Урок на тему: "Engines"
GENERATORS
Task 1. Answer the following questions.
What is a Generator? What types of generators do you know? On which principle does a Generator work? What are the two main parts of an AC Generator? What is the main difference between an AC Generator and DC Generator?
1. Generators are machines that produce electric energy in the form of voltage and current.
2. There are two fundamental types of generators known as AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) generators. Also there are types of generators include diesel, gas, wind, hydroelectric, and solar generators.
3. A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
4. The two main parts of an AC generator are the rotor and the stator.
5. The main difference between an AC generator and DC generator is that AC generators produce alternating current while DC generators produce direct current.
Task 2. Read the following abbreviations and give their full forms.
i.e., a.c., d.c., r.p.m, e.m.f., m.m.f., 317°F, 45°C, etc.
- i.e. - id est (latin for "in other words" or "that is")
- a.c. - Alternating Current
- d.c. - Direct Current
- r.p.m. - revolutions per minute
- e.m.f. - electromotive force
- m.m.f. - magnetomotive force
- 317°F - 317 degrees Fahrenheit
- 45°C - 45 degrees Celsius
- etc. - etcetera (latin for "and so on" or "and other things").
Task 3. Learn to recognize the following international words.
Solenoid, shunt, electrification, dynamo, primitive, rotor, kilowatt, electromagnet, apparatus, industry, plan, elementary - соленоїд, шунт, електрифікація, динамо, примітив, ротор, кіловат, електромагніт, апарат, промисловість, план, елементарно.
Task 4. Read and translate the text, and guess the meaning of Active Words and Expressions given below.
GENERATORS
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power into electrical power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, and internal combustion engines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was built in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids.The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors and generators have many similarities. Many motors can be mechanically driven to generate electricity and frequently make acceptable manual generators.
Electromagnetic generators fall into one of two broad categories, dynamos and alternators.
- Dynamos generate pulsing direct current through the use of a commutator;
- Alternators generate alternating current.
- Field winding or field magnet: The magnetic field-producing component of an electrical machine. The magnetic field of the dynamo or alternator can be provided by either wire windings called field coils or permanent magnets. A generator using permanent magnets is sometimes called a magneto.
- Armature: The power-producing component of an electrical machine. In a generator, alternator, or dynamo the armature windings generate the electric current, which provides power to an external circuit.
The armature can be on either the rotor or the stator, depending on the design, with the field coil or magnet on the other part.The dynamo inverted by Faraday in 1831 is certainly a primitive apparatus compared with the powerful, highly efficient generators and alternators that are in use today. Nevertheless, these machines operate on the same principle as the one invented by the great English scientist. When asked what use his new invention had, Faraday asked in his turn: “What is the use of a newborn child?” As a matter of fact, “the newborn child” soon became an irreplaceable device we cannot do without.Although used to operate certain devices requiring small current for their operation, batteries and cells are unlikely to supply light, heat and power on a large scale. Indeed, we need electricity to light up millions of lamps, run trains, lift things, and drive machines. Batteries could not supply electricity enough to do all this work.That dynamo-electric machines are used for this purpose is a well-known fact. These are the machines by means of which mechanical energy is turned directly into electrical energy with a loss of only a few per cent. It is calculated that they produce more than 99.99 per cent of all the world's electric power. There are two types of dynamos, namely, the generator (Fig. 11) and the alternator. The former supplies d.c. which is similar to the current from a battery and the latter, as its name implies provides a.c. 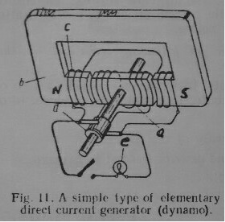
To generate electricity both of them must be continuously provided with energy from some outside source of mechanical energy such as steam engines, steam turbines or water turbines, for example.
Both generators and alternators consist of the following principal parts: an armature and an electromagnet. The electromagnet of a d.c. generator is usually called a stator for it is in a static condition while the armature (the rotor) is rotating.
