План-конспект уроку в 11 кл. з теми: "Люди і екологія"
План-конспект уроку в 11 кл. з т: " Люди і екологія". На уроці розглядаються важливі екологічні проблеми людства. Тема заставляє учнів думати і висловлювати власну думку. На уроці використовуються інтерактивні методи роботи та різні комунікативні вправи
Урок англ.мови з теми: « People and Ecology » в 11 кл.
Вчитель: Ларіна Т.О ЗОШ I-III ст. №4, м. Жмеринка
Procedure
I. Introduction
- Greeting
Good afternoon, boys and girls!
I hope you are ready to work hard. Be calm and confident on your way to knowledge.
- Lead-in
We continue to study the topic “Environmental problems” and the subject matter of today’s lesson is “People and Ecology”.
Well, I think the fact that the Earth is unique doesn’t need to be proved, but it will be interesting to have a look at it from the space. Let’s imagine that we are somewhere in the space. Look out of the illuminator and see our native planet.
(Video “The smoked Earth”) Are you impressed? You see the Earth needs our understanding and help but not destruction. So, we try to discuss some of these problems today.
By the end of the lesson you’ll be able to express your feelings about the ecology, to give your arguments, to respond logically to your friends’ opinions.
- Warming-up
- Today the word “ecology” is on everybody’s lips. Nowadays people understand how important it is to solve the environment problems. Let's start with revising our topical vocabulary. Name the most serious ecological problems we are having now.
Ecological problems:
- water, land and air pollution;
- greenhouse effect;
- global warming;
- radiation;
- deforestation;
- litter problem;
- destruction of the ozone layer.
- Choose the best way to define the terms (the task is on the screen)
|
Pollution: |
|
|
Environment: |
|
|
Ecology: |
|
|
Greenhouse effect: |
|
- T: I suggest you a part of the Greenpeace message for today’s discussion:
“When the last tree is cut down and the last fish killed, the last river poisoned, then…” (Greenpeace message)
Let’s discuss some ecological problems and define the ending of this quotation.
T: Today we have a burning problem. It’s ecology. By the way, what does the word “ecology” mean?
P: I know the word ”ecology” came from Greek word which means “home”.
T: What are the sources of pollution? How are they divided?
P.: The sources of pollution are divided into two groups: natural sources and man – made or anthropogenic sources.
T: What are the natural sources?
P: The natural sources are volcano emissions, dust and sand storms, forest fires, floods.
T: What are the anthropogenic sources?
P: The anthropogenic sources are industrial enterprises, transport, domestic sources, logging etc.
T: Why is air pollution the most dangerous among all kinds of pollution?
P: Human beings can live several weeks without food, a few days without water but only some minutes without air.
T: What does air pollution cause?
P: Air pollution causes acid rains, a damage of the ozone layer, a greenhouse effect, changes in the climate, melting of the glaciers, different diseases.
II. Main part
- Check-in homework
- First you had to replace the words in bold with a synonym using the words in the box.
|
extinct habitats threatening issue captured forested conservation prevent approaches to |
|
|
1. Sally is keen of environmental protection. She wants to save the Earth. |
|
|
2. We must stop our planet from being completely destroyed. |
|
|
3. Animals should be allowed to live in their natural homes. |
|
|
4. More and more animals are being caught and put in zoos. |
|
|
5. Many species of wild animals are no longer in existence. |
|
|
6. The environment is a (an) topic which everyone should know about. |
|
|
7. Tree-covered areas are in danger of disappearing completely. |
|
|
8. Water pollution is endangering sea life. |
|
|
9. We need to find more effective methods of dealing with pollution. |
|
- Your second task was to match the words in the list with the nouns.
|
cid greenhouse factory nuclear oil breeding conservation environmental forest endangered national thick |
||
|
…………………species |
…………………….parks |
……………………..smog |
|
…………………rain |
…………………….waste |
……………………..spills |
|
…………………emissions |
…………………….programmes |
……………………..fires |
|
…………………awareness |
…………………….areas |
……………………..gases |
T: Which of the collocations are used to describe “threats to the environment”?
P: They are: endangered species, acid rain, factory emissions, nuclear waste, thick smog, oil spills, forest fires, greenhouse gases.
T: Which describe “possible ways to solve environmental problems”?
P: They are: environmental awareness, national parks, breeding programmes, conservation areas.
- And the third task was to make some sentences using our grammar “The Second Conditional”. This list includes possible solutions to the ecological problems, so read your sentences.
- use bicycles
- stop using aerosols
- plant new trees
- stop polluting the environment
- create special parks for animals
P: If we used bicycles, we would have less air pollution.
P: If people stopped using aerosols, it would help the environment.
P: If we planted new trees, rainforests wouldn’t disappear.
P: If people stopped polluting the environment, the world would be a safer place.
P: If we created special parks for animals, they wouldn’t be in danger.
- Grammar point
It’s high time to practice grammar. We can use the Second Conditional to talk about 'impossible' situations. Notice that after I / he/ she /it we often use 'were' and not 'was'.
