, спрямовані на навчання працівників міжнародних компаній, а також все зростаючий попит менеджерів, директорів та секретарів на спеціалізовані курси англійської мови, адаптовані під професійну область компанії.
Ділова англійська містить у собі кілька аспектів. Під цим поняттям об'єднані навички бізнес-комунікації, бізнес-кореспонденції, профільної англійської мови. Навички бізнес-комунікації необхідні для спілкування по телефону, проведення презентацій і виступів з використанням характерних мовних зворотів та інтонацій. Такі знання необхідні співробітникам компаній від секретарів до топ-менеджерів і директорів. Навички бізнес-кореспонденції потрібні для ділового листування, її форм і правил. Вивчення професійної англійської лексики найчастіше потрібно юристам, фінансистам, економістам, медикам і спеціалістам інших областей.
Наприклад, для учасників валютного ринку знання англійської мови є одним з обов'язкових умов успішного трейдингу.
Крім того, знання ділової англійської відкриває нові горизонти, дозволяє завжди бути в курсі нових віянь і розробок, дає можливість читати бізнес-літературу мовою оригіналу, не спотворену перекладами, часом недостатньо якісними. Володіння англійською виявляється просто необхідним для участі в міжнародних конференціях, а також при проходженні стажувань на заході, навчання за програмами MBA і в бізнес-школах США і Великобританії.
Additional Resources
- http://eolf.univ-fcomte.fr/index.php?page=business-english
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/learningenglish/general/
- http://www.englishclub.com/business-english/vocabulary.htm
1


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