Alternators may be divided into two types: 1. alternators that have a stationary armature and a rotating electromagnet; 2. alternators whose armature serves as a rotor but this is seldom done. In order to get a strong e.m.f., the rotors in large machines rotate at a speed of thousands of revolutions per minute (r.p.m.). The faster they rotate, the greater the output voltage the machine will produce. In order to produce electricity under the most economical conditions, the generators must be as large as possible. In addition to it, they should be kept as fully loaded as possible all the time.
ГЕНЕРАТОРИ
У виробництві електроенергії генератор — це пристрій, який перетворює рушійну силу в електричну для використання у зовнішньому ланцюзі. Джерела механічної енергії включають парові турбіни, газові турбіни, водяні турбіни, двигуни внутрішнього згоряння і навіть рукоятки. Перший електромагнітний генератор, диск Фарадея, був створений у 1831 році британським ученим Майклом Фарадеєм. Генератори забезпечують майже всю енергію для електричних мереж.
Зворотне перетворення електричної енергії в механічну здійснюється за допомогою електродвигуна, а двигуни та генератори мають багато подібності. Багато двигунів можна механічно приводити в дію для вироблення електроенергії, і вони часто є прийнятними ручними генераторами.
Електромагнітні генератори поділяються на одну з двох широких категорій: динамо-машини та генератори змінного струму.
Динамомашини генерують пульсуючий постійний струм за допомогою комутатора; генератори генерують змінний струм.
Обмотка поля або магніт поля: компонент електричної машини, що створює магнітне поле. Магнітне поле динамо-машини або генератора змінного струму може створюватися або дротяними обмотками, які називаються котушками поля, або постійними магнітами. Генератор, що використовує постійні магніти, іноді називають магнето.
Арматура: компонент електричної машини, що виробляє електроенергію. У генераторі, генераторі змінного струму або динамо-машині обмотки якоря генерують електричний струм, який забезпечує живлення зовнішнього кола.
Якір може бути на роторі або статорі, залежно від конструкції, з котушкою збудження або магнітом на іншій частині.Динамо, перевернуте Фарадеєм у 1831 році, безумовно, є примітивним апаратом порівняно з потужними, високоефективними генераторами та генераторами змінного струму, які використовуються сьогодні. Тим не менш, ці машини працюють за тим же принципом, що і винайдений великим англійським вченим. На запитання, яка користь від його нового винаходу, Фарадей у свою чергу запитав: «Яка користь від новонародженої дитини?» По суті, незабаром «новонароджена дитина» стала незамінним пристроєм, без якого не обійтися.
Незважаючи на те, що батареї та елементи використовуються для роботи певних пристроїв, для роботи яких потрібен малий струм, навряд чи батареї та елементи постачатимуть світло, тепло та електроенергію у великих масштабах. Дійсно, нам потрібна електроенергія, щоб запалити мільйони ламп, запустити поїзди, підняти речі та привести в рух машини. Батареї не могли забезпечити достатньо електроенергії, щоб виконати всю цю роботу.
Те, що для цього використовуються динамо-електричні машини, є загальновідомим фактом. Це машини, за допомогою яких механічна енергія перетворюється безпосередньо в електричну з втратою лише кількох відсотків. Підраховано, що вони виробляють понад 99,99 відсотка всієї електроенергії в світі.
Існує два види динамо-машин, а саме генератор (мал. 11) і генератор змінного струму. Перший постачає d.c. який подібний до струму від батареї, а остання, як випливає з її назви, забезпечує змінний струм.
Щоб виробляти електроенергію, вони повинні постійно отримувати енергію від зовнішнього джерела механічної енергії, наприклад, парових машин, парових або водяних турбін. І генератори, і генератори змінного струму складаються з таких основних частин: якоря та електромагніту. Електромагніт постійного струму. Генератор зазвичай називають статором, оскільки він знаходиться в статичному стані, а якір (ротор) обертається.
Генератори змінного струму можна розділити на два види: 1. генератори змінного струму, які мають нерухомий якір і обертовий електромагніт; 2. генератори змінного струму, у яких якір служить ротором, але це робиться рідко. Щоб отримати сильну ЕРС, ротори у великих машинах обертаються зі швидкістю тисячі обертів на хвилину (об/хв). Чим швидше вони обертаються, тим більшу вихідну напругу вироблятиме машина.
Щоб виробляти електроенергію в найбільш економічних умовах, генератори повинні бути якомога більшими. На додаток до цього, вони повинні бути максимально завантаженими весь час.
Active Words and Expressions
as… as possible, armature, to calculate, compared with, construction, to equip, to be likely, machine, to operate, revolutions per minute (r.p.m.), to rotate, scale, speed, stator, steam power plant, turbine, winding, to install, rated capacity, the former, the latter - як… наскільки це можливо, арматура, розрахувати, порівняти з, конструкція, оснастити, імовірно, машина, працювати, оберти за хвилину (об/хв), обертатися, масштабувати, швидкість, статор, парова електростанція, турбіна, обмотка , встановити, номінальна потужність, колишній, останній.
Task 5. Read the words and their derivatives; find their meaning in the dictionary if you need.
To calculate- calculation- calculator- to miscalculate; construction- to construct- constructor- constructive; to equip- equipment- to reequip; to install- installation; to operate- operation- operative- operator; revolution- to revolve- revolutionary; to rotate- rotation- rotary- rotor; winding- to wind- wind - розрахувати- розрахунок- калькулятор- прорахувати; будівництво- будувати- конструктор- конструктивний; оснастити- оснастити- переобладнати; встановлювати- встановлення; оперувати- операція- оперативник- оператор; революція- обертатися- революційний; обертатися- обертання- ротаційний- ротор; звивати- намотувати- вітер.
Task 6. Translate the following groups of words.
compared with the result, to install the turbine, to equip with reliable installation, stationary equipment, rotor windings, 5000 revolutions per minute, the faster they rotate- the greater the output voltage, principle parts - порівняно з результатом, встановити турбіну, оснастити надійною установкою, стаціонарним обладнанням, обмотки ротора, 5000 обертів за хвилину, чим швидше вони обертаються, тим більше вихідна напруга, принципові частини.
збільшувати швидкість, номінальна потужність мотора, теплова електростанція, перший із згаданих, останній із згаданих, у великому маштабі, добре відомий факт, подвлятися на 2 типи, відігравати важливу роль - increase speed, rated power of motor, thermal power plant, first of mentioned, last of mentioned, on a large scale, well known fact, fall into 2 types, play an important role.
Task 7. Answer the following questions.
1. What does the term “generator” mean? 2. What types of generators do you know? 3. What are the principal parts of a generator? 4. When did Faraday invent the dynamo? 5. Was Faraday an American scientist? 6. Can batteries supply power on a large scale? 7. What do we need electricity for? 8. What are dynamo-electric machines used for? 9. In what condition is the stator of an electromagnet? 10. What does the rotor do?
1) In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power into electrical power for use in an external circuit.
2) There are two fundamental types of generators known as AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) generators. Also there are types of generators include diesel, gas, wind, hydroelectric, and solar generators.
3) Generators and alternators consist of the following principal parts: an armature and an electromagnet.
4) Faraday invented the dynamo in 1831.
5) No, Faraday was a British scientist.
6) Batteries are not typically used for large-scale power generation.
7) We need electricity for a wide range of applications, including lighting, heating, transportation, and communication.
8) Dynamo-electric machines are used for generating electricity.
9) The stator of an electromagnet is typically in a fixed position.
10) The rotor rotates within the magnetic field and produces an electrical current.
Task 8. For five sentences combine suitable parts of the sentence given in columns I and II.
|
I |
II |
|
is a temporary magnet provided by electricity. |
|
is an electrical appliance used in daily life. |
|
is a path to be followed by the current from the source and back to the source. |
|
4. The iron |
is the force that makes electrons move along a conductor. |
|
5.The electromagnet |
is a device by means of which heat is turned into work. |
Task 9. Form adjectives using the suffixes –able, -ful, -less, -ous
control, continue, danger, value, replace, need, rower, peace, use, life
- controllable - контрольований/підкорюваний
- continuable - продовжуваний
- dangerous - небезпечний
- valuable - цінний
- replaceable - замінний
- needless - зайвий/непотрібний
- powerful - потужний
- peaceful - мирний/спокійний
- usable - придатний для використання
- lifeless - мертвий/байдужий до життя
Task 10. Form adverbs using the suffix –ly
Exact, electrical, general, gradual, negative, natural, opposite, previous, usual, easy
- exactly - точно/істинно
- electrically - електрично
- generally - загалом/взагалі
- gradually - поступово
- negatively - негативно/від'ємно
- naturally - природно/естетично
- oppositely - протилежно
- previously - раніше/попередньо
- usually - зазвичай/зазвичай
- easily - легко/просто
Task 11. Define the following terms.
1. electromotive force; 2. electric circuit; 3. heating effect of an electric current; 4. magnetic effect of an electric current; 5. electromagnet; 6. generator
1) Electromotive force (EMF) refers to the energy per unit of charge that a source of electrical power, such as a battery or generator, provides to drive the flow of electric current in a circuit. It is the force or push that drives the movement of electric charge in a circuit, and it is typically measured in volts (V).
2) Electric circuit - a path along which electric current flows, typically consisting of a power source, conductors, and one or more loads that convert the electric energy into another form of energy.
3) Heating effect of an electric current - the process by which electric current flowing through a conductor produces heat, which can be used in electric heaters, furnaces, and other applications.
4) Magnetic effect of an electric current - the phenomenon whereby an electric current flowing through a conductor creates a magnetic field around the conductor, which can be used in electric motors, generators, and other devices.
5) Electromagnet - a magnet produced by a current-carrying conductor that can be turned on and off by controlling the current.
6) Generator - a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by rotating a coil of wire in a magnetic field, producing an electromotive force (EMF) that drives the flow of electric charge in a circuit.
Task 12. Translate the following sentences from Ukrainian into English.
1.Генератор постійного струму — електрична машина постійного струму (генератор), що перетворює механічну енергію на електричну.
2. Дія генератора постійного струму ґрунтується на явищі електромагнітної індукції.
3. Обмотка ротора з'єднана з колектором (механічним перетворювачем змінної ЕРС на постійну напругу).
4. Потужність генераторів постійного струму — від кількох ват до десятків тисяч кіловат, напруга — від одиниць до сотень і тисяч вольт.
5. Генератори постійного струму застосовують для живлення постійного струму електродвигунів, у зварювальних пристроях, електричних установках літаків, тепловозів, автомобілів, у пристроях автоматики (мікрогенератори постійного струму), для електролізу тощо.
6. Генератор змінного струму — система з нерухомого статора (складається із сталевого осердя та обмотки) і ротора (електромагніт із сталевим осердям), який обертається всередині нього.
7. Через два контактних кільця, до яких притиснуті ковзні контакти щітки, проводиться електричний струм.
8. Електромагніт створює магнітне поле, яке обертається з кутовою швидкістю обертання ротора та збуджує в обмотці статора ЕРС індукції.
9. Щоб ротор обертався і створював магнітне поле, яке викликає у статорі ЕРС індукції, йому необхідно надавати енергію.
10. Ротор обертається у електростанціях за допомогою пари (ТЕС та АЕС) або гідротурбін (ГЕС).
1. A direct current generator is a direct current electric machine (generator) that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
2. The action of the direct current generator is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
3. The rotor winding is connected to the collector (mechanical converter of variable EMF to constant voltage).
4. The power of direct current generators ranges from a few watts to tens of thousands of kilowatts, the voltage ranges from units to hundreds and thousands of volts.
5. Direct current generators are used to supply direct current to electric motors, in welding devices, electrical installations of airplanes, diesel locomotives, cars, in automation devices (direct current micro generators), for electrolysis, etc.
6. An alternating current generator is a system of a stationary stator (consisting of a steel core and winding) and a rotor (an electromagnet with a steel core) that rotates inside it.
7. An electric current is conducted through two contact rings to which the sliding contacts of the brush are pressed.
8. The electromagnet creates a magnetic field that rotates with the angular speed of rotation of the rotor and excites EMF induction in the stator winding.
9. In order for the rotor to rotate and create a magnetic field, which causes EMF induction in the stator, it must be supplied with energy.
10. The rotor rotates in power plants using steam (thermal power plants and nuclear power plants) or hydro turbines (hydroelectric power plants).
-
Cool!
-


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
