Презентація "Сучасні педагогічні технології на уроках з іноземної мови – дизайн мислення"


![Дизайн-мислення: визначення поняття Інноваційна методологія, котра поєднує творчий та аналітичний підходи, базується на міждисциплінарних зв’язках та спрямована на задоволення потреб суспільства, шляхом генерування рішень, що характеризуються технологічною доцільністю та економічною життєздатністю [1, с.3-17]. В освітньому середовищі передбачає досвід трансформаційного навчання, що покликано допомогти учням розвити навички продукування креативних рішень та впевненості при вирішенні складних задач, базуючись на використанні аналогій між об’єктами та явищами та поєднанні практичного досвіду і абстрактної концептуалізації [2, с. 308]. Дизайн-мислення: визначення поняття Інноваційна методологія, котра поєднує творчий та аналітичний підходи, базується на міждисциплінарних зв’язках та спрямована на задоволення потреб суспільства, шляхом генерування рішень, що характеризуються технологічною доцільністю та економічною життєздатністю [1, с.3-17]. В освітньому середовищі передбачає досвід трансформаційного навчання, що покликано допомогти учням розвити навички продукування креативних рішень та впевненості при вирішенні складних задач, базуючись на використанні аналогій між об’єктами та явищами та поєднанні практичного досвіду і абстрактної концептуалізації [2, с. 308].](/uploads/files/1896060/217359/233353_images/3.jpg)
![антропоцентризм;наукове обґрунтування (використання спостереження, анкетування, занурення у середовище); розгляд явищ у сукупності їх взаємозв’язків з навколишнім середовищем; міждисциплінарність та співпраця між представниками різних галузей, відділів тощо;генерування на виході певного рішення-прототипу та його експериментальна перевірка на безпосередніх користувачах з метою виявлення недоліків та оцінки отриманих рішень. [2, с. 309]. Принципи, що лежать в основі дизайн мислення антропоцентризм;наукове обґрунтування (використання спостереження, анкетування, занурення у середовище); розгляд явищ у сукупності їх взаємозв’язків з навколишнім середовищем; міждисциплінарність та співпраця між представниками різних галузей, відділів тощо;генерування на виході певного рішення-прототипу та його експериментальна перевірка на безпосередніх користувачах з метою виявлення недоліків та оцінки отриманих рішень. [2, с. 309]. Принципи, що лежать в основі дизайн мислення](/uploads/files/1896060/217359/233353_images/4.jpg)

![стимулювання інтересу молоді до вивчення мови через ілюстрування застосування англійської на практиці;розвиток навичок критичного мислення, мисленнєвих операцій аналізу, синтезу, порівняння; створення суб’єкт- суб’єктної взаємодії учнів між собою; перетворення вчителя на фасилітатора навчального процесу ; створення позитивної атмосфери; сприяння прояву креативності, індивідуальності під час формулювання та розв’язання проблемних задач. [3, с.51] Педагогічний потенціал дизайн-мислення на уроках англійської мови стимулювання інтересу молоді до вивчення мови через ілюстрування застосування англійської на практиці;розвиток навичок критичного мислення, мисленнєвих операцій аналізу, синтезу, порівняння; створення суб’єкт- суб’єктної взаємодії учнів між собою; перетворення вчителя на фасилітатора навчального процесу ; створення позитивної атмосфери; сприяння прояву креативності, індивідуальності під час формулювання та розв’язання проблемних задач. [3, с.51] Педагогічний потенціал дизайн-мислення на уроках англійської мови](/uploads/files/1896060/217359/233353_images/6.jpg)




















![Brown T. 2009. Change by Design: How Design Thinking Transforms Organizations and Inspires Innovation / T. Brown. – New York : Harper. Collins Publishers L. L. C, 2009. – 272 p. Munyai K. A methodology towards sustainable problem solving in higher Education in South Africa [Electronic resource] / K. Munyai // International Association for the Development of the Information Society. – Regime of access : https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED571612.pdf Фурсенко Т. М. Сучасні підходи до викладання іноземної мови:дизайн-мислення / Т. Фурсенко // Наукові записки Вінницького державного педагогічного університету ім. М. Коцюбинського Список використаних джерел: Brown T. 2009. Change by Design: How Design Thinking Transforms Organizations and Inspires Innovation / T. Brown. – New York : Harper. Collins Publishers L. L. C, 2009. – 272 p. Munyai K. A methodology towards sustainable problem solving in higher Education in South Africa [Electronic resource] / K. Munyai // International Association for the Development of the Information Society. – Regime of access : https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED571612.pdf Фурсенко Т. М. Сучасні підходи до викладання іноземної мови:дизайн-мислення / Т. Фурсенко // Наукові записки Вінницького державного педагогічного університету ім. М. Коцюбинського Список використаних джерел:](/uploads/files/1896060/217359/233353_images/28.jpg)

Тема, над якою працюю: “Шляхи і засоби підвищення ефективності та комунікативності у навчанні англійської мови ”ПІБ Гриценко Олена Юріївна Рік народження 1964 Освіта: вища педагогічна, закінчила Київський державний інститут іноземних мов. Спеціальність за дипломом: вчитель англійської мови та літератури Стаж роботи: 31 рік Місце роботи: спеціалізована школа I-III ступенів з поглибленим вивченням англійської мови № 44 міста Києва. E-mail: school_44@ukr.net Персоналія
Дизайн-мислення: визначення поняття Інноваційна методологія, котра поєднує творчий та аналітичний підходи, базується на міждисциплінарних зв’язках та спрямована на задоволення потреб суспільства, шляхом генерування рішень, що характеризуються технологічною доцільністю та економічною життєздатністю [1, с.3-17]. В освітньому середовищі передбачає досвід трансформаційного навчання, що покликано допомогти учням розвити навички продукування креативних рішень та впевненості при вирішенні складних задач, базуючись на використанні аналогій між об’єктами та явищами та поєднанні практичного досвіду і абстрактної концептуалізації [2, с. 308].
антропоцентризм;наукове обґрунтування (використання спостереження, анкетування, занурення у середовище); розгляд явищ у сукупності їх взаємозв’язків з навколишнім середовищем; міждисциплінарність та співпраця між представниками різних галузей, відділів тощо;генерування на виході певного рішення-прототипу та його експериментальна перевірка на безпосередніх користувачах з метою виявлення недоліків та оцінки отриманих рішень. [2, с. 309]. Принципи, що лежать в основі дизайн мислення
вправляння учнів у всіх чотирьох видах мовленнєвої діяльності: читання (при пошуку необхідної інформації для аргументації своєї точки зору), письмо (для ведення «реєстру» запропонованих ідей, опцій, варіантів), говоріння (вираження власної точки зору, її аргументація), слухання (сприймання та розуміння висловлювання колег та опонентів);знаття мовного бар’єру;Педагогічний потенціал дизайн-мислення на уроках англійської мови
стимулювання інтересу молоді до вивчення мови через ілюстрування застосування англійської на практиці;розвиток навичок критичного мислення, мисленнєвих операцій аналізу, синтезу, порівняння; створення суб’єкт- суб’єктної взаємодії учнів між собою; перетворення вчителя на фасилітатора навчального процесу ; створення позитивної атмосфери; сприяння прояву креативності, індивідуальності під час формулювання та розв’язання проблемних задач. [3, с.51] Педагогічний потенціал дизайн-мислення на уроках англійської мови
{5 C22544 A-7 EE6-4342-B048-85 BDC9 FD1 C3 A}Factors Verbs Effects Our personal vehicles/airplanes/ cars To be a major cause of Global warming/ climate change/ pollution/ man-made damage to the environment Power plants / factories and plants/ homes with polluting heat systems.emit/ release/ produce a large portion of. Greenhouse gas emissions/ carbon dioxide/ heat-trapping gases / toxic materials and gases. Deforestation & Tree-Clearing. To bring about/ result in/ cause. Diminishment of an important carbon “sink”Agriculture & Farming To be highly dependent on (liquid) fossil fuel/ carbon-heavy natural gas/ coal
Tell the students that they are going to watch the video on global warming. While watching the video for the first time, give them the task to identify the meaning of the following words and word combinations. With weaker students it may be necessary to elicit the meaning of these phrases before listening. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j. IBBr. T9 F3 Wc To emit CO2 Emissions Heat trapping ability To disrupt a carbon cycle. Fossil fuels Soot 3. Listening
1. Global warming is not caused by human activities. 2. There are four greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, CFC. 3. They are dangerous because of heat reflecting capability.4. Carbon dioxide is a more serious threat than nitrous oxide, methane, CFC. 5. Open fires are half as dangerous as the combustion of fossil fuels. 6. Carbon dioxide is created when carbon combines with oxygen. 7. Aerosol cans are eco-friendly. Having watched the video for the second time, ask the students to identify whether the following sentences are true or false
4.1. Ask the students to choose from the given list stakeholders (a group of people who will benefit or may suffer losses from the implementation of the proposed solutions). Business entities involved in the power industry and industrial production. Consumers of goods and services. Banks and other financial institutions. The President and government Transportation industry Engineers The population of the planet as a whole. Fast-food industry Multinational corporations 4. Empathystyle.text. Decoration. Underlinestyle.text. Decoration. Underlinestyle.text. Decoration. Underlinestyle.text. Decoration. Underline
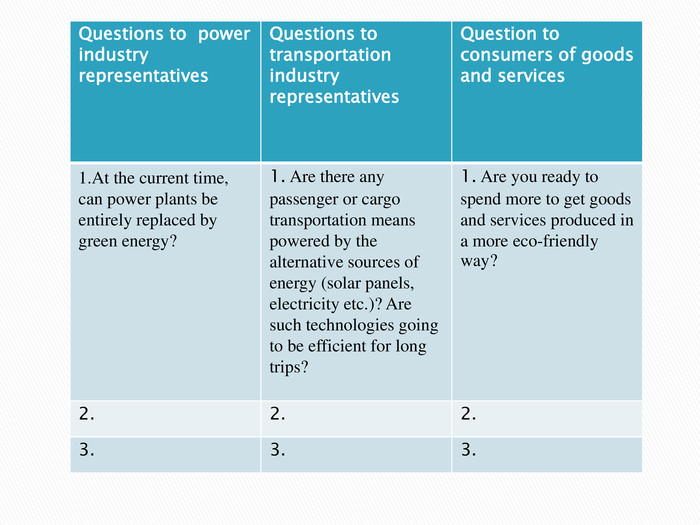
{5 C22544 A-7 EE6-4342-B048-85 BDC9 FD1 C3 A}Questions to power industry representatives Questions to transportation industry representatives Question to consumers of goods and services 1. At the current time, can power plants be entirely replaced by green energy? 1. Are there any passenger or cargo transportation means powered by the alternative sources of energy (solar panels, electricity etc.)? Are such technologies going to be efficient for long trips? 1. Are you ready to spend more to get goods and services produced in a more eco-friendly way? 2.2.2.3.3.3.
5. Definition of the core problem The students are asked to formulate the core problem illustrating a contradiction between the needs of ecology and word population. The Human activity impact on the climate has to be reduced with a growing increase in people`s wants and needs and the high costs of the alternative sources of energy.
Selection of the most rational proposals that can be implemented in practice, and those that are characterized by economic feasibility. The main idea of this stage is to implement the best possible solutions in so-called prototypes – mockups of what is proposed to be done or implemented. This activity is done in groups. 6. Prototype
{5 C22544 A-7 EE6-4342-B048-85 BDC9 FD1 C3 A}I hold the same opinion. I have no objection whatsoever. I see what you mean and I (must) agree with you. I see it that way, too. I share your opinion / view. I was just going to say that. You’re (completely / totally / absolutely) right. You have a point there. I don’t think you’re right. I don’t share your view. I think otherwise. I take a different view. That doesn’t make much sense to me. That’s not always the case. That’s not always / necessarily true. I am not sure I agree with you.
Brown T. 2009. Change by Design: How Design Thinking Transforms Organizations and Inspires Innovation / T. Brown. – New York : Harper. Collins Publishers L. L. C, 2009. – 272 p. Munyai K. A methodology towards sustainable problem solving in higher Education in South Africa [Electronic resource] / K. Munyai // International Association for the Development of the Information Society. – Regime of access : https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED571612.pdf Фурсенко Т. М. Сучасні підходи до викладання іноземної мови:дизайн-мислення / Т. Фурсенко // Наукові записки Вінницького державного педагогічного університету ім. М. Коцюбинського Список використаних джерел:

про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку





























