Урок "CLIL Biology Digestive system"
CLIL lesson plan for subject: Science (Biology)
Developer: Liudmyla Dotsenko
TOPIC: The Digestive System
GLOBAL GOAL: To understand the process of the digestive system
AGE OF STUDENTS: 14-15
LEVEL: B1/B1+
TIMING: 45 minutes
TEACHING OBJECTIVES (What I plan to teach):
Content
- The organs that are a part of the digestive system and the role they play
- The process of the digestive system
- Differentiate between healthy and unhealthy food.
Culture
- To identify their role within a group
- To understand why some people are more/less tolerant to certain types of food than others (tolerance/intolerance)
Cognition:
- Recognizing organs
- Making choices and justifying choices
- Identifying problems
Communication:
- Sharing ideas
- Suggesting solutions
- Stating biological facts
Language of learning
- Time connectives
- key vocabulary: digestion, organ, mouth, saliva, break something down, esophagus (food pipe), enzymes, stomach, acids, liver, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, absorb, swallow, bloodstream, bile, undigested, blood vessels.
LEARNING OUTCOMES (What learners will be able to do by the end of the lesson/s):
By the end of the unit, the learners will be able to:
- Explain the process of digestion
- Recall and name the important organs in the digestive system
- Understand and explain the role of each organ
Learning methods: work with texts, demonstration, visualization, talk, brainstorm.
Procedure steps:
- The teacher announces the topic (1 minute):” Digestion. Human digestive system”
- Introducing necessary vocabulary (2 minutes).
The teacher writes on the board the word DIGEST and students brainstorm (in groups of four) which other words can be derived from this word. (digestion, digestive, indigestion)
- Brainstorm activity in pairs (2 minutes):
Which internal organs take part in digestion? (mouth, teeth, gullet, stomach, small and large intestine, liver, pancreas.)
- Work with text (On Screen B1+ CC7)(10 minutes)
- Students are offered a worksheet (handout 1 from On Screen B1+ CC7) and fill in the missing words: stomach, pancreas, liver, small intestine, large intestine, oesophagus. Then students read out their answers. (Keys: 1. Oestophagus, 2. Liver, 3. Stomach, 4. Pancreas, 5. Small intestine, 6. Large intestine)
- Read the text and find answers to the following questions:
- In which order does food pass organs while being digested? (mouth, oestophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine)
- What does liver produce? (bile which breaks down fat)
- What’s the function of pancreas? (to produce digestive enzymes which break large molecules and small ones)
- Why do vitamins, minerals and water not need to be broken down? (because they are small enough to be absorbed).
- Read again and replace the words in bold in the sentences 1-8 with words from the text.
- Food is broken down into small ones.
- Food passes down it after going through the mouth.
- Food is broken down again in there.
- Digested food is absorbed into it from the small intestine.
- It is contained in undigested food.
- This breaks down fat.
- They are produced in the pancreas.
- They can be absorbed by the body as they are.
Keys: 1) molecules 2) oesophagus 3) stomach 4) bloodstream 5) fibre 6) bile 7) digestive enzymes 8) minerals, vitamins and water.
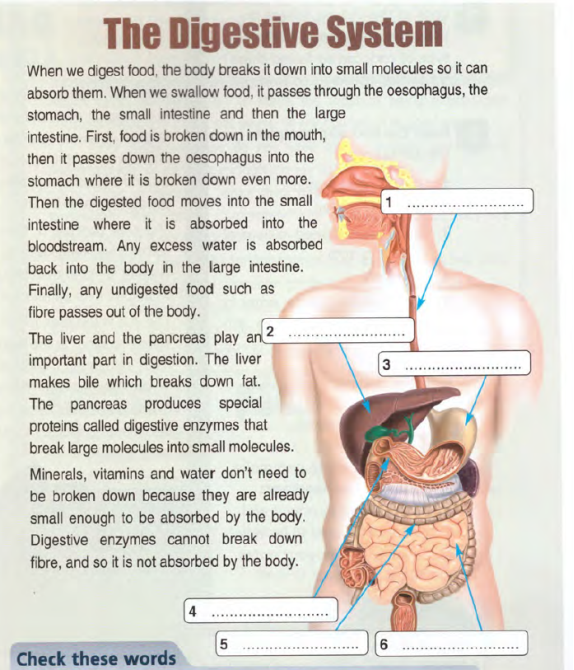
Handout 1.
- Work with video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bFczvJp0bpU (10 minutes)
- Well, one thing is to read about digestive system, but nothing compares with watching the process with your own eye. (students watch a video on digestive system.” Digestive system of human body”) While first watching write down all inside organs mentioned in the video (key: alimentary canal, mouth, anus, Buccal cavity, food pipe, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, saliva glands, villi, blood vessels)
- Students watch the video again and this time fill in the grid. (hand out 2)
|
Part of alimentary canal |
Juices secreted |
What happens there |
|
Mouth |
|
|
|
Stomach |
|
|
|
Small intestine |
|
|
|
Large intestine |
---------------- |
|
Hand out 2
Keys:
|
Part of alimentary canal |
Juices secreted |
What happens there |
|
Mouth |
saliva |
Food is chewed and mixed with saliva |
|
Stomach |
Mucous, digestive juices Hydrochloric acid |
Hydrochloric acid kills bacteria in food and makes food acidic |
|
Small intestine |
Bile juice Pancreatic juice |
Digested food is passed into blood vessels |
|
Large intestine |
------------------- |
Excess of water and salt are absorbed in the large intestine |
- Group work on digestive organs (10 minutes).
Divide class into subgroups of 8 with two or three students in each group depending on your class size. Distribute the Digestive System Index Cards with one organ listed on each card. Assign students to research the organ and outline 5 facts about each organ on the back using reliable internet sources such as Medline Plus.
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/
Students will present their findings to the class.
- Healthy and unhealthy eating habits (7):
Tell students to raise their hands if they know what "nutrients" are. Explain that nutrients are the things in food that are healthy for bodies and help them grow (Vitamins, minerals, protein).
"Healthy food is the best fuel for bodies because it is full of nutrients. Does anyone know any foods that probably have a lot of nutrients? Can anyone think of a type of food that might have almost no nutrients?" Provide examples if needed.
Tell your students that there are a few easy ways to determine whether food is healthy and full of nutrients or bad for you.
"Healthy foods with the most nutrients are natural, so they probably grew from a tree or out of the ground. We don't add much to healthy food or change it a lot because we want it to keep its nutrients." Explain the difference between unhealthy white bread and healthy whole grain bread.
"Unhealthy food has things added to it like sugar, salt, fat, and even preservatives. Preservatives are chemicals put into food to make it last a long time—do you think preservatives are nutritious? Can you think of any food that probably has a lot of preservatives? Unhealthy food is usually not natural or used to be natural until a bunch of stuff was added to it that made it lose its nutrients."
"Healthy foods give us the most energy and make us feel good. Unhealthy food usually makes us feel bad. It can make us tired, cranky, or sick because it doesn't give our body what it needs." Ask students what foods have ever made them feel bad.
Students get list of foods. The task is to divide the foods into two categories:
- Healthy for digestion:
- Unhealthy for digestion.
The list: Apples, grilled chicken, french fries, turkey sandwiches, cookies, chocolate, salad, yoghurt, china seeds, oranges, banana, whole grains, chewing gum, beans, spicy foods, lean meat, whole milk, ginger, unsalted nuts, coffee.
Keys:
|
Good for digestion |
Bad for digestion |
|
Apples Turkey sandwich Salad Yoghurt China seeds Banana Whole grains Lean meat Ginger Unsalted nuts
|
Grilled chicken French fries Cookies Chocolate Beans (contain hard-to-digest sugar and cause gas and stomach upset) Spicy foods (Some people get indigestion or heartburn after eating them, especially when it's a large meal) Whole milk (too fat and cause constipation) Oranges (acid can cause ulcer) Coffee (It can relax the muscle at the top of the stomach, which lets food move back into your esophagus. That can cause heartburn Chewing gum (contains artificial sugar) |
- Round up and feedback (2 minutes): students report on what new lexis that have learnt during the lesson, and what was new for them at the lesson.
- Home assignment (1 minute): using the picture from handout 1 explain how we digest food.


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
