TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATION методична розробка з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)» в закладах фахової передвищої освіти
Лисичанський промислово-технологічний фаховий коледж
TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATION
методична розробка
з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)»
в закладах фахової передвищої освіти
Розробник: Скиба Н.М., старший викладач, викладач вищої категорії Лисичанського промислово-технологічного фахового коледжу
2024
BСТУП
Методична розробка заняття виконана у відповідності з методичними рекомендаціями з підготовки та проведення практичних занять у закладах фахової передвищої освіти. Заняття підготовлено відповідно до робочої і навчальної програми з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)». У методичній розробці заняття подано розгорнутий план-конспект заняття у формі мовного практикуму з використанням методу критичного мислення, методики роботи з лексичним матеріалом, методу лінгвістичного квесту, рольовою грою, перелік літератури та необхідного обладнання, мету і задачі, надано чітку структуру заняття, вдало подано мотивацію пізнавальної діяльності студентів.
Розробка містить багато різноманітних форм та методів роботи (бесіду, читання, мозковий штурм, аудіювання з використанням тематичного відеоролику, роботу з мультимедійними презентаціями, групову та парну роботу,), що відповідають психофізіологічним та індивідуальним особливостям студентів і сприяють успішному досягненню мети заняття.
Методична розробка відкритого заняття відповідає теоретичному й методико-практичному розділам навчальної програми, має інноваційний характер, відповідає новітнім технологіям навчання, спрямована на формування комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців, розвиток пам'яті, уваги, фонематичного слуху студентів, сприяють зацікавленості та формуванню комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців.
Методична розробка може бути рекомендована для викладачів іноземної мови в закладах фахової передвищої освіти в якості як основного, так і довідково-дидактичного матеріалу.
МЕТОДИЧНА РОЗРОБКА ЗАНЯТТЯ
Заняття №
Предмет: Іноземна мова
Група:
Тема заняття: TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATION
Мета: формувати лексичні навички й навички вимови; вдосконалювати навички читання й усного мовлення; розвивати мовну здогадку й мовленнєву реакцію; виховувати зацікавленість у розширенні своїх знань, використовувати раніше вивчені структури, а також збагачувати словарний запас, практикуватися у перекладі речень, розвивати навички логічного викладання думок, пам'ять, виховувати свідоме ставлення до навчання, вчити раціонально використовувати свій час, прищеплювати бажання вивчати іноземну мову.
Обладнання: словники, комп’ютер, роздавальний матеріал
Тип заняття: практичне
Міжпредметні зв'язки: Економіка підприємства, Статистика, Фінанси підприємства, Економічний аналіз, Організація виробництва, Менеджмент, Маркетинг
СТРУКТУРА ЗАНЯТТЯ:
1.Організаційний момент:
1)Привітання
2) Перекличка
3)Перевірка готовності до заняття
2. Мотивація навчальної та пізнавальної діяльності студентів, оголошення теми та цілей заняття.
3.Реалізація теми за планом
4. Підсумок заняття. Оцінювання
5. Домашнє завдання
ХІД ЗАНЯТТЯ:
I. Scanning reading. Читання з повним розумінням змісту прочитаного.
I. Read the text TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATION
Use a dictionary, if necessary.
Business is a word that is commonly used in many different languages. But exactly what does it mean? The concepts and activities of business have increased in modern times. Traditionally, business simply meant exchange or trade for things people wanted or needed. Today it has a more technical definition. One definition of business is the production, distribution, and sale of goods and services for a profit. Profit is the money that remains after all the expenses are paid. Creating an economic surplus or profit is, therefore, a primary goal of business activity.

Starting a business
Starting a business it is necessary to provide capital needed for this business. There is always an element of risk because this business may fail. If the business is successful, the risk-taking has been stifled and invested capital earns part of the profits as a return on the investment and the period during which the capital was at risk.
Capital in this instance is simply the accumulation of previous surpluses on previous business activities. It this way the past is used to finance the future. The accumulation of capital is almost always deliberate, either on the part of individual citizens or on the part of the state. Even in non-capitalistic societies a certain part of the surplus achieved in any enterprise is "ploughed back" into the system in order to promote further growth.
When capital, labour and enterprise combine to make a new business successful, the business must still continue to compete on the market with other companies producing the same type of commodity. The term "market", as used by economists, is a logical extension from the idea of a place set aside for buying and selling. Formally, part of a town was kept as a marketplace, and country people would come in on market days to buy and sell. Markets today need not however be located in any fixed places the sugar market and the cotton market are not geographical locations, but simply sets of conditions which permit buyers and sellers to work together.

In a free market, competition takes place among sellers in order to sell their commodities at the best possible price, and among buyers competition influences prices. Changes in supply and demand have their effects, and it is not surprising that considerable fluctuations in price can take place over periods of weeks and months. Since these modern markets are not normally located in any special place, buyers and sellers do not always have to meet face-to-face. They may communicate by letter, lay cable, by telephone or through their agents. In a perfect market such communications are easy, buyers and sellers are numerous, the competition
Types of business
The different types of business organization to be found in the UK and most other capitalist countries may be classified under five headings: the sole proprietor, the partnership, the joint stock company, the cooperative society, and the public corporation.
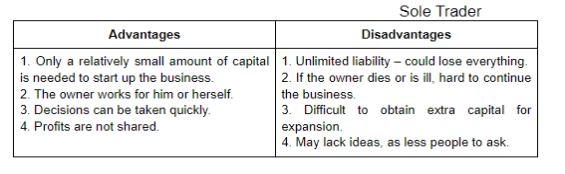
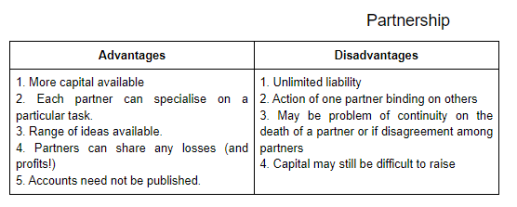
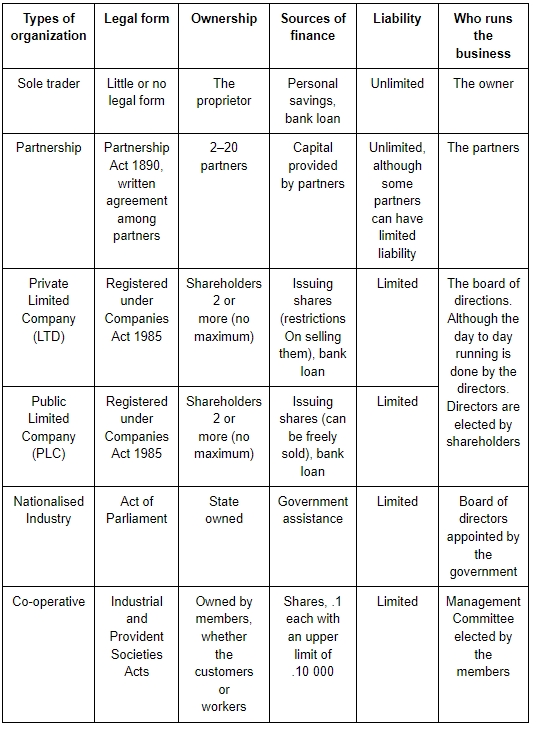
The sole proprietor
This is the simplest and the oldest form of business enterprise and often referred to as the one-person business. A single person provides the capital, takes the decisions, and assumes the risks. He or she is solely responsible for the success or failure of the business and has, therefore, the sole rights to such profits as may be made, or, alternatively, bears the sole responsibility for such losses as may accrue. The strength of this type of firm lies in the direct personal interest of the proprietor in the efficiency of his enterprise. Ownership and control are vested in one person who enjoys all the fruits of success and hence has a great incentive to run the firm efficiency. The great disadvantage of the sole proprietor from an enterprise lies in the fact that the owner is personally liable for the debts incurred by his firm and his liability is unlimited. All his personal possessions are at risk and may be seized to meet creditors demands in the event of the business becoming insolvent. Another disadvantage of this type of firm is the strict limitation of its ability to acquire capital for expansion. Finance is restricted to the amounts which the entrepreneur is able to provide from his own resources and whatever sums he can borrow on his own security. We find the one-person business prevalent in farming, retailing, building, repair and maintenance work, and personal services such as hairdressing.
II. Complete the sentences using the words given:
Possessions, adjustment, proprietor, failure, headings, enterprise, efficiency, ownership, conditions, flexible, failure, liability, debts, decisions, responsible.
- The different types of business organization may be classified under five …
- This is the simplest and the oldest form of business … .
- A single person is solely…for the success or … of the business.
- His … is unlimited.
- … and control are vested in one person.
- This type of organization is extremely … and capable of quick … to change in market … .
- The owner is personally liable for the … incurred by his firm.
- All his … are at risk.
- A single person provides the capital, takes the …, and assumes the risks.

III. Complete the sentences using the proper forms of the verbs in the brackets:
1. The different types of business organization ___ (to find) in the UK may ___ (to classify) under five headings.
2. He ___ (to have) the sole rights to such profits as may ___ (to accrue) or, alternatively, ___ (to bear) the sole responsibility for such losses.
3. The one-person business ___ (to be) still far more numerous than any other type of business organization.
4. Ownership and control ___ (to vest) in one person who ___ (to enjoy) all the fruits of success.
5. He ___ (to have) no need ___ (to consult) colleagues when changes of policy ___ (to require).
6. We should ___ (to expect) this type of organization ___ (to be) extremely flexible.
7. All his personal possession may ___ (to meet) creditors demand.
8. Finance ___ (to restrict) to the amounts which the entrepreneur is able ___ (to provide) from his own resources and whatever sums he can … (to borrow) on his own security.

IV. Translate into English:
1.Індивідуальний підприємець визначає місце своєї діяльності та вкладає у справу свій особистий капітал.2. При створенні товариства необхідно скласти письмову угоду про розподіл капіталу та дивідендів між учасниками (Agreement of Capital and Dividends Share) та статут (Statute), де обумовлено всі положення про управління товариством.3.Для товариства передбачено обмежений термін діяльності та необмежена відповідальність принаймні одного з партнерів. 4.Кожен із основних партнерів може діяти від імені товариства. 5.Основні партнери товариства мають необмежену особисту відповідальність. 6.Створення корпорації – це найскладніший і найдорожчий шлях організації бізнесу. 7.Корпорації випускають акції, що визначають форму розподілу власності. 8.Власниками корпорації часто не ті люди, які нею керують (власниками корпорації є акціонери, а менеджери – необов'язково). 9.Власність корпорації юридично чітко визначено щодо кожного власника, що обумовлює певний захист внесків кожного акціонера або власника акцій. 10.Утримувачі акцій мають право відвідувати збори акціонерів та приймати рішення щодо основних рішень, таких, наприклад, як заміна членів ради директорів, а іноді й президента.
V. Answer the questions:
- What is one modern definition of business?
- How does this modern meaning of business differ from the traditional one?
- What factors have brought about these changes?
- What does production involve?
- What example of distribution is given in the reading?
- Can you think of another example?
- How do goods differ from services?
- In addition to production, distribution, and sale, what other factor is important in defining business?
- What is profit?
- In general, what do companies do with their profit?
- Compare your definition of business with the one given in the reading.
- How are they similar?
- In what ways does your definition differ from the one presented in the text?
- What are the types of business organization to be found in the UK?
- What is the simplest and oldest form of business enterprise?
SUMMARIZING.
Підведення підсумків уроку. Бесіда в режимі T-P1P2.
T: What topic did we start discussing today? What did we read about? What new words and word combinations have you learned? What material was difficult/ interesting/boring? So, you all see where you need more practice and what you can do well.
Setting homework. Постановка домашнього завдання
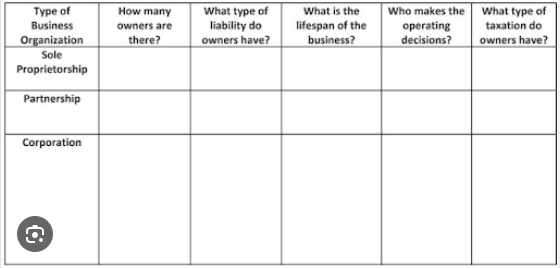
T: Your home task is to write a table on the following topic TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATION. Use your notes from class!

про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
