Методична розробка заняття з Іноземної мови за професійним спрямуванням Units of measurement
Лисичанський промислово-технологічний фаховий коледж

UNITS OF MEASUREMENT
методична розробка
з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)»
в закладах фахової передвищої освіти
Розробник: Скиба Н.М., старший викладач, викладач вищої категорії Лисичанського промислово-технологічного фахового коледжу
2022
ВСТУП
Методична розробка заняття Units of measurement виконана у відповідності з методичними рекомендаціями з підготовки та проведення практичних занять у закладах фахової передвищої освіти. Заняття підготовлено відповідно до робочої і навчальної програми з дисципліни «Іноземна мова ( за професійним спрямуванням)» спеціальності 133 «Галузеве машинобудування» за освітньо-професійною програмою «Обслуговування та ремонт обладнання підприємств хімічної та нафтогазопереробної промисловості» У методичній розробці заняття подано розгорнутий план-конспект заняття у формі мовного практикуму з використанням методу критичного мислення, методики роботи з лексичним матеріалом, методу лінгвістичного квесту, рольовою грою, перелік необхідного обладнання, мету і задачі, надано чітку структуру заняття, вдало подано мотивацію пізнавальної діяльності студентів.
Розробка містить багато різноманітних форм та методів роботи (бесіду, читання, мозковий штурм, аудіювання з використанням тематичного відеоролику, групову та парну роботу,), що відповідають індивідуальним особливостям студентів і сприяють успішному досягненню мети заняття.
Методична розробка заняття Units of measurement спрямована на формування комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців, розвиток пам'яті, уваги, фонематичного слуху студентів, сприяють зацікавленості та формуванню комунікативної компетенції майбутніх фахівців.
Методична розробка може бути рекомендована для викладачів іноземної мови в закладах фахової передвищої освіти в якості як основного, так і довідково-дидактичного матеріалу.
МЕТОДИЧНА РОЗРОБКА ЗАНЯТТЯ
Заняття №
Предмет: Іноземна мова
Група:
Тема заняття: UNITS OF MEASUREMENT
Мета: формувати лексичні навички й навички вимови; вдосконалювати навички читання й усного мовлення; розвивати мовну здогадку й мовленнєву реакцію; виховувати зацікавленість у розширенні своїх знань, використовувати раніше вивчені структури, а також збагачувати словарний запас, практикуватися у перекладі речень, розвивати навички логічного викладання думок, пам'ять, виховувати свідоме ставлення до навчання, вчити раціонально використовувати свій час, прищеплювати бажання вивчати іноземну мову.
Обладнання: словники, комп’ютер, роздавальний матеріал
Тип заняття: практичне
Міжпредметні зв'язки: Фізика, Обладнання підприємств нафтохімічної галузі, Матеріалознавство, Комп’ютерна техніка та прикладне програмне забезпечення, Основи автоматизація технологічних процесів, Комп’ютерна графіка
СТРУКТУРА ЗАНЯТТЯ:
1.Організаційний момент:
1)Привітання
2) Перекличка
3)Перевірка готовності до заняття
2. Мотивація навчальної та пізнавальної діяльності студентів, оголошення теми та цілей заняття.
3.Реалізація теми за планом
4. Підсумок заняття. Оцінювання
5. Домашнє завдання
ХІД ЗАНЯТТЯ:
Find out the words in the dictionary. Write them down and learn.
|
observation, measurement, to put in order, to obtain, length, area, volume, velocity, density, to indicate, to divide, quantity, therefore, to derive from, unit, to convert, a shift, decimal, to define, to reproduce |
ІІ. After-watching task. Завдання на розуміння змісту переглянутого What is the role of Inetrnational System of Units?
III. Read the text. Use the dictionary, if necessary.
Real science has various recognised steps. It always begins with observation followed by classification and measurement. Classification has become the first step towards understanding of a new phenomenon. Phenomena have to be put in some order before anything can be done with them. Measurement is one further step in the process of putting them in order. It is only by measurement that new knowledge enters science.
Much of physics deals with measurements of physical quantities such as length, time, velocity, area, volume, mass, density, temperature and energy. Many of these quantities are interrelated. For example, density is mass divided by volume. Most of the physical quantities are related to length, time and mass. Therefore all the systems of physical units are derived from these three fundamental units.
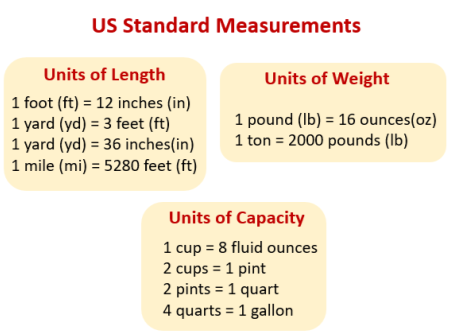
Practically there are three main systems of measurement in use today: the British system of units, the metric system of units and the (International) System of Units (SI). With a few exceptions nearly all the nations of the world use the metric system. The value of the MKS (metre-kilogram-second) system is that its various units possess simple and logical relationships among themselves, while the British system (the f. p. s. — foot-pound-second) is a very complicated one. For example, in the British system 1 mile is equal to 1,760 yards; 1 yard is equal to 3 feet, and 1 foot is equal to 12 inches. In the English system converting one unit into another is a hard and monotonous job, while in the MKS system conversions of one unit to another can be carried out by shifts of a decimal point (comma in Russian writing).
The standard metre of the world was originally defined in terms of the distance from the north pole to the equator. This distance is close to 10,000 kilometres or 107 metres.
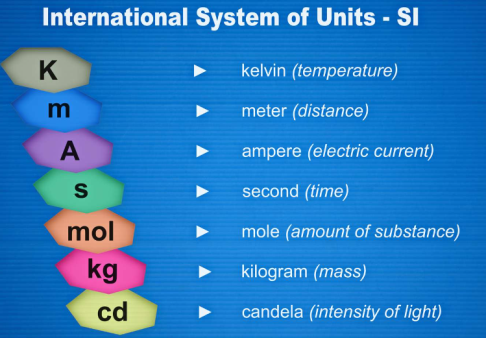
In fact, the SI Units is an internationally agreed coherent system of units derived from the MKS system. The seven basic units in it are: the metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (a), Kelvin (K), mole (mol), and candle (свеча) (cd).
Note. 107 metres – ten to the seventh power metres
IV. Define the parts of speech of the following words and translate them.
a) real – reality, scientific – science, various – variety, observable – observation, measurable – measurement, possible – possibility, physical – physics, quantitative – quantity, derivable – derivation, valuable – value, coherent – coherence;
b) precise – precisely, fundamental – fundamentally, practical – practically, main – mainly, near – nearly, simple – simply, logical – logically, equal – equally, monotonous – monotonously, original – originally, international – internationally, basic – basically.
V. Find Ukrainian equivalents to the following expressions in the text.
- observation followed by classification and measurement
- the first step towards understanding
- have to be put in some order
- new knowledge enters science
- much of physics deals with
- are related to length, time and mass
- are in use today
- the value of MKS system
- possess simple and logical relationships
- was originally defined
VI. Find the sentences that can’t be found in the text. Work in groups. Робота в групах.
- Unit is a quantity adopted as a standard of measurement.
- By measurement it is possible to indicate precisely what has to be done to reproduce given conditions and obtain a desired result.
- The second is a unit for measuring time in all the system.
- Most of the physical quantities are related to length, time and mass, therefore all the system of physical units are derived from these three fundamental units.
- Practically there are three main system of measurement in use today.
- In the English system converting one unit into another is a hard and monotonous job, while in the MKS system conversions of one unit to another can be carried out by shifts of a decimal points.
- Inch is less than foot is.
- 11.500 cubic feet is the measure of volume.
VII. Find English equivalents in the text.
- визнані етапи
- у процесі упорядкування
- справжня наука
- ці якості взаємопов'язані
- маса, поділена на обсяг
- виводиться з
- виходячи з відстані
- щільність
- система виміру
- за невеликим винятком
- цінність метричної системи
- десять у сьомому ступені
VIII. Fill in the missing words.
- Real science always begins with observation ________ by classification and _________.
- Much of physics deals with measurement of physical _____ such as length, time, velocity, area, volume, mass, density, temperature and energy.
- Many of these quantities are _______.
- ______ is mass divided by volume.
- ______, ______, _______ are three fundamental units.
- With a few exceptions nearly all the nations of the world use ______ ______.
- Various units of the MKS system _____ simple and logical ______ among themselves.
IX. Fill in the preposition if necessary.
- Real science always begins ____ observation followed ____ classification and measurement.
- Classification has become the first step towards understanding ____ a new phenomenon.
- Phenomena have to be put ____ some order before anything can be done ____ them.
- Measurement is one further step in the process ___ putting them in order.
- It is only ___ measurement that new knowledge enters ___ science.
- Much of physics deals ___ measurements ___ physical quantities.
- Most of the physical quantities are related ___ length, time and mass. Therefore all the system of physical units are derived ___ these three fundamental units.
- There are three main system of measurement ___ use today.
- The standard metre of the world was originally defined in terms of the distance ___ the north pole ___ the equator.
- This distance is close ___ 10 000 kilometres or 107 metres.

