Навчальний посібник "Pain and symptoms"
Міністерство охорони здоров’я України
Нікопольський медичний коледж
PAIN AND SYMPTOMS
Навчальний посібник
Схвалено на засіданні циклової комісії соціально-економічних, гуманітарних дисциплін та фізичного виховання
Протокол № 6 від 10.01. 2017 р.
Чорновіл І.С. Pain and symptoms: Навч. посібник. – Нікополь: Нікопольський медичний коледж, 2017. – 31 с.
Рецензенти:
Сиротіна Ю.Г., методист Нікопольського медичного коледжу, викладач іноземної мови.
Соколова Н.М., викладач іноземної мови.
Навчальний посібник укладено відповідно до чинної програми з «Англійської мови (за професійним спрямуванням)». Пропонований навчальний посібник призначено для підготовки до практичних занять, факультативних занять, диференційованого заліку, а також самостійного вивчення англійської мови (за професійним спрямуванням).
Для студентів IІ-IV курсів всіх спеціальностей
![]()
ПЕРЕДМОВА
Основною метою навчання англійської мови (за професійним спрямуванням) є формування у студентів вміння використовувати англійську мову практично, що передбачає оволодіння студентами говорінням, аудіюванням, читанням. В рамках викладання іноземної мови в медичному вищому навчальному закладі основна увага приділяється вивченню медичної термінології.
Оскільки англійська мова є засобом обміну інформацією, то тематичні тексти, діалоги з актуальних питань повинні містити інформацію, з допомогою якої реалізується комплексна мета навчання іноземної мови на даному етапі навчання – спілкування з пацієнтами.
Посібник направлено на відпрацювання навичок спілкування медичних працівників з пацієнтами з використанням зрозумілою для пацієнта термінології, вміння ставити прості запитання пацієнтам.
Знання професійної термінології необхідно для заповнення історії хвороби пацієнта після опитування.
Невід'ємною частиною навчання є використання дисків, що містять типові діалоги англійською мовою. Це сприяє розвитку навичок розпізнавання мови на слух, а також не дозволяє звикнути тільки до мови викладача.
В рамках закріплення нової отриманої інформації у посібнику представлені вправи з застосованнм ігрової технології, де студенти самі складають і озвучують діалоги, що дозволяє їм краще представити дану ситуацію і закріпити лексичний матеріал. І тому призначенням цього посібника є:
- забезпечити засвоєння нового лексичного матеріалу, який необхідний для заповнення анамнезу;
- повторення медичної термінології для спілкування з пацієнтами, постановки діагнозу;
- повторення граматичного матеріалу.
PAIn
 in this unit:
in this unit:
- describing types of pain;
- describing degrees of pain;
- asking about pain;
- refersed pain.

Difference between ACHE, PAIN and HURT
An ache is discomfort that continues for some time. It is usually associated with a specific part of the body, such as a headache, a stomachache, a toothache, an earache. After you exercise, the next day your muscles will probably ache. An ache is usually not extremely strong, so you can try to ignore it.
Pain is usually stronger, more sudden, and more difficult to ignore. You would feel pain when you cut yourself or hit your head on something. If you exercise and you injure yourself – break a bone or tear a muscle – you would feel a sudden pain.
We also have the expression “aches and pains,” which describes general and various physical discomforts. Your 90-year-old grandfather might complain about all the “aches and pains” he has at his age!
Hurt is a little different because it is usually used as an adjective or verb, not a noun. To describe an ache or a pain, you could say:
- My ankle hurts. = I have a pain/ache in my ankle.
- My neck hurts. = I have a pain/ache in my neck.
- My shoulders hurt. = I have a pain/ache in my shoulders.
- Hurt is also used to mean “injure”:
- Don’t play with that knife – you could hurt yourself.
- He was badly hurt in the car accident.
Finally, all three of these words can be used to refer to emotional pain as well as physical pain:
-
My son is in prison; the situation is causing me a lot of heartache.
(heartache = emotional anguish) -
It took her years to move past the pain of her divorce.
(pain = emotional injury/discomfort) -
I was extremely hurt that he didn’t invite me to his wedding.
(hurt = upset, sad)
LOCATION AND DESCRIBING PAIN
- Label the pain map using the words in the box.

|
Verb |
Noun |
Adjektive |
|
My head hurts. |
|
|
|
My head aches. |
I’ve got a headfche. |
|
|
|
I’ve got a pain in my head. |
It’s painful. |
|
|
|
His head is sore. |
- Rewtite sentencesa 1-6 so they have the same meaning, but use different words from the table.
- I’ve got a terribly sore throat and I think I’ve got a temperature.
- I hurt my ankle this morning, running up the stairs. It’s still very painlul.
- Have you got a headache? You don’t look very well.
- Ah, poor thing. Her gums really hurt. Her teeth are coming through.
- He’s got stomach ache. I don’t think that chicken was properly cooked.
-
I’ve got a pain in my lower back and it’s really aching. It’s from carring my computer.
- Write at least one sentence for each red arrow in exercise 1 to answer the question: How do you feel?
- Put these words in order to make sentences that patients can use yo describe how their pain changes.
- pain / The / much / is / now / better __________________________
- better / I / today / feel __________________________
- than / worse / yesterday / It’s _________________________
- my leg / worse / in / is / The / much / pain _________________________
5. Match these words for types of pain with their descriptions.

- a throbbing pain a. feels like it is eating you
- a sharp pain b. travels fast along part of your body
- a burning pain c. is steady and not too painful
- stabbing pain d. feels like a muscle is being squeezed
- a shooting pain e. feels like something sharp is stuck into you
- a dull ache f. comes and goes rhythmically
- a gnawing pain g. feels like fire
- a cramping pain h. ia strong and sudden
6. Faces like these are used to help children and people who cannot speak a language say how much pain they feel. Join each adjective to the face it belongs with best.
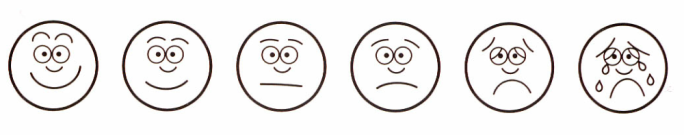
agonizing moderate quite bad slight mild
not bad severe unbearable no pain
- Complete the sentences the the patient use to describe the pain with the words
in the box.

- I still have a headache. It’s like a drum, a real ____________ pain.
- There’s ____________ ache in my lower back. It’s quite a mild pain.
- I get this ____________ feeling two or three hours after food and sometimes it’s very sore.
- It’s kind of ____________ feeling, like pins and needles. I get it in my feet as well, but it’s better than last week.
- Yes, it’s a ____________ pain, like a knife. It’s a severe pain. It really hurts a lot.
- Use the adjective in the table to complete the patient’s descriptions of their pain.

- It always begins wirh a pain on the left side of my head, which gets __________ and __________ and then I start to feel nauseeous. I have to take painkillers and lie down in a darkened room. I start to feel __________ after about an hour or so and by the next day I’m generally __________. For me the __________ case ever lasted for seventy-two hours. On a scale of nought to ten, it’s a ten. It’s __________ pain I know.
- I get this pain all round my forehead and behind my cheekbones. The problem is __________ when I have a cold, so it’s worse in the winter than the summer, but the __________ was last year when I was pregnant. I find the __________ treatment is a nasal spray, but I also feel __________ if I use a warm face pack.
- Look at the information about these three painkillers. Complete the sentences, then write three more of your own.
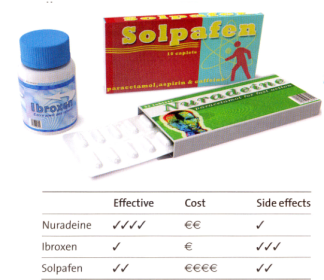
1
- Nuradeine is much ___________ (effective) than Ibroxen.
- Ibroxen is ___________ (cheap) than Nuradeine.
- Ibroxen has ___________ (side effects) than Nuradeine.
- Nuradeine is ___________ (effective).
- _______________________________________________
- _______________________________________________
- _______________________________________________
LISTENING
10. ![]() Listen to four patienten describing their pain. Tick (
Listen to four patienten describing their pain. Tick (![]() ) the boxes that describe the pain, and mark the position on the body.
) the boxes that describe the pain, and mark the position on the body.
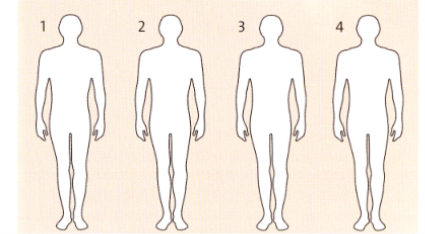
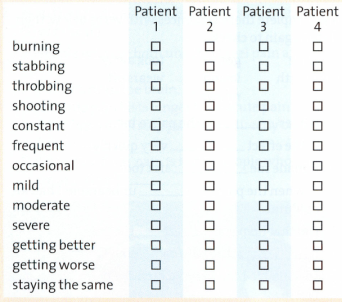
11. ![]() Work with a partner. Try to complete these phrases, then listen ahain and check.
Work with a partner. Try to complete these phrases, then listen ahain and check.
1. Are you still _________ pain?
2. Well, _________ pain around my stomach.
3. I _________ a slight pain, just here _________ my right side.
4. I’ve _________ this throbbing pain _________ my head.
5. I _________ getting this terrible pain _________ my left arm.
12. What kind of pain do you think these conditions might cause. Discuss your thoughts with a partner.
- a deep cut
- migraine
- a tumour
- labour
- a stomach ulcer
- kinney stones
- a broken ankle
- a severed finger
13. ![]() Complete these sentences with verbs below, then , then listen ahain and check.
Complete these sentences with verbs below, then , then listen ahain and check.

- It _________ the pain a bit …
- … the effect _________ very quickly.
- It made me _________ sick too.
- … when the pain _________ unberable, I had an epidural.
- Did tat help you _________ the pain?
- It _________ the pain completely!
- I decided to have gas and air if the pain _________ worse …
- I didn’t like _________ all sensation.
READING
- Before you read the article, discuss these questions with a partner.
- Can you give a definition of “pain”?
- Why do we feel pain?
- What would happen if you could feel no pain?
- Read the article, and decide if these statements are true (T) or false (F).
- People who are born unable to feel pain are unlucky. _____
- Pain starts in the brain. _____
- Chronic pain lasts longer that acute pain. _____
- All drugs which stop pain, work directly on the brain. _____
- “Phantom limb” pain is felt by people who have lost an arm or leg. _____

- Complete the gaps using verbs from the article. You may need to change the tense.
- She wears a mask to p_________ the area of burnt skin.
- The pain in your leg should go when we t_________ your back problem.
- She used breathing exercises, and gas and air to m_________ the pain of childbirth.
- A local unaesthetic will p_________ you felling any pain during the operation.
- Breathing exercises help c_________ the pain to some extent.
- When you s_________ a serious injury, you may not feel pain immediately.
-
Read the article, use the information in the text to complete the sentences.
-

Researches are trying to find out why __________.- people experience pain differently.
- people feel pain.
- pain is important to people.
-
Experiments show that __________.
- pain is worse foe men than women.
- men can take more pain than women.
- children feel less pain than adults.
-
Nurses need to measure a patient’s pain because __________.
- pain is a problem.
- pain is a symptom.
- patients can’t describe it.
-
Medics ask patients for a number to describe __________.
- the kind of pain they have.
- how bad the pain is.
- how often they’ve in pain.
-
To describe pain, medics ask children to
- point to a smiley face.
- think of some numbers.
- say how it feels.
-
You experience referred pain __________.
- only in your internal organs.
- long after an injury.
- in a different place from an injury.
-
SPEAKING
Question to assess pain
- Here are some basic questions to ask a patient when assessing pain. Match the beginning of each sentence to the end
- Where does a. worse?
- Does it b. it hurt?
- When did it start c. does it hurt?
- Does the pain d. describe the pain?
- How much e. hurting?
- Can you f. hurt all the time?
- Does anything make g. stay in one place or more around?
- What makes it h. the pain feel better?
-
Add Wh-question words to form pain assessment questions.
- _________ does it hurt? 5. _________ is the pain?
- _________ long does the pain last? 6. _________ does the pain move to?
- _________ did it start? 7. _________ does the pain feel like?
- _________ do you feel? 8. _________ do you have pain?

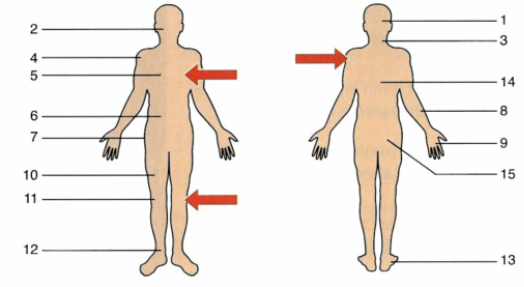
- Look at the diagram showing areas of referred pain. Work with a partner. Discuss which colour you think refers to each of the following parts of the body.
- kidney g. stomach
- appendix h. colon
- ovary i. bladder
-
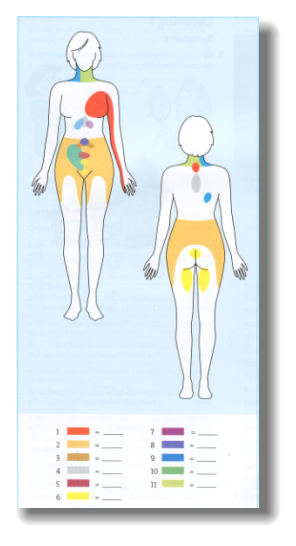 liver and gallbladder j. lung and diaphragm
liver and gallbladder j. lung and diaphragm
- small intestine k. heart
- pancreas
- Work in pairs.
Student A
- You have a problem with your liver which is causing you pain. Imagine the pain you might feel, and be ready to answer the nurse’s questions. Think about the following details.
- where?
- when?
- how bad?
- type of pain?
- same place or moving?
- getting better / worse?
- what helps / makes worse?
- You are the nurse. Ask Student B about the pain they are experiencing, and fill in the chart.
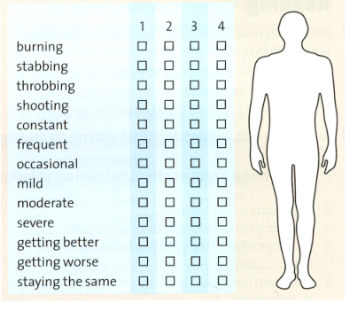
- Change roles. Answer the nurse’s questions.
Student B
- You are in pain after a fall the other day. Imagine the pain you might feel, and be ready to answer the nurse’s questions. Think about the following details.
- where?
- when?
- how bad?
- type of pain?
- same place or moving?
- getting better / worse?
- what helps / makes worse?
- Answer the nurse’s questions.
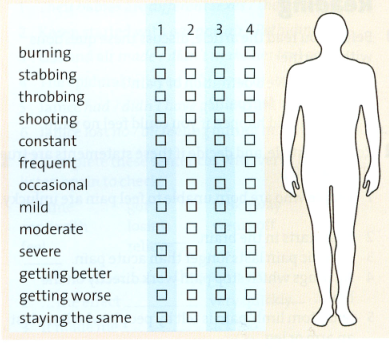
3. Change roles. Now you are a nurse. Ask Student A about the pain they are experiencing, and fill in the chart.
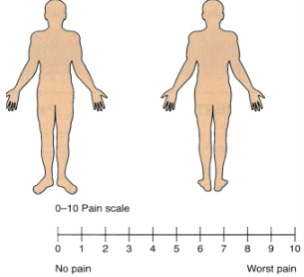
- Work in pairs. Student A is the patient Tony / Antonia Bates. Student B will interview you about your pain. When you have finished, swap roles. Interview Student B and complete the pain map and pain scale below.
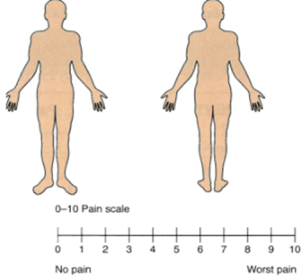

Work in pairs. Student B is the patient Marie / Martin McKoewen. Student A will interview you about your pain. Interview Student A and complete the pain map and pain scale below.

WRITING
- Read this report on a patient’s pain. Can you find and correct five mistakes in it?
The patient has abdominal pain.
It begin suddenly last night as mild
but constant pain all over
abdomen. Now it is more bad,
and is on the right-hand side to the
abdomen. The pain has worse when
he coughs.
- Write a report.
Read the example Pain Report and use the information in the box to write a similar report about a patient with appendicitis, Mrs. Fawza Adnan.

in this unit:
- describing symptoms;
- asking about symptoms.
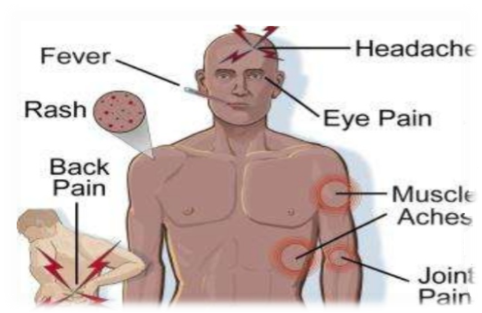

DESCRIBING SYMPTOMS
- Match pictures and words.
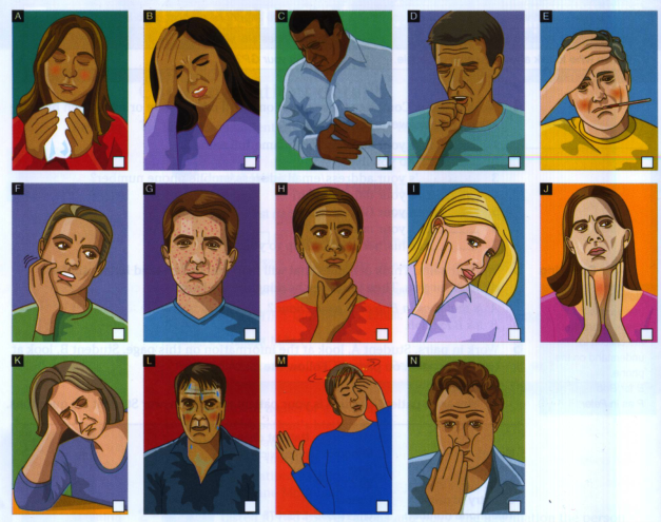

- cough 8. runny nose
- dizzy 9. skin rash
- earache 10. sore throat
- fever 11. stomachache
- headache 12. sweaty
- itchy 13. swollen glands
- nauseous 14. tired
- Complete the sentences about the patients’ injured and symtoms with the correct form of the words in the box.

- Aisha is __________ a lot and having difficulty __________.
- Sandip has __________ in his chest and feels.
- Desiree is ________ heavily from a bad cut and is worried about _________.
- __________ almost immediately.
- Winston’ shoulder and wrist are very __________ and painful. He banged his head hard and still feels __________ and nauseous.
- Jason fell off his bike and has cuts and __________ on his right arm.
- Try to complete the sentences.
- How __________ it feel?
- A little deformed, __________?
- __________ it painful when you move it?
- __________ move youyr toes?
- How __________feeling?
- __________ a sore throat?
- __________ redness?
- __________ going?
- __________ dizzy at all?
- When __________ sick, mostly?
- __________ pain?
- Here are description of four possible conditions that can cause a child to cough in the night. Complete them with words below.

Night coughing
 Asthma
Asthma
Children with asthma cough, and __________ when they breathe out. They become very short of breath when an attack __________.
A cold
Sometimes a child __________ a cough and a fever with a cold. A bad cough can __________ a child vomit.
Croup
Children under three years old sometimes __________ croup. They have a sore throat and they wheeze when they __________ in. When they cough it often __________ like a dog barking.
Pneumonia
The symtoms of pneumonia __________ a temperature of over 39oC, fast breathing, sometimes __________ by voming and sometimes __________ blood.
- A nurse wants to know about symptoms and ask the questions. Write the number of the correct symptom after each question.
- diarrhoea a) Can you feel this?
- spots b) Do you have then on your back too?
- numbness c) How high is it?
- fever d) When you have an attack, do you fall over?
- swelling e) Was there any blood in it?
- nausea f) Do you still fell sick?
- dizziness g) How long has it been this big?
- Complete the sentences with the words from the list.

- She suffered __________ and vomiting.
- __________ is an external symptom.
- She had a __________ abdomen.
- __________ are a typical symptom of chicken pox.
- A deep cut needs __________ to heal properly.
- A __________can cause itching.
- He found a __________ abouve his ankle.
- Her extreme __________ are difficult to live with.
LISTENING
7. ![]() Listen to these patients describe their symtoms, and match each one with their conditions.
Listen to these patients describe their symtoms, and match each one with their conditions.

8. ![]() Listen again and tick the words you hear from this list.
Listen again and tick the words you hear from this list.
READING
- Read the article, and decide if these statements are true (T) or false (F).

- You need signs and symptoms for a diagnosis. _____
- You can’t see symptoms. _____
- Patients presenting symptoms are either strong, mild or weak. _____
- Killer diseases can have weak symptoms. _____
- Non-specific symptoms help a lot of with diagnosis. _____
- Too much information slows up diagnosis. _____
SPEAKING

- Work in pairs. Look at the symptoms in 1 and write adjective, noun, or adjective + noun next to each one.
- Match 1-5 to a-e to make questions.
- Do you a) feel today?
- How do you b) have a runny nose?
- Do you have any c) your symptoms?
- What are d) other symptoms?
- Do you have a e) temperature?
- An anxious father calls the doctor’s surgery and speaks to the practice nurse. Read the answers he gave about his son. Write the nurse’s questions.
- A: ______________? B: My son’s name is Saul Chambers.
- A: ______________? B: He’s three.
- A: ______________? B: He has a bad stomachache.
- A: ______________? B: Yes, it’s 37,5o.
- A: ______________? B: No other symptoms, no.
- Work in pairs. Follow the instructions.
You are ill and these are your symptoms.
Student A Student B
You
- have a skin rash
- have a headache
- have a slight fever (38oC)
- are sweaty
You
- have a very bad cough
- have a very bad sore throut
- are dizzy
- have a running nose
You are the nurse. Ask about patient’s symptoms and tick the symptoms he/she has.

E.g. Hello, how you feel today? Do you have a temperature?
- Work in pairs. You are a patient, describe your symptoms
 Student B
Student B
You have hurt your wrist. Describe your symptoms to the helpline nurse.

Student A
You have a bad stomach and
decide to call to helpline nurse.
You are helpline nurse. Ask the caller questions to find out exactly what the problem is. Use the notes below to help you.
 Student B Student A
Student B Student A

WRITING
-
Read this report about a patient with appendicitis and find three mistakes.

- Write a report on this patient who has food poisoning using these notes.

- Write a report.
Read the example report about the fatal symptoms of one patient. Use the notes in the box to write a similar report about a patient with symptoms of an angina attack.

PROJECT
Research the symptoms of one these illnesses and give a short presentation describing them to the class.
- AIDS
- gangrene
- tuberculosis
- rabies
- malaria
- leprosy
СПИСОК ВИКОРСТАНИХ ДЖЕРЕЛ
- Grice T. Oxford English for Careers Nursing 1 / Student’s book. – Oxford University Press. – 135 p.
- Grice T. Oxford English for Careers Nursing 2 / Student’s book. – Oxford University Press. – 135 p.
- Grice T. Oxford English for Careers Nursing 1 / Practice File. – Oxford University Press. – 78 p.
- Wright R., Cangal B. English for nursing 1 / Student’s book. – Person Longman. – 79 p.
- Wright R., Cangal B. English for nursing 2 / Student’s book. – Person Longman. – 79 p.
- 600+Confusing English Words Explained / Difference between ACHE, PAIN, And HURT. – https://www.espressoenglish.net/difference-between-ache-pain-and-hurt/
ЗМІСТ
ПЕРЕДМОВА…………………………………………………………………..…3
PAIN………………………………………………………………………………..4
Difference between ACHE, PAIN, and HURT……………………………………..5
Location and describing pain……………………………………………………….6
Listening…………………………………………………………………………..10
Reading……………………………………………………………………………12
Speaking…………………………………………………………………………..14
Writing…………………………………………………………………………….19
SYMPTOMS………………………………………………………………….…..20
Describing symptoms………………………………………….………………….21
Listening…………………………………………………………………………..24
Reading………………………………………………………………………...….25
Speaking…………………………………………………………………………..26
Writing…………………………………………………………………………….28
Project……………………………………………………………………………..29
СПИСОК ВИКОРИСТАНИХ ДЖЕРЕЛ…………………..……………………30
1


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
