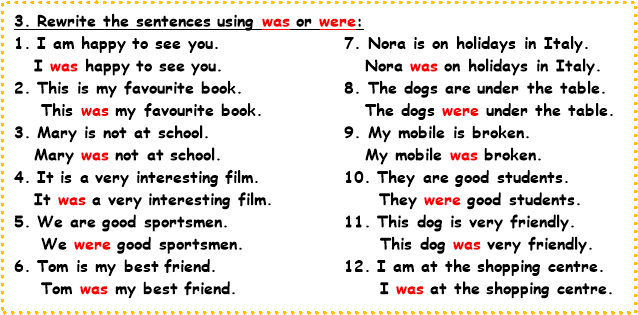
Grammar Practice Worksheet "was/were"
Про матеріал
"Was" and "were" are both past tense forms of the verb "to be" in English. They play a crucial role in expressing actions or states that occurred in the past. Understanding when to use "was" or "were" depends on the subject of the sentence.
Was:
Used with singular subjects (I, he, she, it, singular nouns):
Example: She was happy to see her friends.
It is also used with the pronoun "I": Example: I was at the store yesterday.
"Was" is employed when describing a singular action or state in the past.
Were:
Used with plural subjects (you, we, they, plural nouns):
Example: They were excited about the upcoming event.
"Were" is employed when describing multiple actions or states in the past.
It is also used with the second person singular "you" when referring to more than one person:
Example: You were at the party last night.
It's important to note that "were" can also be used with the past participle in the formation of the past continuous tense. For example:
They were studying when the power went out.
Additionally, "were" is used in hypothetical or unreal situations, often seen in conditional sentences (subjunctive mood):
If I were you, I would reconsider my decision.
In summary, while both "was" and "were" are past tense forms of the verb "to be," their usage depends on whether the subject is singular or plural. Understanding the appropriate use of these forms is essential for constructing grammatically correct sentences in English. doc
Оцінка розробки


Безкоштовний сертифікат
про публікацію авторської розробки
про публікацію авторської розробки
Щоб отримати, додайте розробку
Додати розробку