Збірник текстів для читання з англійської мови (за професійним спрямуванням) для учнів ПТНЗ
МІНІСТЕРСТВО ОСВІТИ І НАУКИ УКРАЇНИ
ДЕПАРТАМЕНТ ОСВІТИ І НАУКИ
ДНІПРОПЕТРОВСЬКОЇ ОБЛАСНОЇ ДЕРЖАВНОЇ АДМІНІСТРАЦІЇ
ОРДЕНА"ЗНАК ПОШАНИ"ВИЩЕ ПРОФЕСІЙНЕ УЧИЛИЩЕ № 75
53600, Покровський район, с. Олександрівка, вул. Шкільна, 10, тел.2-14-95,2-17-93, тел/факс 2-22-79
vpu752015 @gmail.com, веб-сайт: vpu-75.at.ua

с. Олександрівка, 2018 рік

Збірник текстів для читання з англійської мови для учнів професійних (професійнотехнічних) навчальних закладів за спеціальністю «Агроінженерія» за професією «Тракторист-машиніст сільськогосподарського виробництва» - с. Олександрівка, 2018 р.,69с.
Укладач: Микуліна Світлана Миколаївна - викладач англійської мови, спеціаліст І категорії
В даному збірнику представлено 20 текстів для читання для учнів ПТНЗ за спеціальністю «Агроінженерія». До кожного тексту пропонується комплекс завдань, які відповідають принципу комунікативної спрямованості. Всі завдання з читання лексики та граматики побудовані на основі відповідного тексту, щоб допомогти учням набути і розвинути навички у розумінні лексики професійної спрямованості. Збірник містить матеріали для проведення тестів з англійської мови (за професійним спрямуванням). Тести розроблені для виявлення рівня засвоєння знань, вони допомагають систематизувати знання лексики і граматики, дозволяють урізноманітнити методи контролю та перевірки знань і навичок.
Метою даного збірника є стимулювання вивчення англійської мови, для здобуття корисної і цікавої інформації, пов’язаної з майбутньою спеціальністю. Серед типових завдань збірник пропонує наступні:
Ø встановлення правильної/неправильної відповіді;
Ø вибір заголовка, запитання або ключового твердження, що передає головну думку тексту;
Ø реконструкція тексту та заповнення пропусків;
Ø розташування частин тексту в логічній послідовності;
Ø вибір правильної граматичної форми (дієслово, іменник, прислівник, тощо) Ø заповнення пропусків запропонованими словами;
Ø завдання на відповідність.
Мета завдань перевірити рівень сформованості мовної компетенції учнів, їх лексичнограматичні навички, ступень засвоєння ними системних знань про мову, як засобу вираження думок і почуттів людини.
Матеріали збірника призначені як для самостійного опрацювання учнями, так і для роботи під керівництвом викладача.
При використанні збірника для оцінювання знань учнів передбачається робота викладача щодо розробки критерію оцінювання, тому що кожен текст з завданнями може використовуватися як комплекс завдань в цілому, або окремі завдання.
Обговорено та схвалено на засіданні методичної комісії
механізації сільського господарства
Протокол № 4 від 05.11.2018р.
ЗМІСТ
Вступ 4
Текст 1 “What is Agriculture. The Branches of Agriculture” 5
Текст 2 “Agriculture in Ukraine” 7
Текст 3 “Agriculture in Western Ukraine” 9
Текст 4 “Operating and Maintaining Tractors” 10
Текст 5 “Internal Combustion Engine” 12
Текст 6 “ Diesel Starting System” 14
Текст 7 “Agricultural Machinery” 15
Текст 8 “ Round Baler. Planter” 17
Текст 9 “Tractors” 18
Текст 10 “Ploughs” 19
Текст 11 “Diesel Engine” 21
Текст 12 “Application and variations of tractors” 22
Текст 13 “Selecting Tractors” 24
Текст 14 “Cooling system” 26
Текст 15 “Cultivator” 28
Текст 16 “Harrows” 30
Текст 17 “Forage Harvester” 31
Текст 18 “Combine harvester” 32
Текст 19 “Wheat” 34
Текст 20 “Maize” 36
Appendix 38
Тестові завдання “Check yourself” 47
Відповіді до тестів “ Keys” 52
Vocabulary 53
Література 69
ВСТУП
Незалежна Україна має зв’язки з багатьма країнами світу, сотні спільних підприємств з’являються в багатьох містах країни, тисячі людей їдуть за кордон. Тому однією з характерних рис сучасного життя є великий інтерес до вивчення іноземних мов. Особлива увага приділяється вивченню лексики за професійним спрямуванням.
Іноземна мова, зокрема англійська, є невід’ємним засобом міжкультурного, ділового спілкування. Рівень усвідомлення учнями отриманих на уроках знань має рішуче значення. Завдяки тестовим контрольним роботам викладач має змогу проаналізувати, наскільки повно і правильно учні засвоїли матеріал, а також де є прогалини та скласти план подальшої роботи з урахуванням набутої інформації.
Даний збірник розрахований на студентів ІV-V-их курсів з метою перевірки знань та навичок. У пропонованій роботі використовуються різні завдання до тематичних текстів, тестові завдання, які містять лексичні та граматичні завдання з тих тем по спеціальності, які вивчались протягом курсу. Тести допомагають систематизувати знання лексики і граматики, дозволяють урізноманітнити методи контролю та перевірки знань і навичок. Для виконання тестів студентам необхідно повторити вивчені граматичні теми та лексичні одиниці, що сприяє узагальненню та систематизації вивченого матеріалу.
Оцінювання має ґрунтуватися на позитивному принципі, що, насамперед, передбачає врахування рівня навчальних досягнень студента, а не ступеня його невдач. Згідно з цим тестові завдання прості, цікаві, чітко сплановані, зрозумілі для студентів. Дана методична розробка відповідає вимогам навчальної програми з дисципліни. Посібник призначений для учнів та викладачів професійно – технічних навчальних закладів.
TEXT 1
1. Read the text. What is Agriculture. The Branches of Agriculture.
Agriculture is an important branch of economy. Economic growth of any country depends on the development of agriculture which supplies people with food and clothing and industry with raw materials.
The word “agre” is a Latin word. It means the cultivation of fields in order to grow crops. Now agriculture also includes the use of land to breed farm animals.
We do not know when people began to grow crops. It was many thousand years ago. Now crop production and animal husbandry are highly developed branches of agriculture.
Life is impossible without plants. They play a highly important role in everyday life of people. Plants that are grown by farmers are known as farm crops. They are used for many different purposes. Most of them are used directly as food for people, some are consumed by farm animals, others are used in industry and medicine.
In order to increase crop yields and animal products our farmers apply widely intensive technologies.
There are two main branches of agricultural production – crop production and animal husbandry.
Crop production is the practice of growing and harvesting crops. The most important crops grown by man are grain crops, vegetables and grasses. In order to obtain high yields crops are grown under favourable soil and climatic conditions.
Animal husbandry is a branch of agriculture including the breeding of farm animals and their use. Dairy and beef cattle, hogs, sheep and poultry are widely bred throughout the world. Farm animals are highly important sources of food for man. They are kept for the production of such nutritious products as meat, milk and eggs.
Many crops grown by man are used in feeding livestock. At the same time manure produced by farm animals is an important source for the maintenance of soil fertility. Most of the nutrients taken by plants from the soil are thus returned. Applying manure, farmers improve the physical condition of the soil.
Thus, crop production and animal husbandry are closely connected with each other.
2. Answer the following questions on the text.
1). Why is agriculture very important?
2). What are the two branches of agriculture? 3. What does the Latin word “agre” mean? 4). Is life possible without plants?
5). Where are farm crops used?
6). How do people increase crop yields?
7). What is crop production?
8). What are the main farm crops?
9). What does animal husbandry include?
10). What products do farm animals produce?
11). What is manure used for?

3. Finish the sentences.
1). Agriculture is an important … .
2). Economic growth of any country depends on … .
3). The word “agre” means the cultivation … .
4). Life is impossible … . 5). Farm crops are … .
6). There are two main branches of agricultural production - … .
7). Animal husbandry is a branch of agriculture including the breeding of … .
8). Crop production is the practice of … .
9). The most important crops grown by man are … .
10). Farm animals are highly important … .
11). Farmers improve the physical condition of the soil …
4. Find the Ukrainian equivalents in the second column.
|
1. agriculture |
a. врожай |
|
2. crop production |
b. галузь |
|
3. consume |
c. тваринництво |
|
4. use |
d. джерело |
|
5. branch |
e. худоба |
|
6. purpose |
f. стан |
|
7. yield |
g. сільське господарство |
|
8. animal husbandry |
h. отримати |
|
9. livestock |
i. виробництво |
|
10. obtain |
j. рослинництво |
|
11. source |
k. мета |
|
12. production |
l. споживати |
|
13. condition |
m. використовувати |
5. Find the sentences in the text and translate them where are said about the fact …
1) що дає сільське господарство промисловості;
2) що означає слово сільське господарство;
3) як використовують рослини, які вирощує людина;
4) який основний шлях збільшення продуктів харчування сьогодні.
6. Name the Ukrainian equivalents of the following international words.
|
effective - |
to mechanize - |
|
climate - |
tendency - |
|
machine - |
tradition - |
|
tractor - |
traditional - |
|
combine - |
industrial - |
|
bulldozer - |
adaptation - |
|
specialist - |
economic - |

TEXT 2
1. Read the text. Agriculture in Ukraine.
For centuries agriculture has been an integral part of everything Ukrainian. The symbols of earth, fertility, plants and sun are everywhere. Traditionally mostly peaceful peasants populated the territory of Ukraine. The ancient practice of living off the soil and agricultural products has made Ukraine one of the world leading producers of grains, vegetable, oils, sugar. If you are looking for the country with favorable conditions for agricultural business there is hardly a better option than Ukraine.
Despite the dramatic changes Ukrainian economy has been passing through during the last decades, the national agricultural sector still holds its strong positions mainly due to its abundant resource base. The major alimentary products exported internationally are grains, rapeseeds, vegetables, sugar, sunflower oil, milk powder and meat.
20% of the agricultural exports including non-food batches go to Russia, while the countries of the European Union take up to 17% of the volume. China, Turkey and the United States of America receive 7%, 6% and 4% of food exports from Ukraine respectively.
Sugar and oil processing is another major segment of the Ukrainian economy. Research showed that one out of four people in Ukraine works in agriculture or forestry which speaks expressively enough for the largest European country with 46 million people.
Experts claim only 45-50% of the Ukrainian arable lands are used to cultivate crops while meat and poultry production has drastically decreased over the past decade despite the world’s growing demand for food. Private farmers run their businesses mainly due to legal agreements allowing using the land for the time periods from 5 to maximum 49 years. The economic forecasts proving agricultural output of Ukraine is not likely to be seriously affected by the world financial crisis make this country one of the most attractive for exploration and investments.
2. Answer the questions.
1. What is an integral part of everything Ukrainian?
2. Who is populated the territory of Ukraine?
3. What country is a better option for agricultural business?
4. What are the major alimentary products grown in Ukraine?
5. How many people works in agriculture?
6. How many Ukrainian arable lands are used to cultivate crops?
3. Complete the sentences.
1. The ancient practice of living off the soil and agricultural products has made Ukraine one of the world leading producers of …..
2. The national agricultural sector still holds its strong positions mainly due to … .
3. Ukraine exports 20% of the agricultural products while the countries of the European Union
… .
4. Another major segment of the Ukrainian economy is …
5. Ukrainian meat and poultry production has drastically decreased over the past decade despite … .
6. Our country is one of the most attractive for … .

4. Find the equivalents.
|
1. |
plants |
a. обробляти |
|
2. |
favorable |
b. сільськогосподарські культури |
|
3. |
mainly |
c. угода |
|
4. |
sunflower |
d. рослини |
|
5. |
include |
e. сприятливий |
|
6. |
volume |
f. головним чином |
|
7. |
enough |
g. соняшник |
|
8. |
cultivate |
h. включати |
|
9. |
crops |
i. обсяг |
|
10. |
agreement |
g. достатньо |
5. Translate the sentences into English.
1. Україна – це країна зі сприятливими умовами для сільськогосподарського бізнесу. ________________________________________________________________________________
2. Україна є одною з всесвітньо відомих виробників зерна, олії, овочів та цукру.
________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Основні продукти, які Україна експортує на світовий ринок – це соняшникова олія, зерно, цукор, молочні продукти та м’ясо.
________________________________________________________________________________
4. Дослідники показали, що в Україні один з чотирьох людей працює в сільському господарстві.
________________________________________________________________________________
5. В Україні тільки 45%-50% родючих грунтів використовують для вирощування сільськогосподарських культур.
________________________________________________________________________________
6. Read the text again. Tick (+) True, (-) False or write (?) if there is no information.
1. Experts claim only 55-60% of the Ukrainian arable lands are used to cultivate crops while meat and poultry production has drastically decreased over the past decade despite the world’s growing demand for food.
2. The ancient practice of living off the soil and agricultural products has made Britain one of the world leading producers of grains, vegetable, oils, sugar.
3. The symbols of earth, fertility, plants and sun are everywhere.
4. Sugar and oil processing is another major segment of the Ukrainian economy.
5. There are two main branches of agricultural production – crop production and animal husbandry.
6. China, Ukraine and the United States of America receive 7%, 6% and 4% of food exports from Britain respectively.
TEXT 3
1. Complete the text with the words from the box.
grain planting, population, is rich in, agro-industrial complex, sugar beet and potato, climate
conditions, cattle, flax and potato, north-western, horses, north-western part, widespread.
Agriculture in Western Ukraine
This region ______________diverse agricultural and natural resources. Geographically it can be divided into the Western part (or Carpathians) and the_________________________. Carpathians region includes Lviv, Zakarpattya, Ivano-Frankivsk and Chernivtsi regions.
The total area is 56,6 thousands km² with the ________________reaching 6,1 mln people.
The __________________________of the area includes agriculture and processing industries. In a forest-steppe area cattle breeding, pig breeding, __________________, flax and sugar beet cultivation are______________________.
In the mountains the ______________breeding prevails. Due to the geological and
____________________these lands can’t be used for arable planting. Therefore, sheep breeding traditionally played the leading role here. The steep mountain slopes are suitable for this agricultural sector. Polonyny or subalpine grasslands are covered with bilous – plant which only sheep can eat. _________________are also popular here. In Zakarpattyaregion you can find lots of households involved into viticulture, gardening and tobacco cultivation.
The __________________area consists of Rivne and Volyn region where 2,2 million people live. The total area is 40,3 thousand km². The average density of the population is 55 people per 1 km² which is the lowest rate in the country.
People mostly cultivate rye, flax, hop, winter-crops, wheat,____________________. However the region tends to live off cattle breeding: pig and sheep breeding, poultry, rabbit and fish farming, as well as beekeeping are popular.
Thousands of family households are small and most are poorly equipped. Local farmers work in fields as they have been doing for years. They cut hay with hand scythes, carts and ploughs are driven by______________.
2. Read the text again. Tick (+) True, (-) False or write (?) if there is no information
1.This region is poor in diverse agricultural and natural resources.
2. Geographically it can be divided into the Western part (or Carpathians) and the East-Western part.
3.Carpathians region includes Lviv, Zakarpattya, Ivano-Frankivsk and Chernivtsi regions. 4.The total area is 52,6 thousands km² with the population reaching 6,7 mln people.
5.The agro-industrial complex of the area includes agriculture and processing industries.
6.In the mountains the poultry breeding prevails.
7.The steep mountain slopes are suitable for this agricultural sector.
8.People mostly cultivate rye, flax, hop, winter-crops, wheat, sugar beet and potato.
9.Local farmers cut hay with hand scythes, carts and ploughs are driven by horses.
3. Translate the words into English.
|
природні ресурси - |
льон і картопля - |
хмель- |
|
сільське господарство - |
домогосподарство - |
зимові культури- |
|
рогата худоба - |
жито - |
пшениця та цукровий буряк - |
TEXT 4
1. Read the text.
Operating and Maintaining Tractors
1. A tractor must be well maintained and operated so that the need for repair is reduced to a minimum. Repairs are expensive and there may be difficulties in getting the necessary parts and installing them.
2. A tractor operator should be able to operate, adjust and maintain his tractor. He should have knowledge and skill necessary for doing unspecialized tractor repair. The more specialized repair such as reboring cylinders, replacing worn parts is to be done by a qualified mechanic.
3. Most tractor service work includes the engine, so the repair and adjustment information on engines is useful.
4. A clutch is a disk mechanism operating on a friction basis. A clutch permits the gradual application of power from the engine to the load. It permits the disengagement of the engine from the drive mechanism for starting, for shifting of gears and for idling.
Clutch should be check periodically, since the pedal linkage wears with use and may need adjustment. A tractor operator must know the method of adjusting the linkage. Lack of clearance of the clutch pedal may reduce power and cause overheating.
5. When a tractor’s transmission needs repairing, special equipment is necessary. Several checks on the transmission can be made by the operator of a tractor.
- If oil leaks are present the gaskets need tightening or replacing.
- The axle bearing is to be examined by lifting each wheel up and down with a bar and by pushing and pulling each wheel side wards.
- Rear wheel brakes should be checked for wear and for the adjustment needed.
- The belt pulley bearing and drive gear need checking for wear. The belt pulley mechanism needs regular cleaning and servicing, a special lubrication device being used for its lubrication.
- New lubricant must be added to maintain the oil at its proper level.
- After draining the transmission it is flushed with kerosene and refilled with transmission lubricant.
6. The belt pulley is usually located in the right side or at the back. On some tractors the belt pulley may or must be removed when the tractor is not being used for belt work.
7. The power take – off shaft on a tractor is powered directly from the engine and may be used to operate machines. It is usually controlled by a separate disk clutch which is operated hydraulically. Thus, the motion of the tractor does not affect the speed of the PTO – shaft and starting or stopping the PTO – shaft does not affect the speed of the tractor. One must stop the shaft before dismounting from a tractor.
8. The steering mechanism is to be examined for wear and for repairs and adjustment needed. If the steering is of the hydraulic type, there is no mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the front axle. If the steering mechanism has a mechanical linkage, the linkage should be lubricated and checked for wear periodically.
9. Tractors are often equipped with brakes that are hydraulically operated. The tractor operator has to inspect the brake mechanism before adjusting the hydraulic break valve and the brake pedals.
10. All trailing implements are often attached to the drawbars being equipped with different types of drawbars. The tractor operator must follow instructions regarding hitching and adjusting the drawbar.
11. The proper care and preventive maintenance of a tractor are very important so that break downs and expensive repairs are as rare as possible.
2. Find in the text English equivalents to the given Ukrainian one.
|
тракторист |
перемикання передач |
|
керувати |
присутнє витікання мастила |
|
регулювати і обслуговувати трактор |
вісь підшипника |
|
неспеціалізований ремонт трактора |
гальма заднього колеса |
|
заміна зношених частин |
підшипник шківа ременя |
|
поступове застосування |
диск зчеплення |
|
кермо |
рульовий механізм |
3. Answer the questions.
1. What must a tractor - operator do to operate and maintain a tractor well?
2. For which details the periodically checking and adjusting are needed?
3. Which are the types of steering?
4. The tractor operator has to inspect the brake mechanism before adjusting the hydraulic break valve and the brake pedals, doesn’t he?
5. Must the tractor operator follow instructions regarding hitching and adjusting the drawbar?
6. Must the tractor operator do the examination of steering mechanism?
7. Has the tractor operator to inspect the brake mechanism before adjusting the hydraulic break valve and the brake pedals?
4. Complete the sentences using the proper words from the box into the gaps. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
a. large; b. clutches; c. multipurpose; d. axle; e. special; f. four-wheel; g. farm.
1. The classic ..… tractor is a simple open vehicle, with two very large driving wheels on an
..… below and slightly behind a single seat.
2. Some ..… drive tractors have the standard "two large, two small" configuration typical of smaller tractors, while some have four …… , powered wheels.
3. Larger types of modern farm tractors include articulated four wheel or eight-wheel drive units with one or two power units which are hinged in the middle and steered by hydraulic
.…… or pumps.
4. A farm tractor is …… power unit.
5. The area to be cultivated, the type of crops grown and the soil – all require a tractor of .
….… design.

TEXT 5
1. Read the text.
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE
Internal combustion is the process of burning of fuel within the engine. The fuel burns within the engine and provides forces. These forces provide the engine power.
Internal combustion engines have stationary, rotary and reciprocation parts.
Stationary Engine Parts The stationary engine parts are the cylinder block, the crankcase and the cylinder head.
The cylinder block is one of the basic parts of the engine. The process of combustion takes place within the cylinders. Tractor engines have some cylinders.
The crankcase is a part of the cylinder. It supports the crankshaft and the camshaft and keeps the lubricating oil near the engine parts.
The cylinder heads close the cylinders. The cylinders and the cylinder heads form the combustion chambers.
The burning of fuel takes place within the combustion chambers.
Rotary Engine Parts Rotary engine parts are the crankshaft, the flywheel and the camshaft. The crankshaft changes reciprocating motion of pistons to rotary motion. The camshaft opens the valves of the engine.
2. Fill in the blanks with the proper words from the box.
Cylinder heads, camshaft, burning, crankcase, crankshaft, cylinder block
.
1.The……..…….. changes reciprocating motion of pistons to rotary motion.
2. The ………….. opens the valves of the engine.
3. The ……….…. is one of the basic parts of the engine.
4.The cylinders and the …………… form the combustion chambers.
5. The …………. of fuel provides forces.
6. The ………….. keeps the lubricating oil near the engine parts.
3. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1.The crankcase has the lubrication oil.
2. The cylinder block and the crankcase are stationary engine parts.
3. The engine has rotary parts.
4. The camshaft, the flywheel are rotary parts.
5. Crankshaft changes motion.
6. Crankcases support crankshafts.
7. These forces provide power.
8. The piston moves within the cylinder. 9. The cylinder head close the cylinders.
10. The process of combustion takes place within the chamber.

4. Form with the help of suffix – ion the nouns using the verbs given below and translate them into Ukrainian.
For example: To connect – connection – з’єднувати - з’єднання
To complete -… ………………. закінчувати - …
To act - … ………………. діяти - …
To rotate - … ………………. обертатися - …
To convert - … ………………. перетворювати - …
Toignite - … ……………… запалювати - …
To lubricate - … ………………. змащувати - …
Circulate - … ………………. обертатися, циркулювати -…
To vibrate … ……………… вібрувати, коливатися - … To compress - … ……………… стискати - …
5. Match the English and Ukrainian equivalents of word – combinations.
1. Cylinder block – a. колінчастий вал і розподільчий вал
2.  Piston rings
– b. мастило
Piston rings
– b. мастило
3. Combustion chamber – c. обертальний рух
4. Intake valves – d.циліндрична головка
5. Engine parts motion – e. зворотньо – поступальний рух
6. Fuel combustion process – f.енергія двигуна внутрішнього згорання
7. Internal combustion engine power - g. процес згорання пального
8. Reciprocating motion - h. рухомі частини двигуна
9. Cylinder head - i. впускні клапани
10. Rotary motion - j.камера згорання
11. Lubricating oil - k. поршневі кільця
12. The crankshaft and the camshaft - l. циліндричний блок
6. Make up the sentences using the given words.
1. Within, burns, the fuel, the cylinder.
__________________________________________________________________________
2. Of, changes, reciprocating, the crankshaft, the motion, pistons.
__________________________________________________________________________
3. The crankcase, is, of, a part, the engine.
___________________________________________________________________________ 4. Study, we, engines.
___________________________________________________________________________ 5. Takes place, the combustion, chamber, in, burning, the process, of.
___________________________________________________________________________

TEXT 6
1. Read the text and do the tasks.
Diesel Starting System
Some diesels use an additional gasoline engine for starting. The small engine is attached to the diesel by means of clutch. The gasoline engine is known to crank the diesel until the diesel starts. Exhaust from the starting engine is used to heat the intake manifold of the diesel engine. After a short warm – up period, the compression lever is returned so that the diesel will start. Most farm tractor diesels use electric starting motors similar to those used in gasoline engine tractors. They are operated from the battery on the tractor. In warm weather starting is usually not a problem, but for cold weather starting there are several starting aids. Some tractors are equipped with electric plugs to heat the intake manifold warms the air entering the engine so that the engine will start when cranked by the starter.
To start an engine either may also be used. Either has a low ignition point so that the heat of compression in cold weather is enough to ignite the either. This will then ignite the fuel charge. Fuel is highly explosive and must be injected into the engine only when the starter is cranking the engine.
Engine – block heaters can also be used to start the diesel engine. These heaters are usually electrically operated and heat either the oil in the crankcase or the engine coolant.
2. Put “True” if the sentence is corresponds to the text and “False” if the sentence doesn’t correspond to the text.
1. The small engine is attached to the diesel by means of clutch connection.
2. After a long warm – up period the diesel will start.
3. Most farm tractor diesels use electric starting motors.
4. In warm weather starting is usually a problem, because there are several starting aids.
5. Some tractors are equipped with electric plugs and a crank.
6. The heat of compression in cold weather is enough to ignite the diesel engine.
3. Find the English equivalents to the given Ukrainian ones.
|
1. додатковий бензиновий двигун для запуску 2. нагрівати впускний патрубок 3. компресійний рівень 4. електричні пускові двигуни 5. електричні свічки
|
6. низька точка запалювання 7. паливний заряд 8. високо вибуховий 9. двигунні пічки 10. двигунний охолоджувач
|
4. Answer the questions.
1. Which type of engine has an additional gasoline engine for starting?
2. By what a way is the small engine attached to the diesel?
3. What is used to heat the intake manifold of the diesel engine?
4. Do the most farm tractor diesels use electric starting motors similar to those used in gasoline engine tractors?
5. Are some tractors equipped with electric plugs or batteries?Why is used an engine to start?
TEXT 7
1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian.
Agricultural Machinery
The system of food and fiber production in agriculture is highly mechanized. These mechanized systems extend from initial tillage of the soil through planting, agricultural practices during the growing season, protection from pests, harvesting, livestock feeding and delivery for processing.
The tendency has been to large self – propelled special – purpose machines; in tillage the tendency has been to large four - , six – or eight wheel or crawler tractors which trail high – capacity plows or discs and alsosubsoilers used to loosen compacted soils.
Farm machines have undergone changes and improvements to become the modern and effective agricultural power units of today. New developments have made them more efficient, versatile, safe, convenient and powerful. Continuous improvements in design produced highly mechanized machinery with hydraulic linkage and control system.
While many implements such as plows, cultivators and fertilizer spreaders are usually mounted on tractors, there are many that are too large and are trailer behind and controlled and operated hydraulically. Some multi - purpose machines are used where a high degree of precision is needed for precision tillage, planting, bed shaping and fertilizing. They have to till the soil, form seedbeds, form irrigation furrows, either … plant the seed or cultivate the crop and apply fertilizer in one pass through the field. The use of aircraft has revolutionized many farming operation: fertilizers and herbicides, are applied from the air.
Farming operation includes plowing, harrowing, planting, tilling, harvesting, drying and processing crops.
Soil preparation for planting usually involves plowing and harrowing. Plowing is often the most important farming operation, not only because of the basic nature of the work but also from the standpoint of power required.
The essential feature of plowing by moldboard is that a layer of soil is separated from the underlying subsoil and is turned, so that any vegetation or manure present on the surface is buried and a layer of soil from below is brought to the surface where it is exposed to the action of weathering agents and of agricultural implements.
The harrowing of the plowed soil is designed to break clods, level the surface and destroy weeds. A wide variety of implements are classified as harrows, the most common kinds being the disc harrow and the knife harrow. Previously, the function of seedbed preparation was performed entirely by the implements classified as harrows. With the introduction of power farming, it is now performed in large part by field cultivators, rotary tillers and various designs of rollers. Power – driven rotary tillers perform the function of both plowing and harrowing.
2.Answer the questions
1. Which kinds of agricultural machines do you know?
2. Which information about agricultural machines?
3. Which implements do you know?
4. Which farming operations do you know?
5. Which farming operations does the soil preparation involve?
6. Which kinds of harrow do you know?

3.Match English and Ukrainian variants.
|
1. Fiber production – 2. Initial tillage – 3. Growing season – 4. Livestock feeding – 5. high – capacity plows – 6. subsoilers – 7. versatile – 8. convenient – 9. plow – 10. cultivator – 11. fertilizer spreader – 12. to till the soil – 13. form seedbeds – 14. formirrigation furrows – 15. moldboard – 16. a layerof soil – 17. manure – 18. vegetation – 19. weather in gagents – 20. to break clods – 21. knife harrow – |
a. ножова борона b. розбивати грудки c. обробляти землю d. формувати грядки e. рослинність f. плуг g. гній h. зручний i. відвал j. розкидач добрив k. культиватор l. вегетаційний період m. шар грунту n. формувати поливні борозни o. глибокі розрихлювачі p. годівля тварин q. універсальний r. плуги високої ємності s. початкова обробка t. вивітрювання компонентів u. виробництво штучного волокна |
4. Complete the sentences with the proper words from the brackets and translate them into Ukrainian.
1.The system of food and fiber production in agriculture is highly ……………...…(specialized/ mechanized/qualified) .
2. Many ………………….. (implements/transport/ mechanisms) such as plows, cultivators and fertilizer spreaders are usually mounted on tractors.
3. Farming operation includes plowing, harrowing, planting, tilling, harvesting, drying and processing ………………………...… (plants/soils/crops).
4. Soil preparation for ………………….………….(planting/irrigation/tilling) usually involves plowing and harrowing.
5. The …………………………………..…..(plouging /disking/harrowing) of the plowed soil is designed to break clods, level the surface and destroy weeds.
TEXT 8
1. Read the texts Text1A Round Baler.
A baler is a piece of farm machinery used to compress a cut and raked crop (such as hay, cotton, straw, or silage) into compact bales that are easy to handle, transport, and store. Several different types of balers are commonly used, each producing a different type of bale – rectangular or cylindrical, of various sizes, bound with twine, strapping, netting, or wire.
The most common type of baler in industrialized countries today is the large round baler. It produces cylinder-shaped "round" or "rolled" bales. Grass is rolled up inside the baler using rubberized belts, fixed rollers, or a combination of the two. When the bale reaches a predetermined size, either netting or twine is wrapped around it to hold its shape. The back of the baler swings open, and the bale is discharged. The bales are complete at this stage, but they may also be wrapped in plastic sheeting by a bale wrapper, either to keep hay dry when stored outside or convert damp grass into silage.
Text 2 A Planter.
A planter is an agricultural farm implement towed behind a tractor, used for sowing crops through a field. It is connected to the tractor with a draw-bar, or a three-point hitch. Planters lay the seeds down in precise manner along rows. Seeds are distributed through devices called row units. The row units are spaced evenly along the planter. Planters vary greatly in size, from 1 row to 48, with the biggest in the world being the 48-row John Deere DB120. The space between the row units also vary greatly. The most common row spacing in the United States today is 30 inches.
On smaller and older planters, a marker extends out to the side half the width of the planter and creates a line in the field where the tractor should be centered for the next pass. The marker is usually a single disc harrow disc on a rod on each side of the planter. On larger and more modern planters, GPS navigation and auto-steer systems for the tractor are often used, eliminating the need for the marker. Some precision farming equipment such as Case IH AFS uses GPS/RKS and computer controlled planter to sow seeds to precise position accurate within 2 cm. In irregular shaped field, the precision farming equipment will automatically hold the seed release over area already sewn when the tractor has to run overlapping pattern to avoid obstacles such as trees.
Older planters commonly have a seed bin for each row and a fertilizer bin for two or more rows. In each seed bin plates are installed with a certain number of teeth and tooth spacing according to the type of seed to be sown and the rate at which the seeds are to be sown. The tooth size (actually the size of the space between the teeth) is just big enough to allow one seed in at a time but not big enough for two. Modern planters often have a large bin for seeds that are distributed to each row.
Vocabulary: baler (a bale) – тюковязальник (тюк), planter- сівалка
2. Put “planter” or “baler” and complete the sentences. Translate them into Ukrainian.
Ø A 1 _____ is a piece of farm machinery used to compress a cut and raked crop into compact bales.
Ø A 2 _________ is an agricultural farm implement , used for sowing crops through a field.
Ø 3 ____________ vary greatly in size.
Ø Different types of 4 _______________ produce the different type of bales.
Ø Older 5 _____ commonly have a seed bin for each row and a fertilizer bin for two or more rows.
Ø The 6 ______________ has a single disc harrow on its side.
TEXT 9
1. Read the text
Tractors
Power is supplied. Power can be supplied. Power can be supplied in various forms. The tractor can pull machines. The tractor can push machines. It can drive machines by means of a belt. It can drive machines by means of a belt from a belt pulley. The tractor supplies power to machines from the power-takeoff shaft.
The power is measured. It is measured by kilowatts or horse powers. Tractors are classified according to the power. Tractors are classified according to the power produced.
Crawlers are used for heavy operations. Crawlers or track laying tractors must be used for heavy operations. Large crawlers must be used for heavy operations. Crawlers have tracks. Tracks have a grip. Tracks have the grip on the ground. Tracks increase the grip of the tractor on the ground. The crawlers are able to push or pull heavy loads and machines.
The tractors may have tires. The tires can be placed farther apart. The tires can be placed closer or farther apart according to the distance between the rows. We are able to place tires closer or farther apart according to the distance between the rows that must be cultivated. Wheeled tractors may have implements and machines on them. Implements are mounted on the tractor. This is done by the three-point linkage.
There are tractors with diesel or gasoline engines. The diesel engine will use less fuel than the gasoline engine for the same work done. The fuel should be clean. The oil must be changed regularly. It is necessary to change the oil regularly. It is necessary to change the oil regularly because it provides tractor' s useful work.
2. Define the parts of speech of the following words.
various, gaseous, famous, numerous
3. Compare the words with Ukrainian ones.
machine, kilowatt, gasoline, cultivation, system, battery, filter, motor, radiator.
4. Fill in the gaps with proper words and word-combinations
1. The tractor can supply power to the machines from the ……...(power-take-off shaft, belt pulley, three-point linkage).
2. The tyres can be placed closer or farther apart………...(according to, by means of) distance between the rows.
3. The crawlers are usually .............(small, large, various).
4. The tractor can ……………...(increase, pull, do) machines.
5. The crawlers are able to …………….. (produce, push, drive) heavy loads.
6. Implements are mounted on the tractor by means of ..(a belt pulley, tyres, a three-point linkage).
7. The fuel should be .....................(heavy, clean) and have no water.
TEXT 10
1. Read and translate the text
PLOUGHS
There are various forms of the plough. The plough is an implement used for soil cultivation. It has become the implement used for soil preparation. The plough has been used for many centuries. It has been used for preparation of seedbeds.
A plough is an implement with one or more mould-boards. Mould boards cut the soil. Mould boards cut and turn the soil. They cut soil slices. They cut furrow slices. Both mounted and semimounted types of ploughs are being produced. A semi-mounted plough is not lifted off the ground. The number of mould boards is not the same on different ploughs. It depends on the type of soil and the tractor size.
There are three types of ploughs, conventional plough being one of them. Some trailed models of conventional ploughs are in common use. Most reversible ploughs are mounted, but some of the larger models are semi-mounted.
Disc ploughs have large rotating discs. The plough may have a disc coulter. The plough has a body. It also has legs. The plough body is attached to legs. Legs are bolted to the frame. The base of a plough body is called the frog. The share cuts the bottom of the furrow slice.
There are many types of mould boards, each producing its special surface.
There are three main types of a plough. The main types of plough body are general-purpose type and digger type. The digger type is used for deep ploughing. It is used in soil preparation for root crops. Digger bodies have a higher power requirement than the general-purpose type.
The plough has been used in its different forms for many centuries. It has become the main implement used for the preparation of seedbeds.
A plough is an implement with one or more mould-boards which cut and turn the soil. Modern ploughs are commonly fully mounted on the tractor hydraulic system.
Some are semi-mounted with the front supported by the tractor hydraulic linkage and the rear by one or more wheels.
2. Define the suffixes:
adjustable, movable, usable, comfortable, replaceable, measurable, attachable; reversible, possible, flexible, visible, compressible.
3. Combine the words by the suitable principle:
implement, hydraulic, conventional, rarely, rotate, digger, classify, ignition, commonly, organize, crawler, reversible, generate, gravity, electrify, lubricator, suitable, arrangement, full.
4. Translate the words. Define the role of the suffix –ly:
full – fully; main – mainly; mechanical – mechanically; proper –properly; common – commonly; rare – rarely; close – closely; chemical – chemically.
5. Complete the table. Define the role of the prefixes ir-, in-, іm-, il-. Translate the words.
flexible possible movable visible legal measurable rational
|
ir |
in |
im |
il |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. Compare the words with Ukrainian ones.
|
Generator - |
|
|
Generate - |
|
|
Systematic - |
|
|
Classify - |
|
|
Gravity - |
|
|
Typical - |
|
|
Transformer - |
|
|
Hydraulically - |
|
|
Organizer - |
|
|
Mechanize - |
|
7. Translate the sentences using the different forms of the verb to have:
1. A modern plough has up to six mould boards.
2. When the piston has reached the bottom of its stroke the inlet valve closes.
3. Both conventional and reversible ploughs have been produced by our plant.
4. The driver has to attach the plough correctly.
5. The pneumatic tyres have become so efficient and so popular that they are the standard part of all wheeled tractors.
6. Modern tractors usually have a four-stroke engine.
7. We have to set all mould boards at the same angle.
8. Write down 10 verbs from the text and make Past Indefinite and Past Participle forms.
For example: repair- repaired- repaired
TEXT 11
1. Read the text. Match the number of paragraphs (1 – 5) with the proper headings.(A – E).
a. The fuel system of the diesel engine
b. The best condition to run
c. The starting system
d. Operation of diesel engine
e. The reason of inefficient running of diesel engine.
1. The diesel engine is known to be almost the same as the petrol but because of higher pressures it contains stronger parts. The method of operation of the diesel differs from that of other engine. Instead of fuel - air engines air mixture employed in other engines air only is taken to the cylinder. The air inside the cylinder is compressed and its temperature is rises. It results in the ignition of the fuel charge injected into it. Thus the fuel is ignited in the diesel engine.
2. The diesel fuel system operates under two pressure levels. The low pressure part of the system contains the fuel tank, fuel pumps and fuel filters. The high pressure parts of the system contain the injection pump, the high pressure lines leading to the injection nozzles.
3. We know some diesels to employ auxiliary gasoline engines for starting. These engines are used to crank the diesel until it starts. Most farm tractor diesels use electric starting motors similar to those used on gasoline engine tractors. They are operated from the battery on the tractor.
4. In diesel engines the fuel injection system is found to be the most usual cause of trouble. A smoky exhaust in a diesel engine is believed to be the sign of unsatisfactory work. If the engine runs for long time in this condition, the piston valves and injection nozzle become coated with carbon and this is sure to cause inefficient running and maу lead to more serious trouble.
5. Diesel engines are supposed to run best when the temperature of the cooling water reaches 75
– 850C.
2. Find in the text the English equivalents of the word – combinations to the Ukrainian given below.
1.Метод керування дизельним двигуном; 2. Вищі тиски; 3. Повітря в середині циліндра;
4. Запалювання паливного заряду; 5. Паливна система дизельного двигуна; 6. Паливний бак;
7. Паливні помпи; 8. Паливні фільтри; 9. Інжекторна помпа; 10. Інжекторні форсунки; 11. Бензинові двигуни; 12. Двигуни електричного запуску; 13. Вихлоп диму; 14. Клапани циліндра; 15. Неефективний пробіг; 16. Температура охолоджуючої води.
3. Answer the questions:
1. What’s the diesel engine?
2. Which is the method of operation of the diesel engine?
4. How does the fuel diesel system operate?
5. What is used for starting in most diesel engines?
6. What is the sing of the unsatisfactory work of the diesel engine?
TEXT 12
1. Read the text.
Application and Variations of Tractors
A variety of specialty farm tractors have been developed for particular uses. These include "row crop" tractors with adjustable tread width to allow the tractor to pass down rows of corn, tomatoes or other crops without crushing the plants, "wheatland" or "standard" tractors with fixed wheels and a lower center of gravity for plowing and other heavy field work for broadcast crops, and "high crop" tractors with adjustable tread and increased ground clearance, often used in the cultivation of cotton and other high-growing row crop plant operations, and "utility tractors", typically smaller tractors with a low center of gravity and short turning radius, used for general purposes around the farmstead. Many utility tractors are used for nonfarm grading, landscape maintenance and excavation purposes, particularly with loaders, backhoe heavy fields, pallet forks and similar devices. Small garden or lawn tractors are designed for suburban and semirural gardening and landscape maintenance also exist in a variety of configurations.
Some farm-type tractors are found elsewhere more often than on farms: with large universities' gardening departments, in public parks. These are often fitted with grass (turf) tires which are less damaging to soft surfaces than agricultural tires.
Space technology has been incorporated into agriculture in the form of GPS devices, and robust onboard computers installed as optional features on farm tractors. These technologies are used in modern, precision farming techniques. The spin-offs from the space race have actually facilitated automation in plowing and the use of auto steer systems (drone on tractors that are manned but only steered at the end of a row), the idea being to neither overlap and use more fuel nor leave streaks when performing jobs such as cultivating. Several tractor companies have also been working on producing a driverless tractor.
The durability and engine power of tractors made them very suitable for engineering tasks. Tractors can be fitted with engineering tools such as dozer blades, buckets, hoes, rippers, etc. The most common attachments for the front of a tractor are dozer blades or buckets. When attached to engineering tools, the tractor is called an engineering vehicle.
2. Find the Ukrainian equivalents
1. Adjustable tread width a.радіус повороту
2. increased ground clearance b. збільшений дорожній просвіт
3. turning radius c. регульована ширина протектора
4. backhoes d. екскаватор
5. pallet forks e. кермові системи
6. auto - steer systems f. вила для піддонів
3. Match the words from the right column with the words from the left column.
1. To pull - a. a cargo car
2. To tow - b. a rototiller
3. To disc – c. stubble (стерня)
4. To plant – d. the fruit trees
5. To plow – e. a heavy field
4. Match the words with their definitions.
1. A tractor plows a field using … a. a rototiller
2. A tractor pulls… b. a pump
3. A farm tractor used to power …for irrigating a plot of land c. a chisel plow.
4. A garden tractor tows … d. a cargo cart
5.A tractor with … for grain. e. a chaser bin
6.A … tractor performs various earth works. f. backhoe-loader
5. Look at the images and name the farm implements.

6. Look at the figure and say which constructive parts a tractor has.
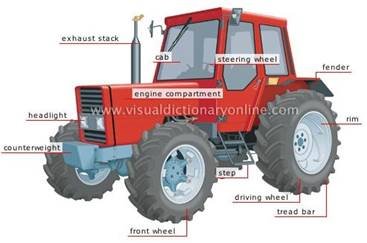 1. exhaust stack –
2. steering
weal - 3. fender
–
1. exhaust stack –
2. steering
weal - 3. fender
–
4. driving wрeеl –
5. tread bar - 6. headlight - 7. counterweight -
8. engine compartment -
9. rim -
10. step -
a. обід
b. вихлопна труба
c. передні фари
d. кермо
e. привідне колесо
f. протектор
g. східця
h. крило
i. двигунний відсік
j. противага
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TEXT 13
1. Read the text and match 1 –to 12 with A to L.
SELECTING TRACTORS
1. Tractor power is used extensively on farms. The types of tractor usually employed for work in agriculture include from the row – crop to general – purpose tractors standard wheel types, utility tractors and tracklayers.
2. A tractor should be selected after considering the advantages and disadvantages of different types. Original cost, adaptability, soil conditions, work to be done and economy are factors to consider in selecting a tractor.
3. Efficiency of the tractor selected also depends on operating, maintaining and adjusting it by an operator. Row crop type is especially designed for cultivating row crops. Row crop tractors are known to have been used since 1924.
4. Because of great number of row crops, different width between rows, low – or high - growing plants row – crop tractors must be adaptable to various field conditions and do many field operations. These tractors are usually called general – purpose tractors. Using three types of front - wheel equipment increases efficiency of row – crop tractors.
5. The distance between the centers of the rear wheels is also adjustable in row – crop models. Thus the tractor can be adapted to low – or high - growing plants and to various row widths; wheels will run between rows and cause a minimum of plant damage.
6. There are some other features common to row – crop models. By applying high vertical clearance (called cultivating clearance) a tractor operator can work in high – growing crops. Row – crop models are provided with the differential brakes. When one break is used it retards or stops one wheel and other wheel causes the tractor to make a short turn. Cultivating often requires short turns at the row ends.
7. Equipment for row – crop models usually includes belt pulley drawbar, power – take – off and hydraulic system. Engine power of tractors may be from about 20 hp to more than 100hp. The row – crop tractor is more often used than any other type.
8. Standard wheel type is the oldest type. It is not designed for cultivating row crops, but is most useful for supplying power to trailed implements.
Four - wheel standard tractors with engine of 200 hp or more operate large implements or combinations of implements. In some models the front wheels are driven by hydraulic power.
9. Utility tractors may be with either fixed or adjustable tread. With adjustable tread they can be used for a wide variety of row crops. These tractors have less vertical clearance than the row - crop models and so they have more stability. Utility tractors are widely used for open field work – plowing and haying operations. Commonly used models have engines from 35 to 65 hp.
10. Tracklayers for agriculture have a lot of uses. Diesel engines are popular in tracklayers. Tracklayers are widely employed for field work requiring heavy loads. They are good on soft, wet, swampy ground. Preparing ground for irrigation and maintaining irrigation systems are tasks for which these tractors are designed.
11. Almost any tractors can be used in orchards. But tractors specially designed for this work are more useful. Wheel tractors for orchards are furnished with narrow tread and short wheel base.
Most orchard tractors have a low center of gravity which increases tractor stability.
12. Lawn and garden tractors are small wheel type tractors. They are widely used in parks and gardens. Farmers think them useful for farm operations that require special accuracy – thinning and weeding, for example.
A. Belt pulley drawbar, power – take – off and hydraulic system is the equipment of the row – crop tractor.
B. Four - wheel tractors are most useful for supplying power to trailed implements.
C. These tractors have less vertical clearance and can be used for a wide variety of row crops.
D. They are good on soft, wet, swampy ground.
E. These tractors are widely used in parks and gardens.
F. These tractors are good for orchards.
G. All types of tractors are widely used on farms.
H. There are main factors which are considering in selecting a tractor.
I. Efficiency is one of the characteristics of the tractor power.
J. General purpose tractors do many field operations.
K. Row – crop tractors adapted to low – or high – growing plants and to various row width. L Row – crop tractor has the differential brakes.
2.Write out the sentences with Passive Voice from the text above.
For example: Tractor power is used extensively on farms.
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
3.Answer the questions:
1. Where the different types of tractors are employed?
2. Which advantages and disadvantages should be considered in selecting tractors?
3. What determines the efficiency of the tractor?
4. Which tractors are usually called general – purpose tractors?
5. Can the row crop tractor be adaptable to various field conditions and many field operations?
6. Which is the equipment of the row crop tractors?
7. Which type of a tractor is the oldest?
8. Which may be the utility tractor?
9. Which is the main application of the utility tractor?
10. Which kinds of tractors do you know else?
TEXT 14
1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian.
Heat is being produced in the combustion chamber of the engine as the fuel is being burned. Some of this heat goes into useful power, some is lost through the exhaust gases, and some must be removed by cooling system of the engine. The cooling system removes about one – third of the heat produced. The heat passes through the cylinder walls into the coolant or into the air. The engine temperature must be controlled.
An engine equipped with a liquid – cooling system has a water jacket around the cylinder walls and the cylinder head of the engine. The water jacket is connected to the radiator by passages. The engine is cooled by coolant circulating from the water jacket through the radiator from top to bottom and back through the water jacket from bottom to top. The air flowing past the radiator takes heat from the coolant. The fan keeps a constant flow of air past the radiator and helps in the cooling process.
Two types of liquid – cooling systems: the thermosyphon system and the forced – circulation system are used on farm tractors. The thermosyphon system is a system in which the circulation of coolant is caused by difference in temperature between the coolant in the water jacket and that circulating in the other parts of the cooling system.
The forced – circulated system has all the parts that are in the thermosyphon system but it also has a water pump and a thermostat. The water pump is used for continuous circulation of the coolant. The thermostat controls the flow of the coolant through the cooling system and regulates the temperature.
The radiator has tubes through which the coolant is circulating. The fan behind the radiator removes heat from coolant.
Small stationary engines are air – cooled. Air – cooling system forces air past the hottest of the engine block. The air is forced through the system by a fan. It is necessary to keep the inlet to the fan clean because a reduced air flow will cause the engine overheating.
2. Find the English equivalents from the text to given Ukrainian below.
1.камера згорання; 7. циркуляція охолоджувача;
2. вихлопні гази; 8. постійний потік повітря;
3. циліндричні стінки; 9. процес охолодження;
4. температура двигуна; 10. водяна помпа;
5. водяний жакет; 11. маленькі стаціонарні двигуни;
6. циліндрична головка двигуна; 12. перегрівання двигуна.
3. Answer the questions.
1. What is the main aim of the cooling system of the engine?
2. What are the main elements of the liquid cooling system?
3. What are there two types of liquid cooling system in the engine?
4. What are the main parts of the forced - circulated cooling system?
5. Which kind of engine has the air - circulated cooling system?
4. Match the English and Ukrainian equivalents
|
1. Hose - |
a. трубки |
|
2. Drain petcock – |
b. термосифонна система |
|
3. The forced – circulated system – |
c. повітряна система охолодження |
|
4. Useful power – |
d. охолоджувач |
|
5. The coolant – |
e. корисна потужність |
|
6. A liquid –cooling system – |
f. вентилятор |
|
7. Fan – |
g. охолоджувач |
|
8. Thermosyphon system – |
h. спускний кран |
5. Сomplete the sentences using the words in the brackets. Translate them into Ukrainian.
1. An engine equipped with a liquid – cooling system has a water jacket around the cylinder ……….(valve, walls, rings) and the cylinder head of the engine.
2. The thermosyphon system is a system in which the circulation of …………………(coolant, fuel, oil) is caused by difference in temperature between the coolant in the water jacket and that circulating in the other parts of the ………………… (ignition, fuel, cooling) system.
3. The forced – circulated system has all the parts that are in the thermosyphon system but it also has a …………………………. (oil, water, high pressure) pump and a thermostat.
6. Put the sentences into correct order.
• The radiator is circulating has which the coolant tubes through
________________________________________________________________________________ The circulation of the coolant water pump is used for continuous
________________________________________________________________________________
• Two types the thermosyphon system of liquid – cooling systems: and they are used on farm forced – circulation system tractors.
________________________________________________________________________________ The removes about – third of the cooling system heat produce done.
____________________________________________________________________
TEXT 15
1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian. Match the headings with the proper paragraphs.
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
5 |
|
A. A cultivator in the small-scale gardening
B. A way of attachment of a cultivator on the tractor
C. Some sense of cultivator
D. The goal of the cultivating
E. A cultivator looks like a chisel plow.
Cultivator
1. A cultivator is any of several types of farm implement used for secondary tillage. One sense of the name refers to frames with teeth (also called shanks) that pierce the soil as they are dragged through it linearly. Another sense refers to machines that use rotary motion of disks or teeth to accomplish a similar result. The rotary tiller is a principal example.
2. Cultivators stir and pulverize the soil, either before planting (to aerate the soil and prepare a smooth, loose seedbed) or after the crop has begun growing (to kill weeds—controlled disturbance of the topsoil close to the crop plants kills the surrounding weeds by uprooting them, burying their leaves to disrupt their photosynthesis, or a combination of both). Unlike a harrow, which disturbs the entire surface of the soil, cultivators are designed to disturb the soil in careful patterns, sparing the crop plants but disrupting the weeds.
3. Cultivators of the toothed type are often similar in form to chisel plows, but their goals are different. Cultivator teeth work near the surface, usually for weed control, whereas chisel plow shanks work deep beneath the surface, breaking up hardpan. Consequently, cultivating also takes much less power per shank than does chisel plowing.
4. Small toothed cultivators pushed or pulled by a single person are used as garden tools for small-scale gardening, such as for the household's own use or for small market gardens. Similarly sized rotary tillers combine the functions of harrow and cultivator into one multipurpose machine.
5. Cultivators are usually either self-propelled or drawn as an attachment behind either a twowheel tractor or four-wheel tractor. For two-wheel tractors they are usually rigidly fixed and powered via couplings to the tractors' transmission. For four-wheel tractors they are usually attached by means of a three-point hitch and driven by a power take-
off (PTO). Drawbar hookup is also still commonly used worldwide. Draft-animal power is sometimes still used today, being somewhat common in developing nations although rare in more industrialized economies.
2. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. A cultivator is a type of farm implement used for secondary tillage.
2.A cultivator has a frame with teeth (also called shanks) that pierce the soil as they are dragged through it linearly.
3. Cultivators stir and pulverize the soil, either before planting or after the crop has begun growing. 4. Cultivator teeth work near the surface, usually for weed control, whereas chisel plow shanks work deep beneath the surface, breaking up hardpan.
5. Cultivators are usually either self-propelled or drawn as an attachment behind either a two-wheel tractor or four-wheel tractor.
3. Answer the questions
1. Which a type of farming implement is used for secondary tillage?
2. Which is a main constructive part of a cultivator?
3. Which is the main aim of usage of a cultivator?
4. Find the English equivalents to the given Ukrainian ones.
1. обертовий рух дисків-
2. подібний результат- 3. збагатити грунт повітрям- 4. перервати їх фотосинтез- 5. дрібне садівництво-
6. маленькі зубчасті культиватори- 7. тягове зчеплення-
8. самохідний-
5.Match the words 1-10 with a-j.
a. Secondary tillage –
b. Pierce the soil –
c. Rotary tiller –
e. Weed control –
f. Beneath the surface –
g. Pulverize the soil –
h. The topsoil –
i. Crop plants –
j. The surrounding weeds –
1. під поверхнею
2. роторний культиватор
3. проколюють грунт
4. культурні рослини
5. боротьба з бур’янами
6. вторинна обробка грунту
7. навколишні бур’яни
8. верхній шар грунту
9. Розпушувачі
10. розпорошувати грунт
TEXT 16
1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian.
Harrows
A disc harrow is a farm implement that is used to cultivate the soil where crops are to be planted. It is also used to chop up unwanted weeds or crop remainders. It consists of many iron or steel discs which have slight concavity and are arranged into two or four sections. When viewed from above, the four sections would appear to form an "X" which has been flattened to be wider than it is tall. The discs are also offset so that they are not parallel with the overall direction of the implement. This is so they slice the ground they cut over a little bit to optimize the result. The concavity of the discs as well as their being offset causes them to loosen and pick up the soil they cut. Modern disc harrows are tractor-driven and are raised hydraulically. Some large ones even have side sections which rise up vertically to allow easier road transport or better storage configurations.
Disc harrows are primarily used to chop up soil that has been recently plowed to eliminate clumps and loosen the soil if it has been packed. They are also used to chop up old crops, such as cornstalks, to make the land easier to plow and to eliminate clogging in the plowing process. The disc is a secondary implement primarily used to break down soil clods into smaller units. By so doing it allows easier penetration of water into the soil, increases soil aeration and enhances the activity of soil biota.
2. Match the words 1-10 with a-j.
1) to chop up unwanted weeds or crop remainders a. зрубувати небажані бур’яни чи
залишки урожайних культур
2) penetration b. легка вгнутість
3) flattened c. сплющений
4) loosen the soil d. зсув
5) overall direction of the implement e. загальний напрямок знаряддя
6) eliminate clumps f. усунути грудки
7) offset g. розпушити грунт
8) cornstalks h. стебла кукурудзи
9) clogging i. засмічення
10) slight concavity j. проникнення
3. Answer the questions:
1. Which implement is named a disc harrow?
2. For which purpose a disc harrow is used?
3. What are the main design features of a disc harrow?
TEXT 17
1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian.
Forage Harvester
A self-propelled John Deere 5730 Forage Harvester.
A forage harvester (also known as a silage harvester, forager or chopper) is a farm implement that harvests forage plants to make silage. Silage is grass, corn or other plant that has been chopped into small pieces, and compacted together in a storage silo, silage bunker, or in silage bags. The silage is then fermented to provide feed for livestock. Haulage is a similar process to silage but using grass which has dried.
Forage harvesters can be implements attached to a tractor, or they can be self-propelled units. In either configuration, they have either a drum (cutter head) or a flywheel with a number of knives fixed to it that chops and blows the silage out a chute of the harvester into a wagon that is either connected to the harvester or to another vehicle driving alongside. Larger machines also have paddle accelerators to increase material speed and improve unloading characteristics. Once a wagon is filled up, the wagon can be detached and taken back to a silo for unloading, and another wagon can be attached. Because corn and grass require different types of cutting equipment, there are different heads for each type of silage, and these heads can be connected and disconnected from the harvester. Maize and whole crop silage are cut directly by the header, using reciprocating knives, disc mowers or large saw-like blades. Kernel processors (KP), modules consisting of two mill rolls with teeth pressed together by powerful springs, are frequently used when harvesting cereal crops like corn and sorghum to crack the kernels of these plant heads. Kernel processors are installed between the cutter head and accelerator. In most forage harvesters, the KP can be quickly removed and replaced with a grass chute for chopping non-cereal crops.
Today's largest machines have engines producing up to 1,100 horsepower (820 kW), are fitted with headers able to cut up to a 35-foot (11 m) swath of corn in a single pass, and an output exceeding 400 tons of silage per hour (Krone).
Silage made from grass, canola, oats or wheat are chopped in pieces 5 to 76 millimeters (depending on knife, cutter head, and length of cut transmission configuration) and treated with additives including bacteria, enzymes, mold inhibitors, and preservatives to accelerate the fermentation process. When silage is made of corn or sorghum additives are not necessary because of the high sugar and starch levels in the plants. Additives however are frequently added to corn and sorghum to augment their fermentation.
Vocabulary: forage harvester – кормозбиральний комбайн, silage harvester – силосний комбайн
2. Complete the sentences using given words in the brackets. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. A forage harvester is a farm implement that harvests forage plants to make … (silage/haylage).
2. Silage is grass, corn or other… (animal/plant) that has been chopped into small pieces, and compacted together in the silage bunker.
3. Forage harvesters can be implements attached to … (a tractor/a combine), or they can be selfpropelled units.
4. Corn and grass require different types of … (chopping/cutting) equipment.
5. When silage is made of corn or sorghum … (inhibitors /additives) are not necessary because of the high sugar and starch levels in the plants.
TEXT 18
1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian. Combine Harvester
The combine harvester, or simply combine, is a machine that harvests grain crops. The name derives from its combining three separate operations comprising harvesting—reaping, threshing, and winnowing—into a single process. Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, oats, rye, barley, corn (maize), soybeans and flax (linseed). The waste straw left behind on the field is the remaining dried stems and leaves of the crop with limited nutrients which is either chopped and spread on the field or baled for feed and bedding for livestock.
Combine harvesters are one of the most economically important labor saving inventions, enabling a small fraction of the population to be engaged in agriculture.
Cutting unit. This unit cuts the standing grain and delivers it to the feeding mechanism. Main parts of this unit are reel, the dividers, the cutter bar and the auger. The reel is the first part to touch the standing grain. It can be adjusted up and down and also forward and backward.
Dividers separate the standing grain and define the swath to be cut.
The cutter bar and knife are similar to those on a mover.
Feeding unit. This unit – if properly adjusted – carries away the cut grain from the cutter bar and feeds it into the cylinder.
Threshing unit. From 80 to 90 per cent of the grain separation takes place between the cylinder and the concaves. The stationеry concave bars and open grates are located below the cylinder Various types are used, but they all do the same work. Together with the cylinder, the concaves cause the grain to pass between the rapidly revolving cylinder and stationary surface. Grain falling through the grates is then collected on the grain pan and fed onto the sieves for cleaning.
Separating unit. Most of the threshed grain is separated from the straw at the concaves and at the finger grate at the rear of the cylinder. The grain falls through openings in the bottom of the rack to the grain pan or to the grain conveyor.
Clearing unit. This unit removes the chaff and fine residue from the threshed grain. It cleans grain by means of the combined action of sieves and air blast.
Grain handling unit. This unit conveys the clean threshed grain auger, clean grain elevator, and grain tank.
Vocabulary: Grain handling unit - вивантажувальний пристрій для збирання очищеного зерна reaping– жнива, threshing unit– молотарка, winnowing— копання, the chaff and fine residue – солома і мілкі відходи, grain auger – шнековий навантажувач зерна, grates– решітки
2. Answer the questions.
1. What is a combine harvester?
2. Which principle units of a combine do you know?
3. Which is a function of a cutting unit?
4. What does the feeding unit do?
5. Which is the function of the threshing unit?
3. Find and write.
Principle Units of a Combine
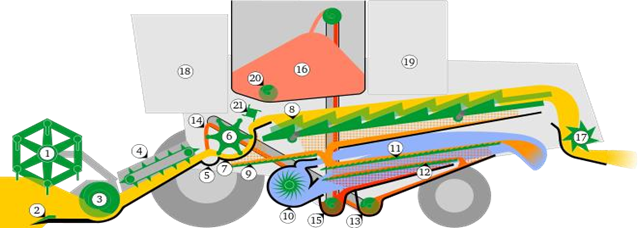
1. Reel - котушка 11) to pаdjustablesieve – верхнє регульоване
2. cutter bar – різак 12) bottom sieve – нижнє сито
3. header auger – ведучий шнек 13) tailings conveyor – хвостовий конвеєр
4. grain conveyor (feeding) –зерноконвеєр 14) rethreshing of tailings - обмолот хвостів
5. stone trap –каменеуловлювач 15) grain auger – зерновий шнек
6. threshing drum–молотильний барабан 16) grain tank – зерновий бункер
7. concave - підбарабання, деко 17) strawchopper- подрібнювач соломи
8. straw walker - соломотряс 18) driver'scab – кабіна комбайнера
9. grain pan – зерновий піддон 19) engine – двигун
10.
![]() fan -
вентилятор 20) unloading auger – розвантажувальний шнек
fan -
вентилятор 20) unloading auger – розвантажувальний шнек
21) impeller- робоче колесо
4. Match the names of units with their definitions.
1. Cutting unit – a. removes the chaff and fine residue from the threshed grain.
2. Clearing unit – b. separates the threshed grain from the straw.
3. Separating unit – c. has the stationеry concave bars and open grates.
4. Grain handling unit – d. carries away the cut grain from the cutter bar.
5. Threshing unit – e. cuts the standing grain and delivers it to the feeding mechanism.
6. Feeding unit - f. conveys the clean threshed grain auger, clean grain elevator.
TEXT 19
1. Read the text “Wheat” and translate it into Ukrainian.
Wheat-growing was extensively practiced throughout Europe in prehistoric, times and this cereal was of great importance in the ancient civilizations of Persia, Greece and Egypt. It spread to all the temperate countries where it now plays a major part in the food supply of many nations and it is also widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical areas.
Cultivation. It is often said that winter wheat does best on a well-formed seed-bed. Plugging should be done as early c as possible and the normal depth would-be in the region of 6 inches. The type of seed-bed required for winter wheat can be described as one with a reasonable tilt in the top 2–3 inches, with a surface containing a high proportion of clods, the largest of these being about the size of a man' s hand. This is to prevent capping, a condition which can easily arise with heavy rain, when the soil surface runs together forming a crust.
Managing. With all crops it is essential to ensure that adequate supplies of phosphate and potash are available during the first few weeks of growth. Once observed it is not possible to correct properly any deficiency and both of these major elements are required either in advance of drilling or they may be combine-drilled with the seed. Combine drilling g is the most economical way of applying these fertilizers, but with winter wheat time of sowing being of prime importance, the fast method of application using fertilizer spinners is more often preferred. For average conditions 30 units (one unit is equal to 1.12 lb. and is the same as 1% on analysis) each of phosphate and potash will be sufficient. If the soil is rich in nitrogen, then 30 units/acre of fertilizer nitrogen would suffice, but under average conditions levels up to 60 units are considered economic rising to 80 units in the low rainfall areas. Previous cropping, local environment and to some extent cultural techniques can also influence the optimum level of this nutrient. When the soil is likely to supply some nitrogen for early growth of a winter crop, then it is unlikely that any autumn fertilizer nitrogen would be required. The short, stiff-strewed varieties of wheat can stand high levels of fertilizer nitrogen whereas the taller ones used to produce quality straw will only tolerate moderate amounts. Of all the cereals winter wheat will give the highest response to his fertilizer and to obtain the best return the proper dressing should be applied at the correct time. As far as spring wheat is concerned up to 60 units of nitrogen can be economic. It should be applied prior to drilling or combine drilled with the seed. Seeding Rates. The amount of seed required for autumn wheat will vary between 1 and 2.5 cwt/acre. Early sowings need the least since the temperatures for germination are higher than those later on and a larger number of the seeds produce plants. As one goes north the autumn temperatures become significantly lower and hence to obtain the optimum number of plants it is necessary to sow larger quantities of seed
Harvest. Winter wheat is normally harvested from August to October (in Britain), depending on the type of summer experienced and also the geographical location. Spring wheat matures much later than winter wheat and later than the other cereals.
Following a hot, dry summer grain may be combine-harvested under very good conditions; and if the moisture does not exceed 14% then it can be stored without drying. Moisture tests can be carried out at harvest and these are often used to indicate the stage of ripeness or readiness for combining.
Most of the wheat being cut by combine harvester, there is still a small, but significant acreage, which is hindered to satisfy the demand for long straw. It is said to be binder-ripe when the grain is fairly firm, has a cheesy texture and does not exude any milky fluid when pressed. This stage is usually reached between 1 and 2 weeks before it can be combine-harvested. The actual binding should not take place until the morning dew has disappeared. Once cut the grain will mature in the ear and the straw will dry out.
2. Find synonyms of the following words and wordcombinations in the text:
|
widely area to grow best important to see rightly enough fertilization to be high in before |
local conditions to withstand to use (fertilizers) as to to differ stand yield to ripen to show |
3. Define to which parts of speech belong the next words and translate them without dictionary:
1)extent, extensive, extensively, to extend;
2) to supply, the supply, supplying, supplied, supplier;
3) content, to contain, containing, container;
4) to form, the form, forming, formed, formation, formless;
5) deficient, deficiency;
6) dry, dryly, to dry out, dryer, dryness.
4. Fill in the gaps with necessary words from the text:
v The time and method of……... the land for wheat depends principally on the …….. that is followed by it.
v Unless the rainfall is high it is desirable to have the land prepared .......... of seeding to permit settling of the …….....and accumulation of………... .
v When the land is to be plowed after a small grain there should be a month
.......................plowing and seeding.
TEXT 20
1. Read the text “Maize” and translate it into Ukrainian.
Maize
Types of Maize. Several thousand varieties of maize are now grown throughout the world and most of these can be allocated to one of the seven most important groups: dent maize, flint maize, sweet corn, soft maize, popcorn, waxy maize, pod maize.
Soil Requirements. Successful, maize cultivation is more frequently and more easily achieved on soils, which are of medium texture. As the soils become lighter the greater is the chance of their―drying out‖ in midsummer and although there is really nothing else against them, the very light sandy soils should be avoided. Having suggested light to medium textured soils for maize, it must also be stressed that organic status and fertility should be high. The maize land should be free draining in order that as much of the heat as possible is employed in raising soil temperatures and not removing excess of soil moisture. The soil should be naturally free draining to enable a full rooting system to develop in a plentiful supply of oxygen. Maximum yields are believed to be obtained between pH 4 and 9. Some scientists believe maize to be successfully cultivated on the moderately acid soils (pH 6–7 as optimal). Others say that maize growing can be successful under alkaline conditions provided there are no serious deficiencies of the micro-nutrients.
Application of Fertilizers. It has been suggested that phosphate and potash should be applied to the land well in advance of drilling and the nitrogen incorporated into the seedbed just prior to drilling, otherwise much of it would be lost by leaching. One should remember that germination is much retarded by fertilizers in contact with the seed.
Cultivation. With a more extensive and deeper rooting system than the other cereals, maize will require deeper plugging, cultivations and seedbeds to obtain maximum growth. Autumn plugging is advisable on stronger soils and it may be left until the early spring when textures are light. Cultivations which follow should be to a depth of 4-5 inches. They kill the weeds after germination: inter row cultivation can follow crop emergence to obtain further weed control. Chemical means are often preferred. Seed-beds should be uniform and fine to obtain a quick germination and to assist the action of herbicides in their control of weeds.
Seeding. Minimum temperatures for growth of maize are around 50° F (10° C) and thus early spring sowings are of little value except when the soils are warmer than usual. Under cool conditions seeds rot. When the average t° is over 50° F the emergence of maize will take approximately two weeks. Late spring frosts can also be damaging to seedling maize, although with the cold tolerant varieties being introduced, there is every chance that this crop may now survive the first few degrees of frost.
Sunshine and Solar Energy. Little is said and written about sunshine and solar energy requirements with this cereal. It is, however, assumed that for satisfactory growth and ripening of the crop high levels of bright sunshine are required. Maize is quite unique in its mode of growth and extent and duration of its leaves. They grow in a manner which facilitates efficient use of radiant energy by trapping most of the sun' s rays and since the duration of full leaf extends almost to grain maturity, the sun' s energy can be transferred to grain yield throughout the whole life of the plant. A point close to optimum leaf area is obtained early and maintained almost to grain maturity thus making maize one of the most efficient utilizes and converters of solar energy into plant energy particularly when the whole plant is considered as the economic yield.
2. Fill in the gaps with necessary words from the text
1. When there is not enough potassium in the soil, we say the soil is …... in potassium.
2. ……. is the process which removes excess of soil moisture.
3. Best yields of maize are achieved on soils of medium ….... and high …....
4. Nitrogen fertilizer should be….... into the soil, otherwise much of it will be lost by ….... .
5. Cultivations and ........help to control…….. .
6. The average temperature for the ………. of maize is over fifty degrees F.
3. Which statement don’t correspond to the text make necessary changes
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. It' s advisable that nitrogen be applied long before plowing.
2. They recommend that maize land should be free draining.
3. It' s necessary that the students know different varieties.
4. It is not desirable that maize be planted in warm soil.
5. Chemical means are seldom used in weed control.
6. To obtain quick germination the seed-bed must be fine.
4. Build the comparative and superlative forms of adjectives.
APPENDIX
TEST 1 Variant 1
1. Match the English and Ukrainian word – combinations.
1. Reciprocating move - a) гази, що розширюються
2. The starting system - b) зворотно – поступальний рух
3. Cylinder head - c) обертальні рухи
4. Engine operation - d) камера згорання
5. Camshaft - e) циліндрична головка
6. Cooling system - f) акумуляторна батарея
7. Combustion chamber - j) керування двигуном
8. Storage battery - h) впускні клапани
9. Intake valves - i) відпрацьовані гази
10. Burned gases - j) розподільчий вал
11. Rotary motions - k) система охолодження
12. Expanding gases - l) пускова система
2. Put the missing words. Use the words from the box given below.
a. strokes; b. movement; c. piston; d. bottom; e. end; f. operates.
Engine 1__ on cycles. There are four strokes of the 2__ in one cycle of engine operation. There two outward 3__toward the crankshaft and two inward strokes away from the crankshaft. When the piston is at the 4__ of the stroke away from the crankshaft (inward stroke) this is a top dead center (TDC). When the piston is at the end of the out – ward – stroke (toward the crankshaft) this is 5__ dead center (BDC). The piston 6__ from TDC to BDC is an engine stroke.
3. Translate the given sentences into Ukrainian.
1. Internal combustion is the process of burning of fuel within the engine.
2. The cylinders and the cylinder heads form the combustion chambers.
3. Pistons, rings, valves, connection rods are reciprocation engine parts.
4. The electrical system of the engines has a storage battery or a magneto.
5. The air inside the cylinder is compressed and its temperature is rises.
6. The diesel fuel system operates under two pressure levels.
Variant 2
1. Match the English and Ukrainian word – combinations.
1. crankcase – a. нерухома частина двигуна
2. high efficiency – b. свічки запалювання
3. lubrication oil - c. висока ефективність
4. crankshaft - d. інжекторна помпа
5. spark plugs - e. поршневі кільця
6. piston rings - f. мастило
7. connection road - g. масляний фільтр
8. fuel combustion process - h. картер
9. intake valves - i. колінчастий вал
10. oil filter - g. шатун
11. injection pump - k. впускні клапани
12. stationary engine part - l. процес згорання пального
2. Put the missing words. Use the words from the box given below.
a. combustion; b. tractor; c. engine; d. lubricating; e. crankcase; f. cylinder.
The stationary 1__ parts are the cylinder block, the crankcase and the cylinder head. The 2__ block is one of the basic parts of the engine. The process of 3__takes place within the cylinders. 4__ engines have some cylinders .The 5__is a part of the cylinder. It supports the crankshaft and the camshaft and keeps the 6__ oil near the engine parts. The cylinder heads close the cylinders. The cylinders and the cylinder heads form the combustion chambers.
3.Translate the given sentences into Ukrainian.
1. The fuel burns within the engine and provides forces.
2. The cylinder block is one of the basic parts of the engine.
3. Piston rings control and absorb heart from the piston.
4. The engine valves are of two types: intake valves and exhaust valves.
5. The low pressure part of the system contains the fuel tank, fuel pumps and fuel filters.
6. Most farm tractor diesels use electric starting from the battery on the tractor.
TEST 2 Variant 1
1. Match the words and word – combinations with their translations.
1. a crawler - a. комунальний трактор
2. vehicle b. трактор для косіння газонів
3. plowing - c. гусеничний трактор
4. disking - d. бульдозер
5. steering - e. противага
6. a utility tractor - f. транспортний засіб
7. drawbar - g. орання
8. driving wheel - h. дискування
9. threadbar - i. рульове управління
10. counter weight - j. причіпний механізм
11. a lawn tractor- k. привідне колесо
12. backhoe loader - l. Протектор
2. Put the missing words and complete the given text.
a. shifting; b. adjusting; c. clutch; d. clearance; e. engine; f. periodically; g. disk.
A clutch is a 1__ mechanism operation in a tractor basis. A 2__ permits the gradual application of power from the engine to the load. It permits disengagement of the 3 __from the drive mechanism for starting, for 4__of gears and for idling.
Clutch should be checked 4__, since the pedal linkage wears with use and may need adjustment. A tractor operator must know the method of 5__the linkage. Lack of 6__of the clutch pedal may reduce power and cause overheating.
3. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. A tractor is an engineering vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling, a trailer or machinery used in agriculture or construction.
2. A farm tractor has a drawbar for pulling tillage tools and power – take - off shaft for driving implements or operating a belt pulley.
3. Tractor can be generally classified as two – wheel drive. Two – wheel drive with front wheel assist. Four –wheel drive, or track tractors (with other two or four powered rubber tracks)
4. Answer the questions:
1. Which tractors are usually called general – purpose tractors?
2. What must a tractor operator do to operate and maintain a tractor well?
3. Must the tractor operator do the examination of steering mechanism?
Variant 2
1. Match the words and word – combinations with their translations.
1. linkage - a. садовий трактор
2. tillage - b. зчеплення
3. towing - c. кермо
4. planting - d. обробка грунту
5. irrigation - e. двигунний відсік
6. clutch - f. буксирування
7. rear wheel - g. вихлопна труба
8. power – take – off shaft - h. зрошування
9. exhaust stack - i. вал відбору потужності
10. engine compartment - j. з’єднання
11. steering wheel - k. заднє колесо
12. garden tractor - l. садіння
2. Put the missing words and complete the given text.
a. Repairs; b. unspecialized; c. installing; d. to operate; e. replacing; f. maintained.
A tractor must be well 1 __and operated so that the need for repair is reduced to a minimum. 2__ are expansive and there may be difficulties in getting the necessary parts and 3__ them.
A tractor operator should be able 4__, adjust and maintain his tractor. He should have knowledge and skill necessary for doing 5__ tractor repair. The more specialized repair such as reboring cylinders, 6__worn parts is to be done by a qualified mechanic.
3. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. The tractor can pull or push machines; it can supply power to machines from the power – take – off shaft and it can drive machines by means of a belt pulley.
2. The classic drawbar is simply a steel bar attached to the tractor to which the hitch of the implements was attached with a pin or by a loop and clevis.
3. large type of modern farm tractors include articulated four – wheel or eight – wheel drive units with one or two power units which are hinged in the middle and steered by hydraulic clutches or pumps.
4. Answer the questions:
1. Which is the main application of the utility tractor?
2. For which details the periodically checking and adjusting are needed?
3. The tractor operator has to inspect the brake mechanism before adjusting the hydraulic brake valve and the brake pedals, doesn’t he?
TEST 3
Variant 1 1. Match the English and Ukrainian equivalents.
1. idling - a. паливний заряд
2. engine wear - b. кулачкові підшипники
3. a hose - c. повітряна система охолодження
4. drain petcock - d. легке навантаження
5. gear – type pump – e. холостий хід
6. a thermostat - f. муфта зчеплення
7. a working surface - g. шланг
8. clutch - h. спускний кран
9. air – cooling system – i. зубчаста помпа
10. light – load - j. термостат
11. camshaft bearings - k. робоча поверхня
12. fuel charge - l. зношування двигуна
2. Put the missing words into the gaps and complete the text.
a. rations; b. combustion; c. carburetor; d. intake; e. pump; f. gasoline.
The 1__ engine fuel system must supply the engine with a mixture of air and fuel that burns within the cylinders. Gasoline engines use a 2__ mixing the fuel and air and delivering the mixture to the engine through the 3 __ manifold. Air – fuel 4 __ vary for idling, light – load and heavy – load operations. Diesel engines have a high – pressure 5 __ forcing the fuel through injector into the 6 __chamber.
3. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. A lubrication system is a necessary in order to deliver the oil to the moving parts of the engine.
2. Oil filters are located between the oil pump and engine parts to reduce engine wear.
3. Heart is being produced in the combustion chamber of the engine as the fuel is being burned.
4. Two types of liquid – cooling systems: the termosyphone system and the forced – circulated system are used on farm tractors.
5. Some diesels use an additional gasoline engine for starting.
Variant 2
1. Match the English and Ukrainian equivalents.
1. a float - a. мастильний фільтр
2. an intake manifold - b. корінні підшипники
3. a fan - c. поплавок
4. spark - d. водяний жакет
5. useful power - e.важке навантаження
6. a water pump - f. впускний патрубок
7. a working surface g. корисна потужність
8. a water jacket - h. вентилятор
9. the forced – circulated system - i. робоча поверхня
10. heavy – load - j. іскра
11. connection road bearings - k. водяна помпа
12. oil filter - l. система примусового охолодження
.
2. Put the missing words into the gaps and complete the text.
a. system; b. temperature; c. heat; d. walls; e. chamber; f. useful.
Heat is being produced in the combustion 1 __ of the engine as the fuel is being burned. Some of this heat goes into 2 __ power, some is lost through the exhaust gases, and some must be removed by cooling 3 __ of the engine. The cooling system removes about one – third of the 4 __ produced. The heat passes through the cylinder 5 __ into the coolant or into the air. The 6 __ must be controlled.
3. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. Engine lubrication is provided by an oil pump located in the oil pan.
2. Spark ignition engine uses an electric ignition system providing of the fuel charge.
3. The cooling system removes about one – third of the heat produced.
4. The forced – circulated system has all parts that are in the thermosyphon system but it also has a water pump and thermostat.
5. The radiator has tubes through which the coolant is circulating.
TEST 4 Variant 1
1. Match the images with their names.

1. 2. 3. 4.
a. a planter; b. a combine harvester; c. cultivator; d. a disc harrow
2. Put the missing words into the gaps and complete the text. Use the words from the box.
a. process; b. grass; c. feed; d. pieces; e. silage; f. implement.
A forage harvester (also known as a silage harvester, forager or chopper) is 1 __ that
harvests forage plants to make silage. Silage is 2 __, corn or other plant that has been chopped into small 3 __ , and compacted together in a storage silo, silage bunker, or in 4 __bags. The silage is then fermented to provide 5 __for livestock. Haulage is a similar 6 __ to silage but using grass which has dried.
3. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. The system of food and fiber production in agriculture is highly mechanized.
2.A plough is an implement with one or more mold - boards which cut and turn the soil.
3. Cultivators stir and pulverize the soil either before planting (to aerate the soil and prepare a smooth, loose seedbed) or after the crop has begun growing.
4. A disc harrow is a farm implement that is used to cultivate the soil where crops are to be planted. 5. A forage harvester (also known as a silage harvester, forager or chopper) is a farm implement that harvests forage plants to make silage.
6. A baler is a piece of farm machinery used to compress a cut and raked crop (such as hay, cotton, straw, or silage) into compact bales.
Variant 2 1. Match the images with their names.

1. 2. 3. 4.
a. a disc harrow; b. a forage harvester; c. a cultivator; d. a baler
2. Put the missing words into the gaps and complete the text. Use the words from the box.

A disc 1 __ is a farm implement that is used to cultivate the soil where crops are to be planted. It is also used to chop up unwanted weeds or crop 2. __. It consists of many iron or steel 3. __ which have slight concavity and are arranged into two or four sections. When viewed from above, the four 4. __ would appear to form an "X" which
3. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. Some multi - purpose machines are used where a high degree of precision is needed for precision tillage, planting, bed shaping and fertilizing.
2.Modern ploughs are commonly fully mounted on the tractor hydraulic system.
3. Unlike a harrow, which disturbs the entire surface of the soil, cultivators are designed to disturb the soil in careful patterns, sparing the crop plants but disrupting the weeds.
4. Modern disc harrows are tractor-driven and are raised hydraulically.
5. Forage harvesters can be implements attached to a tractor, or they can be self-propelled units.
6. A planter is an agricultural farm implement towed behind a tractor, used for sowing crops through a field.
TEST “Check yourself”
І. Define a "superfluous" word that does not fit in the content of a group of words.
1. a) agriculture; b) cultivation; c) field; d) book;
2. a) farm; b) plant; c) student; d) animal;
3. a) crop; b) plant; c) grass; d) development;
4. a) animal; b) livestock; c) cattle; d) grain;
5. a) beef cattle; b) meat; c) sheep; d) poultry;
6. a) meat; b) milk; c) plant; d) egg;
7. a) water; b) sunlight; c) wheat; d) air;
8. a) plant; b) root; c) flower; d) stem;
9. a) rice; b) barley; c) potatoes; d) wheat;
10. a) agriculture; b) crop production; c) industry; d) animal husbandry.
ІІ. Define the word closest to the value of the given one.
1. land -
a) pasture; b) farm; c) ground; d) agriculture;
2. agriculture –
a) cultivation; b) life; c) crop production; d) yield;
3. cereals –
a) legumes; b) tuber crops; c) grain; d) yield;
4. grow –
a) go; b) raise; c) harvest; d) plant;
5. cost –
a) price; b) profit; c) income; d) value;
6. remuneration –
a) money; b) salary; c) bill; d) cost;
7. want –
a) demand; b) wish; c) need; d) income;
8. labour –
a) work; b) laboratory; c) problem; d) profit;
9. grain –
a) cereals; b) legumes; c) wheat; d) potatoes;
10. livestock –
a) poultry; b) cattle; c) fish; d) sheep.
III. Find the word opposite to the value of the given one.
1. to plant -
a) to grow; b) to raise; c) to use; d) to harvest;
2. income –
a) profit; b) expenses; c) output; d) cost;
3. disease –
a) control; b) health; c) quality; d) insect;
4. private –
a) state; b) own; c) central; d) marketable;
5. warm –
a) cold; b) cool; c) hot; d) worm;
6. to improve –
a) to spoil; b) to spend; c) to approve; d) to cultivate;
7. to increase –
a) to grow; b) to decrease; c) to plan; d) to improve;
8. a producer –
a) customer; b) consumer; c) worker; d) manager.
IV. Identify the correct translation from English into Ukrainian.
1. to grow -
a) рости; b) збирати; c) іти; d) вчити;
2. to use –
a) постачати; b) забезпечувати; c) використовувати; d) застосовувати;
3. apply –
a) забезпечувати; b) застосовувати; c) постачати; d) збільшувати;
4. dairy cattle –
a) молочна худоба; b) птиця; c) м’ясна худоба;d) вівці;
5. cost –
a) витрата;b) дохід; c) вартість;d) ціна;
6. profit –
a) ціна; b) вартість; c) оплата;d) прибуток;
7. mechanization –
a) інтенсифікація;b) механізація; c) електрифікація;d) хімізація;
8. income –
a) прибуток; b) прихід; c) дохід; d) збут;
9. quality –
a) якість; b) кількість; c) дохід; d) ефективність;
10. costs –
a) дохід; b) вартість; c) витрати;d) ціна.
V. Choose the right variant.
1. Я буду працювати на фермі.
a) I work on a farm.
b) I’ll work on a farm.
c) I was working on a farm.
d) I’m working on a farm.
2. У сільському господарстві є дві галузі.
a) Are two branches in agriculture.
b) Two branches are in agriculture.
c) There is two branches in agriculture.
d) There are two branches in agriculture.
3. Економіка сільського господарства розглядає економічні проблеми.
a) Agricultural economics deal with the economic problems of agriculture.
b) Agricultural economics deals with the economic problems of agriculture.
c) Agricultural economics dealing with the economic problems of agriculture.
d) Agricultural economics are dealing with the economic problems of agriculture.
4. Збір врожаю – фінальна ланка у сільськогосподарському виробництві.
a) Harvesting is the final stage in agricultural production.
b) Harvesting is the primary stage in agricultural production.
c) Harvesting isn’t the primary stage in agricultural production.
d) Harvesting is the final stage in industry.
5. Є багато видів врожайно-збиральних машин.
a) There is many kinds of harvesting machinery.
b) There are many kinds of harvesting machinery.
c) There many kinds of harvesting machinery.
d) There are kinds of harvesting machinery.
VI. Choose the right answers.
1. Why is agriculture important?
a) It is an important branch of economics.
b) It supplies people with food.
c) It supplies people with food and clothing and industry with raw materials.
d) It supplies industry with raw materials.
2. What are the two branches of agriculture?
a) industry and economics;
b) crop production and animal husbandry;
c) crop production and environment;
d) cattle breeding and crop production.
3. What does crop production mean?
a) It is the practice of growing crops.
b) It is the practice of harvesting crops.
c) It is the practice of growing and harvesting crops.
d) It is the practice of breeding cattle.
4. What are the main parts of a plant?
a) foot and stem;
b) stem, leaves, flowers;
c) root, stem, leaves, flowers;
d) root, stem, leaves, flowers, seeds.
5. What does animal husbandry include?
a) breeding of farm animals and their use;
b) breeding of farm animals;
c) production of milk, meat and eggs;
d) feeding of animals.
6. What is agricultural economics?
a) a field of economics, dealing with crop production;
b) a field of economics, dealing with economic problems of agriculture;
c) a field of economics, dealing with economic problems of enterprise;
d) a field of economics, dealing with crop and animals.
7. What does agronomy deal with?
a) Agronomy deals with the cultivation of fields.
b) Agronomy deals with the cultivation of fields for regular production of crops: food crops, feed crops and industrial crops.
c) Agronomy means the preparation of the ground for planting seeds.
8. What does agricultural engineering mean?
a) Agricultural engineering means the application of engineering knowledge to agriculture.
b) Agricultural engineering means the application of engineering knowledge to industry.
c) Agricultural engineering means the application of mathematics knowledge to agriculture.
d) Agricultural engineering means the application of new experience to agriculture.
9. What are the conditions for the development of Ukrainian agriculture?
a) fertile soils;
b) fertile soils and warm climate;
c) fertile soils, temperately warm climate, a well-developed industry processing agricultural raw materials.
10. What vegetables do they grow in Ukraine?
a) cabbage and tomatoes;
b) cucumbers and red beet;
c) onion and garlic;
d) cabbage, tomatoes, cucumbers, red beet, carrot, onion, garlic, etc.

VII.Fill the gaps.
1. The word “ager” is a … word.
a) Russian; b) Greek; c) Latin; d) English. 2. Life is … without plants.
a) possible; b) impossible; c) important; d) difficult. 3. Agriculture … people with food and clothing.
a) applies; b) supplies; c) includes; d) use.
4. The most important plants grown by people are grain crops, vegetables and…
a) fruit; b) trees; c) grasses; d) flowers. 5. Crop production and animal husbandry are closely … with each other.
a) connected; b) depend; c) developed; d) cultivated. 6. Production cost is the main indicator of the … of a farm.
a) effect; b) marketing; c) efficiency; d) enterprise.
7. Agriculture and … are closely connected with each other.
a) cattle breeding; b) economics; c) environment; d) crop production. 8. … are plants growing where they are not wanted.
a) seeds; b) weeds; c) wheat; d) grasses.
9. Animal husbandry includes … of farm animals and their use.
a) breeding; b) feeding; c) selection; d) production. 10. The most important group of farm animals is … .
a) poultry; b) sheep; c) fish: d) cattle.
VIII. Choose the right variant.
1. My uncle often … on a farm.
a) works; b) is working; c) work; d) worked. 2. When I entered the room, children … .
a) read; b) reads; c) was reading; d) were reading. 3. I … him today.
a) saw; b) see; c) have seen; d) had seen. 4. She … TV now.
a) watchers; b) is watching; c) is watched; d) was watching. 5. I … her up tomorrow.
a) rang; b) ring; c) have rung; d) shall ring. 6. I … English for two years.
a) have studied; b) have been studying; c) studied; d) was studying. 7. When my mother came I already … my work.
a) have done; b) was doing; c) had done; d) did. 8. She … in Canada since April.
a) was not; b) did not be; c) has not been; d) is not. 9. He said he … to London next year.
a) would go; b) will go; c) went; d) go. 10. She said she … her friend yesterday.
a) visited; b) has visited; c) have visited; d) had visited.
KEYS
Task 1
|
1 |
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
d |
|
c |
d |
d |
b |
c |
c |
a |
c |
c |
|
Task 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
c |
|
a |
c |
b |
d |
b |
b |
a |
a |
b |
Task 3
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
d |
b |
b |
a |
a |
a |
b |
b |
Task 4
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
a |
c |
b |
a |
c |
d |
b |
c |
a |
c |
Task 5
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
b |
d |
b |
a |
b |
Task 6
|
1 |
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
c |
|
b |
c |
d |
a |
b |
b |
a |
c |
d |
|
Task 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
c |
|
b |
b |
c |
a |
c |
c |
b |
a |
d |
|
Task 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
a |
|
d |
c |
d |
d |
b |
c |
c |
a |
d |
VOCABULARY
A
Again (adv.) – знову
Agricultural (a) – сільсько–господарський
Agriculture (n)– сільське господарство
Ahead (adv.) – попереду
Aid (v) – допомагати
Alarm (n) – сигнал тривоги, сигнальний пристрій
Alert (n) – тривога, поперед жувальний сигнал
Alfalfa (n) – люцерна
Alongside (prep) – поряд з
Alteration (n) – зміна, деформація
Alternative (a) – змінний
Although (cj) – хоч, незважаючи на
Altogether(adv.) –зовсім, цілком
Amount (n) – кількість, величина
Analog(ue) (n) –безперервна фізична величина Angle (n) – кут
Appear (v) – з’являтися
Applicable (a) – (n) – потік
Application (n) – застосування
Apply (v) – застосовувати
Area (n)- площа, район
сross – sectionarea (n) – площапоперечного перерізу Arm (n) – плече, тримач
Arrange (v) – розміщувати
Arrangement (n) – розміщення
As (cj) – як, так як
As … as (cj) – так … як
Aspect (n) – вигляд
Aspirator (n) – витяжний вентилятор
Assemble (v) – збирати
Assist (v) – допомагати
Associate (v) – пов’язувати
Assume(v) – припускати
Assure (v) – гарантувати
Attach (v) – приєднувати
Attachment (n) – приєднання
Auger (n) – конвеєр, шнек
Grainauger (n) – зерновий конвеєр
Deliveryauger (n) – розвантажувальний конвеєр
Auxiliary (a) – допоміжний
Available (a) – придатний
Average (a) – середній
Axial (a) – осьовий
Axle (n) –ведучий міст
В.
Back (n) – задній, назад
Backrest (n) – спинка
Backward (a) – спрямований назад, зворотній
Baffle (n) – дросель, глушник
Bale (n) – тюк
Band (n) – смуга
Bank (n) – група, набір, блок циліндра
Bar (n) – пруток, стрижень
Barley (n) – ячмінь
Bat (n) – било, бияк
Beam(n)– балка. брус
Bearing (n) – підшипник
Mainbearing (n) – корінний підшипник
Bed (n) – грядка
Belt (n) – пас, ремінь
Beltpulley (n) – ремінний шків
Drivebelt (n) – привідний ремінь
Beneath(prep) – внизу, під, нижче
Blade (n) – лопата, ніж, лезо
Blast (n) – потік
Block (n) – вузол, блок
Blockage (n) – засмічення, закупорення
Bore (v) – свердлити, розточувати
Bowl (n) – поплавкова камера
Brake (n) – гальмо, гальмувати
Breakdown (n) – поломка, несправність
Broadcast (v) – розкидати
Brush (v) – прочісувати
Bury (v) – закопувати
С.
Cab (n) - кабіна
Cage (n) – решітчастий барабан Camshaft (n) – кулачковий вал Canvas (n) – стрічка (конвеєра)
Capability (n) - здібність
Capable (a) - здібний
Capacity (n) – ємність, номінальна потужність, продуктивність, місткість Carry (v) – підтримувати
Carryaway (v) – відводити, відносити
Carryon (v) – проводити, вести
Carryout (v) - виконувати
Closedcentеr - замкнутий центр
Centrifugal (a) - відцентрований
Chaff (n) - полова
Chaffer (n) - полововловлювач
Chain (n) feederchain (n) – ланцюг, кормороздатчик, ланцюговий конвеєр
Channel (n) – канал, жолоб
Cumbersome (a) – громіздкий, обтяжливий
Consider (v) – розглядати, вважати
Charge (n) – заряд
Chart (n) – схема, діаграма
Chassis (n) – шасі, ходова частина
Chisel (n) – культиватор
Circuit (n) – ланцюг
Circulate (v) – циркулювати
Circumstance (n) – обставина
Cleaner (n), – очищувач
Clearance (n) – шляховий просвіт
Clod (n) – брила, грудка землі
Clover (n) – конюшина Clutch (n) – зчіпна муфта
Coat (n) – покриття
Coil (n) – котушка, обмотка
Collect (v) – збирати
Combine (n) – комбайн
Combine (v) – об’єднувати
Common (a) – звичайний, простий
Compact (v) -ion (n)- ущільнювати,ущільнення
Compare (v) – порівнювати
Compatible (a) – сумісний
Complete (a) – повний, завершений
Compose (v) – складати
Compress (v) – стискати
Concave (n) – підбарабання
Condense (v) – згущувати Confine (v) – обмежувати
Connect (v) – з’єднувати
Conserve (v) – зберігати
Consider (v) – розглядaти, вважати
Consolidate(v) – тверднути
Consult (v) – радитись
Consume (v) – споживати
Convenient (a) – зручний
Conventional (a) – стандартний
Convert (v) – перетворювати
Convey (v) – транспортувати,
Conveyer (n) – конвеєр
Cross – drilled (a)- перехресно - просвердлений
Cope (v) – справлятися
Corn (n) – зерно, збіжжя, кукурудза
Corrosion (n) - корозія
Coulter (n) – ніж плуга
Couple (v) – з’єднувати
Coupler (n) – з’єднувальний пристрій
Coupling (n) – муфта, зчеплення
Cover (v) – загортати
Crank (v) – заводити (прокручувативал двигуна)
Crankcase (n) – картер
Crankshaft (n) – колінчастий вал
Crawler (n) – гусеничний трактор
Companion crop – супровідна культура
Laid crop – вилягла культура
Root crops – коренеплоди
Cultivate (v) – обробляти землю,вирощувати
Rotary cultivator – ротаційна фреза
Curve (n) – крива (лінія)
Cushioning (n) – амортизація
Cutter (n) – різець, фреза, подрібнювач
Cumbersome (a) – громіздкий
Curve (n)- крива
Cushioning (n) – амортизація
Cutter (n) – різець, фреза
D.
Decelerator (n) – сповільнювач процесу
Decrease (v) – зменшувати
Define (v) – визначати
Definitely (adv) - ясно
Deflect (v) - відхиляти
Demand (n) – вимога, потреба, сировина
Denote (n) - позначити
Density (n) - щільність
Depth (n) - глибина Detach (v) - відокремлювати
Determine (v) - визначати
Detonation (n) - вибух
Digger (n) – відрізняти (ся)
Dirt (n) - бруд
Discharge (n) – розряд, розвантаження
Disengage (v) – вимикати, роз’єднувати
Disengagement (n) – роз’єднання
Dispersal (n) – розвіювання, розкидування
Displacement (n) – перестановка, об’єм
Distinguish (v) - розрізняти
Distribution (n) - розподіл
Disturb (v) – порушувати, збивати (наладку)
Divert (v) – відводити
Downward (adv) – вниз, донизу
Draft(draught) (n) – тяга, зчеплення
Drain(n) - осушувати
Drainage (n) – дренаж, осушення
Draughtlink (n) – силовий регулятор
Draw (drew, drawn) - тягти
Drawing – втягувати, всмоктувати
Drawbar(n) – зчіпний пристрій, тяговий брус
wide – swingdrawbar – маятниковий зчіпний п-й. Drill – сівалка, рядова сівалка
cross – drilled (a)- перехресно - просвердлений
Drop (v) - зменшувати
Drum (n) - барабан
Dry (a) - сухий
Dual (a) - подвійний
Durability (n) – міцність, тривалість
Dust (n) - пил
Dynamic (a) - активний
E
Ease (v) - полегшувати
Eccentric (n) - ексцентрик
Edible (a) - їстивний
Employ (v) – застосовувати
Enable (v) – давати змогу
Efficiency (n) – ефективність, к.к.д
Efficient (a) -ефективний
Effort (n) - зусилля
Elevator (n) - елеватор
Eliminate (v) – усувати, ліквідовувати
Engage (v) – зчіпляти, з’єднувати
Enhance (v) – посилювати
Enormous (a) – величезний
Ensure (v) – забезпечувати
Envelope (v) – обгортати
Equip (v) – обладнати, постачати
Estimate (v) – оцінювати
Ether (n) – ефір
Excess (n) – надлишок Expose (v) – піддавати (чомусь)
External (a) – зовнішній
F.
Farming (n) – сільське господарство
Powerfaming (n) – механізоване сільськегосподарство
Fatigue (n) – втома
Fault (n) – несправність, поломка
Faulty (a) – несправний
Favorable (a) – сприятливий
Feed (v) – подавати
Feeder (n) – конвеєр
Fertilizer (n) – добрива
To apply fertilizer – вносити добрива
Foodandfiber – продукція с/г господарства
Filler (n) – навантажувальний пристрій
Fin (n) – радіаторна пластина
Fit (v) – точно відповідати
Fix (v) – закріплювати
Flight (n) – виток, скребок елеватора
Augerflight (n) – виток шнека
Float (n) – поплавок Fluid (a) –рідкий
Flush (n) – струмінь
Forage (n) – корм, фураж
Forced (a) – примусовий
Force out (v) – виштовхувати
Forge (v) – кувати
Freshly (adv) – свіжий, новий
Frog (n) – стойка, башмак (плуга)
Furnish (v) – постачати, доставляти
Furrow (n) – борозна
G.
Gain (v) – отримувати
Gasket (n) – прокладка Gauge (n) – вимірювальний прилад
Reversegear (n) – шестерня зворотного ходу
Gearbox (n) – коробка передач
Governer (n) – регулятор
Gradual (a) – поступовий
Grain (n) – зерно,хлібні злаки
Grass (n) – трава, пасовище
Grate (n) – решітка, грохот
Fingergrate (n) – гребінчаста колосникова решітка
Grip (n) – зчеплення, захват
Guide (v) – керувати
H.
Handle (v) – обходитися
Handling (n) – керування, транспортування
Harrow (n) - борона Powerharrow (n) – силова борона spike – toothharrow (n) – пружинна борона
Harvester (n) - комбайн
Forage harvester (n) – кормозбиральний комбайн
Hay (n) - сіно
Headland (n) – край поля
Heater (n) – нагрівач, обігрівач
Heavy – duty (a) - потужний
Hinge (v) –з’єднувати шарнірно, підвішувати на шарнірах
Hitch (n) зачеп, захват, навісний пристрій
Hoe (n) - мотика Hilly (a) – горбистий
Hook (n) - крюк
Horticulture(n) - садівництво
Housing (n) – корпус, чохол
Humus (n) - гумус
I.
Idling (n) – холостий хід, робота на холостому ходу
Ignite (v) – запалювати, займатися
Ignition (n) – запалювання, спалах
Impeller (n) – робоче колесо, крильчатка
Inclination (n) – нахил, укіс, спад
Incline (v) – нахилятися
Indicate (v) – позначати, показувати
Indication (n) – ознака, показання
Inhibit (v) – перешкоджати, затримувати
Initial (a) – початковий, вихідний
Inject (v) – впорскувати
Injector (n) – інжектор, форсунка
Inlet (n) – впуск, пусковий отвір
Inner (a) – внутрішній
Intake (n) – впуск
Integrate (n) – об’єднувати Intend (v) – мати намір, збиратися
Intercooler (n) – проміжний охолоджувач
Intricate (a) – складний
Invert (v) – перевертати
Involve (v) – включати, охоплювати, містити в собі
Inward (a) – внутрішній, спрямований в середину
Irrelevant (a) – недоречний, що не стосується справи
J.
Joint (n) – з’єднання, стик, шов
Journal (n) – цапфа, шийка вала
K.
Knob (n) – кнопка, ручка
L.
Laborious (a) –трудомісткий Landside (n) – польова дошка (плуга)
Lawn (n) – газон
Leak (v) – теча, давати течу
Leg (n) –стійка культиватора
Lever (n) ричаг
Life (n) – строк служби, довговічність
Lift (v) – піднімати
Link (n) – ланка, зв'язок, зв’язувати
Linkage (n) –зчеплення, важільний механізм, важільна передача
Three – pointlinkage (n) – три точковий навісний пристрій
Liquefy (V)– перетворювати у рідкий стан
Livestock (n) – домашня худоба
Lock (n) – замок, стопор
Longitudinal (a) – поздовжній
Loosen (v) – послабляти, роз’єднувати, розрихлювати грунт
M.
Maintain (v) – зберігати, підтримувати
Maintenance (n) – збереження, догляд, експлуатація
Makeup (v) – складати, комплектувати
Manifold (n) – патрубок, трубопровід
Maneuverability (n) – маневреність
Manure (n) – гній, добриво
Mean (n) – засіб, спосіб
Mechanism (n) – механізм
Feeding mechanism (n) – конвеєр
Meter (n) – лічильник
Might (n) – міць, сила
Moisten (n) – змочувати (ся)
Moisture (n) – вологість, сирість
Monoxide (n) – оксид
Muddy (a) – брудний, мулистий
Muffler (n) - глушник
Multi – cylinder (n) – багатоциліндровий
N.
Narrow (a) – вузький
Newly (adv.) – недавно, наново Nozzle (n) – наконечник, сопло, форсунка
Nutrient (n) – поживна речовина
O.
Objective (n) – мета
Obstruct (v) – перешкоджати
Obtain (v) – отримувати
Obvious (a) – очевидний, явний
Odorless(a) – без запаху
Oil (n) – мастило, нафта, змащувати Opening (n) – отвір
Operator (n) – механік, оператор, водій
Orchard (n) – фруктовий сад
Outer (a) зовнішній
Output (n) – потужність
Overheat (n) – перегрів, перегріватися
Overload (n) – перевантаження
Owingto (prep) – внаслідок, завдяки
P.
Paddle (n) –лопасть, затвор
Pan (n) – піддон, лоток, корито
Grainpan (n) – транспортна дошка
Оilpan (n) – масляний піддон
Panel (n) – панель, щит управління
Park (v) – ставити на стоянку
Particular (a) – особливий
Pass (n) – прохід, пропуск
Passage (n) – прохід, канал
Path (n) – шлях
Spiralpath (n) – спіральна (гвинтова) траєкторія
Penetrate (v) – проникати, заглиблювати
Perforate (v) – пробивати, просвердлювати
Perform (v) – виконувати, здійснювати, виробляти
Performance (n) – технічна характеристика, експлуатаційні якості
Permit (n) – дозволяти, допускати
Pest (n) – шкідник, паразит
Petrol (n) – бензин, керосин
Petroleum (n) – нафта, гас
Pick (v) – збирати, підбирати
Pickup (v) – підбирач сіна Pilot (v) – керувати, вести
Pin (n) – палець
Pistonpin (n) – поршневий палець
Pipe (n) – труба, трубопровід
Piston (n) – поршень
Planter (n) –садильник
Plough (v) – плуг, орати
Ploughing (n) – оранка
Plug (n) – свічка
Sparkplug (n) – свічка запалювання
Plunger (n) – плунжер
Point (n) – носок лемеша, точка
Precision (n) – точність, точний
Previously (adv.) – заздалегідь, раніше
Prior (a) – попередній
Propel (v) – приводити в рух, рухати
Prove (v) – виявлятися, підтверджувати
Provide (v) – забезпечувати, постачати
Pull (v) – тягнути
Pulley (v) – блок, шків
Beltpulley (n) – привідний шків
Belt driven pulley (n) – клинопасова передача
Pulverize (v) – розпилювати, розпушувати
Pump (v) – помпа, нагнітати
Push (n) – поштовх, штовхати
Q.
Quality (n) – якість
Quantity (n) – кількість
Quick – detach (a) –швидкозйомний
R.
Rack (n) – зубчаста рейка straw rack (n) – соломотряс
Ram (n) – плунжер
Range (n) – ряд, серія, діапазон, коливатися
Rapid (a) – швидкий
Rare (a) – рідкісний
Rate (n) – швидкість
Rated (a) – номінальний
React (v) – реагувати
Rearward (a) –задній
Realize (v) – здійснювати
Rear (a) – задній, задня частина
Rebore (v) – розточувати (під час ремонту)
Receive (v) – отримувати
Reciprocation (a) – зворотно - поступальний
Reclaim (v) – виправляти
Reclamation (n) – освоєння (землі), меліорація
Recognize (v) – визнавати
Reduce (v) – зменшувати, знижувати
Reduction (n) – зменшення
Reel (n)- мотовило Refer (v) – відсилати, стосуватися
Regard (v) – розглядати, вважати Relation (n) – співвідношення
Relationship (n) – зв'язок
Relatively (adj.) – відносно
Release (v) – звільнення, звільняти, випускати
Reliable (a) – надійний
Reliability (n) – надійність, міцність
Remain (v) – залишатися
Remove (v) – усувати, віддаляти, знімати
Repair (n) – ремонт, лагодження
Replace (v) – заміняти, заміщати
Require (v) – вимагати
Requirement (n) – вимога
Resemble (v) – бути подібним
Residue (n) – залишки, відходи
Resist (v) – витримувати, протистояти, опиратися
Respect (n) – відношення
Restoration (n) – відновлення
Restore (v) – відновлювати
Retain (v) – зберігати
Retard (v) –сповільнювати
Return (a) – повернення, зворотна подача
Reverse (a, v) – зворотний, реверсивний, давати задній хід
Review (n) – огляд
Revolution (n) – обертання
Revolve (v) – обертатися
Ride (rode, ridden) (v) – рухатися
Right – handed (a) – правосторонній
Rigid (a) – жорсткий, нерухомо прикріплений
Rim (n) – обід
Ring (n) – кільце
Rise (rose, risen) – підніматися, зростати
Road (n) – дорога
Rod (n) – прут, стержень, брус Connectingrod (n) - шатун
Roll (n) – каток, ролик, котитися
Roller (n) – ролик, каток
Roof (n) – дах
Root (n) – корінь
Rooty (a) –з безліччю коріння
Rotary (a) – обертальний
Rotate (v) – обертатися
Rotor (n) – ротор
Rough (a) – грубий, нерівний, шершавий
Row (n) – ряд, міжряддя
Rowcrop (a) – розрихлював Rubber (n) – гума, каучук
Rugged (a) – масивний, міцний
Run (ran, run) – працювати
S.
Safe (a) – надійний, безпечний
Safely (adv.) – надійно
Safety (n) – безпека
Satisfactory (a) – задовільний, достатній
Satisfy (v) – задовольняти, відповідати
Save (v) – економити
Scheme (n) – схема, проект
Scraper (n) – скрепер
Screen (n) – екран, решето, сито Seal (n) – ущільнення, герметичність
Seed (n) – насіння
Seedbed (n) – рілля, підготовлений до посіву грунт
Self – ignite (v) – самозапалюватися
Self – propelled (a) – самохідний Semi – digger (n) – плуг з передплужником
Semi – mounted (a) – напівнавісний
Separate (v) – сепарувати, відокремлювати
Separator (n) – молотарка (у комбайні), соломотряс (молотарки)
Set (set, set) – набір, комплект, встановлювати
Several (pron.) – декілька Shaft (n) – вал
power - take – off – shaft (PTO) (n) – вал відбору потужності
Shaker (n) – вібраційний гуркіт
Shallow (a) – мілкий, неглибокий
Shape (n) – форма
Share (n) –лемех
Sharpen (v) – точити, заточувати
Sharpness (n) – гострота, гострота заточки
Shed (n) – намет, майстерня, ангар
Shell (n) – кожух, корпус
Shoe (n) – сошник
Sieveshoe (n) – решітчастий стік
Shop (n) – майстерня
Shut (v) – виключати, зупиняти, перекривати
Side – hill – (n) – схил
Side – hill plough (n) – зворотній плуг
Side - wards (a) – спрямована вбік
Sieve (n) – сито, решето
Sieve for cleaning (n) – решето очистки
Sift (v) – сіяти
Significant (a) – значний, істотний
Similar (a) –подібний Simple (a) – простий
Simplicity (n) –простота
Simplify (v) – спрощувати
Simultaneous (a) – одночасний
Since (cj) – так як, оскільки, з того часу
Single (a) – єдиний, окремий
Skid (n) – полозок, опорна лижа
Skill (n) – навичка, майстерність
Slice (n) – пласт
Slight (a) – слабкий, тонкий
Slightly (adj.) – злегка, трохи
Slip (v) – ковзати, буксувати
Slope (n) – схил
Slot (n) – проріз, щілина
Slow (a) – повільний
Smoke (n) – дим, кіптява
Smoky (a) – димний, кіптявий
Smooth (a) – гладенький, рівний, плавний
Soft (a) – м’який, слабкий
Solely (adv.) – тільки, виключно

Soil (n) – грунт
Soil – engaging parts – грунтозахватні частини
Solid (n) – твердий, масивний, міцний
Solution (n) – рішення
Somewhat (adv.) – щось, дещо
Sophisticated (a) – ускладнений
Sound (a) –міцний
Spark (n) – іскра
Specification (n) – інструкція
Forward speed (n) – передня поступальна швидкість
Reverse speed (n) – задня швидкість
Spike (n) – вістря, клин, загострений стержень
Spray (n) – струмінь
Sprayer (n) – розпилювач, оприскувач Spread (v) – розповсюджувати, розкидати
Spreader (n) – розкидач
Spring (n) – пружина
Sprocket (n) – ланцюгове або зубчасте колесо
Stack (n) – труба
Stalk (n) - стебло
Standpoint (n) – точка зору
Start up (v) – запускати
Steady (a) – стійкий, постійний, рівномірний
Steam (n) – пара
Steam – powered (a) – той, що приводиться в рух парою
Steel (n) – сталь
Forget steel (n) – штампований із сталі
Steep (a) – крутий
Steering (n) – рульове управління
Step (n) – ступінь, стадія
Sticky (a) – липкий, в’язкий
Stirup (v) – піднімати (пилюку)
Stony (a) – кам’янистий
Storage (n) – зберігання, нагромадження
Straight (a) – прямий, правильний, рівний
Straw (n) – солома Stress (n)- напруга
Strike (struck) – бити, вдарятися Stroke (n) – такт, хід поршня
Power stroke (n) – робочий хід
Stubble (n)- стерня
Subsoil (n) – підґрунтя, розпушувач підгрунтя
Subsoiler (n) – підґрунтовий розрихлював, грунтозаглиблювач
Substance (n) – речовина
Suck (v) – всмоктувати
Sufficient (a) – достатній
Sugar beet (n) – цукровий буряк
Suit (v) – влаштовувати, відповідати
Suitable (a) – придатний
Supply (v) – постачати

Suspension (n) – підвіска
Swampy (a) – болотяний, болотистий Swath (n) – смуга скошеної трави, прокіс, ряд
Swathing (n) – рядкування
Sweep (n) – культиваторна лапа, волок, гребка
T.
Tachometer (n) – тахометр Tailing (n) – обрізування корінців
Tailings (n) – необмолочене колосся
Tank (n) – бак, резервуар
Tend (v) – мати тенденцію
Tension (n) – напруга, розтяжка
Thinning (n) – проріджування
Thresh (n) – дросель,
Throttle (n) – дросельна заслонка
Thrust (n) – напір, поштовх
Sidethrust (n) – боковий тиск
Tight (n) – ущільнений, герметичний
Till (v) – обробляти
Tillage (n) – обробіток грунту
Tiller (n) – ґрунтообробне знаряддя, грунтовафреза
Tilt (v) – перекидатися
Tool (n) – інструмент
Torque (n) – момент обертання
Trail (v) – тягнути
Trailer (n) – причіп
Transverse (a)– переносити, переміщати
Trap (v) – вловлювати, захоплювати
Trash (n) – сміття, рослинні залишки
Tread (n) – ширина ходу, колія
Tricycle (a) – триколісний
Truck (n) – автомобіль
Turbocharged (n) – з турбонадувом
Turnover (n) – перекидання
Tyre (n) – шина, покришка
U.
Undergo (v) – випробувати
Unit (n) – одиниця, агрегат, переносити
Cleaning unit (n) – очисний пристрій
Cutting unit (n) – різальний агрегат, жатка Feeding unit (n) – транспортний засіб
grain–handling unit (n) – вивантажувальний пристрій для збору очищеного зерна header – unit (n) –жниварка power unit (n) – силовий агрегат separating unit (n) – сепарувальний пристрій

unlikely (adv) – навряд чи upright (a) – вертикальний Usefulness (n) – корисність, придатність
Utilization (n) – використання
Utilize (v) – використовувати
V.
Value (n) – величина, значення, цінність
Valve (n) – клапан
Vane (n) – лопасть
Guidevane (n) – направляюча лопасть
Variable (a) – мінливий, змінний Vary (v) – змінюватися
Vehicle (n) – транспортний засіб
Vibrate (n) – вібрувати
Volume (n) – об’єм
W.
Walker (n) – платформовий соломотряс
Strawwalker(n) – клавішний соломотряс
Warm – up (n) – теплий, нагрівати
Warning (n) – попередження
Waxу (a) – восковий
Wear (n) – зношування
Weed (n) – бур’ян
Weeding (n) – прополювання
Deadweight– власна вага Wet (a) – сирий, вологий
Wheat (n) – пшениця Wheel (n) – колесо
Wheelbase (n) – колісна база
Steering wheel (n) – рульове управління
Windrower (n) – рядкова жниварка
Windrowing (n) – валкоутворення, згрібання у валки
Y.
Yield (n) - врожай

ЛІТЕРАТУРА
1. Богацький І.С. Бізнес – курс англійської мови. - К:,2005
2. Бородіна Г.І. Англійська мова для студентів факультетів механізації сільського господарства. –К: Вища школа, 2002
3. Верба Л.Г. граматика сучасної англійської мови .- К:, 2002
4. Ільєнко А.П. Говоримо англійською.- К: Либідь, 1997
5. Карпусь И.А. Английский деловой язик,- К: 2002
6.Кондратюк С.Ю. «Англійська мова. Навчальний посібник» К: Центр учбової літератури; 2008
7. Маслова Г.В. Пособие для сельскохозяйственных техникумов.- М: высшая школа, 1991
8.Моос Б.Е. Сборник текстов на английском языке .-К : вища школа, 1979
9. Пазюк Л.К. Граматика англійської мови. – Донецьк, 2005
10. Письменная О.А. Английский язык для офиса. - М: , 2006
11. Шпак В.Г. Англійська мова.- К: Вища школа, 1995
12. Ятель Г.П. Англійська мова для студентів технічних вузів.- К:Вища школа, 1995
13. EnglishГ. І. Бородіна, А.М. Спєвак, Т.Г. Богуцька, 1994
14. Інтернет ресурси


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
