Presentation "A Brief History of the English Language" part 1
A Brief History of the English
Language
part 1
We can categorize the development of
English into 3 distinct eras:
- Old English from 450 to 1100
- Middle English from 1100 to 1500
-Modern English from about 1500 up until the present
English is a Germanic language, Does that mean English is
German? No. Germanic is a word used for the group of people from a particular part of the world who once probably spoke the same language, a language that doesn't exist today,
Germanic languages now include German, English, Dutch,
Swedish, Danish and quite a few more,
The history of the English Language is a history of invasion and the movement of people,
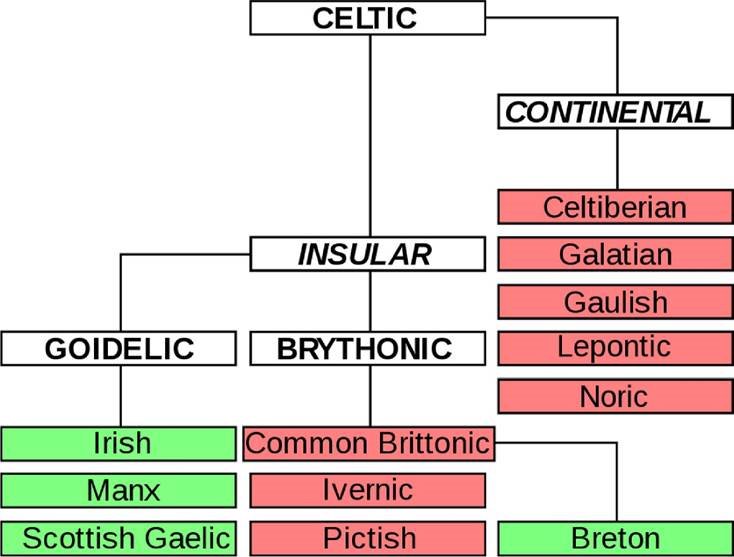
The Celtic People
 During the 1st millennium
During the 1st millennium
BC, Celtic languages were spoken across much of
Europe and central Anatolia, The inhabitants of Britain spoke the Celtic language, But most of the Celtic speakers were pushed west and north by the invaders mainly into what is now
Wales, Scotland and Ireland,
|
Celcic |
|
|
Today there are six living languages: the four continuously living languages Breton, Irish,
Scottish Gaelic and Welsh, and the two revived
(BiapoaxeHi) languages Cornish and Manx,
Cornish
Cumbric
Welsh
The Romans

Before the Romans arrived there was no written language in Britain. The Romans changed all that by teaching important Britons how to read and write and how to speak the Roman
language - Latin,
A few Latin words "stuck" with the Celtic locals, And even today, two thousand years later, a lot of our words come from Latin, like 'enormous' and 'victory' and 'lavatory',
We use prefixes like -pro and -sub in Modern English as the result,
Germanic Tribes
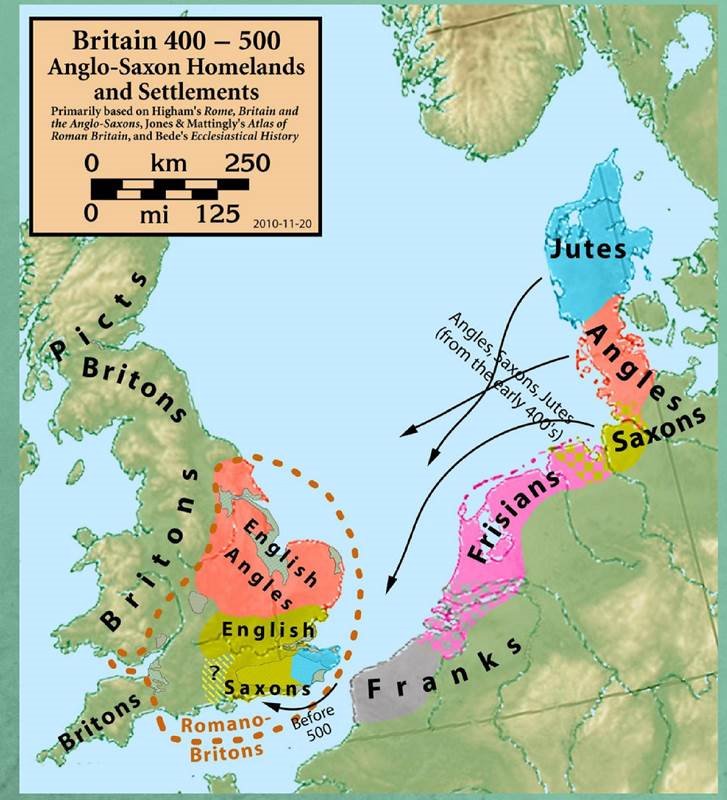 The history of the English language really started with the arrival of three
The history of the English language really started with the arrival of three
Germanic tribes who invaded
Britain during the 5th century AD, These tribes, the Angles, the Saxons and the Jutes, crossed the North Sea from what today is Denmark and northern Germany. The Angles came from "Englaland" and their language was called "Englisc" - from which the words "England" and "English" are ![]() derived (nOXOAfiTb).
derived (nOXOAfiTb).![]()
The invading Germanic tribes spoke similar languages, which in Britain developed into what we now call Old
English,
 Old English did not sound or look like English today. Native English speakers
Old English did not sound or look like English today. Native English speakers ![]() now would have great difficulty understanding Old English. Nevertheless, about half of the most commonly used words in
now would have great difficulty understanding Old English. Nevertheless, about half of the most commonly used words in
Modern English have Old English roots and determined many of the essential characteristics of the English language,
The words be, strong and water, for example, derive from Old English, Old English was spoken until around 1 1 00,

We can't but mention Vikings, The Viking Age, and their relationship with England, lasted from approximately 800 to 1 1 50 AD, Vikings invaded Britain, bringing with them another language called Old Norse.
From there, we get words like reindeer (niBHi l-lHYIV1 oneHb), dirt, choose, egg, Thursday that is Thor's Day (God's name)- it comes from the Old Norse,
About 1% of Modern English comes from Old Norse- it's about 2000 words,
 Beowulf, a poem written in Old
Beowulf, a poem written in Old
English
The Norman Conquest ![]()
In 1 066 William the Conqueror,

 modern France), invaded and conquered England, The new conquerors (called the
modern France), invaded and conquered England, The new conquerors (called the
Normans) brought with them a kind of French, and it started sneaking into the English language,
French became the language of the Royal Court, and the ruling and business classes. Old English was spoken by common people, people in the lower classes. There was a kind of linguistic class division, where the lower classes spoke English and the upper classes spoke French,
Today we have pairs of words which have almost the same meaning, One from Old English and one from
Old French:
Lawyer and attorney
Hunt and chase
Pig and pork
Cow and beef
Weird and strange  and liberty
and liberty
About 10000 English words that we use today are from French, basically the
Norman Conquest,
Questions
-What are the key events which determines the history of the English language?
-English is a Germanic language, What does it mean?
-What language did the local Britons speak before the Romans came?
-Did the Romans influence the local language?
-What were the language changes brought by the AngloSaxons?
-What are the words which came from the Old Norse (Vikings)?
-Do we still use the words brought by the Norman Conquest?


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку

