Методична розробка "Іноземна мова (за професійним спрямуванням) для здобувачів освіти сфери ресторанного господарства"
Міністерство освіти і науки України
Департамент освіти і науки Полтавської обласної державної адміністрації
Державний професійно-технічний навчальний заклад
“Полтавське вище професійне училище ім. А.О. Чепіги”
Посібник
“Іноземна мова
(за професійним спрямуванням)
для здобувачів освітисфери ресторанного господарства”
Укладач:Н.ГОНТАРЮК
Полтава – 2021
Гонтарюк Н.О. Посібник “Іноземна мова(за професійним спрямуванням)”для здобувачів освіти сфери ресторанного господарства”– Полтава.: ДПТНЗ “Полтавське ВПУ ім. А. О. Чепіги”, м. Полтава, – 75 ст.
Розглянуто та схвалено рішенням навчально–методичної ради Навчально–методичного центру професійно–технічної освіти у Полтавській області, протокол № __ від _____________ року.
Розглянуто і схвалено на засіданні методичної комісії суспільно–філологічних дисциплін ДПТНЗ «Полтавське ВПУ ім. А.О.Чепіги», протокол № 3 від 08 жовтня2021року.
Укладач:
Гонтарюк Н.О., викладач іноземної мови Державного професійно-технічного навчального закладу “Полтавське вище професійне училище ім. А.О.Чепіги.
Рецензент:
Близнюк О.М., викладач англійської мови Регіонального центру професійно–технічної освіти №1 м.Кременчука
Посібник орієнтований на вивчення іноземної(англійської) мови(за професійним спрямуванням)здобувачами освіти з професій “Кухар», «Кондитер”, “Майстер ресторанного обслуговування”.
Навчальний посібник складається з однієї частини, вона містить інформацію, яка зорієнтована на формування уздобувачів освіти компетентності з англійської мови, а також на розвиток навичок монологічного та діалогічного мовлення, перекладу та розуміння текстів.
Завдання кожного рівня підпорядковано цілям навчання чотирьох видів мовленнєвої діяльності: читанню, аудіюванню, говорінню та письму.
З метою більш ефективного засвоєння фахової англомовної лексики в посібнику даний короткий термінологічний словник.
Запропонована система вправ сприяє вдосконаленню англомовних навичок здобувачами освіти у сфері ресторанного господарства.
Посібник призначений для використання викладачами предмета “Іноземної (англійської) мови (за професійним спрямуванням)”для здобувачів освітиз професій “Кухар”, “Кондитер”, “Майстер ресторанного обслуговування”.
Contents
Introduction……………………………………………………..4
Part I. Assortment of food products…………………………...6
Unit 1.Food from Around the World ……………………………6
Unit 2. Flour products…………………………………………...13
Unit 3. Vitamins ……………………………………………….. 18
Unit 4. Fruits ……………………………………………………26
Unit 5. Vegetables……………………………………………....34
Unit 6. Milk and Dairy products………………………………...40
Unit 7.Meat ……………………………………………………..44
Vocabulary…………………………………………………………....50
References…………………………………………………………….75
ВСТУП
INTRODUCTION
Посібник розрахований для роботи із здобувачами освіти, які вивчають специфіку та особливості роботи закладів ресторанного господарства, володіють англійською мовою в межах середньої школи та вивчають іноземну (англійську) мову (за професійним спрямуванням)з професій “Кухар”, “Кондитер”, “Майстер ресторанного обслуговування”.
Беручи до уваги специфіку освітніхвимог до здобувачів освіти, а також їхньої майбутньої професії, підібрано оригінальні тексти (борошняні вироби, м’ясніта молочні продукти, вітаміни, овочі та фрукти).
Використання матеріалів посібника сприятиме отриманню й розумінню професійної англомовної лексики та її вживанню у відповідних ситуаціях.
Посібник складається з однієї частини. У першому розділі посібника подані оригінальнітексти з урахуваннямспецифіки навчальних вимог до здобувачів освіти.
Тематика текстів має не тільки велике інформаційне, а й пізнавально–виховне значення, забезпечує багатий лексико-граматичний навчальний матеріал, формує у здобувачів освіти почуття розуміння і поваги до іншомовної культури, звичаїв і традицій у харчуванні.
Тексти з оригінальних джерел подаються лексичним коментарем “Activevocabulary” і завданнями (Task).
Варто відмітити, що в посібнику подаються різноманітні вправи для розвитку діалогічного та монологічного мовлення.
Для полегшення самостійної роботи здобувачів освіти над збагаченням їхнього словникового запасу в посібнику подано короткий словник найбільш вживаних термінів та професійної лексики.
Навчальний посібник можна використовувати для аудиторної та самостійної роботи здобувачами освіти з професій “Кухар, Кондитер, Майстер ресторанного обслуговування”.
 PART I.ASSORTMENT OF FOOD PRODUCTS
PART I.ASSORTMENT OF FOOD PRODUCTS

Unit 1. Food from Around the World
Task 1. Read the text and discuss it
Food from Around the World
Food is now international. We can eat burgers anywhere in the world today, but they started in the United States. The Americans were the first to produce “fast food”. Pizza was an Italian recipe but it became popular in the United States and spread from there all over the world. “French fries” is the American name for fried chipped potatoes, which in England are called “chips”.
 Do you have Indian or Chinese restaurants where you live? In Chinese food, the meat, fish and vegetables are cut into small pieces and cooked very slightly. Indian food, on the other hand, is cooked slowly, with a lot of hot species. Mexican food is very spicy too. The countries of the Eastern Mediterranean also like food with a strong taste. They gave us “kebabs”, pieces of meat cooked on long sticks, and many different kinds of salad.
Do you have Indian or Chinese restaurants where you live? In Chinese food, the meat, fish and vegetables are cut into small pieces and cooked very slightly. Indian food, on the other hand, is cooked slowly, with a lot of hot species. Mexican food is very spicy too. The countries of the Eastern Mediterranean also like food with a strong taste. They gave us “kebabs”, pieces of meat cooked on long sticks, and many different kinds of salad.
What other national dishes do you know? English people still enjoy their “fish and chips” which you can buy in a take away and eat straight from the paper. In Spain, a “paella” is a family favorite –
a dish of rice with different kinds of seafood. And an Italian usually includes a dish of pasta with a delicious sauce.
If you can’t travel to these countries, try a restaurant. If you can’t do that, buy a recipe book and cook something different at home!
Task 2. Answer the following question
- What are the most popular traditional dishes in your country?
- What do you know about their history, how are they made, etc.?
- What food would you recommend to somebody visiting your country for the first time?
- What is the difference between meals and meal times in England and Ukraine?
- What is your favorite dish?
- Do you know the recipe for one of your national dishes? (list the ingredients and write instructions)
- If you are living abroad, what is the food that you miss most from home?
Task 3. Let's get acquainted with interesting information. Read the text and discuss it. Top Five Strangest Foods From Around the World
Sannakji
 The Korean delicacy sannakji, is something quite different, as the seafood isn't quite dead. Live baby octopus are sliced up and seasoned with sesame oil. The tentacles are still squirming when this dish is served and, if not chewed carefully, the tiny suction cups can stick to the mouth and throat. This is not a dish for the fainthearted.
The Korean delicacy sannakji, is something quite different, as the seafood isn't quite dead. Live baby octopus are sliced up and seasoned with sesame oil. The tentacles are still squirming when this dish is served and, if not chewed carefully, the tiny suction cups can stick to the mouth and throat. This is not a dish for the fainthearted.
Bugs
 The practice of eating insects for food is called entomophily and is fairly common in many parts of the world, with the exceptions of Europe and North America. It is not uncommon to find vendors selling fried grasshoppers, crickets, scorpions, spiders and worms on the streets of Bangkok, Thailand. Insects are high in protein and apparently consist of important fatty acids and vitamins.
The practice of eating insects for food is called entomophily and is fairly common in many parts of the world, with the exceptions of Europe and North America. It is not uncommon to find vendors selling fried grasshoppers, crickets, scorpions, spiders and worms on the streets of Bangkok, Thailand. Insects are high in protein and apparently consist of important fatty acids and vitamins.
Fried - brain sandwiches
 Long before the era of Mad-Cow Disease, a sandwich made from fried calves' brain, thinly sliced on white bread was a common item on the menus in St. Louis, Missouri, the USA. The sandwich is still available in the Ohio River Valley, where the brains are now heavily battered and served on hamburger buns.
Long before the era of Mad-Cow Disease, a sandwich made from fried calves' brain, thinly sliced on white bread was a common item on the menus in St. Louis, Missouri, the USA. The sandwich is still available in the Ohio River Valley, where the brains are now heavily battered and served on hamburger buns.
Balut
 It is a fertilized duck or chicken egg with a nearly-developed embryo that is boiled and eaten in the shell. It is easily one of the strangest foods in the world. Balut is very common in the Philippines, Cambodia and Vietnam and usually sold by street vendors. It is said balut tastes like egg and duck (or chicken), which is essentially what it is.
It is a fertilized duck or chicken egg with a nearly-developed embryo that is boiled and eaten in the shell. It is easily one of the strangest foods in the world. Balut is very common in the Philippines, Cambodia and Vietnam and usually sold by street vendors. It is said balut tastes like egg and duck (or chicken), which is essentially what it is.
Haggis
 A traditional Scottish dish, haggis is made with the minced heart, liver and lung of a sheep mixed with onion, spices, oatmeal, salt and stock, and boiled in the sheep's stomach for a few hours. Larousse Gastronomies, a popular encyclopedia of gastronomic delights, claims that haggis has "an excellent nutty texture and delicious savory flavor."
A traditional Scottish dish, haggis is made with the minced heart, liver and lung of a sheep mixed with onion, spices, oatmeal, salt and stock, and boiled in the sheep's stomach for a few hours. Larousse Gastronomies, a popular encyclopedia of gastronomic delights, claims that haggis has "an excellent nutty texture and delicious savory flavor."
Task 4. Answer TRUE of FALSE according to the text
1.Sannakji is made of live animals__________________
2. Entomophagy refers to eating snakes and worms
_______________________________________________
3. The brains of live animalsare still eaten inthe USA ___________________
4. Fried brainscause mad cow disease __________
5. Haggis has a nutritional value______________________
6. Haggis is made of heart, lung and liver_______________________________________________
7. Balutis eaten in Europe___________________________
Task 5. Complete the sentences with the words from the box.
|
Roast beef |
Ukrainian
|
|
Varenyky |
German |
|
Sushi |
Japanese |
|
Pizza |
Indian |
|
Moussaka |
Russian |
|
Biryani |
English |
|
Lasagna |
French |
|
Dumplings |
Italian |
|
|
|
|
.....is a typical.....dish |
.....is a typical.....dish |
|
|
|
|
.....is a typical..... dish |
.....is a typical..... dish |
|
|
|
|
.....is a typical.....dish |
…..is a typical….dish |
|
|
|
|
.....is a typical.....dish |
…..is a typical….dish |
Task 6.Underline the odd word out
- A bar of chocolate, soap, bread
- A carton of orange juice, bacon, milk
- A cup of coffee, meat, tea, hot chocolate
- A bowl of salad, cake, soup, cereal
- A jar of honey, jam, potatoes, mustard
- A box of chocolate, vinegar, biscuits
- A glass of wine, beer, ham, milk, juice
- A slice of sausage, bread, butter, cake
- A bottle of cola, beef, lemonade, milk
- A bag of flour, sugar, salt, ketchup
Task 7. Choose the right answer
- You should noteat so many sweets; they are …for you.
a) badb) disagreeable c) unhealthy d) unsuitable
- My aunt could tell fortunes from tea ….. .
- buds b) grounds c) leaves d) seeds
- Would you …the salt, please?
- carry b) deliver c) give d) pass
- This avocado …rather hard.
- feels b) senses c) smells d) tastes
- Oranges are said to be …for me but I don’t likethem much.
- appetizing b) good c) healthy d) nourishing
- “What would you like to drink, Miss Delicate, some …or something stronger?"
- brandy b) cider c) sherry d) whisky
- In the jar, there was a …which looked like jam.
- material b) powder c) solid d) substance
- Pork chop is one of my favourite….
- bowls b) courses c) dishes d) plates
- These are …potatoes, whichcan be eaten.
a)fresh b) new c) ripe d) young
 Unit 2. Flour products
Unit 2. Flour products
Task 1. Choose the correct word in bold
- How many/much biscuits would you like?
- How many/much chocolate did you eat?
- There isn`t many/much sugar in this tea?
- There isn`t many/much milk left?
- I didn`t use many/much eggs to make the omelets’?
- How many/much lettuce in this salad?
- We haven`t many/much wine for the party?
- How many/much hot dogs would you like?
Task 2. Read the text and discuss it
 Flour is made from the endosperm, the central part of the wheat kernel; 70 to 75 pounds of flour are commonly obtained from 1000 pounds of wheat. Varieties of wheat may differ markedly in mill ability. The white wheat is as a group are perhaps the easiest to mill, and they produce a high yield of flour. White flour may be divided into two major classes — bread flour and pastry flour. Bread flour is used to make rolls and Vienna bread, as well as the common sliced, wrapped white bread. Pastry flour is used for cakes, cookies, piecrusts, doughnuts, crackers and biscuits. Pastry flours have about 6 per cent to 9 per cent of protein. They are made from softer wheat’s compared to those used for bread flours. They generally are made from soft wheat’s in order to obtain the low-protein type necessary to make pastries and rich cakes. The strength of soft-wheat flours may be measured by amount of water they absorb in a slightly acid or weakly alkaline
Flour is made from the endosperm, the central part of the wheat kernel; 70 to 75 pounds of flour are commonly obtained from 1000 pounds of wheat. Varieties of wheat may differ markedly in mill ability. The white wheat is as a group are perhaps the easiest to mill, and they produce a high yield of flour. White flour may be divided into two major classes — bread flour and pastry flour. Bread flour is used to make rolls and Vienna bread, as well as the common sliced, wrapped white bread. Pastry flour is used for cakes, cookies, piecrusts, doughnuts, crackers and biscuits. Pastry flours have about 6 per cent to 9 per cent of protein. They are made from softer wheat’s compared to those used for bread flours. They generally are made from soft wheat’s in order to obtain the low-protein type necessary to make pastries and rich cakes. The strength of soft-wheat flours may be measured by amount of water they absorb in a slightly acid or weakly alkaline  solution. Strength appears to be proportional to the amount absorbed. The cereal grains are the edible seeds products by certain plants of the grass family. They provide 20 to 80 per cent of the food energy in different countries of the world. Cereal grains have many natural advantages as foods. They are nutritious. The grains are not bulky. They can be stored for long periods, are transformed cheaply long distances. Baked products made from flour or meal include pan breads, loaf breads, pastries, pancakes and flat breads. All cereal grains have high energy value, mainly from the starch fraction but also from the protein and fat.
solution. Strength appears to be proportional to the amount absorbed. The cereal grains are the edible seeds products by certain plants of the grass family. They provide 20 to 80 per cent of the food energy in different countries of the world. Cereal grains have many natural advantages as foods. They are nutritious. The grains are not bulky. They can be stored for long periods, are transformed cheaply long distances. Baked products made from flour or meal include pan breads, loaf breads, pastries, pancakes and flat breads. All cereal grains have high energy value, mainly from the starch fraction but also from the protein and fat.
The mineral and vitamin composition varies considerably among the cereals and among varieties within species.
It reflects the plates where they are grown, the conditions of storage, and the portion of the kernel that is utilized. Cereal foods should be eaten and are eaten with meat, fish, vegetables, milk and other foods. The  food value of cereals depends on their chemical composition and the availability of the constituents for use by the human body.
food value of cereals depends on their chemical composition and the availability of the constituents for use by the human body.
Corn is processed by the wet milling process to make oil, starch, and syrup for food purposes. The most important quality characteristics of grain are full maturity, freedom from type of mold, spoilage, and animal or insect contamination, and if dried artificially, drying at temperatures below 135°. Yellow corn contains appreciable amount of vitamin A. White corn contains a trace. High quality oats are matured, unweather, free from foreign material and other grains, and of high weight per bushel. Manufacturers of rolled oats believe that grain high in protein and low in fat makes the best product. Rolled oats with a high fat content are chunky, become rancid easily, and produce party water porridge when cooked. Rye flour, generally mixed with relatively large amounts of wheat flour, is used to make specially bread. The starch liquefying enzyme must be present in the proper amount especially when relatively rye bread is baked.
Task 3. Answer the questions
- How many groups of food are prepared from cereal grains?
- What products are made from cereal grains?
- What products are beverages made from?
- What is the general characteristic for all cereal grains?
- What is flour made from?
- How many classes may white flour be divided into?
- What is bread flour used for?
- What is pastry flour used for?
- What are bread flours made from?
- What are pastry flours made from?
Task 4. Fill in the gaps using the words in the box.

Kernel, white, oats, rice, hull, barley, corn, grains, wheat
1. Cereals include the small ______, wheat, corn or maize, and the various grain sorghums.
2. _______ supplies flour for bread, macaroni, crackers, and other foods.
3. _______ is classified as yellow, white and mixed.
4. _______ resembles wheat in appearance but has a longer and more slender head.
5. _______ are classified by color of the ______as white, red, black and mixed oats.
6. _______ oats are preferred for milling, but yellow and red oats also are used.
7. Rice qualityis rated _______ shape and uniformity, milling, less broken kernels and cooking characteristics.
8. _______ fresh from the combine harvester usually is high in moisture and requires prompt and careful drying.
Task 5. Put each of the following words into its correct place in the passage below.

Afternoon, lunch, rolls, bacon, meals, breakfast, English, menu, supper, juice, syrup
Most people eat three …a day – breakfast, … anddinner. Some people eat the fourth meal,.., late at night. Its basic … tradition provides an extra light meal served in the late ….Its basic … usually includes tea and special tea cakes or cucumber sandwiches.
Meals vary in different countries. ….. in the United States may include fruit or fruit ….., coffee, toast and a choice of cereal or ….. and eggs. Many people like pancakes with maple …for breakfast. Europeans sometimes have an early breakfast of …and coffee or hot chocolate.

Unit 3. Vitamins
Task 1. Read and translate the text.
VITAMINS — FAT-SOLUBLEVITAMINS
1Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential for good health. Although they are necessary in only small amounts, each one has specific vital functions to perform. Most vitamins can not be obtained from the human body, and therefore must be obtained from the diet. The body is capable of storing some vitamins (A, D, E, K and B12), but the rest need to be provided by the diet. Vitamins can be divided into 2 groups: water-soluble (B complex and C) and fat-soluble (A, D, E and K). As for water-soluble vitamins, they are easily destroyed during processing, storage, and the preparation and cooking of food.
2Vitamin A (retinol) is essential for healthy vision, eyes, skin and growth. Good sources include dairy products, liver, eggs and oily fish. Vitamin A can also be obtained from beta-carotene, the pigment found in highly colored fruit and vegetables.
3Vitamin D is essential for growth and the absorption of calcium, and thus for the formation of healthy bones. It is also involved in maintaining a healthy nervous system. The amount of vitamin D occurring naturally in foods is small, and it is found in very few foods — good sources are oily fish, eggs and liver, as well as breakfast cereals, margarine and full-fat milk that are fortified with vitamin D. Most vitamin D, however, does not come from the diet but is made by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight.
4Vitamin E is not one vitamin, but a number of related compounds called tocopherols that function as antioxidants. Good sources of vitamin E are vegetable oils, polyunsaturated margarines, wheat germ, sunflower seeds, nuts, oily fish, eggs, wholegrain cereals, avocados and spinach.
 5Vitamin K is essential for the production of several proteins, including prothrombin which is involved in the clotting of blood. Vitamin K exists in 3 forms, 191 one of which is obtained from food while the other two are made by the bacteria in the intestine. Vitamin K1, which is the form found in food, is present in broccoli, cabbage, spinach, milk, margarine, vegetable oils, particularly soya oil, cereals, liver, alfalfa and kelp.
5Vitamin K is essential for the production of several proteins, including prothrombin which is involved in the clotting of blood. Vitamin K exists in 3 forms, 191 one of which is obtained from food while the other two are made by the bacteria in the intestine. Vitamin K1, which is the form found in food, is present in broccoli, cabbage, spinach, milk, margarine, vegetable oils, particularly soya oil, cereals, liver, alfalfa and kelp.
6Vitamin B12 is vital for growth, the formation of red blood cells and maintenance of a healthy nervous system. B12 is unique in that it is only found in foods of animal origin. Good sources of vitamin B12 include liver, kidneys, oily fish, prawns, meat, cheese, eggs and milk.
Task 2. Match the vitamins with their other names.
|
|
tocopherols |
|
Vitamin D |
vitamin K1 |
|
Vitamin E |
retinol |
|
Vitamin K |
cholecalciferol |
|
fat-soluble vitamins |
B-complex and vitamin C |
|
water-soluble vitamins |
cyanocobalamin |
|
vitamin B12 |
A, D, E, K and B12 |
Task 3. Read the interview! Never mind if you don’t understand everything. Try to find the answer to the following question: “From what food do we get these things?”
 Interview
Interview
INTERVIEWER: Maureen’s going to answer lots of questions about how to train the athletics. She’s also going to answer your questions about food. What should young people eat, Maureen, if they want to be fit and healthy?
MAUREEN: Well, the most important thing is balance and variety. When you’re training, your body needs lots of different things so you must eat different kinds of food. You should eat lots of fresh fruit and vegetables because they give you lots of vitamins, especially Vitamin C which is important.
You should also eat enough food with carbohydrates, because when you’re training you need a lot of energy. You should eat bread, potatoes and pasta. All these things give you carbohydrates. But you mustn’t eat too many sweets or chocolates because you’ll put on weight and they’re bad for your teeth.
Finally, protein is important when you’re training. For protein you must eat meat and vegetables, like beans. You should also eat plenty of eggs and milk. Eggs and milk also give you calcium which is important for your bones.
One other thing – you must eat regularly every day. You mustn’t eat your meals at different times, for example, or eat a lot one day and a little the next.
You should also have a good breakfast and you shouldn’t eat too much before training, it’s very bad for you.
Oh, I nearly forgot: when you’re training, you must never smoke cigarettes!
INTERVIEWER: Thank you very much, Maureen. And that’s all we’ve got time for today on Sport Today. Next week we’ll be talking to Les Hardy, the rugby player, so send in your questions now!
Task 4. Read the interview once more and write down the names of foods where you can find
|
Vitamins |
Carbohydrates |
Protein |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Task 5. Decide whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Vitamins are divided into three groups.
2. Beta-carotene acts as a source of vitamin A.
 3. Tomatoes, carrots, Spanish peppers, red chili peppers, apricots, peaches, and vitamin A are good sources of beta-carotene.
3. Tomatoes, carrots, Spanish peppers, red chili peppers, apricots, peaches, and vitamin A are good sources of beta-carotene.
4. Vitamin D is necessary for the maintenance of a healthy nervous system.
5. Vitamin D can be found in a lot of foods.
6. Vitamin E is only one vitamin.
7. Vitamin K is known to exist in three forms.
8. Vitamin B12 is found in foods of both vegetable and animal origin.
Task 6. Read and translate the text.
WATER-SOLUBLE VITAMINS
1 The B Complex vitamins have very similar roles to play in nutrition, and many of them occur together in the same foods. Vitamin B1 (thiamin) is essential in the release of energy from carbohydrates. Good sources include milk, offal, meat (especially pork), wholegrain and fortified breakfast cereals, nuts and pulses, yeast extract and wheat germ.
2 Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is vital for growth, healthy skin and eyes, and the release of energy from food. Good sources include milk, meat, offal, eggs, cheese, fortified breakfast cereals, yeast extract and green leafy vegetables.
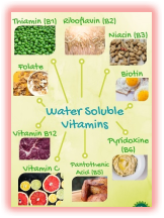 3 Niacin (nicotinic acid), sometimes called vitamin B3, plays an important role in the release of energy within the cells. Unlike the other B vitamins it can be made by the body. Good sources include meat, offal, fish, fortified breakfast cereals and pulses.
3 Niacin (nicotinic acid), sometimes called vitamin B3, plays an important role in the release of energy within the cells. Unlike the other B vitamins it can be made by the body. Good sources include meat, offal, fish, fortified breakfast cereals and pulses.
4 Pantothenic acid, sometimes called vitamin B5, is involved in a number of metabolic reactions, including energy production. This vitamin is present in most foods (excepting fat, oil and sugar). Good sources include liver, kidneys, fish roe, yeast, egg yolks, wheat germ, fresh vegetables and pulses.
5 Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) helps the body to utilize protein and contributes to the formation of hemoglobin for red blood cells. B6 is found in a wide range of foods including meat, liver, fish, eggs, wholegrain cereals, some vegetables, pulses, brown rice, nuts and yeast extract.
6 Folate (folic acid) is involved in the manufacture of amino acids and in the production of red blood cells. Folate may also help to protect against heart disease. 195 Good sources of folate are green leafy vegetables, liver, pulses, eggs, wholegrain cereal products, wheat germ,  nuts and fruit, especially grapefruit and oranges.
nuts and fruit, especially grapefruit and oranges.
7 Biotin is needed for various metabolic reactions and the release of energy from foods. Good sources include liver, oily fish, kidneys, egg yolks and brown rice.
8 Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is essential for growth and vital for the formation of collagen (a protein needed for healthy bones, gums, teeth, blood capillaries and all connective tissue.) It plays am important role on the healing of wounds and fractures, and acts as a powerful antioxidant. Vitamin C is found mainly in fruit (lemons, kiwi, pineapple, berries, and apricots) and vegetables.
Task 7. Match a water-soluble vitamin (Column A) with its other name (Column B)
|
A |
B |
|
|
ascorbic acid |
|
vitamin B2 |
pyridoxine |
|
vitamin B3 |
folic acid |
|
vitamin B5 |
riboflavin |
|
vitamin B6 |
pantothenic acid |
|
folate |
thiamin |
|
vitamin C |
niacin, or nicotinic acid |
Task 8. Fill in the table with the names of foods that contain a certain water-soluble vitamin (see the text “Water-Soluble Vitamins”).
|
B1 |
B2 |
B3 |
B5 |
B6 |
folate |
biotin |
C |
|
milk |
eggs |
pulses |
vegetables |
fish |
oranges |
liver |
fruit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Task 9. Answer the questions.
1. How do we classify vitamins? 2. What do we call vitaminsthat are soluble in fat? 3. What harm does vitamin A do to the body? 4. What do we call provitamin A? 5. What can you say about vitamin D? 6. What are sterols? 7. What do human skin and skins of all animals contain? 8. What is cholesterol transformed into when exposed to ultraviolet light? 9. Where is vitamin D present? 10. What are the 29 properties of vitamin E? 11. What is tocopherol? 12. Is vitamin E soluble in water? 13. What are the properties of vitamin B? 14. Where is vitamin В present? 15.Why was vitamin C called ascorbic acid? 16. What does the deficiency of vitamin С lead to?