- If I were you, I would go there.
- If she were really happy in her job, she would be working much harder.
Let’s practice our grammar in reading and speaking activities.
- Reading and Speaking
The aim of this part of the lesson is to teach you to find out and appreciate the information, analyze it and draw conclusions using your logical thinking.
1) Pre-reading activity:
Look at the screen. There are some little texts there. Skim the texts and answer the question “What ecological problems are children talking about?”
While-reading activity:
Read what each person says.
Post-reading activity:
Answer the questions:
- Why can Roberta hardly breathe when she’s riding her bike?
- What does acid rain kill?
- What would happen if public transport were better?
- What will happen if hunters continue to kill endangered species?
- What happens when trees disappear?
- What do trees produce? Why is it important to us?

Scan the texts and fill in the correct word:
|
T: What would you do if you were the leader of your country?
P1: If I were the leader of my country, I would…
2) Pair Work
Read the descriptions and match them with the problems listed (on the screen).
Problems: litter (C), urban sprawl (A), deforestation (E), acid rain (D), water contamination (F), destruction of the ozone layer (B).
Now in pairs discuss the causes and the results of these problems. Start with: The problem of….is caused by… As a result….

3) Group Work
T: Now let’s work in small groups.
Read the table, then discuss the problems and their effects, express your agreement and suggest the solutions. Don’t forget that you are a group and everyone must take part in work and speak in the presentation.
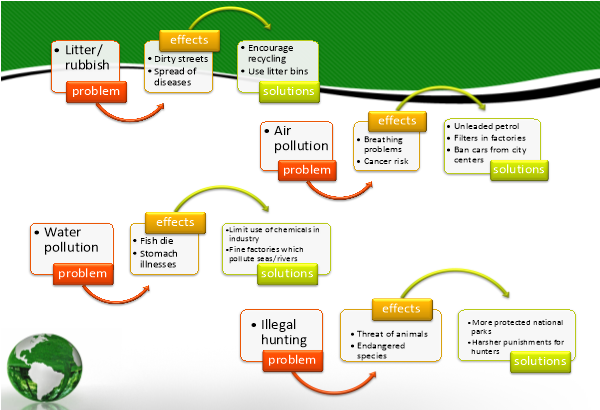
T: Thank you for your work. It was excellent but I have one more task for you.
- Listening
T: Have you ever heard about a global organization “Greenpeace”? What is its goal?
P: The goal of this organization is to protect our planet’s environment.
1) Pre-listening activity:
T: Let’s listen to the story about Greenpeace.
Look at the blackboard, there are some words and word-combinations. Pay attention:
- to bear witness – свидетельствовать
- sea otters – морские выдры
- а bald eagle – белоголовый орел
- а peregrine falcon – сокол-сапсан
- to spark a flurry – вызвать шквал(эмоций)
- a bird sanctuary – птичий заповедник
- Amchitka – геогр. остров у берегов Аляски
Before listening read the following statements and try to guess the answers.
Give me your opinions, but the correct answers you will check up while listening.
|
2) While-listening activity:
Now listen to the story, you can make your notes and then underline the correct word and check your opinions.
T: Have you guessed all the words?
3) Post-listening activity:
Listen again and say what Greenpeace is. Answer my questions:
1. When and where did a small team of activists set sail?
2. What was the mission of these activists?
3. What was the result of their journey?
4. What can you say about Greenpeace today? (3answers)
5. What is the main goal of Greenpeace?
III. Summary
- Reflection
T: At the beginning of the lesson I have proposed you a part of the Greenpeace message:
“When the last tree is cut down and the last fish killed, the last river poisoned, then …” (Greenpeace message)
T: Please give your own ending of this quotation.
T: Look at the screen, there is a whole Greenpeace message there:
“When the last tree is cut down and the last fish killed, the last river poisoned, then you will see that you cannot eat money” (Greenpeace message)
T: Do you agree with it?
- Marks
- HW
Your home task for the next lesson will be to find out some information about our region’s ecological problems.
You can work in groups. The first group can collect information about water pollution, the second one – about air pollution, the third one – about land pollution, and the last one – about endangered species in our region.
T: I hope you understand that the problem of pollution doesn’t have any borders and we have to protect nature in all the countries, in the whole world.
Our lesson is coming to the end and I want to thank everybody who took part in our work. Our work was great and we’ll continue it in our next lessons.
HO-1(Key)
|
extinct habitats threatening issue captured forested conservation prevent approaches to |
|
|
1. Sally is keen of environmental protection. She wants to save the Earth. |
conservation |
|
2. We must stop our planet from being completely destroyed. |
prevent |
|
3. Animals should be allowed to live in their natural homes. |
habitats |
|
4. More and more animals are being caught and put in zoos. |
captured |
|
5. Many species of wild animals are no longer in existence. |
extinct |
|
6. The environment is a (an) topic which everyone should know about. |
issue |
|
7. Tree-covered areas are in danger of disappearing completely. |
forested |
|
8. Water pollution is endangering sea life. |
threatening |
|
9. We need to find more effective methods of dealing with pollution. |
approaches to |
HO-2 (Key)
|
acid greenhouse factory nuclear oil breeding conservation environmental forest endangered national thick |
||
|
endangered species |
national parks |
thick smog |
|
acid rain |
nuclear waste |
oil spills |
|
factory emissions |
breeding programmes |
forest fires |
|
environmental awareness |
conservation areas |
greenhouse gases |
HO-3(Key)
- Having more buses would improve public transport in cities.
- Heavy traffic causes a lot of air pollution.
- If we created more parks in our cities, they would be nicer places to live in.
- It’s so polluted I can’t breathe properly.
- Many people hunt endangered species for their fur.
- Acid rain destroys plants.
Pair work

Group work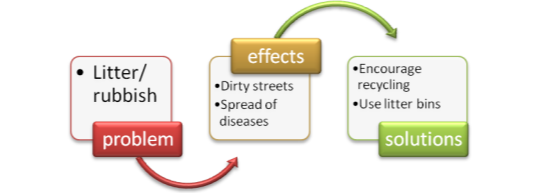
- –Dropping litter can cause dirty streets. –That’s true. I think we should use litter bins instead of dropping litter carelessly. –That’s a good idea. To stop pollution, I think we should encourage industries to use cleaner methods of production. – In addition, we also could recycle more of our waste, so there would be less rubbish.
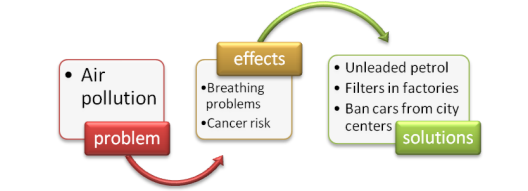
- –Air pollution can cause serious breathing problems. – That’s true. And not only that, it can also cause disease like cancer. – I think that factories should have filters put in to reduce air pollution. – Banning cars from city centers is also a good idea. – I agree. We could also drive cars which run on unleaded petrol, then, air pollution in towns could be reduced.
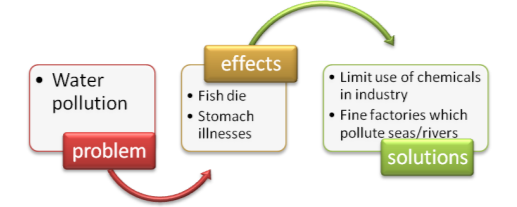
- – Water pollution can cause stomach illnesses. – That’s true. And not only that, but also many fish die. – I think that industries should stop using so many harmful chemicals. – I agree. Moreover, governments should fine factories which pollute the seas and rivers.
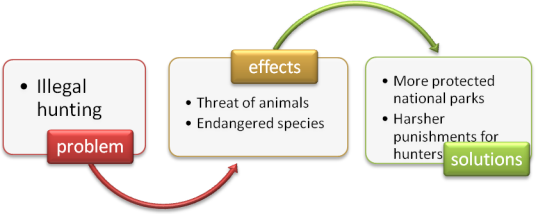
- – Illegal hunting can cause threat to animals. – That’s true. Animals are in danger because hunters kill them limitlessly. –I think governments should introduce harsher punishments for illegal hunters. –I agree. Governments could also help by creating more protected national parks. – Moreover, raising public awareness about endangered species is a good idea.
HO-4(Key)
- A small team of activists set sail from Vancouver, Canada/the USA.
- Greenpeace is an international ecological/political organization.
- It campaigns to stop/to continue climate change.
- The goal of Greenpeace is to expose/to hide ecological criminals.
- It unites/separates people of different colours living in different continents and speaking different languages.
Listening
Greenpeace
In 1971, motivated by their vision of a green and peaceful world, a small team of activists set sail from Vancouver, Canada, in an old fishing boat. These activists, the founders of Greenpeace, believed a few individuals could make a difference.
Their mission was to «bear witness» to US underground nuclear testing at Amchitka, a tiny island off the West Coast of Alaska. Amchitka was the last refuge for 3000 endangered sea otters, and home to bald eagles, peregrine falcons and other wildlife.
The journey sparked a flurry of public interest. Nuclear testing on Amchitka ended the same year, and the island was later declared a bird sanctuary.
Today, Greenpeace is an international ecological organization that has 3 million supporters worldwide. Its headquarters are based in Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
Greenpeace unites people of different colours living in different continents and speaking different languages. The common mission of this organization is preserving life on the earth in its full variety.
Greenpeace does not support any political party. As a global organization, Greenpeace focuses on the most crucial worldwide threats to our planet's environment. It campaigns to stop climate change, save the oceans, stop whaling, say no to genetic engineering, stop the nuclear threat, and eliminate toxic chemicals. The mountaineers of Greenpeace hang the slogans “Stop acid rains”, “Pure rivers”, “Clean seas”, “Stop criminals”, “No fish, no future” on factories chimneys, on ships, on Big Ben, on the Statue of Liberty, on the Statue of Redeemer.
The goal of Greenpeace is to expose environmental criminals.


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