X. After-reading task. Завдання на перевірку розуміння змісту прочитаного. Define whether the sentences are TRUE or FALSE.
- Real science begins with measurement followed by observation.
- Velocity is mass divided by volume.
- Most of physical quantities are related to length, time and mass.
- Foot is a unit of area in the British system of measurement.
- The standard metre of the world was defined in terms of the distance from the north pole to the south pole.
XI. Give answers to the next questions. Make up a dialogue
- What are the recognised steps in real science?
- Why are classification and measurement so important in real science?
- What is unit?
- What are the three fundamental units?
- What systems of measurement are widely in use all over the world?
- Why is the metre system widely in use all over the world?
- What are the units of length in the MKS/British system?
- How was the metre originally defined?
- What standard unit is used for measuring area/volume/mass/time?
XII. Put questions to the following sentences.
- Real science has various recognised steps. (Special)
- It always begins with observation. (Alternative)
- Phenomena have to be put in some order. (General)
- There are three main system of measurement in use today. (Disjunctive, Special)
- Nearly all the nations of the world use the metric system. (Alternative)
XIII. Dictation-translation.
- Справжня наука завжди починається зі спостереження, потім слідує класифікація та вимір.
- Більшість фізики пов'язана вимірами таких фізичних величин як довжина, час, швидкість, площа, обсяг, маса, щільність, температура і енергія.
- Фактично існує три основні системи вимірювань, якими ми користуємося сьогодні.
- Стандартний метр світу спочатку був визначений на підставі відстані від північного полюса до екватора.
- Цінність метричної системи вимірів у тому, що її різні одиниці перебувають у простих і логічних відносинах друг з одним.
4. Summarizing. Підведення підсумків уроку. Бесіда в режимі T-P1-P2.
T: What topic did we start discussing today? What did we read about? What new words and word combinations have you learned? What material was difficult/ interesting/boring? So, you all see where you need more practice and what you can do well.
5. Setting homework. Постановка домашнього завдання
T: Your home task is to learn by heart new words and word combinations, read and translate the text History of the SI System

1


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