Unit 4. Fruits
Task 1. Read the text and discuss it
 Fruits are important sources of vitamins and carbohydrates like fiber and sugar. They are low in calories and naturally sweet. Fruits and their juices are good sources of water, too.Different fruits contain different vitamins, so it is important to eat a variety of fruits. Mangoes, papayas, melons and citrus fruits, like oranges and grapefruit, are high in vitamin C. Cantaloupe, apricots, peaches, and nectarines are sources of vitamin A. Whole fruits like apples and grapes contain more fiber than fruit juices and sauces, like applesauce and grape juice. Dried fruits like figs, prunes and raisins are good sources of fiber, too. Canned fruits packed in syrup have a lot of added sugar. They are higher in calories than fresh fruits. When you shop for canned fruits, look for fruit that is packed in juice instead of syrup. The divisions of the fruits grown in warm, temperate and tropical climates are:
Fruits are important sources of vitamins and carbohydrates like fiber and sugar. They are low in calories and naturally sweet. Fruits and their juices are good sources of water, too.Different fruits contain different vitamins, so it is important to eat a variety of fruits. Mangoes, papayas, melons and citrus fruits, like oranges and grapefruit, are high in vitamin C. Cantaloupe, apricots, peaches, and nectarines are sources of vitamin A. Whole fruits like apples and grapes contain more fiber than fruit juices and sauces, like applesauce and grape juice. Dried fruits like figs, prunes and raisins are good sources of fiber, too. Canned fruits packed in syrup have a lot of added sugar. They are higher in calories than fresh fruits. When you shop for canned fruits, look for fruit that is packed in juice instead of syrup. The divisions of the fruits grown in warm, temperate and tropical climates are:
1. Stone-fruit— date, olive, mango, etc.
2. Berries and berry-like fruit — banana, plantain, fig, orange, pineapple, lime, lemon, citron, grapefruit, melon, etc.
 3. Nuts or shell fruit— coconut, almond, Brazil nut, chestnut, etc. No fruit is more widely cultivated in temperate climates than the apple. Its cultivation has become so extensive due to an appreciation of its qualities. Apples may be a moderately good source of ascorbic acid, depending on whether it is a summer apple, a fall or a winter apple, whether it is eaten soon after harvest or several months later, and whether it is unpaired or pared. Pears are a popular fruit in Great Britain, both in a fresh and a canned condition. The pear is of the same genus as apple, and is a native of Europe and Western Asia in their temperate regions. The peach is considered to be of Chinese origin.
3. Nuts or shell fruit— coconut, almond, Brazil nut, chestnut, etc. No fruit is more widely cultivated in temperate climates than the apple. Its cultivation has become so extensive due to an appreciation of its qualities. Apples may be a moderately good source of ascorbic acid, depending on whether it is a summer apple, a fall or a winter apple, whether it is eaten soon after harvest or several months later, and whether it is unpaired or pared. Pears are a popular fruit in Great Britain, both in a fresh and a canned condition. The pear is of the same genus as apple, and is a native of Europe and Western Asia in their temperate regions. The peach is considered to be of Chinese origin.
Nectarines are in reality a delicate variety of peach, and much richer in flavor than their relative. They have smooth skins in contrast with the hairy exterior of the peach. There are from six to a dozen varieties grown out of doors in favorable situations, while a number of more delicate kinds are cultivated under glass. Grapes are grown in two ways: in the open air; and hot-houses.
The dates known to commerce emanate from a species of palm-tree which grows in the Canada Islands, Northern Africa, the South-East of Asia, and the North-West of India. The oblong fruit of the palm-tree is well known to consumers. The saccharine nature of the flesh makes it very pleasant to the palate. The finest dates are produced in the "Sunken Gardens" in Algiers, and are known by the name of DegletNur. In countries that experience cold and frosty nights, the young trees have to be protected with canvas or some similar covering. The planting is generally done in rows, seven or eight yards apart. The fruit bearing capacities of the trees differ, according to the quality of species and degree of care spent upon their cultivation. One tree gives an annual crop of 60 lb. of dates; mother yields 100 lb. and the finest specimens have been known to yield 500 lb.
If the pineapples are for local consumption they are gathered when greenor when the color is just changing. Of course, some varieties travel better than others, so that the discretion of the grower has to be used. The fruit is removed gently by breaking the stem or by cutting with a knife about an inch below the stem. Should the break or cut take place too near the fruit, the latter is liable to decay.
 Task 2. Fill in the gaps using the words in the box.
Task 2. Fill in the gaps using the words in the box.
pounds; figs; crops; stuffed; species; cultivated;grapefruit;pineapples; varieties; preserved; olives
1. The leaves of the __________ tree are large, and large white flowersare formed on the branches. 2. The fruit often weighs from ten to fourteen ________, but the average weight for table use is about one pound.
3.The most perfect ________ grown outdoors can be found in the Hawaiian Islands in the Pacific Ocean, about 2,000 miles from San Francisco. 4. The _______ known to commerce are grown chiefly in Asia, Syria, the Spanish Peninsula, and the South of France. 5. There are about 360 _________of figs grown, the colors of which range from dark purple to yellow, white, and green. 6. The trees usually bear two ________, one in the spring and the other in the autumn. 7. Figs are _________ in several ways, in syrup, brandy, etc. 8. They are ________ also, and in that form find a ready sale. 9. In Eastern India, the fig tree, known as the Indian rubber tree, provides most of the world's reserves.10. The olive is an evergreen tree or shrub extensively _________ in numerous subtropical countries. 11. Green ________ intended for collection is collected when the growth period ends, but before the final ripening.
Task 3. Match the meaning and the word
|
Fruit |
a) long curved tropical fruit with yellow skin |
|
|
b)soft green fruit with small black seeds and a thin brown skin covered with many short hairs |
|
Grape |
c) a part of a plant, tree or shrub that contains seeds |
|
Water - melon |
d) a small round fruit of orange or yellow color and has one large seed |
|
Apricot |
e) a fruit with hard yellow skin and sour juice |
|
Kiwi |
f) a small round green or purple fruit that grows in bunches on the vine and is often used for making wine |
|
Lemon |
g) dry brown fruit growing on a tree |
|
Tangerine (mandarin) |
h) a dried grape |
|
Nut |
i)A very large orange edible fruit that grows on the ground |
|
Raisin |
j) A large fruit like a nut with a thick, hard, brown shell covered in fiber and containing hard, white flesh that can be eaten and has a clear liquid |
|
Pumpkin |
k) round yellow or pink fruit with a thick skin, has a bitter taste, similar to a large orange |
|
Coconut |
l) juicy round fruit with a thick red skin and many small seeds inside |
|
Pomegranate |
m) large round fruit with a hard green skin, juicy red flesh and lots of black seeds |
|
Grapefruit |
n) a small sweet orange fruit, similar to an orange, with a peel that is easily removed |
 Task 4. Group the words below under the following headings:
Task 4. Group the words below under the following headings:
Apple, pear, lemon, peach, pine apple, grapes, strawberries, lime, currants, raspberries, plum, melon, fig, mango, kiwi, banana, orange, bilberries, quince, black berries, pomegranates, apricot,
olives, gooseberries, grapefruit, avocado,coconut, date, walnut, hazelnut, peanut, almond, chestnut, cranberries, nectarine
|
pippin – fruit
|
stone – fruit
|
exotic – fruit
|
berries |
nuts (shell fruit)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Task 5. Do the crossword puzzle and find out which word is hidden.
|
1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
2. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
4. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
5. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
6. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
7. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
8. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
9. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
10. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
- It’s a blue or green fruit with many small berries.
- It’s a yellow fruit. It’s very sour.
- It’s a dish made of cucumbers, tomatoes, onions and other vegetables.
- It’s a lovely tasty thing. It’s very sweet. It can be black or milk or white. Candies are made of it.
- It’s a crunchy autumn fruit. It can be red, yellow, and green.
- Apples, bananas, plums are …
- It’s a round fruit of a bright color. The name of the fruit is the same as the name of the color.
- Monkeys like this yellow fruit.
- These are two pieces of bread with a layer of food between them.
- It’s a drink. In Ukraine people drink it hot, but in some other countries people drink it cold.
Task 6. Find the words below in the grid.
Words can go horizontally, vertically and diagonally, backwards or forwards.
|
R |
W |
L |
Y |
R |
R |
E |
B |
P |
S |
A |
R |
L |
L |
M |
|
P |
L |
G |
M |
X |
M |
K |
G |
L |
M |
E |
L |
O |
N |
P |
|
I |
K |
L |
K |
G |
T |
R |
X |
D |
M |
E |
Y |
N |
W |
N |
|
N |
C |
I |
B |
W |
R |
P |
V |
K |
L |
W |
F |
B |
O |
A |
|
E |
H |
W |
X |
L |
K |
A |
R |
P |
P |
Y |
D |
M |
P |
E |
|
A |
E |
I |
S |
L |
F |
R |
P |
E |
J |
T |
E |
R |
E |
G |
|
P |
R |
K |
A |
T |
M |
A |
A |
E |
L |
L |
I |
N |
A |
N |
|
P |
R |
N |
C |
N |
R |
R |
R |
M |
F |
C |
Z |
V |
C |
A |
|
L |
Y |
M |
V |
T |
A |
A |
B |
G |
O |
R |
V |
B |
H |
R |
|
E |
H |
Q |
V |
M |
K |
N |
W |
T |
T |
B |
U |
N |
B |
O |
|
N |
N |
B |
P |
N |
N |
C |
A |
B |
Z |
B |
D |
I |
R |
M |
|
E |
P |
A |
R |
G |
J |
R |
Q |
B |
E |
M |
T |
M |
T |
C |
|
Y |
T |
T |
K |
D |
M |
L |
Q |
F |
T |
R |
M |
W |
K |
D |
|
P |
L |
U |
M |
K |
B |
L |
U |
E |
B |
E |
R |
R |
Y |
T |
|
H |
T |
B |
L |
A |
C |
K |
B |
E |
R |
R |
Y |
Y |
H |
K |
Apple, apricot, banana, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, grape, grapefruit, kiwi, lemon, melon, orange, peach, pear, pineapple, plum, raspberry, strawberry.
Task 7. Answer the questions.
- How are the fruits grown in warm, temperate, and tropical climates divided?
- What is the origin of peach?
- Describe the taste and peel of nectarines?
- How many ways are there to grow grapes? Name them?
- In what countries are dates grown?
Task 8. Translate into English
- Яблука – унікальні плоди, тому що в них містяться майже всі вітаміни і мінеральні елементи.
- Сорти персиків можна класифікувати за двома групами: пухнасті та гладкі.
- Виноград вирощують на відкритій площі і в теплицях.
- Серед сортів мигдалю розрізняють солодкі і гіркі.
- Банани є плодами трав’яної рослини із родини бананових.


Unit 5. Vegetables
Task 1. Read the text and discuss it
It has long been known to everyone that vegetables should make up the bulk of the human diet. From early childhood, parents teach their children to eat as many vegetables as possible. Vegetables contain a huge amount of vitamins and minerals necessary for the human body. Vegetables are different, they differ in color, size, taste, have certain useful properties. A garden is a place where vegetables grow. Basically, people grow them on their own, look after them, water them, protect them from the scorching sun, from harmful insects, and fertilize the soil.
Vegetables can grow both above the ground and in the ground. For example, tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, eggplant, cabbage grow on beds above the ground. Onions, beets, radishes, carrots, potatoes - grow in the ground.
Dishes from vegetables are usually taken at the very beginning of a meal, whether it is lunch or dinner, because they contribute to the rapid digestion of food and saturate the body with useful substances.
There are also vegetables that can fight various diseases. Carrots help improve vision, onions fight viral germs, cabbage is good for the heart, and  beets are recommended for people with respiratory diseases.
beets are recommended for people with respiratory diseases.
At least 10 mineral elements are needed for the proper growth and development of the body. Extensive investigations have shown that calcium, phosphorus, and iron, except in rare instances, are the only mineral elements that are not present in quantities sufficient for the needs of the body. The green vegetables are sources of the important mineral elements. Potatoes, sweet potatoes and mature onions contain appreciable quantities of phosphorus. A certain quantity of bulky food is necessary for good health; vegetables are the main source of roughage.
Most vegetables, particularly the leafy ones, as celery, cabbage, spinach, and lettuce are characterized by high water content and relatively high percentage of cellulose or fibre. Because of their succulence and relativelly large bulk, the leafy vegetables and most of the root crops probably aid in the digestion of the more concentrated foods.
Task 2. Match the meaning and the word
|
Bell pepper |
|
|
Beet |
|
|
|
|
|
Salad |
|
|
Lettuce |
|
|
Haricot |
|
|
Garlic |
|
|
parsley |
 Task 3. Explain the meaning of verbs:
Task 3. Explain the meaning of verbs:
fry, roast, bake, stew, boil, salt, cut, peel, pour, slice, mix, make, wash, cool, spice, grease, put, grate, chop, microwave, dress, stir, grill.
Task 4. Answer the questions.
1. What vegetables are important in the human diet?
2. What vegetables are rich in proteins?
3. What vegetables are important sources of carbohydrates?
4. What classification of vegetables do you know?
5. What kinds of vegetables belong to the salad crops?
6. What kinds of vegetables belong to the bulb crops?
Task 5. Fill in the gaps using the words in the box.
 Pumpkins, asparagus, kale, broccoli, species, folic, acid, leafy, phosphorus, potatoes, turnips
Pumpkins, asparagus, kale, broccoli, species, folic, acid, leafy, phosphorus, potatoes, turnips
- Potatoes, sweet potatoes and mature onions contain appreciable quantities of ________. 2. The _______, green and yellow vegetables contribute about 33 per cent of the vitamin A supplied by the major food groups. 3. They supply also about 25 per cent of the ascorbic acid, appreciable quantities of thiamine, niacin, and ________ _______. 4. _______ and sweet potatoes supply about 16 per cent of ascorbic acid, while citrus fruits and tomatoes furnish about 34 per cent. 5. The vegetables ranking highest in vitamin A are carrots, turnip, greens, spinach, sweet potatoes, beet greens, mustard greens, winter squash, chard, and _______. 6. The only stored vegetables of much importance that do not have to complete with the fresh product are sweet potatoes, winter ________, and winter squashes. 7. Most of the root crops such as beets, carrots, parsnips, rutabaga’s and ________ keep best in a relative cold, humid atmosphere, while sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and squashes keep best in a relative warm, dry atmosphere. 8. ________, a genus of the lily family, has at least 150-________ native of Europe, Asia and Africa. 9. There are many known types of ____, but they all probably belong to the same species.
Task 6. Match the meaning and the word
|
Vegetable |
|
|
|
My name is long and rhymes with tower. What am I? |
|
Cabbage |
|
|
Onion |
|
|
Carrot |
|
|
Asparagus |
|
|
Cucumber |
|
|
Cauliflower |
|
Task 7. Find the words below in the grid.
Words can go horizontally, vertically and diagonally, backwards or forwards.
|
P |
T |
J |
N |
W |
P |
R |
C |
O |
V |
M |
C |
O |
R |
N |
T |
|
T |
I |
F |
T |
J |
H |
A |
K |
K |
N |
C |
N |
A |
E |
B |
K |
|
S |
K |
N |
Q |
L |
B |
Q |
K |
M |
D |
I |
M |
L |
X |
L |
Z |
|
U |
E |
Z |
R |
B |
V |
K |
C |
N |
N |
N |
O |
X |
C |
E |
N |
|
G |
E |
J |
A |
U |
K |
R |
A |
Y |
N |
L |
R |
N |
E |
O |
M |
|
A |
L |
G |
L |
F |
T |
C |
U |
L |
Z |
T |
Y |
R |
L |
T |
F |
|
R |
E |
T |
G |
X |
T |
H |
L |
Z |
W |
J |
R |
J |
E |
A |
N |
|
A |
C |
A |
R |
R |
O |
T |
I |
I |
M |
H |
M |
T |
R |
T |
Y |
|
P |
K |
T |
X |
M |
R |
Y |
F |
V |
L |
H |
O |
Q |
Y |
O |
G |
|
S |
A |
F |
R |
J |
R |
L |
L |
V |
K |
O |
P |
Q |
S |
P |
C |
|
A |
K |
R |
A |
Q |
T |
P |
O |
Z |
R |
J |
C |
P |
N |
I |
Z |
|
W |
M |
E |
S |
B |
Y |
D |
W |
T |
H |
Y |
I |
C |
L |
H |
V |
|
J |
R |
N |
N |
K |
I |
E |
R |
D |
A |
K |
A |
F |
T |
R |
X |
|
N |
P |
Y |
N |
N |
K |
X |
E |
B |
T |
N |
X |
R |
O |
C |
K |
|
N |
T |
M |
L |
J |
B |
P |
H |
C |
F |
G |
M |
L |
X |
Q |
B |
|
B |
Y |
Z |
Q |
K |
B |
N |
H |
F |
E |
O |
T |
A |
M |
O |
T |


Unit 6. Milk and Dairy products
Task 1. Read the text and discuss it
Cow milk is the most complete of all foods having nearly all the constituents of nutritional importance to man, though it has little iron and vitamins C and D. There is not any other product of animal origin having such an amount of carbohydrate, in the form of disaccharide lactose. It is a very good source of vitamins A, B, C, of calcium. Milk contains fat, sugar, proteins and all the other minerals.
 Any person needs about half a liter every day, of which an increasing proportion consists of skimmed and semi-skimmed products. In a mixed diet milk is valuable for its content of high quality protein, and is a rich source of riboflavin.
Any person needs about half a liter every day, of which an increasing proportion consists of skimmed and semi-skimmed products. In a mixed diet milk is valuable for its content of high quality protein, and is a rich source of riboflavin.
Whole milk can be a good source of energy, which is particularly important for young children. Skimmed or semi-skimmed milks may be useful for those who drink a lot of milk and who wish to reduce their fat intake.
Milk is widely used by man. It can serve as a basis for many important foods. It is a basic product for the preparation of such products as butter, different kinds of cheese, cakes, some kinds of bread and sweets.
Task 2. Decide whether the following statements are True or False.
1. Cow milk has all the nutrients necessary for man.
 2. Cow milk has a lot of iron and vitamin C.
2. Cow milk has a lot of iron and vitamin C.
3. Cow milk does not have many carbohydrate in the form of disaccharide lactose.
4. Milk is a good source of calcium and other minerals.
5. Every person needs a liter of milk every week.
6. Milk for grown-up people must be skimmed or semi-skimmed, and whole milk can be recommended for young children.
7. Milk contains high quality protein, and is a rich source of riboflavin.
8. Milk is not used for the preparation of bread and biscuits.
Task 3. Match the words and phrases (1-5) with the definitions (A-E).
|
milk |
Aa thick liquid dairy product that contains fat |
|
cream |
B a soft dairy product made with cream and milk |
|
cheese |
C a soft dairy product made of bacteria |
|
yogurt |
D white liquid produced by cows |
|
cream cheese |
E a solid or semi-solid dairy product |
Task 4. What kinds of milk do you know? Fill in the spaces with the suitable words.

![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()

![]()



Task 5. Read and translate the text “Milk Products — Cream”
 CCream is derived from fresh milk either by skimming off the fatty layer which rises to the surface or in a mechanical separator. In a mechanical separator the cream of any desired fat content may be obtained. The constituents of cream are the same as those of milk, but in a different proportion. Minimum fat contents for different types of cream can be specified: — half cream, 12 per cent by weight as milk fat; — single cream, 18 per cent; — whipped cream, 35 per cent; — double cream, 48 per cent; — clotted cream, 55 per cent. Right: Cream tea. These compare with 3.9 per cent fat in milk.
CCream is derived from fresh milk either by skimming off the fatty layer which rises to the surface or in a mechanical separator. In a mechanical separator the cream of any desired fat content may be obtained. The constituents of cream are the same as those of milk, but in a different proportion. Minimum fat contents for different types of cream can be specified: — half cream, 12 per cent by weight as milk fat; — single cream, 18 per cent; — whipped cream, 35 per cent; — double cream, 48 per cent; — clotted cream, 55 per cent. Right: Cream tea. These compare with 3.9 per cent fat in milk.
Task 6. Decide whether the following statements are True or False.
 1. Cream is usually derived from pasteurized milk.
1. Cream is usually derived from pasteurized milk.
2. We can derive cream in a mechanical separator.
3. Any fat content of cream may be obtained in a mechanical separator.
4. The constituents of cream are not the same as those of milk.
5. Kinds of cream can be specified by their fat content.


Unit 7. Meat
Task 1. Read and translate the text.
 Meat is valued as a portion of complete protein food, containing all the amino acids necessary for the human body. The fat of meat, which varies widely with the species, quality, and cut, is a valuable source of energy and influences the flavor, juiciness, and tenderness of the lean.Parts such as livers, kidneys, hearts, and other portions are excellent sources of vitamins and of essential minerals, easily assimilated by the human system.
Meat is valued as a portion of complete protein food, containing all the amino acids necessary for the human body. The fat of meat, which varies widely with the species, quality, and cut, is a valuable source of energy and influences the flavor, juiciness, and tenderness of the lean.Parts such as livers, kidneys, hearts, and other portions are excellent sources of vitamins and of essential minerals, easily assimilated by the human system.
Meat is digesting slowly, but 95 percent of meat protein and 96 percent of fat are digesting.
Fats tend to retard the digestion of other foods; thus, meat with a reasonable proportion of fat remains longer in the stomach, delaying hunger and giving “staying power.” Extractives in meat cause a flow of saliva and gastric juices, creating the desire to eat and ensuring ease of digestion.
 The most widely consumed meat is beef,the flesh of mature cattle that normally weigh from 450 to 540 kg (1,000 to 1,200 pounds) and yield between 55 and 60 percent of their weight in meat. Veal, the flesh of calves of cattle, is much less fatty than beef.
The most widely consumed meat is beef,the flesh of mature cattle that normally weigh from 450 to 540 kg (1,000 to 1,200 pounds) and yield between 55 and 60 percent of their weight in meat. Veal, the flesh of calves of cattle, is much less fatty than beef.
The pig is the world’s second largest provider of meat. When taken to slaughter, pigs generally weigh between 90 and 135 kg (200 and 300 pounds) and provide about 70 to 74 percent of that weight in meat.
Meat from lambs and sheep is produced on a much smaller scale than either beef or pork (less than one-tenth of that provided by cattle, for example). They ordinarily weigh between 45 and 70 kg (100 and 150 pounds), although the most select lambs may weigh no more than 14 to 18 kg (30 to 40 pounds) and yield about 48 to 50 percent of their weight in meat.
The meat-products industry, though called meatpacking, includes the slaughtering of animals. The steps in this process generally include stunning, bleeding, eviscerating, and skinning. Carcasses are then inspected and graded according to government-set standards of quality.
The usual methods of preserving meat from bacteria and decay are refrigerating, freezing, curing, freeze-drying, and canning.
Meats are marketed as fresh or processed goods or become ingredients of various meat products, including many types of sausages and luncheon meats. They also yield a number of important by-products.
Task 2. Do you think the methods of preparing meat dishes are correct? Correct the mistakes
|
Meat dish |
Method of Cooking |
|
|
in the pot |
|
boiled sausages |
on the grill |
|
roast beef |
in the frying pan |
|
baked chicken |
in the saucepan |
|
grilled pork |
on the open fire |
|
stewed lamb |
in the oven |
 Task 3. Read the recipe. Fill in the gaps with the words in bold. Guess what recipe it is
Task 3. Read the recipe. Fill in the gaps with the words in bold. Guess what recipe it is
Pre-heat, stir (3), melt, roast, make, cook, put, weigh,
cover, cook, serve
Ingredients:
Serves: 4
25 Gram Butter (1 oz)
1 Medium Onion, finely chopped
110 Gram Fresh breadcrumbs (4 oz)
1 Tablespoon Fresh sage, chopped
1 Small Eating apple, peeled, cored, grated
1 Egg
1 Duckling, washed and dried
450 Gram Cooking apples, peeled, cored, sliced (1 lb)
1 Tablespoon Water
Sugar, a little (optional)
 ….. oven to 180 °C / 350 °F / Gas 4. To …the stuffing, … half the butter in a medium saucepan and ….. the onion until softened. ….. in the breadcrumbs, sage, eating apple and egg. Shape the stuffing into small balls and place in a roasting tin.
….. oven to 180 °C / 350 °F / Gas 4. To …the stuffing, … half the butter in a medium saucepan and ….. the onion until softened. ….. in the breadcrumbs, sage, eating apple and egg. Shape the stuffing into small balls and place in a roasting tin.
…..the duckling, prick the skin all over with a sharp skewer or fork.
Place on a wire rack or trivet in another roasting tin. …..for 30-35 minutes per 450g (1 lb). …..the stuffing balls for the last 30 minutes of the calculated cooking time.
Meanwhile, make the apple sauce. ….. the apples and water in a pan. …..tightly and cook for about 10 minutes, until the apples are tender, shaking the pan occasionally. …..in the remaining butter and beat with a wooden spoon until smooth. …..in a little sugar, if liked. …..the duckling with the apple sauce and thin gravy.
Task 4. Match the meaning and the word
|
Fish |
|
|
Meat |
|
|
Bacon |
|
|
Mutton |
|
|
Beef |
|
|
|
|
|
Veal |
|
|
Chop |
|
|
Cutlet |
|
 Task 5. Fill in the gaps using the words in the box.
Task 5. Fill in the gaps using the words in the box.
Connective tissue, fibers, cells, sources, tissue,
solutions, structure, muscle, pigments, tenderness
-
 Meat represents one of the most popular _______ of protein. 2. An examination of meat _______ enables us to form a picture of the parts.3. The muscle ______ are to be like in structure and tapering at each end. 4. These are held together by the so called _______. 5. Fat _______ may be found held within the meshes of the connective tissue. 6. Bundles of muscles fibersare held to the bony _______ of the animal by dense strands of connective tissues called tendons. 7. Within the muscle fibers are _______ of salts, vitamins A and B complex and others in small quantities, enzymes and certain proteins — myosin (globulin), mitogen (albumin) and derived proteins. 8. The muscle fibers of red meat contain more hemoglobin and muscle ________ than the light or colorless meat. 9. Glycogen and dextrose are present in greater or lesser amount in all _______ fiber. 10. The location and distribution of the fat greatly affect the ________ of the meat.
Meat represents one of the most popular _______ of protein. 2. An examination of meat _______ enables us to form a picture of the parts.3. The muscle ______ are to be like in structure and tapering at each end. 4. These are held together by the so called _______. 5. Fat _______ may be found held within the meshes of the connective tissue. 6. Bundles of muscles fibersare held to the bony _______ of the animal by dense strands of connective tissues called tendons. 7. Within the muscle fibers are _______ of salts, vitamins A and B complex and others in small quantities, enzymes and certain proteins — myosin (globulin), mitogen (albumin) and derived proteins. 8. The muscle fibers of red meat contain more hemoglobin and muscle ________ than the light or colorless meat. 9. Glycogen and dextrose are present in greater or lesser amount in all _______ fiber. 10. The location and distribution of the fat greatly affect the ________ of the meat.
Task 6. Answer the questions
- What’s your favorite kind of meat?
- How often do you eat steak?
- Are you a vegetarian or not?
- Do you eat beef?
- Do you prefer fish or meat?
- Are you a great eater?
- Do you think a vegetarian diet is better than a diet that includes meat?
VOCABULARY

A
absorb – поглинати, всмоктувати
abundant – у великій кількості
according (to) – відповідно до, згідно з …
acid – кислота
acidic – кислий
adjustment – пристосування
affect – впливати на
affluent – у великій кількості
albumen – яєчний білок
allowance – раціон
annually – щорічно
antioxidant – антиоксидант
appetizer – закуска (перед обідом)
appetizing – апетитний
application – застосування
apply – вживати, застосовувати
asparagus – спаржа
assume – вважати, припускати
attempt – робити спробу
available – наявний
avoidance – уникнення
 B
B
bacterium – бактерія (pl. –ria)
bake – пекти(ся)
bakery – пекарня
bakershop – булочна
barley – ячмінь
pearlbarley – перлова крупа
batter – збите тісто (без дріжджів)
beat – бити, збивати
beef – яловичина
beefsteak – бифштекс
beer – пиво
beet – буряк
sugarbeet – цукровий буряк
beneficial – корисний
bile – жовч
bin – відро для сміття
biscuit – сухе печиво
bitter – гіркий
blackcurrant – чорна смородина
blanch – бланшувати
blend (n, v) – суміш, поєднання; змішувати
(food) blender – міксер
braise – тушкувати (м'ясо)
broil – смажити(ся) на вогні
broth – бульйон
buckwheat – гречана крупа
burlap - мішковина
buliotka – бульонниця
bulk – груба їжа
bun –булочка
butter – масло, намазувати маслом
butterfat – молочний жир
buttermilk – маслянка, сколотини

C
café – кафе, кав’ярня
caffeine – кофеїн
cake – кекс, торт, тістечко
calcium – кальцій
camembert – камембер (сорт сиру)
candy – цукерка, льодяник
canned – консервований
canning – консервування
canteen – їдальня
carbohydrate – вуглевод
carbon – вуглець
carve – різати
cashew – кеш`ю (горіх)
castersugar – цукрова пудра
catering – громадське харчування
cattle – велика рогата худоба
cauliflower – кольорова капуста
caviar – ікра
celery – селера (бот.)
cell – клітина (біол.)
cellulose – клітковина, целюлоза
cereal – хлібний злак
chestnut – каштан
chewinggum – жувальна гумка
coagulate – коагулювати
coat (n;v) – шар; покривати шаром
cob – качан кукурудзи
cocoa-butter – масло какао
cocoanut – кокосовий горіх
cod – тріска
composition – склад, сполука
concern – непокоїти, торкатись (теми)
condensed – згущений
condensedmilk – згущене молоко
confectionery – кондитерські вироби
cook (n;v) – кухар; варити, готувати страву
cookery – кулінарія
cookies – печиво, булочка
course – страва
covering – оболонка
cream – вершки
sourcream – сметана
crush – товкти, дрібнити
crusty – покритий скоринкою
cuisine – кухня
curd – сир
cut – різати

D
dairy – молочний
decanter – графин
decrease – зменшуватися
deep-fried – смажений у фритюрі
deficiency – недостатність, дефіцит
defrost – розморожувати
derive – походити (від), отримувати
deserve – заслуговувати
destruction – руйнування, знищення
diffusion – розповсюдження, поширення
digest – перетравлювати, засвоювати (про їжу)
digestible – легкотравний
dine – обідати
dirty – брудний
dish – страва, блюдо
dissolve – розчинятися
diverse – різноманітний
drawn (fish) – вительбушена (риба)
dress – заправляти (страви )
dressedfish – розділена риба (напівфабрикат )
dressing – приправа
dried - сухий, сушений
drink (n; v) – напій; пити
softdrinks – безалкогольні напої
drinkingwater – питна вода
drip – капати
dripping – топлений жир
drymilk – сухе молоко

E
eel – вугор
edible – їстівний; той, що їдять
effect – дія
effective – ефективний
emulsification – утворення емульсії
emulsifier – емульгатор
emulsion – емульсія
endorse – схвалювати
enhance – підсилювати
enzyme – ензим, фермент
equipment – обладнання, устаткування
escape – вивітрюватися, випаровуватися
establishment – установа, відомство
evaporation – випарювання
evenly – рівно, рівномірно
except – крім, за винятком
expenditure(s) – витрати
expensive – дорогий
exude – поширювати навколо себе

F
fat – жир
fatty – жирний
favourable – сприятливий
feast – бенкет
ferment – бродити (хім.)
fermenting – ферментуючий
fertiliser – добриво
fibre – волокно, фібра
fiery – запальний
fig – інжир, фіга
figure – цифра, малюнок
figureout – вираховувати
filbert – лісовий горіх, ліщина
fillet – філе
filling – начинка, наповнювач
fin – плавник
fin-fish – плавниковариба
flavour – аромат
flavouring – ароматизатор
flesh – м’якоть
flour – борошно
food – їжа
fortify – підкріплювати
fragrant – духмяний
fresh – свіжий
fridge – холодильник
freeze – заморожувати
fruitful – плідний
fry – смажити
fuel (n;v) – паливо

G
gap – прогалина, дефіцит
garlic – часник
garnish – гарнір
gelatin – желатин
geneticallymodified – генетичномодифікований
GMO – генетичномодифікованіорганізми
ginger – імбир
glacier – льодниця (глейсер)
glut – велика кількість
goat – цап, коза
goods – товари
gooseberry – аґрус
grade – якість, сорт, ґатунок, оцінка
grain(s) – зерно, зернові (культури)
grape – виноград
grapefruit – грейпфрут
grate – терти (на тертушці)
gravy – підлива
grease – мазати жиром, змащувати
greens (herbals) – зелені(салатні) культури
grill – смажити на рашпері (решітці)
groundcoffee – мелена кава
gullet – стравохід

H
haddock – пікша (вид тріски)
half (-ves) – половина (половини)
ham – шинка
halve – зменшувати наполовину
hamper – шкодити
harmful – шкідливий, побічний
hazelnut – фундук (лісовий горіх)
head – голова
healthy – корисний (для здоров’я)
herbal – трав’яний
herbalist – знавець трав
herring – оселедець
hemoglobin – гемоглобін
homogenization – гомогенізація
homogenizedmilk – гомогенізоване молоко
honey –мед
horse-radish – хрін
huge – величезний
hull – шкарлупа, шолуха
hunger – голод
behungry – бутиголодним

I
icy – льодяний, холодний, як лід
include – включати
inedible – неїстівний
ingredient – інгредієнт, складовачастина
injure – шкодити, руйнувати
inorganic – неорганічний
insoluble – нерозчинний
invite – запрошувати
iodine – йод
ion – іон
iron – залізо
irregular – нерегулярний, неправильний, непостійний
isolated – ізольований

J
jam – варення, джем
jar – банка
jelly – желе
jetlag – порушення добового режиму організму
job – робота, праця
join – приєднуватися, вступати
juice – сік
juicy – соковитий
junkfood – нездорова (жирна) їжа

K
keen (on) – дужебажатичогось
keep – зберігати
kernel – зерно
kidney – нирка
kitchen – кухня
kiwi – ківі
knock – стукати

L
lactose – лактоза (молочнийцукор )
lamb – м'ясомолодогобаранчика
lard – сало, смалець
large – великий
layer – шар
lb (libra) – фунт (дорівнює 0,41 кг )
leafy – листковий
lean – пісний
lettuce – салат
lid – кришка
light – легкий
lime – лайм
liquid – рідина
litter – сміття
liver – печінка
liveroil – риб’ячийжир
lobster – омар
low – calories –низькокалорійний
lump – грудочка (цукру )
lungs – легені

M
macaroon – мигдальне печиво
macaroni – макарони
mackerel – макрель, скумбрія
main – головний
maize – кукурудза
malt – солодовий напій
mango – манго
manufacture – виробництво
margarine – маргарин
marmalade – варення, повидло, мармелад
marshmallow – зефір
mayonnaise – майонез
meal – їжа, вживання їжі
melon – диня
melt – танути
microelement – мікроелемент
microorganism – мікроорганізм
milk – молоко
millet – просо, пшоно
mint – м’ята
mix – змішувати
mixture – суміш
muscular – м’язовий
mushroom – гриб
mustard – гірчиця
 mutton – баранина
mutton – баранина
N
natural – природний, натуральний
nectarine – нектарин
need–потреба, потребувати
numerous – численний
nut – горіх
nutrient – поживна речовина
nutrition – харчування
nutritional, nutritive – поживний

O
oat – овес
obtain – одержувати, отримувати
oil – олія
olive – маслина, олива
on the average – усередньому
onion – цибуля
onsale – упродажу
order (n;v) – замовлення; замовляти
origin – походження
overall – загальний
oyster – устриця

P
palatable – смачний, приємнийнасмак
pan – каструля
parsley – петрушка
pasta – паста, здобнетісто, пастила, клейстер
pastry – кондитерськівироби
pea – горох
peach – персик
peanut – землянийгоріх, арахіс
pear – груша
pearlbarley –перлова крупа
peel – чистити, лущити, зніматишкірку
pepper – перець
pickle – маринувати, солити
picnic – пікнік
pie – пиріг
pig – свиня
pineapple – ананас
pinto – плямистий
pippin–пепінка (сорт яблук)
pizza – піца
plain – простий
plant – рослина
plateaus - тарілочки
plum – слива
poison – отрута
poisonous – отруйний
pomegranate – гранат
pork – свинина
porridge – (вівсяна) каша
pot – казанок, кухоль
potato – картопля
poultry – свійська птиця
pound – фунт (=0,41 кг)
pour – лити(ся), полити
pourout – витікати
prepare – готувати, приготувати
preservation – зберігання, консервування
pretty – досить
produce – виробляти
profitable – сприятливий
prolific – плодючий
prune – чорнослив
pulp – м’якость
pumpkin – гарбуз
pure – чистий
put – покласти

Q
quality – якість
quantity – кількість
quarter – чверть
quiet – спокійний
quince – айва
quite – цілком
quit – кидати

R
radiation – радіація
radish – редиска
raisin – родзинка
raspberry – малина
rare – рідкісний
ration – раціон
raw – сирий
refreshment – закуска і напої
refrigerator – холодильник
require – вимагати
requirement – потреба
restaurant – ресторан
restore – відновляти
restriction – обмеження
retain – зберігати
rib – ребро
rice – рис
rich – жирний
ripe – стиглий
ripen – визрівати, дозрівати
roasted – смажений
rock-fish – морськийокунь
roll – булочка
root – корінь, коренеплід
round – круглий
run – керувати
rural style – сільський стиль
rush – зростання
rye – жито

S
salad – салат
salami – салямі
sale – продаж
salmon – лосось
salt – сіль
sardine – сардина
sauce (n;v) – соус; приправляти соусом
saucepan – каструля
saucer – блюдце
sausage – ковбаса, сосиска
save – берегти
savouryflavour – духмяний, пікантний аромат, смак
scaldedcream – заварний крем
scalefish – чистити рибу від луски, лускати рибу
scallop – гребінець (молюск)
seafood – морські продукти
seasoning – присмака, приправа
seed – насіння
seek – шукати
serve – подавати, обслуговувати
serving – порція
sesame – кунжут
setting – згущення,загустіння
sheep – вівця
shell (n;v) – шкарлупа; очищати від шкарлупи;
shrimp – креветка маленька
sieve – решето
simmer – варити на малому (повільному) вогні
sink – раковина
slice (n;v) – скибка, кусень; різати тоненькими шматочками
slim – стрункий
smell (n;v) – нюх, запах; відчувати запах, нюхати, пахнути
smoke – коптити
smoked – копчений
smooth – гладкий
snack (n;v) – закуска, перекусити
soft – м’який
soggy – просочений
soluble – розчинний
solubility – розчинність
olution – розчинник
solvent – розчин
soup – суп
sour – кислий
sour cream – сметана
sparkling – іскристий
species (sing; plur) – сорт, вид (види, сорта)
spinach – шпинат
spoon – ложка
sprinkle – посипати
sprouts – брюссельськакапуста
squash – кабачок
squeeze – чавити, давити
squid – кальмар
st = stone (1st = 6,36 кг )
starch – крохмаль
steak – стейк, шматокм’ясачирибидлясмаження
steam – варитинапарі
steep – просочувати
stew – тушкувати (м'ясо, овочі, фрукти тощо )
sticky – липкий
stir – розмішувати
stomach – шлунок
store – зберігати, запасати
stove – піч
strawberry – полуниця
stuff – начиняти
substance – речовина, субстанція
sugar-beet – цукровий буряк
sunflower – соняшник
supper – вечеря
supplement – добавка (харчова)
sweet – солодкий
sweetener – підсоложувач

T
taint – псувати
takeaway – ресторан, де беруть їжу додому
tangerine – мандарин
tart - пиріг
taste (n; v) – смак; дегустувати, куштувати
tea – чай
tea – pot – чайник (для зварки)
tender – ніжний, м’який
thyme - чебрець
tinned – консервований
tough – твердий, жорсткий
toxic – токсичний
toxicity – токсичність
tray – таця
treat – приготування, частування
treatment – обробка, ставлення, поводження
trout – форель
tuna – тунець
tureen - супниця
turkey – індичатина
turnip – ріпа

U
undernutrition – недоїдання
understand – розуміти
unusual – незвичний
urgent – нагальний
urn – електричнийсамовар
use (n; v) – застосування; застосовувати, вживати
useful – корисний
utensils – приладдя (кухонне)

V
valuable – цінний
valuate – оцінювати
vanilla – ваніль, ванільний
variety – різноманітність
veal – телятина
vegetable – овоч
vegetarian – вегетаріанець; рослинний, овочевий
venison – оленина
vinegar – оцет
visitor – відвідувач
vitamin – вітамін
volume – об’єм
vomit – блювати
vulnerable – вразливий

W
wafers – вафлі
waiter – офіціант
waitress – офіціантка
walnut – волоський горіх
water – вода
wet – сирий; зволожувати, змочувати
weight – вага
wheat – пшениця
whey – сироватка
whip – збивати (вершки)
whisky – віскі
white – білий; білок (яйця)
wholemilk – незбиране молоко
wildgame – дичина
wine – вино
wipe – витирати
wrap – загортати

Y
yeast – дріжджі
yield (n; v) – урожай, збірплодів, виробіток, вихід (продукції); виробляти, давати (врожай)
yogurt – йогурт
yolk – жовток (яйця)
yum! – чудово!
REFERENCES
1. Кухарська В.Б. Навчальний посібник для студентів харчових спеціальностей. – Київ: Інкос, 2012.- 352с.
2. Є.С. Смірнова, Л.В. Юрчук Англійська мова для студентів технологічних спеціальностей та сфери обслуговування харчової промисловості: Навч.-метод. посіб. – К.: НУХТ, 2012.-232 с.
3. Карпюк О.Д. Англійська мова: Підручник для 11-го класу загальноосвітніх навчальних закладів. Рівень стандарту. - Тернопіль: «Видавництво «Астон», 2019.- 256 с.
5.https://www.fruitsinfo.com/spring-fruits.html#api
6. https://forum.say7.info/topic6024.html
7. http://rep.btsau.edu.ua/bitstream/BNAU/4903/3/inozemna_mova.pdf
1


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку