Методична розробка на тему «Medicines and their forms».
Розробку укладено для тих, хто вивчає англійську мову за професійним спрямуванням в галузі медицини.
У роботі медичного працівника знання лікарських засобів є одним з найважливіших моментів у професійній діяльності. Вивчення даної теми допоможе студентам-медикам покращити свої знання лікарських форм, способи та особливості їх застосування.
Міністерство охорони здоров’я України
Комунальний заклад «Бериславський медичний фаховий коледж»
Херсонської обласної ради
Методична розробка
на тему «Medicines and their forms».
Викладач: Запорожець О.М.
Розглянуто, схвалено на засіданні циклової комісії
гуманітарної та соціально-економічної підготовки
Протокол № 2 від «29» жовтня 2024 р.
Голова циклової комісії ____ОЛЕНА Запорожець
Берислав 2024 р.
Тема: Medicines and their forms
Курс: І (I семестр)
Спеціальність: «Сестринська справа», «Лікувальна справа».
Кількість навчальних годин : 2
Тип заняття : формування знань, умінь і навичок.
Актуальність: У роботі медичного працівника знання лікарських засобів є одним з найважливіших моментів у професійній діяльності. Вивчення даної теми допоможе студентам-медикам покращити свої знання лікарських форм, способи та особливості їх застосування.
Мета:
Навчальна: ознайомити з лексичними одиницями теми та навчити їх використовувати в усному та писемному мовленні; вчити складати речення для опису та призначення ліків;
Практична: практикувати навички монологічного та діалогічного мовлення в рамках теми, навички аудіювання, читання та письма;
Розвиваюча: розвивати мовленнєву гнучкість та критичне мислення; формувати вміння пошуку та відтворення нової інформації в рамках теми;
Виховна: формувати навики здорового способу життя; виховувати толерантне ставлення до людей та любов до обраної професії.
Тип заняття: практичне
Навчальне забезпечення:
- Англійська мова для медсестер = English for nurses / David Austin, Tim Crosfield. – К.: Медицина, 2011. – 176 с.
- Захарчук І. Англійська мова. Здоров’я: Підручник. – 2-е вид., стер. – К.: Медицина, 2007. – 176 с.
- Саблук А.Г. English for medical students – Англійська мова для студентів-медиків: підручник / А.Г. Саблук, Л.В. Левандовська. – К.: ВСВ «Медицина», 2012. – 575 с.
- Інтерактивна вправа - https://learningapps.org/display?v=pa6gddd1524
- Відеоролик - https://learningapps.org/display?v=pa6gddd1524
PROSEDURE
I. GREETING AND AIM
1. Greeting.
2. Warm up.
- Look at these notes and match the “five rights” (1-5) to illustrations A-E.
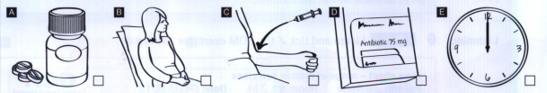
1. right patient 3. right medication 5. right route
2. right time 4. right dose
- Why it is important to remember “five rights of medications”?
Today we’ll talk about medicines, their forms and applications.
II. THE MAIN PART
1. Read and determine what is the difference between drug, medicine and remedy?
Drug: drugs usually have a bad connotation, as they are usually associated with illegal drugs. However, when you are talking about prescription medication you may call them prescription drugs.
Medicine: this is the most general term for any type of medication.
Remedy: this is usually not used when describing everyday medicine like cold or allergy medicine. This is usually used to describe treating diseases like cancer or diabetes, more serious illnesses. Remedy is also sometimes used metaphorically, like “She was the remedy for my broken heart”.
2. Vocabulary presentation.
powder - порошок
tablet - таблетка
dose - доза
dosage - дозування
pill - пігулка
ointment - мазь
suppository - свічка
globule - пілюля
ampule - ампула
solution - розчин
tincture - настійка
infusion - настій
decoction - відвар
drops - краплі
medicine - ліки, медикамент
drug - ліки, лікарський препарат; наркотик
medication - лікарський засіб
remedy - засіб; ліки
poison - отрута
signature - підпис
at the chemist’s – в аптеці
single dose - разова доза, на один прийом
a total dose - загальна доза
dosed drugs - дозовані ліки
drug administration - призначення/застосування ліків
drug action - дія ліків
overdosage of medicines - передозування ліків
healing ointment - лікувальна мазь
cough mixture - мікстура від кашлю
nasal drops - краплі в ніс
cod liver oil - риб’ячий жир
sleeping draught - снодійний засіб
adhesive plaster - лейкопластир
doctor’s prescription - рецепт (призначення) лікаря
teaspoonful (tablespoonful) - чайна (столова) ложка
3. Vocabulary practice.
1) Interactive exercise.
Match the words with illustrations.
https://learningapps.org/display?v=pa6gddd1524
2) Work in pairs. Match the forms from vocabulary to these routes. You can use some words more than once.
1. (into the) ear __________ 6. (into the) rectum _________
2. (into the) eye __________ 7. (on the) skin _____________
3. (by) mouth ____________ 8. (under the) skin __________
4. (into the) muscle _______ 9. (under the) tongue _______
5. (into the) nose__________ 10. (into the) vein __________
3) Complete the sentences with the words given below.
1.He often uses ... 2. She gave her son ... 3.1 take these ... and... three times a day. 4. She applies ... on his back. 5. The nurse makes ... 6. She has a weak heart and she’s got... at the chemist’s.
(mustard plaster, injections, vitamins, cod liver oil, heart drops, tablets and powders)
4. Listening 1.
1) Listen to four nurses talking about medication and tick ![]() the medical problem for each patient.
the medical problem for each patient.

|
1. Katy |
heart problems |
ear infection |
nausea |
skin rash |
|
2. Ted |
heart problems |
ear infection |
nausea |
skin rash |
|
3. Mrs. Fox |
heart problems |
ear infection |
nausea |
skin rash |
|
4. Ali |
heart problems |
ear infection |
nausea |
skin rash |
2) Listen again and complete this table.
|
|
Medication form |
Route |
|
Katy |
|
|
|
Ted |
|
|
|
Mrs. Fox |
|
|
|
Ali |
|
|
5. Reading.
1) Read and translate the following text.
CLASSIFICATION AND MAJOR CHARACTERISTICS OF DRUGS
A drug or medicine is any substance or mixture of substances which is taken into the body for the purpose of improving one’s physical or mental condition. In the past, medicines were usually mixtures of many plants and mineral substances, prescribed in Latin by physicians and made up by pharmacists into elixirs, powders or ointments that were often strange smelling and tasting. Today we live in an entirely different era of drugs and medicines.
Rarely are prescriptions written in Latin and reraly does the pharmacist himself prepare the drugs. Instead, most medicines are manufactured in large quantities in the form of tablets, capsules, timereleased particles, creams, suppositories and liquids for oral use or injection. Production, distribution and availability of each type of drug is controlled by legislation dating back to the first half of this century, although new laws continue to be made.
Nowadays, before a drug is introduced on the market, it must meet stringent standards of safety and effectiveness, since it may be used by millions. To determine whether it does meet these requirements, it is first tested in many animals and later in human volunteers and persons with specific diseases which the drug is designed to treat.
All drugs can be grouped according to the action they possess. The main groups are:
- Antiseptic and disinfectants kill bacteria by poisoning them.
- Expectorants are used for assisting in coughing by reducing the irritation of throat.
- Cough mixtures are used to suppress coughing.
- Laxatives make the bowels move.
- Analgesics soothe or relieve pain.
- Tonics are taken to strengthen the body and immune system.
- Application for skin and mucous membrane includes ointments, lotions, and liniments.
The drugs can be classified according to their form. The main groups are:
- Pill is a small ball or tablet of medicine for swallowing whole.
- Tablet is a small shaped piece of compressed medicine.
- Ointment is a semi-solid medicinal preparation made from oil or fat and used on the skin.
- Tincture is alcoholic or hydroalcoholic solution.
To add that list we can’t but mention decoctions, solutions, infusions, powders, and suppositories.
The major characteristics of drugs are:
- Therapeutic effect is a selective action on an organ.
- Side effects are an undesirable action (nausea, vomiting, and rash, etc).
- Allergic reaction is an expected individual reaction.
To these we can add indication, shelf life, and storage condition.
Drugs are most commonly can be administered in a number of ways:
- Orally, as a liquid or solid, that is absorbed through the stomach.
- Inhaled, (breathed into the lungs), as a vapour.
- Parentarally (by injection): intramuscular, intravenous.
- Rectally as a suppository, that is absorbed by the colon.
- Vaginally as a suppository, primarily to treat vaginal infections.
- Topically as applications for the skin.
Many drugs can be administered in a variety of ways.
2) Answer the following questions.
1. Can you find the definition of a drug given in the text?
2. How did medicines look like in the past?
3. Are most medicines manufactured nowadays? In what forms?
4. By whom is production, distribution and availability of drugs controlled?
5. What happens before a drug is introduced on the market?
6. In what two groups can the drugs be classified?
7. What is the action of antiseptics?
8. What are expectorants used for?
9. What are the applications?
10. What forms of drugs do you know?
11. Can you describe the major characteristics of drugs?
12. How are drugs administered?
3) Are the following sentences true (T)or false (F)?
1. In the past, medicines were made up by pharmacists into elixirs, powders or ointments.
2. Today pharmacist in the chemist’s himself prepare all the drugs.
3. Nowadays drugs are first tested in animals and later in human volunteers before they are introduced on the market.
4. All drugs can be grouped according to the action they possess.
5. Laxatives soothe or relieve pain.
6. Tonics are taken to strengthen the body and nervous system.
7. Tablets, ointments, powders, suppositories are the forms of drug.
8. Side effects are desirable action of a drug.
9. Drugs are most commonly administered orally, parentarally, rectally, topically and by inhalation.
4) Translate into English.
придушувати кашель;
зменшувати біль;
слизова оболонка;
водно-спиртовий розчин;
небажана дія;
очікувана індивідуальна реакція;
умови зберігання
6. Speaking.
1) Make up sentences using the following word combinations.
to take a powder for...
to take a tablet three times a day
to take a pill after (during, before) meal
to put an ointment on...
to keep suppositories in a cool place
to wash hands before using globules
to keep ampules in a dark place
to read doctor’s instructions before giving a solution
to shake a bottle with a mixture before use
to take an infusion
to give a decoction four times a day before meal
to keep drops in a dark place
to take twenty drops of a tincture
to take a teaspoonful on an empty stomach
to take a tablespoonful of...
to give a prescription
to prescribe medicine (treatment)
2) Read and act out the dialog.
Father: Doctor, when I came home, I found my little son asleep. At first that seemed normal, but when I entered the bathroom there was a bottle of my wife’s sedative on the floor. I’m afraid the child took some of it.
Doctor: Do you know what kind of sedative1 it was?
Father: No, doctor. I only know it was one of sedatives. Here it is.
Doctor: Well, it is better to do stomach washing2. Nurse, have everything ready for stomach washing.
III. THE ENDING
1. Listening 2.
Watch a short video clip which illustrating the process of making medicines and retell it.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RY7uS9bm3Zk
2. Home task.
1) Learn the vocabulary.
2) Communicative situations.
1. Describe the chemist’s where you usually buy medicines.
2. Make up a dialog between a customer and a chemist.
3. Give instructions for administration of any drugs.
4. You are not feeling quite well. You go to the chemist’s and ask the chemist to give you some tablets.


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
