Методична розробка заняття The Nature of Matter.The Basic Constituents of Matter з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)»
Лисичанський промислово-технологічний фаховий коледж

THE NATURE OF MATTER. THE BASIC CONSTITUENTS OF MATTER
методична розробка
з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)»
в закладах фахової передвищої освіти
Розробник: Скиба Н.М., старший викладач, викладач вищої категорії Лисичанського промислово-технологічного фахового коледжу
2022
ВСТУП
Методична розробка заняття The Nature of Matter.The Basic Constituents of Matter виконана у відповідності з методичними рекомендаціями з підготовки та проведення практичних занять у закладах фахової передвищої освіти. Заняття підготовлено відповідно до робочої і навчальної програми з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)» спеціальності 133 «Галузеве машинобудування» за освітньо-професійною програмою «Обслуговування та ремонт обладнання підприємств хімічної та нафтогазопереробної промисловості». У методичній розробці заняття подано розгорнутий план-конспект заняття у формі мовного практикуму з використанням методу критичного мислення, методики роботи з лексичним матеріалом, методу лінгвістичного квесту, рольовою грою, перелік необхідного обладнання, мету і задачі, надано чітку структуру заняття, вдало подано мотивацію пізнавальної діяльності студентів.
Розробка містить багато різноманітних форм та методів роботи (бесіду, читання, мозковий штурм, групову та парну роботу, що відповідають індивідуальним особливостям студентів і сприяють успішному досягненню мети заняття.
Методична розробка заняття відповідає теоретичному й методико-практичному розділам навчальної програми, має інноваційний характер, відповідає новітнім технологіям навчання, спрямована на формування комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців, розвиток пам'яті, уваги, фонематичного слуху студентів, сприяють зацікавленості та формуванню комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців.
Методична розробка може бути рекомендована для викладачів іноземної мови в закладах фахової передвищої освіти в якості як основного, так і довідково-дидактичного матеріалу.
МЕТОДИЧНА РОЗРОБКА ЗАНЯТТЯ
Заняття №
Предмет: Іноземна мова
Група:
Тема заняття: The Nature of Matter.The Basic Constituents of Matter
Мета: формувати лексичні навички й навички вимови; вдосконалювати навички читання й усного мовлення; розвивати мовну здогадку й мовленнєву реакцію; виховувати зацікавленість у розширенні своїх знань, використовувати раніше вивчені структури, а також збагачувати словарний запас, практикуватися у перекладі речень, розвивати навички логічного викладання думок, пам'ять, виховувати свідоме ставлення до навчання, вчити раціонально використовувати свій час, прищеплювати бажання вивчати іноземну мову.
Обладнання: словники, комп’ютер, роздавальний матеріал
Тип заняття: практичне
Міжпредметні зв'язки: Фізика, Обладнання підприємств нафтохімічної галузі, Матеріалознавство, Електротехніка, Процеси та апарати, Комп’ютерна техніка та прикладне програмне забезпечення, Основи автоматизація технологічних процесів, Комп’ютерна графіка
СТРУКТУРА ЗАНЯТТЯ:
1.Організаційний момент:
1)Привітання
2) Перекличка
3)Перевірка готовності до заняття
2. Мотивація навчальної та пізнавальної діяльності студентів, оголошення теми та цілей заняття.
3.Реалізація теми за планом
4. Підсумок заняття. Оцінювання
5. Домашнє завдання
ХІД ЗАНЯТТЯ:
- Find out the words in the dictionary. Write them down and learn.
|
various, substance, evidence, to compose, tiny, a particle, a molecule, to exert, a force, nucleus (nuclei), to interact, to be neglected, to be provided, charge |
II. Read the text: The Nature of Matter. The Basic Constituents of Matter. Use a dictionary, if necessary.
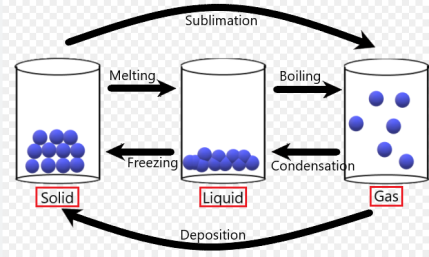
Physics is concerned with studying the properties of matter, forces, and energy and their various interactions. In trying to understand the behavior of solids, liquids, and gases physicists regard substances in terms of their basic constituents.
Experimental evidence supports the idea that matter in all three possible phases is composed of tiny particles, called molecules, which are continuously in motion. For any given single substance, the molecules are identical in mass, structure, and other properties. All molecules in a substance exert a force on each other.
Molecules consist of groups of atoms, which themselves consist of electrons and nuclei. In solids and liquids, the molecules move relatively slowly and they therefore interact fairly strongly. But in the study of gases, the molecular force can often be neglected because the molecules are, on average, widely separated and interact relatively briefly. Despite the minuteness of molecules, evidence of their existence is provided by various phenomena, such as Brownian motion.
Just as substances can be broken down into molecules, molecules can be broken down into atoms. An atom is the smallest particle that can represent a particular chemical element.
There are three types of particles that can be considered as making up a typical atom. Central nucleus is comprised of neutrons and protons. The neutron is a particle with no electrical charge, whereas the proton has a single positive charge. Both have roughly the same mass. Circulating about this central region, held in orbit under the influence of the proton’s positive charge, are the electrons. These are subatomic particles, each with a single negative charge and an extremely small mass.
Electrons play a major role in determining the properties of the various elements.
III. Distribute the words into four columns and translate them.
|
Model: |
What? |
What kind of? |
What to do? |
How? |
|
|
use |
useful |
to use |
usefully |
|
What? |
What kind of? |
What to do? |
How? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
relatively, evidence, various, fairly, particle, exert, neglect, roughly, motion, possible, minuteness, subatomic, interact, widely, phenomenon, misunderstand, substance, briefly, average, provide, compose, property, continuously, molecular, behavior, identical, nuclei, particular, influence, move, extremely
IV. Find the sentences that can’t be found in the text
- Physics is concerned with studying various phenomena in nature.
- Matter in all three possible phases is composed of tiny particles called molecules.
- Evidence of the existence of molecules is provided by various phenomena, such as Brownian motion.
- Every substance or material can be divided into particles known as molecules.
- Just as substances can be broken down into molecules, molecules can be broken down into atoms.
- An atom is the smallest particle that can represent a particular chemical element.
- In a stable atom, the total positive charge of the nucleus is equal to the total negative charge of the electrons.
- The neutron is a particle with no electrical charge, whereas the proton has a single positive charge.

V. Translate the following word combinations into Ukrainian
- evidence of the existence
- three types of particles
- the influence of the positive charge
- the properties of the element
- a model of the atom
VI. Fill in the missing words.
- Physics is concerned with studying the ___ of matter, forces and energy.
- Experimental ___ supports the idea that matter in all three phases is composed of ___, called molecules.
- For any given single ___, the molecules are identical.
- All molecules in a substance ___ a force on each other.
- In solids and liquids, the molecules move ___ slowly and therefore they ___ fairly strongly.
- Molecules can be broken down into ___.
- The ___ is a particle with no electrical charge.
VII. Match the lines with definition of the next word combinations
|
різні взаємодії |
trying to understand |
|
крихітні частки |
negative charge |
|
ідентичні за масою, структурою та іншими властивостями |
various interactions |
|
мати приблизно однакову масу |
matter in all three possible states |
|
підтвердження існування |
have approximately the same mass |
|
. у середньому |
tiny particles |
|
відносно повільно рухатися |
identical in mass, structure and other properties |
|
незважаючи на недовговічність |
influence by force |
|
матерія у всіх трьох можливих станах |
on average |
|
впливати силою |
revolving around the central region |
|
представляти окремо взятий хімічний елемент |
consist of electrons and nuclei
|
|
намагаючись зрозуміти |
under the influence of the positive charge of the proton |
|
обертаючись довкола центральної області |
represent a single chemical element |
|
негативний заряд |
relatively short interaction |
|
відносно коротко взаємодіяти |
|
|
складатися з електронів та ядер |
move relatively slowly |
|
відносно повільно рухатися |
confirmation of the existence of |
|
під впливом позитивного заряду протона |
despite the fragility |
VII. Fill in the prepositions, if necessary.
- Physics is concerned ___ studying the properties of matter, forces and energy.
- Molecules consist ___ groups ___ atoms
- But ___ gases, the molecular force can be neglected.
- Just as substances can be broken ___ ___ molecules, molecules can be broken ___ ___ atoms.
- There are three types ___ particles that can be considered as making ___ a typical atom.
- The neutron is a particle ___ no electrical charge.

VIII. Define whether the sentences are TRUE or FALSE.
- Physics is concerned with numbers, chemical reactions and different functions.
- All molecules in an atom exert a force on each other.
- Molecules consist of nothing. They are not dividable particles.
- In solids and liquids, the molecules move relatively slowly.
- An atom is the biggest particle that can represent a particular chemical element.
- There are 6 types of particles that can be considered as making up a typical atom.
- The neutron is a positively charged particle.
- Proton is a particle with no electrical charge.
IX. Practice with someone asking and answering.
- What is physics concerned with?
- In what way do physicists regard substances?
- What idea does experimental evidence support?
- Are the molecules identical only in mass for any given single substance?
- Do all molecules in a substance exert a force on each other?
- What do molecules consist of?
- How do the molecules move in solids and liquids?
- Why can the molecular force often be neglected in the study of gases?
- What provides evidence of the existence of molecules?
- Into what constituents can molecules be broken down?
- What is the smallest particle that can represent a particular chemical element?
- How many types of particles are there, particles that can be considered as making up a typical atom?
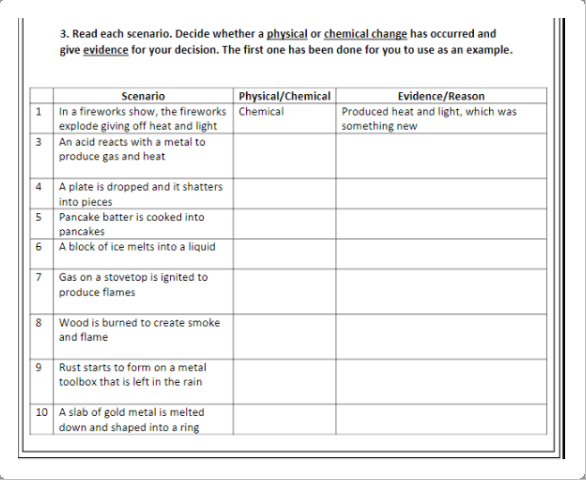
X. Activity box. Test your knowledge

4. Summarizing. Підведення підсумків уроку. Бесіда в режимі T-P1-P2.
T: What topic did we start discussing today? What did we read about? What new words and word combinations have you learned? What material was difficult/ interesting/boring? So, you all see where you need more practice and what you can do well.
5. Setting homework. Постановка домашнього завдання
T: Your home task guess the crossword using the active vocabulary of the lesson

1


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку

