FACTORS OF PRODUCTION методична розробка з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)» в закладах фахової передвищої освіти
Лисичанський промислово-технологічний фаховий коледж

FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
методична розробка
з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)»
в закладах фахової передвищої освіти
Розробник: Скиба Н.М., старший викладач, викладач вищої категорії Лисичанського промислово-технологічного фахового коледжу
2024
ВСТУП
Методична розробка заняття виконана у відповідності з методичними рекомендаціями з підготовки та проведення практичних занять у закладах фахової передвищої освіти. Заняття підготовлено відповідно до робочої і навчальної програми з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)». У методичній розробці заняття подано розгорнутий план-конспект заняття у формі мовного практикуму з використанням методу критичного мислення, методики роботи з лексичним матеріалом, методу лінгвістичного квесту, рольовою грою, перелік літератури та необхідного обладнання, мету і задачі, надано чітку структуру заняття, вдало подано мотивацію пізнавальної діяльності студентів.
Розробка містить багато різноманітних форм та методів роботи (бесіду, читання, мозковий штурм, аудіювання з використанням тематичного відеоролику, роботу з мультимедійними презентаціями, групову та парну роботу,), що відповідають психофізіологічним та індивідуальним особливостям студентів і сприяють успішному досягненню мети заняття.
Методична розробка відкритого заняття відповідає теоретичному й методико-практичному розділам навчальної програми, має інноваційний характер, відповідає новітнім технологіям навчання, спрямована на формування комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців, розвиток пам'яті, уваги, фонематичного слуху студентів, сприяють зацікавленості та формуванню комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців.
Методична розробка може бути рекомендована для викладачів іноземної мови в закладах фахової передвищої освіти в якості як основного, так і довідково-дидактичного матеріалу.
МЕТОДИЧНА РОЗРОБКА ЗАНЯТТЯ
Заняття №
Предмет: Іноземна мова
Група:
Тема заняття: FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
Мета: формувати лексичні навички й навички вимови; вдосконалювати навички читання й усного мовлення; розвивати мовну здогадку й мовленнєву реакцію; виховувати зацікавленість у розширенні своїх знань, використовувати раніше вивчені структури, а також збагачувати словарний запас, практикуватися у перекладі речень, розвивати навички логічного викладання думок, пам'ять, виховувати свідоме ставлення до навчання, вчити раціонально використовувати свій час, прищеплювати бажання вивчати іноземну мову.
Обладнання: словники, комп’ютер, роздавальний матеріал
Тип заняття: практичне
Міжпредметні зв'язки: Економіка підприємства, Статистика, Фінанси підприємства, Економічний аналіз, Організація виробництва, Менеджмент, Маркетинг
СТРУКТУРА ЗАНЯТТЯ:
1.Організаційний момент:
1)Привітання
2) Перекличка
3)Перевірка готовності до заняття
2. Мотивація навчальної та пізнавальної діяльності студентів, оголошення теми та цілей заняття.
3.Реалізація теми за планом
4. Підсумок заняття. Оцінювання
5. Домашнє завдання
ХІД ЗАНЯТТЯ:
I. Scanning reading. Читання з повним розумінням змісту прочитаного.
I. Read the text FACTORS OF PRODUCTION. Use a dictionary, if necessary.
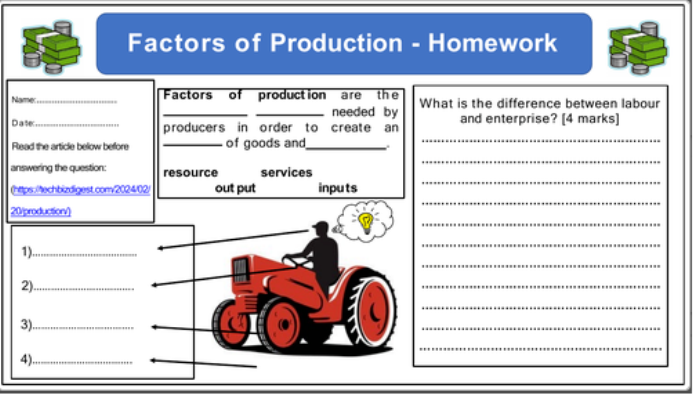
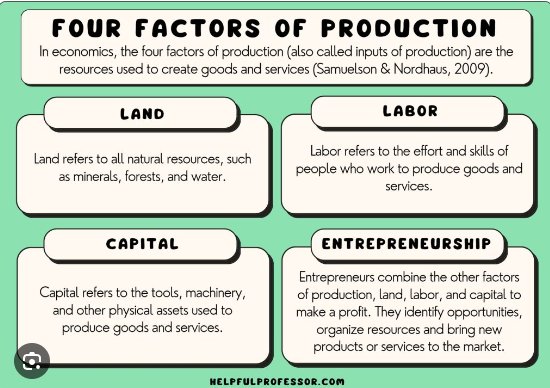
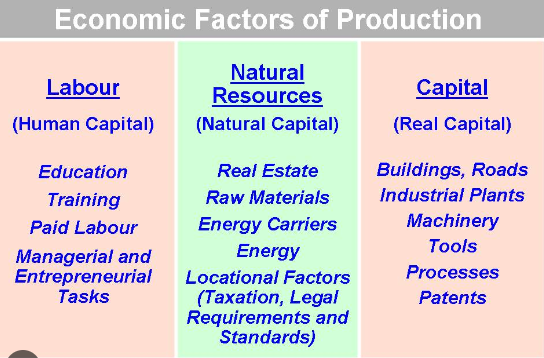
In economic theory, factors of production (or productive inputs) are the resources employed to produce goods and services. The factors of production include natural resources, human resources, capital and entrepreneurship. Each factor of production has a place in economic system, and each has a particular function. People who own or use a factor of production are expecting a “return or reward”. This generates income which, as it is spent, becomes a kind of fuel that drives the economy.
Natural Resources or «Land»
Natural resources are the things provided by nature that go into the creation of goods and services. They include such things as minerals, wildlife and timber resources. Economists also use the term «land» when they speak of natural resources as a factor of production. The price paid for the use of land is called rent. Rent becomes income to the owner of the land.
Human Resources or «Labor»
Economists call the physical and mental effort that people put into the creation of goods and services labor. The price paid for the use of labor is called wages. Wages represent income to workers, who own their labor. Human labour produces both goods and services. The national labour force are those people who are available for work within the nation, i.e. the working population.
Capital
To the economist, physical capital (or «capital» as it is commonly called) is something created by people to produce other goods and services. A factory, tools and machines are capital resources because they can be used to produce other goods and services. The term capital is often used by business people to refer to money they can use to buy factories, machinery and other similar productive resources. Payment for the use of someone else's money, or capital, is called interest. But money, as such, produces nothing: hence, it is not to be considered as an economic resource. Real capital— tools, machinery, and other productive equipment - is an economic resource; money or financial capital is not. The process of producing and accumulating capital goods is known as investment.
Entrepreneurship
Closely associated with labor is the concept of entrepreneurship, the managerial or organizational skills needed by most firms to produce goods and services. The entrepreneur brings together the other three factors of production. When they are successful, entrepreneurs earn profits. When they are not successful, they suffer losses. The reward to entrepreneurs for the risks, innovative ideas and efforts that they have put into the business, they obtain the money that remains after the owners of land, labor and capital have received their payments.

ІІ. Give English equivalents to the following:
А гроші з обміну, гроші з розрахунку, в звороті для fixed payment, в strict economic sense, financial reward, in terms of money, human labour, distinctions of social class, payment of wages, national labour force, it should be необхідний, self-employed, fixed wage, на отримання прибутку, reward of private enterprise, a negotiated rate, як результат productive work, до share the surplus, плата за, інші елементи, на бік ризику, risk has been justified, as return on the investment, previous business activities, a deliberate policy of saving surpluses, to create capital, the assets possessed by a person.
III. Read the international words and guess their meanings:
Продуктивні сили, виробничі відносини, виробництво матеріальних благ, впливати, взаємозв'язок продуктивних сил і виробничих відносин, форма власності на засоби виробництва, форми розподілу матеріальних благ, життєві інтереси, взаємини людей, здатність людини до праці, кількість і якість, кваліфікована робоча сила, створювати додаткову вартість, постійний капітал , змінний капітал, оборотний капітал, готовий товар.

IV. Make sentences by adding a suitable beginning to the following:
1. …. but with the payment of wages in return of work.
2. ….. is not labour in the strict economic sense.
3. ……is known as profit.
4. ……in return for a fixed payment.
5. ……the working population.
6. ……also a means of measuring the value of men’s labour.
V. Agree or disagree with the following statements:
1. There is always an element of risk in starting a business.
2. If the business is not successful, the risk has been justified.
3. All railways, houses, land, airports shares are capital.
4. Profit is the surplus which accumulates as a result of productive work.
5. The employees, the employers and the providers of capital bear the risk.
6. A deliberate policy of saving surpluses may be only collective.
7. The employer obtains the surplus after he pays the wages of his employees.
VІ Fill in the gaps using the words given
(Retail clerk, services, takes part, accumulating, account, human effort, market, risk, limited, consumer, bankruptcy, simplified, entrepreneurial)
- Economic resources are _____ or scarce.
- There is an apparent need for a _____ classification of such resources, which we shall meet with the following categories: (1) property resources—land or raw materials and capital; (2) human resources—labor and _____ ability.
- The process of producing and _____ capital goods is known as investment.
- Thus the services of a logger, _____, machinist, teacher, professional football player, and nuclear physicist all fall under the general heading of labor.
- The entrepreneur is a _____ bearer.
- The reward for his or her time, efforts, and abilities may be attractive profits or losses and eventual _____.
- The world _____ for oil can also be a source of favorable shifts in aggregate supply.
8. The people who ___ in production are also ___ .
9. There are social and political problems which have to be taken ___ .
10. Labour is ___ to the production of goods and ___ .
VІІ Translate into English
- Для зручності продуктивні ресурси зазвичай ділять чотирма основні категорії, які називаються чинниками виробництва.
- Праця — діяльність людей, спрямовану задоволення потреб індивіда і суспільства.
- Як економічна категорія, праця є одним із факторів виробництва.
- Процес праці включає три основних фактора: - доцільну діяльність людини; - предмет, на який спрямована праця; - кошти праці, з допомогою яких людина впливає щодо праці.
- Капітал - це сукупність відносин і предметів, виражених у вигляді вартості, здатної приносити додаткову вартість або збиток.
- Капітал включає всі ті продуктивні ресурси, які створені людьми: інструменти, машини, інфраструктуру, а також нематеріальні речі, наприклад, комп'ютерні програми.
- Розподіл будь-якої кількості блага може бути поліпшено за допомогою обміну.
- Підприємницька здатність - в економічній науці - здатність людини: - Використовувати певне поєднання ресурсів для виробництва товару; - приймати розумні послідовні рішення; - Застосовувати нововведення; і - йти на (виправданий) ризик.
- Підприємництвом можна займатися у різних сферах. Крім загального підприємництва, виділяють соціальне та технологічне підприємництво.
- Земля - один із чотирьох основних факторів виробництва, який для того, щоб стати продуктивним, зазвичай має з'єднуватися з працею та капіталом.
VII. Answer some questions:
- What are the factors of production?
- What is the fuel that drives the economy?
- What are the natural resources?
- What, in economic theory, is “labour”?
- What is called “the price paid for the use of labour”?
- Why is necessary to treat labour somewhat differently from the other factors of production?
- How may be the working population be defined?
- What is the capital?
- How is capital created?
- What is the role of entrepreneurship in production?
SUMMARIZING.
Підведення підсумків уроку. Бесіда в режимі T-P1P2.
T: What topic did we start discussing today? What did we read about? What new words and word combinations have you learned? What material was difficult/ interesting/boring? So, you all see where you need more practice and what you can do well.
Setting homework. Постановка домашнього завдання
T: Your home task is to write a table on the following topic FACTORS OF PRODUCTION. Use your notes from class!


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку