Збірник на тему "У лікаря"
Даний матеріал є зібраним з різних англомовних джерел, обробленим, доповненим та зміненим згідно вимог навчальної програми для студентів-медиків. Може бути використаним також у спеціалізованих школах із поглибленим вивченням англійської мови.
Комунальний вищий навчальний заклад
«Нікопольський медичний коледж»
Дніпропетровської обласної ради»
Збірник матеріалів
для студентів медичних спеціальностей
до теми
A VISIT OF THE DOCTOR.
AT THE DOCTOR

Упорядник: викладач іноземної мови Сиротіна Ю.Г
- Booking a Doctor's Appointment
Patient
- I need to make an appointment.
- I need to see the doctor.
- When is the doctor free?
- I need to renew my prescription.
- Do you think the doctor could squeeze us in today?
- I need to make an appointment for my husband.
- My child needs to come in for a check-up.
- The doctor wants to see me again in two week's time.

Receptionist
- What is your chart number?
- What is the appointment regarding?
- Which day/what time is good for you?
- Is January the 3rd okay with you?
- How does four o'clock sound?
- We'll see you then.
- I'm sorry the doctor is not taking new patients.
- We'll call you if there are any cancellations.
- We're running an hour behind schedule.
- Dr Jones is away. You'll be seeing Dr Lindsay.
Sample Conversation
|
Receptionist: |
Doctor's office. Jane speaking. How can I help you? |
|
Caller: |
I need to make an appointment with Dr. Harris. |
|
Receptionist: |
Do you know your chart number? |
|
Caller: |
No, sorry. It's at home and I'm at work right now. |
|
Receptionist: |
No problem. What's your name, please? |
|
Caller: |
George Mason. |
|
Receptionist: |
Okay Mr Mason. Hold one moment while I grab your chart, please. |
|
Caller: |
Sure. |
|
Receptionist: |
Thanks for waiting. Now, what do you need to see the doctor about? |
|
Caller: |
Well, I've been fighting a cold for more than a week, and I think I might have a chest infection or something. My cough is getting worse each day. |
|
Receptionist: |
Hmm. Doctor Harris is off tomorrow. Do you think it can wait until Wednesday? |
|
Caller: |
Oh, I was really hoping to get in today or tomorrow in case I need some antibiotics. Maybe I'll have to go to the walk-in-clinic instead. |
|
Receptionist: |
Actually, we had a cancellation for 2:00pm today if you can get away from the office. |
|
Caller: |
Gee, it's almost 1:00pm already. I think I can make it if I leave right now. |
|
Receptionist: |
We're running a bit behind schedule, so you can probably count on seeing the doctor around 2:30. |
|
Caller: |
That's great. Thanks for fitting me in. |
|
Receptionist: |
No problem, Mr. Mason. We'll see you in an hour or so. |
Check your understanding
|
|
Why does the caller phone the doctor's office? |
|
|
|
|
Which is true about George Mason? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
2.Medical Supplies and Tools Here is a list of some of the most common supplies found in doctor's offices, operating rooms, and medical kits. Study the vocabulary and try the matching exercise.
Match the comments with the supplies that are needed:
Answers: 1c, 2a, 3d, 4h, 5i, 6f, 7j, 8g, 9b, 10e |
3.Medical Specialists
Medical specialists are experts in certain fields of medicine. They either treat specific parts of the body, such as the back or the brain, or they specialize in certain diseases, such as cancer. Family doctors keep a list of local specialists and can help patients choose the right specialist for each medical issue. In many cases specialists require a referral from a family doctor before they will see a patient. Here is a list of the most common types of specialists. Study the list and then check your understanding by taking the quiz.
|
allergist: |
specializes in determining food and environmental allergies |
|
anesthesiologist: |
specializes in pain prevention during surgery |
|
cardiologist: |
heart specialist |
|
chiropractor: |
back specialist |
|
dentist: |
tooth specialist |
|
dermatologist: |
skin specialist |
|
fertility specialist: |
helps people who have difficulty getting pregnant |
|
gynecologist: |
specializes in women's needs |
|
massage therapist: |
specializes in muscle relaxation |
|
midwife: |
helps women deliver babies in a natural way |
|
naturopath: |
specializes in natural cures and remedies |
|
neurologist: |
brain specialist |
|
obstetrician: |
specialist for pregnant women |
|
occupational therapist: |
specializes in workplace health |
|
oncologist: |
tumour specialist, including cancer |
|
ophthalmologist: |
specializes in eye diseases |
|
pediatrician: |
specialist for babies and children |
|
physical therapist: |
specializes in the body's movement |
|
podiatrist: |
foot specialist |
|
psychiatrist: |
specialist in mental health |
|
radiologist: |
specializes in imaging tests |
Read the patient complaints. Which specialist does each patient need?
|
1 |
I have a terrible rash on my arms and legs. I think I'm allergic to dairy food, but it also might be grass. |
|
|
2 |
My husband and I just took a home pregnancy test, and it came out positive. We want to know when we are due and we want to make sure the fetus is healthy. |
|
|
3 |
I still can't walk and it's been three months since my accident. I hate being stuck in a wheelchair. |
|
|
4 |
The test results show that I have an advanced form of blood cancer. |
|
|
5 |
My left eye has an infection that won't go away and my vision has been blurry for two weeks now. |
|
|
6 |
I don't want to take any drugs that will cause me to become addicted to them, but I do need some sort of pain relief. |
|
|
7 |
I've been having major chest pains this week. I'm also having trouble breathing. |
|
|
8 |
I get terrible acne and I have tried all of the products in the pharmacy. I don't know what to do now. |
|
|
9 |
My baby is not developing properly. She hasn't put on any weight in two months and she keeps getting ear infections. |
|
|
10 |
My husband and I have been trying to get pregnant for three years. We have tried everything that the books suggest. |
|


 4.Doctor's Diagnosis
4.Doctor's Diagnosis
Physician
- Your test results have come in.
- I'm afraid the prognosis isn't good.
- You have a long road to recovery.
- We have several options to discuss.
- The blood test came back negative.
- The transfusion was a success.
- It looks like you're ready to go home.
- I'd like to keep you here over night.
- We'll know more in a few days.
- You're not in the clear yet.
- We've ruled out diabetes.
- I'm hoping to get to the bottom of this soon.
Patient
- I don't understand what this means.
- Am I going to need surgery?
- Is it good news or bad?
- When will the tests results come in?
- How long do I have to stay in the hospital?
- What is the success rate?
- Are they going to run more tests?
- Is this a common problem for people my age?
- I'd like to discuss other options.
- I'm going to get a second opinion.
Sample Conversation
|
Doctor: |
Hi Jessica. How are you feeling today? |
|
Patient: |
A bit better. |
|
Doctor: |
That's good to hear. Are you still feeling nauseous? |
|
Patient: |
No, I haven't felt sick to my stomach since you switched my medication. |
|
Doctor: |
Great. Say, your test results came in this morning. |
|
Patient: |
It's about time. Is it good news or bad? |
|
Doctor: |
I guess it's a bit of both. Which do you want first? |
|
Patient: |
Let's get the bad news over with. |
|
Doctor: |
Okay. It looks like you're going to need surgery to remove the tumour from your leg. After the operation you're going to have to stay off your feet for at least three weeks. That means no soccer. |
|
Patient: |
I was afraid you were going to say that. |
|
Doctor: |
Now for the good news. The biopsy shows that the tumour is benign, which means it's not cancerous. We're going to take it out anyway just to be on the safe side. |
|
Patient: |
Wow, that's a load off my mind. Thanks Doctor. |
|
Doctor: |
Don't get too excited. We still need to get to the bottom of all of this weight loss. |
|
Patient: |
I've probably just been so worried about this stupid lump. |
|
Doctor: |
These things often are stress related, but we're still going to do a few blood tests just to rule a few things out. |
|
Patient: |
Things like what? Cancer? |
|
Doctor: |
Actually, I'm thinking more along the lines of a food allergy. |
Check your understanding
|
1. |
Why did the woman have to switch medication? |
|
|
2. |
What bad news does the doctor give the patient? |
|
|
3. |
What medical procedure did the patient already undergo? |
|
 5.Visiting Hours
5.Visiting Hours
Part of being a nurse, involves dealing with the people who are close to your patients. When a patient is staying in a hospital or other health facility, it is often necessary to welcome, monitor, and inform visitors on a daily basis. In many cases you may form stronger relationships with the patients' visitors than the patients themselves. Depending on the condition of the patient, certain loved ones will be allowed to visit, while others will not. It is a difficult time for people who have loved ones in the hospital. Showing them compassion and explaining the rules is much easier if you have the necessary English skills.
Study the different people that may come to visit the patient. Then read some typical concerns and questions that visitors may have, and some appropriate responses that you may be able to give them.
Immediate family
-
Mother and Father (patient's parents)
Husband or Wife (the man or woman the patient is married to)
Son and Daughter (children of the patient, boy and girl)
Brother and Sister/siblings (other children of the patient's parents)
Extended family
-
Grandmother and Grandfather (mother and father of patient's parents)
Aunt and Uncle (brother and sister of patient's parents)
Niece and Nephew (girl and boy child of patient's siblings)
Cousins (children of patient's aunt or uncle)
Friends and other loved ones
-
Best friend (patient's closest friend)
Room-mate (a person the patient lives with)
Neighbour (a friend who lives near the patient)
Co-worker (a person who works with the patient)
Boyfriend or Girlfriend (the man or woman the patient loves/dates)
Fiancé (the man or woman the patient is engaged to marry)
Questions and Concerns of Loved Ones
- We're Michael's grandparents.
- Could you tell me which room Mrs Smythe is in?
- Is my child going to be okay?
- When can we speak with the doctor?
- What time are visiting hours?
- I'm trying to locate my sister. (I'm trying to find my sister's room.)
- Is there anything you can do to make him more comfortable.
- My child would like something to drink.
- Is there somewhere I can lie down for a while.
- Could you tell me where the chapel is?
- Please tell her to get well soon.
Questions and Responses from Nurses
- What is your relation to Jessica?
- You'll have to come back during visiting hours.
- Ms Lee is too tired for visitors.
- Room 7 is down the hall to your right.
- I'll give you two some privacy now.
- Does your daughter need anything?
- I'm afraid she's not having a very good day today.
- We do the best we can around here.
- There's a quiet room for families down the hall.
- The doctor would like to have a word with you. (The doctor wants to speak to you.)
- She's doing much better this morning.
- He's in isolation because of the transplant.
- We had to transfer your mother-in-law to the ICU.
- It's in your brother's best interest.
Sample Conversation
|
Nurse: |
I'm afraid visiting hours are over, sir |
|
Visitor: |
My wife's in room 3B. |
|
Nurse: |
Sorry, you'll have to come back in the morning. |
|
Visitor: |
And leave her all alone overnight? |
|
Nurse: |
I'm afraid that's the policy, sir. |
|
Visitor: |
Surely you can make an exception? What if she needs me in the night? |
|
Nurse: |
Don't worry, we'll look after her. What she really needs is her rest. |
|
Visitor: |
Some of her friends want to see her too. When can they come? |
|
Nurse: |
Visiting hours are from 9 to 11 in the morning and 4 to 7 in the evening, but I'm afraid while your wife is on bedrest the doctor has requested that only immediate family members come in to see her. |
|
Visitor: |
Can't her friends even stop by to bring her flowers? |
|
Nurse: |
Flowers are not permitted in this ward. We just can't risk any germs that might come in with them. |
|
Visitor: |
Well, I guess it's all in her best interest. |
|
Nurse: |
Thanks for understanding. Now, I'm going to bring your wife her dinner. Why don't you head home and get something to eat yourself? |
|
Visitor: |
Okay. I really hate to leave her, but that's probably a good idea. |
|
Nurse: |
She's in good hands here. I'll tell her you were here and that you'll see her in the morning. |
Check your understanding
|
1. |
What is the man's relation to the patient? |
|
|
2. |
Why does the nurse send the man away? |
|
|
3. |
The nurse thanks the man because... |
|
6.A Physical Examination
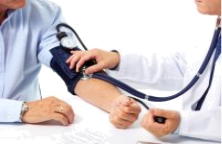 Doctor: When did you last come in for a physical exam?
Doctor: When did you last come in for a physical exam?
Patient: I had my last physical two years ago.
Doctor: Have you had any other exams recently?
Blood work, an EKG or an ultra-sound?
Patient: Well, I had a few X-rays at the dentist's.
Doctor: How have you been feeling in general?
Patient: Pretty well. No complaints, really.
Doctor: Could you roll up your left sleeve? I'd like to take your blood pressure.
Patient: Certainly.
Doctor: 120 over 80. That's fine. You don't seem to be overweight, that's good. Do you exercise regularly?
Patient: No, not really. If I run up a flight of stairs, it takes me a while to get my breath back. I need to get out more.
Doctor: That would be a good idea. How about your diet?
Patient: I think I eat a pretty balanced diet. You know, I'll have a hamburger from time to time, but generally I have well-balanced meals.
Doctor: That's good. Now, I'm going to listen to your heart.
Patient: Ooh, that's cold!
Doctor: Don't worry it's just my stethoscope. Now, breathe in and hold your breath. Please pull up your shirt, and breathe deeply... Everything sounds good. Let's take a look at your throat. Please open wide and say 'ah'.
Patient: 'ah'
Doctor: OK. Everything looks ship shape. I'm going to order some blood work and that's about it. Take this slip to the front desk and they'll arrange an appointment for the tests.
Patient: Thank you doctor. Have a nice day.
Key Vocabulary
physical examination (exam) to pull on one's shirt to exercise regularly
balanced diet well-balanced meals stethoscope
to breath in to hold one's breath to breathe deeply
to open wide to look ship shape slip
front desk to arrange an appointment blood work
EKG ultra-sound x-rays
to roll up sleeves overweight - underweight
7.Joint Pain
Patient: Good morning. Doctor Smith?
Doctor: Yes, please come in.
Patient: Thank you. My name is Doug Smith.
Doctor: What have you come in for today Mr Anders?
Patient: I've been having some pain in my joints, especially the knees.
Doctor: How long have you been having the pain?
Patient: I'd say it started three or four months ago. It's been getting worse recently.
Doctor: Are you having any other problems like weakness, fatigue or headaches?
Patient: Well I've certainly felt under the weather.
Doctor: Right. How much physical activity do you get? Do you play any sports?
Patient: Some. I like to play tennis about once a week. I take my dog on a walk every morning.
Doctor: OK. Let's have a look. Can you point to the area where you are having pain?
Key Vocabulary
- joint pain
- knees
- weakness
- fatigue
- headache
- to feel under the weather
- physical activity
- to play sports
- to have pain
8.Prescription Abbreviations
Understanding What Your Doctor Writes on a Prescription

Prescription abbreviations are directions for your pharmacist.
Doctors use prescription abbreviations (based on Latin words) that tell your pharmacist which medication to give you and directions on how to use that medication.
If you learn to understand the medical shorthand used by your doctor, you can read your own prescription immediately after it is written. This will help make sure that you know what medication you are getting and it will give you a chance to ask questions about your doctor's instructions.
Understanding Your Prescription May Help Prevent a Medical Error
The more you understand about your prescription, the less likely it is that you will have a medical error. For example, your pharmacist may make a mistake reading your doctor's handwriting. If your doctor's writing is not clear and easily read, your prescription may take longer to fill or you may be given the wrong dose or the wrong directions.
As a smart medical consumer, it is a good idea to check your prescription and make sure that it is filled correctly at the pharmacy. If you think there is an error or a discrepancy, you can alert the pharmacist or call your doctor.
Some doctor's offices now use electronic prescribing. You may receive a printed prescription to take to the pharmacy, or your prescription may be faxed or e-mailed to the pharmacy. Ask to see a printout of these prescriptions before leaving your doctor's office.
If you do not understand what your prescription says, do not be shy. Ask your doctor or another healthcare provider in the office for assistance. Your questions may help detect and prevent an error.
A Dr. Mike Quick Tip: Ask your doctor to write down on the prescription for what condition your medication is being used; e.g., not just "take once a day" but "take once a day for high cholesterol."
Generic vs. Brand Name
When writing a prescription, your doctor may use either the "generic" name of the medication or the "brand name". For example, sertraline is the "generic" name and Zoloft is the "brand name" used to identify a medication frequently prescribed for the treatment of depression.
In many states, pharmacists are allowed to dispense a generic medication, even if your doctor writes a prescription for the brand name version of the drug. However, if your doctor writes "DAW" (which means "dispense as written") or initials a box labeled "DAW" on your prescription, the pharmacist cannot legally substitute a generic medication for the brand name one.
Reading Your Prescription
Your prescription is usually written on a pre-printed pad with your doctor's name, address, and phone number. You may also see, either on the top or bottom of the prescription, special identification numbers, such as your doctor's Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) number for narcotics or controlled substances.
Of course, there is space for your name and address, your age, the date, a place for your doctor's signature, and a blank area in which your doctor writes the following directions:
- Name of the medication
- Dose of the medication
- How often to take the medication
- When to take the medication
- How to take the medication
Additionally, your doctor will indicate how much medicine the pharmacist should give you and the number of times that your prescription can be refilled.
Commonly Used Medical Abbreviations
Your doctor may use different abbreviations or symbols. If you do not understand them, ask your doctor or pharmacist for clarification.
How Often to Take Your Medication
ad lib - freely, as needed
bid - twice a day
prn - as needed
q - every
q3h - every 3 hours
q4h - every 4 hours
qd - every day
qid - four times a day
qod - every other day
tid - three times a day
When to Take Your Medication
ac - before meals
hs - at bedtime
int - between meals
pc - after meals
How Much Medication to Take
caps - capsule
gtt - drops
i, ii, iii, or iiii - the number of doses (1, 2, 3, or 4)
mg - milligrams
ml - milliliters
ss - one half
tabs - tablets
tbsp - tablespoon (15ml)
tsp - teaspoon (5ml)
How to Use Your Medication
ad - right ear
al - left ear
c or o - with
od - right eye
os - left eye
ou - both eyes
po - by mouth
s or ø - without
sl - sublingual
top - apply topically
Often the abbreviation "sig" will appear just before the directions on the prescription. "Sig" is short for the Latin, signetur, or "let it be labeled."
How to Read Your Doctor's Prescription - Some Examples
Example #1: Your diagnosis is high cholesterol
Zocor 10 mg.
This is the name of the medication and the dose.
Sig: i po qhs
Your instructions are to take 1 pill, by mouth, at bedtime.
Dispense #90
You will be given 90 pills, enough for about 3 months.
Refill 0 times
Your doctor has indicated no refills, most likely because she would like to check your blood cholesterol and then decide if you need more medication or a different dose.
DAW left blank
Your pharmacist will most likely give you simvastatin, the generic version of Zocor.
Example #2: Your diagnosis is type 2 diabetes
Glucophage 500 mg.
This is the name of the medication and the dose.
Sig: i po bid pc
Your instructions are to take 1 pill, by mouth, twice each day, after meals - this means that you should take this medication right after breakfast and right after dinner.
Dispense #90
You will be given 90 pills, enough for about 3 months.
Refill 3 times
Your doctor has indicated 3 refills, enough medication for one year. This may mean that your diabetes is "stable" and well controlled on this medication.
DAW left blank
Your pharmacist will most likely give you metformin, the generic version of Glucophage.
Example #3: Your diagnosis is high blood pressure
Diovan 40 mg.
This is the name of the medication and the dose.
Sig: i po qd
Your instructions are to take 1 pill, by mouth, once each day - you most likely can take this medication either before or after a meal since your doctor did not say otherwise.
Dispense #90
You will be given 90 pills, enough for about 3 months.
Refill 0 times
Your doctor has indicated no refills, most likely because she would like to check your blood pressure and then decide if you need more medication or a different dose.
DAW left blank
Your pharmacist will give you Diovan since there is no generic available for this drug. 
9.The Most Prescribed Medications by Drug Class
Almost 4 billion prescriptions for medications were written in the United States in 2010, an all-time high. Major studies that analyzed the financial impacts of increased therapeutic drug use on treatment outcomes and spending have come to different conclusions. However, it is known that many diseases can be prevented, treated effectively or cured through prescription medications.
"In some cases, the use of prescription medicines keeps people from needing other expensive health care such as being hospitalized or having surgery," notes the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Nine-out-of-10 senior citizens in the United States and more than half (58 percent) of all non-seniors regularly rely on a prescribed drug, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
All classes of drugs have seen an increase in prescriptions filled over the last 5 years except diuretics, penicillins, and hormonal contraceptives, according to the IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics. IMS's analysis included all prescription medications dispensed through retail pharmacies, food store pharmacies, mail orders and long-term care facilities.
Generics Surpass Branded Drug Scripts
Generic drugs represented 75 percent of all filled prescriptions in 2010, up from 57 percent in 2004, according to IMS. While the number of generic prescriptions dispensed increased 5.9 percent; branded prescriptions declined by 7.6 percent.
The Most Prescribed Medications by Class
1. Lipid Regulators
Lipid regulators, mainly statin drugs, are used to prevent dyslipidemia (high blood cholesterol) and other cardiovascular problems and have been prescribed for the prevention and treatment of many other illnesses including osteoporosis and post-menopause complications. More than 255.4 million prescriptions for statins and other lipid lowering drugs were filled in 2010.
Pfizer's Lipitor (atorvastatin calcium) was the highest selling branded statin, followed by Crestor (rosuvastatin calcium) by AstraZeneca, Other branded statins included Mevacor (lovastatin), Pravachol (pravastatin sodium), Zocor (simvastatin), Lescol (fluvastatin sodium), Vytorin (Ezetimibe/Simvastatin), and Pitavastatin.
Awareness campaigns directed at physicians and directly to consumers have contributed to the growth in this class of drugs.
Antidepressants are one of the fastest growing classes of prescribed drugs. In 2010, more than 253.6 million prescriptions were filled for antidepressants, according to the IMS report./
One of the main factors driving the increase in scripts for antidepressants is that a growing number of primary care providers and others practicing outside the field of psychiatry are writing the prescriptions for patients who have not received a clinical psychiatric diagnosis, according to a study published in Health Affairs journal in August 2011.
"Our analysis found that between 1996 and 2007, the proportion of visits at which antidepressants were prescribed but no psychiatric diagnoses were noted increased from 59.5 percent to 72.7 percent," wrote co-authors Ramin Mojtabai, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, and Mark Olfson, with the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Columbia University n New York, and a research psychiatrist at New York State Psychiatric Institute.
3. Narcotic Analgesics
Narcotic analgesics are prescribed for the relief of severe pain. In 2010, more than 244,300 prescriptions were filled for these types of pain killers.
Some leading narcotic analgesics include Oxycodone (oxycodone), Vicodin (hydrocodone and acetaminophen), codeine, morphine, Percocet (acetaminophen and oxycodone), and Ultram (tramadol).
4. Beta Blockers
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents or beta blockers (plain and in combination with other drugs, are prescribed for the treatment of heart disease, particularly high blood pressure, as well as glaucoma, hyperthyroidism and migraines. More than 191.5 million prescriptions for beta blockers were filled in 2010.
Commonly prescribed beta blockers include Brevibloc (esmolol), Coreg (carvedilol), Inderal (propranolol), Lopressor, Toprol-XL (metoprolol), Normodyne, Trandate (labetalol), Sectral (acebutolol), Tenormin (atenolol) and Zebeta (bisoprolol)./
5. Ace Inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are used in the treatment of high blood pressure, scleroderma, migraines and other conditions. In 2010, pharmacies dispensed more than 168.7 million prescriptions for ACE inhibitors.
ACE inhibitors include Lotensin (benazepril), Capoten (captopril), Vasotec (enalapril), Fosinopril, Prinivil, Zestril (Lisinopril), Univasc (Moexipril), Aceon (perindopril), Accupril (quinapril), Altace (ramipril) and Mavik (trandolapril).
Other top-ranking classes of drugs by millions of prescriptions filled are:
6. Antidiabetes; 165
7. Respiratory Agents; 153.3
8. Anti-Ulcerants; 147.1
9. Diuretics; 131
10. Anti-Epileptics; 121.7
11. Tranquilizers; 108.6
12. Thyroid Preps; 107.2
13. Calcium Antagonists (Plain & Combo); 97.9
14. Antirheumatics; 95
15. Hormonal Contraceptives; 92.3
16. Angiotensin II; 83.7
17. Penicillins; 76.1
18. Macrolides & Similar Type; 73.9
19. Vitamins & Minerals; 71.9
20. Hypnotics & Sedatives; 66
Vocabulary
|
Word |
Meaning |
Example sentence |
|
abnormal |
not normal for the human body |
This amount of weight loss is abnormal for women your age. |
|
ache |
pain that won't go away |
I can't sleep because my knees ache in the night. |
|
acute |
quick to become severe/bad |
We knew the baby was coming right away because the woman's labour pains were acute. |
|
allergy noun |
a body's abnormal reaction to certain foods or environmental substances (eg causes a rash) |
Your son is extremely allergic to peanuts. |
|
ambulance |
emergency vehicle that rushes people to a hospital |
We called the ambulance when Josh stopped breathing. |
|
amnesia |
a condition that causes people to lose their memory |
I can't remember the accident because I had amnesia. |
|
amputation noun |
permanent removal of a limb |
We had to amputate his leg because the infection spread so quickly. |
|
anaemia noun |
occurs when the body doesn't have enough red blood cells |
I have low energy because I am anaemic. |
|
antibiotics |
medication that kills bacteria and cures infections |
My throat infection went away after I started the antibiotics. |
|
anti-depressant |
medication that helps relieve anxiety and sadness |
The anti-depressants helped me get on with life after Lucy died. |
|
appointment |
a scheduled meeting with a medical professional |
I've made you an appointment with a specialist in three week's time. |
|
arthritis |
a disease that causes the joints to become swollen and crippled |
My grandmother can't knit anymore because the arthritis in her hands is so bad. |
|
asthma (attack) |
a condition that causes a blockage of the airway and makes it difficult for a person to breathe |
I carry an inhaler when I run because I have asthma. |
|
bacteria |
a disease-causing organism |
To prevent the spread of bacteria it is important that nurses wash their hands often. |
|
bedsore |
wounds that develop on a patient's body from lying in one place for too long |
If you don't get up and take a walk, you will develop painful bedsores. |
|
benign |
not harmful (not cancerous) |
We're hoping that the tests will show that the lump in your breast is benign. |
|
biopsy |
removal of human tissue in order to conduct certain medical tests |
The biopsy ruled out a number of illnesses. |
|
blood count |
the amount of red and white blood cells a person has |
You will be happy to know that your blood count is almost back to normal. |
|
blood donor |
a person who gives blood to a blood bank or other person |
Blood donors have to answer questions about their medical history. |
|
blood pressure |
the rate at which blood flows through the body (high/low) |
High blood pressure puts you at risk of having a heart attack. |
|
brace |
a device that holds injured body parts in place |
You will probably always have to wear a brace on your ankle when you jog. |
|
breech |
position of an unborn baby in which the feet are down and the head is up |
We thought it was going to be a breech birth, but the baby turned himself around. |
|
broken |
a bone that is divided in two or more pieces as a result of an injury |
We thought it was just a sprain, but it turned out his leg was broken. |
|
bruise noun |
injured body tissue that is visible underneath the skin |
The woman was badly bruised when she came into the emergency room. |
|
Caesarean section, C-section |
procedure that involves removing a baby from its mother through an incision in the woman's lower abdomen |
The baby was so large that we had to perform a Caesarean section. |
|
cancer |
disease caused by the uncontrollable growth of cells |
There are many different options when it comes to treating cancer. |
|
cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) |
restoring a person's breath and circulation |
You saved your brother's life by performing CPR. |
|
cast |
a hard bandage that is wrapped around a broken bone to keep it in place |
My leg was in a cast for graduation. |
|
chapel, chapeline |
a place where loved ones can go to pray for a patient's recovery; |
If you want a place to pray, the chapel is on the third floor. |
|
chemotherapy |
type of treatment used on cancer patients |
My mother has already had three rounds of chemotherapy. |
|
chickenpox |
a virus commonly contracted by children, characterized by itchy spots all over the body |
It is best to get chickenpox as a child so that you don't get it worse as an adult. |
|
coroner |
a person who determines the cause of death after a person dies |
We only call the coroner if we think a death is suspicious. |
|
critical condition |
requiring immediate and constant medical attention |
You can't see her right now; she's in critical condition. |
|
crutches |
objects that people with injured legs or feet use to help them walk |
I'd rather hop on one foot than use crutches. |
|
cyst |
a sac in the body-tissue filled with fluid (sometimes diseased) |
We're going to remove the cysts just to be on the safe side. |
|
deaf |
unable to hear |
The accident left the patient both deaf and blind. |
|
deficiency |
a lack of something necessary for one's health |
The tests show that you have an iron deficiency. |
|
dehydrated |
in need of water |
It is easy for the elderly to become dehydrated in this heat. |
|
dementia |
loss of mental capacity |
It is hard to watch a loved one suffering with dementia. |
|
diabetes |
type of disease typically involving insulin deficiency |
People with diabetes have to constantly check their blood sugar levels. |
|
diagnosis |
medical explanation of an illness or condition |
The doctor would prefer to share the diagnosis with the patient himself. |
|
discomfort |
experiencing pain |
This pain medication should relieve some of your discomfort. |
|
disease |
a medical disorder that is harmful to a person's health |
I understand that this disease runs in your family. |
|
dislocated |
when a bone is temporarily separated from its joint |
You will have to wear a sling because of your dislocated shoulder. |
|
emergency |
a medical problem that needs immediate attention |
It is important that children know which number to dial in case of an emergency. |
|
ER (emergency room) |
the hospital room used for treating patients with immediate and life-threatening injuries |
The child was rushed into the ER after he had a severe allergic reaction to a bee sting. |
|
external |
on the outside |
This cream is for external use only. Do not get it near your ears, eyes, or mouth. |
|
false negative |
a test that incorrectly comes back negative |
We had two false negative pregnancy tests, so we didn't know we were having a baby. |
|
family history |
medical background of a person's family members |
The doctor was concerned about my family history of skin cancer. |
|
fatal |
causing death |
The doctor made a fatal error when he wrote the wrong prescription. |
|
fever noun |
higher than normal body temperature |
He is very feverish, and his temperature is near danger point. |
|
flu (influenza) |
many types of respiratory or intestinal infections passed on through a virus |
People who have the flu should not visit hospital patients. |
|
fracture noun |
broken or cracked bone |
Your wrist is fractured and needs a cast. |
|
germ |
a micro-organism, especially one that causes disease |
Flowers are not allowed in the ward to avoid the risk of germs being brought in. |
|
genetic |
a medical condition or physical feature that is passed on in the family |
The disease is part genetic and part environmental. |
|
growth |
a ball of tissue that grows bigger than normal, either on or under the skin |
That growth on your shoulder is starting to worry me. |
|
heart attack |
instance in which blood stops pumping through the heart |
People who smoke are at greater risk of having a heart attack. |
|
HIV |
the virus that infects the human T-cells and leads to AIDS |
HIV can be passed down from the mother to her fetus. |
|
hives |
bumps that appear on the surface of the skin during an allergic reaction |
I broke out in hives after I ate that potato casserole. |
|
illness noun |
general term for any condition that makes a person feel sick for a certain period of time |
Her illness went away when she started eating better. |
|
immune system |
the parts of the body that fight diseases, infections, and viruses |
You can't have visitors because your immune system is low. |
|
immunization noun |
an injection that protects against a specific disease |
Babies are immunized three times in their first year. |
|
incision |
cut in the body made during surgery |
I had to have stitches to close the incision. |
|
inconclusive |
Unclear |
We have to do more x-rays because the first ones were inconclusive. |
|
infant |
young baby |
The nurse will demonstrate how to bathe an infant. |
|
infection noun |
diseased area of the body (viral or bacterial) |
The wound should be covered when you swim to prevent it from becoming infected. |
|
inflamed |
appearance (red and swollen) of an injured body part |
My right ankle was so inflamed it was twice the size of my left one. |
|
injury |
damage to the body |
Her injuries were minor; just a few cuts and bruises. |
|
intensive care unit (ICU) |
section of the hospital where patients get constant attention and doctors rely on specialized equipment |
She will remain in the ICU until she can breathe on her own. |
|
internal |
under the skin, inside the organs |
The doctors will be monitoring her for any internal bleeding. |
|
itchy |
feeling discomfort on the skin's surface |
If you are allergic to this medication your skin will get red and itchy. |
|
IV |
a tube that pumps liquids and medication into a patient's body |
The toddler was so dehydrated that the doctor decided to get him on an IV. |
|
lab results |
tests that come back from a laboratory and help doctors make a diagnosis |
The lab results have come in and you are free to go home. |
|
lab (laboratory) |
place where samples of blood/urine etc. are taken for testing |
I'll take these samples down to the lab on my way out. |
|
life support |
a machine that keeps patients alive by helping them breathe |
The woman has severe brain damage and is currently on life support. |
|
life-threatening |
when injuries and conditions are extremely serious |
The victim was shot in two places but the bullet wounds are not life-threatening. |
|
light-headed |
feeling of dizziness and being off-balance, caused by lack of oxygen in the brain |
If you are feeling light-headed again, lie down and call me. |
|
malignant |
expected to grow and get much worse (especially related to cancerous cells) |
I'm afraid at least one of the tumours is malignant. |
|
medical school (med. school) |
place where someone trains to be a doctor |
After eight years of medical school I can finally practice medicine. |
|
newborn |
an infant that is less than three months old |
You have to support her neck because she is still a newborn. |
|
numb |
no feeling in a certain body part |
The needle will make your lower body feel numb. |
|
OR (operating room) |
the place where major surgeries and operations take place |
You must wear a face mask and gloves while you are in the OR. |
|
operation noun |
a medical procedure that involves going inside a person's body in an attempt to fix a problem |
The operation lasted seven hours, but it was successful. |
|
pain |
strong discomfort in certain areas of the body |
We gave your husband some medicine to relieve some of the pain. |
|
pain killer, pain reliever |
type of medicine that takes away some or all of the discomfort of an illness or injury |
You can take two pain killers every four hours. |
|
paralyzed |
unable to move certain areas of the body |
We thought her legs were paralyzed for life, but she is learning how to walk. |
|
patient |
a person staying in a hospital or medical facility |
The patients in Room 4 are not getting along. |
|
pharmacist |
a person who fills a doctor's prescription and gives people advice about medication |
Ask the pharmacist if there is a generic brand of this medication. |
|
pharmacy, drugstore |
a place where people go to buy medication and other medical supplies |
You should be able to buy a bandage at the pharmacy. |
|
physician |
Doctor |
Ask your family physician to refer you to a specialist. |
|
poison noun |
a substance that is very dangerous if it enters the human body |
The child was bitten by a poisonous snake. |
|
prenatal |
of the time period leading up to giving birth |
The woman was well prepared for labour because she took the prenatal classes. |
|
prescription noun |
the correct amount and type of medication needed to cure an illness or relieve symptoms |
You will need to visit your doctor to get another prescription. |
|
privacy noun |
being alone; personal (eg test results) |
You will have to pay for a private hospital room if you don't want a room-mate. |
|
radiation |
high energy X-rays that destroy cancer cells |
If the radiation doesn't kill all of the abnormal cells, the cancer will come back. |
|
residency |
part of a doctor's training that takes place in the hospital; |
John is a resident under Dr Brown. |
|
routine check-up |
a doctor's appointment to check a person's general health |
I'd like to see you a year from now for a routine check-up. |
|
scrubs |
plain uniform (usually green, white, or blue) worn by medical professionals |
I have some extra scrubs in my locker. |
|
scrub up |
carefully wash hands before and after seeing a patient |
I have to scrub up and get ready for surgery. |
|
second opinion |
input from a second doctor about an illness or symptom |
I went to another doctor to get a second opinion about these headaches. |
|
seizure |
sudden violent movements or unconsciousness caused by electrical signal malfunction in the brain |
People who suffer from epilepsy are prone to seizures. |
|
shock |
body not getting enough blood flow |
The woman was in shock after being pulled from the river. |
|
side effects |
other symptoms that might occur as a result of a certain medication or procedure |
One of the side effects of antidepressants is a loss of appetite. |
|
sore |
Painful |
I have a sore throat and a runny nose. |
|
spasm |
the uncontrollable tightening of a muscle |
Ever since I injured my leg I've been having muscle spasms in my upper thigh. |
|
specialist |
a doctor that is an expert in a certain kind of medicine |
My family doctor is sending me to a specialist. |
|
sprain |
an injury (less serious than a break) to a joint (ankle, wrist, knee etc) |
I sprained my knee playing soccer. |
|
stable condition |
a patient is stable if their medical condition is no longer changing rapidly |
You can see your husband now; he is in a stable condition. |
|
sting |
sharp, temporary pain |
It may sting when I insert the needle. |
|
stress noun |
worry that causes muscles to tighten and blood pressure to rise |
You need to take some time off work and relieve some of your stress. |
|
swelling noun |
ligaments (parts that hold the joints together) growing bigger and rounder after an injury to a joint |
I knew my ankle was sprained because it was so swollen. |
|
symptoms |
pain or physical changes that occur because of an illness or disease |
You have all of the symptoms of a diabetic. |
|
temperature |
amount of heat measured in a body; higher than normal temperature |
We brought Jesse to emergency because he was running a (high) temperature. |
|
tender |
painful when touched or used |
The incision was tender after the surgery. |
|
test results |
medical information that helps doctors understand a patient's condition or body |
The test results came back negative. You aren't pregnant. |
|
therapy |
treatment aimed at improving a person's mental or physical condition |
I was able to go back to work a few weeks after starting the therapy. |
|
transplant |
moving of an organ from one human to another |
The heart transplant saved your life. |
|
ultrasound |
a test that examines the body's internal organs and processes using sound waves (often used during pregnancies) |
The ultrasound shows that we are expecting a baby boy. |
|
umbilical cord |
the lifeline from the mother to the fetus (when cut at birth this forms the belly button) |
I had an emergency C-section because the umbilical cord was wrapped around the baby's neck. |
|
unconscious |
alive, but appearing to be asleep and unaware of the surroundings |
I hit my head on the steering wheel and was still unconscious when the ambulance arrived. |
|
urine sample |
a small amount of the body's liquid waste that is tested for different medical reasons |
The urine sample tells us how much alcohol is in your blood. |
|
vein |
the thin tubes that transport blood around the body and back to the heart |
I'm just looking for the best vein in which to insert the needle. |
|
virus |
a dangerous organism that causes the spread of minor and major diseases |
The virus is contractable through the exchange of bodily fluids. |
|
visiting hours |
time of day when friends and family are allowed to visit patients in hospital |
I'm afraid you'll have to come back during visiting hours. |
|
vomit |
discharge of a person stomach contents through the mouth |
The pregnant woman can't stop vomiting. |
|
ward |
a section of a hospital or health facility where patients stay |
I should warn you that we're entering the mental health ward. |
|
wheelchair |
a chair on wheels used for transporting patients from place to place |
If you get in the wheelchair I'll take you down to see the garden. |
|
wound noun |
injury to body ("flesh wound" means not deep) |
The wounded soldiers are being airlifted to the hospital. |
|
x-ray |
a photograph of a person's bones and organs |
The technician took x-rays of my shoulder to make sure it wasn't broken. |
CONTENT
1.Booking a Doctor's Appointment
2.Medical Supplies and Tools
3.Medical Specialists
4.Doctor's Diagnosis
5.Visiting Hours
6.A Physical Examination
7.Joint Pain
8.Prescription Abbreviations
9.The Most Prescribed Medications by Drug Class
Vocabulary
A compiled training book (supplemented and changed) is offered for medical students at a higher medical school. It will be useful for teachers of English and all those wishing to learn English on their own.
Considered and approved at the meeting of the cyclic commission.
Reviewer: Chornovil Iryna, Teacher of English
![]()


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку


