Методична розробка "Англійська мова крізь призму технічної творчості"
ДЕПАРТАМЕНТ ОСВІТИ І НАУКИ ЗАПОРІЗЬКОЇ МІСЬКОЇ РАДИ
Позашкільний навчальний заклад
«СТАНЦІЯ ЮНИХ ТЕХНІКІВ»
Запорізької міської ради Запорізької області
«Англійська мова крізь призму
технічної творчості»
підготувала:
керівник гуртка «Англійська мова
в технічному світі»
Кобріна Катерина
Володимирівна
Запоріжжя, 2019
Вимоги часу й розпочата радикальна реформа системи освіти в Україні, відмова від авторитарного стилю навчання на користь особистісно орієнтованого підходу, на застосування методів, які сприяють розвитку творчих здібностей особистості з урахуванням індивідуальних особливостей учасників навчального процесу й спілкування, актуалізує проблему пошуку інноваційних підходів до вивчення іноземних мов.
Актуальність вибору теми зумовлена необхідністю пошуків нових оцінок та підходів у позашкільній освіті. Одним із таких підходів, що суттєво збагачує навчальний процес позашкільної освіти, є метод навчальних проектів, використання якого змінює традиційний підхід до навчання вихованців.
Метод проектів - це система навчання, за якої вихованці здобувають знання і уміння в процесі планування і виконання конкретних завдань, що поступово ускладнюються; це комплекс пошукових, дослідницьких, графічних та інших видів робіт, виконаних з метою практичного або теоретичного розв’язання важливої проблеми, дозволяє реально інтегрувати різні навчальні предмети.
Проект - (від лат. - кинутий вперед) - це задум, план, прообраз передбачуваного або можливого об’єкта, сукупність документів і розрахунків, необхідних для його створення. Проект - це результативна дія.
Новизна досвіду полягає у використані проектної технології як метод активізації пізнавальної діяльності вихованців. Сьогодення вимагає від сучасної освіченої людини і вихованця зокрема, не лише загальних знань з англійської мови. А насамперед, зросла потреба у фахівцях, які володіють певною технічною термінологією і вміють легко розібратися у технічній документації: інструкціях, рекомендаціях до експлуатування приладів, кресленнях тощо, які написані англійською мовою.
Все це вимагає суттєвого реформування у підході до викладання англійської мови.
Провідна ідея досвіду полягає у впровадженні в діяльність гуртка, «Англійська мова в технічному світі», проектних технологій, інноваційного метода в навчально-виховній діяльності, з метою самостійно конструювати свої знання й орієнтуватися в інформаційному просторі, розкриття в кожному вихованці потенційно закладених можливостей, що відповідають індивідуальним здібностям та потребам гуртківців.
Технологія досвіду
Значне місце у програмі гуртка відводиться проектним технологіям, які потребують поетапну підготовку, орієнтуючи вихованців на досягнення конкретних результатів. Гуртківці розробляють творчі проекти: ведуть Мовне Портфоліо, створюють презентації, повідомлення, колажі, аплікації, малюють, конструюють та моделюють різні поробки.
Проектна технологія як метод активізації пізнавальної діяльностью вихованців орієнтована на самостійну роботу – індивідуальну, групову, парну – яку діти виконують протягом певного часу. Він включає в себе сукупність дослідницьких, пошукових, проблемних методів, творчих за своєю суттю.
Проектні технології мають певні переваги:
- Дозволяє перевірити та закріпити на практиці теоретичні знання (практико зорієнто-ваний метод пізнання).
- Забезпечує продуктивний зв'язок теорії та практики y процесі навчання.
- Життєвим результатом проекту є продукт, а умовами, інструментами його досягнення є компетенція вихованця (вчуся діючи).
- Вихованець набуває життєвий досвід.
- Формування вмінь та навичок, які в подальшому позитивно виливатимуть на його життєдіяльність.
- Інтегрований характер. Допомагають вихованцям оволодівати основами наукового дослідження ( визначати мету, ставити цілі, знаходити та аналізувати інформацію, оформляти результати творчої діяльності).
- Стимулює уяву та творчу активність виховаців.
- Навчає навичок колективної та групової пошукової діяльності.
- Сприяє розвитку пізнавальної, практичної, творчої соціальної, компетентності вихованців.
Базуючись на перевагах проектних технологій у роботі гуртка було знайдено свій «ключ рішення» - який дозволяє органічно інтегрувати знання дітей із різних сфер: комп’ютера, побутової техніки, обладнання, транспорту, споруд тощо, дати можливість знайти свій власний шлях і презентувати своє власне бачення з вивчаємої теми з англійської мови. Практична цінність творчого проекту полягає у можливості застосовувати отриманні знання на практиці, пошук нестандартних форм, презентацій своїх знань.
У гуртку «Англійська мова в технічному світі» провідний метод є метод проектів. Навчальна програма спрямована на формуванні у вихованців ПНЗ компетенностей: пізнавальної , практичної, творчої, соціальної.
Враховуючи гуманітарний наврям гуртка , важливо щоб вихованці набули знання та вміння мовні: говоріння, фонетика, лексика, орфографія та мовленнєві вміння: аудіювання, говоріння, читання, письмо.
На заняттях у гуртку кожен вихованець не засвоює готові уявлення і поняття, а має можливість самостійно з безлічі вражень, знань і понять побудувати свій проект, своє уявлення про світ. Проектування на кожному етапі поєднує думку дитини з дією і дію з думкою, культуру гуманітарну з культурою технічною, працю з творчістю. ( Додаток 1, проекти дітей).
Значною мірою зросла необхідність у вихованців збагачувати словниковий запас комп’ютерної термінолексики англійською мовою, вивчати специфічну термінологію, найменування технічних приладів та обладнання, їх побудову, виконувати певні конструкторські дії і при цьому вживати англійську мову. В наш час зросла потреба у фахівцях, які володіють технічними знаннями англійської мови.
Проектна робота – вид роботи , метою якої є підготовка кінцевого продукту англійською мовою – альбому, подання інформації тощо.
Суть проекту полягає у виконанні завдання, спрямованого, насамперед, на досягнення практичних результатів: підготовка колажів, альбомів, малюнків, макетів, плакатів, написання листів, стінгазет, презентацій, виставок . У процесі виконання завдання вихованці спілкуються між собою та з керівником англійською мовою, вчаться створювати зміст своєї навчальної діяльності і засвоювати його в ході підготовки та захисту обраного проекту.
Проектна діяльність – це поширена технологія навчання, метою впровадження якої є формування готовності вихованців до вирішення пізнавальних або практичних завдань у нестандартних ситуаціях. У проектному навчанні проявляється поєднання теоретичних знань і практичних дій при вирішенні конкретної проблеми.
Застосовуючи проектну технологію під час навчання в гуртку, ми маємо можливість ознайомити дітей з культурою і традиціями різних країн. Ми перетворюємося з пасивних слухачів на активних учасників роботи, що допоможе запам’ятати ці проекти. У дітей з’являється велика впевненість у своїх здібностях, інтерес до вивчення мови, змінюється ставлення до заняття, поліпшуються оцінки і відчувається чималий прогрес у вивченні предмета.
Використання проектів у навчально - виховній діяльності ідеальні для різнорівневих груп, оскільки кожне завдання може бути виконане вихованцями, що мають різний рівень підготовки. У процесі діяльності вихованці реально спілкуються між собою і з навколишнім світом англійською мовою.
Робота над впровадженням проектів в гуртку починається вже на початковому рівні. Спочатку – це елементарні розповіді, вірші, “Mind Maps” (карти асоціацій), кросворди, пізніше – описи, ігри, вікторини, інтерв’ю, твори-роздуми, стіннівки, плакати, буклети, фото-колажі, доробки, мультимедійні презентації. Проекти – це усні, письмові чи комп’ютерні розв’язки поставленої проблеми.
За методом проекту можна опрацювати будь-яку тему англійської мови науково – технічного напрямку. Під час першого заняття вивчення нової теми завжди оголошуються теми майбутніх проектів. Після діагностування вихованці об’єднуються у групи чи пари за інтересами і починають працювати, якщо це – групова чи парна робота. У кожній групі діти мають свої обов’язки: збирач інформації, ілюстратор, дизайнер, редактор. Якщо індивідуальна, то вихованці самостійно обирають форму проектної роботи:
1. «Транспорт» ("Transport" ). Діти виготовляють картки, де малюють схематичне зображення різних видів транспорту, складають ці картки в конверти, які наклеюють на спеціальні зошити або блокноти. Під час заняття ми усно з’ясовуємо, які види транспорту існують, які зручніші, даємо характеристуку кожному виду. (Додаток. Заняття 1 )
2. «Роботи» («Robots»). Вихованці отримують знання з будови та основних властивостей роботів, вчаться описувати, дають характеристику та мотувають для чого потрібні роботи, в яких сферах життєдіяльності вони можуть знадобитися. У своїй «Творчій майстерні» діти створюють власних роботів – макети, плакати, постери. (Додаток . Заняття 2)
3. «Комп’ютер мій помічник», «Улюблені веб сайти» («Favourite websites»). Ця тема вивчається на основному рівні навчання, головне завданння – це розглянути та з’ясувати які веб сайти знають та використовують вихованці. Розглядаємо такі веб сайти як : WIKIPEDIA , Expedia.com , Amazon.com , IMDB , Facebook , Ebay , Google . (Додаток . Заняття 3)
4. «Повсякденні технології» ( «Everyday technology»). Розглядаємо ті повсякденні пристрої, технологій без яких наше життя важко уявити( мобільний телефон, планшет, комп’ютер, ноутбук, фотоапарат, карти пам’яті, флеш карта, фен, мікрохвильова піч, пилосос, посудомиюча та пральна машинка тощо.) Надаємо характеристику кожному пристрою, різновиди, недоліки та переваги.
5. Проекти "Навчаємось вчитися" ("Learning to learn") з практичними ідеями та порадами щодо роботи над мовою (вивчення слів, правил, робота з словниками та посібниками, тощо). Результати такої роботи оформлюються у вигляді яскравих пам’яток.
6. Анкетування, інтерв’ю, дослідження на тему, що вивчається. Результат такої роботи оформлюється у вигляді таблиць із висновками та постерів) ( quiz).
7. Аудіо-екскурсія по місту (створення сценарію, презентації з теми). При опрацюванні теми «У місті» пропонуємо вихованцям порівняти архітектури нашого міста та Лондона. (Додаток)
8. Проектні роботи, які стосуються тем "Я, моя родина, мої друзі" "У місті", "Зовнішність": розповідь про себе з опорою (для вихованців початкового та середнього етапу навчання), де опора виготовляється у вигляді шестикутників, складених у своєрідну "квітку", де на кожній "пелюстці" вихованець має розкрити певне питання (своє ім’я, вік, місце проживання, школа, улюблений гурток, шкільні друзі, домашні тваринки, уподобання тощо), "Родинні дерева";
9. Розклад уроків англійською мовою. Складаємо розклад уроків, а також створюємо презентацію «Школа моєї мрії» або «Незвизна споруда майбутнього» («Schools in future»)
10.Досить цікаві проектні роботи, які мають вигляд рекламних постерів (планування вечірки, реклама гуртків чи клубів за інтересами тощо).
11. "Створи свою власну автівку" (до теми «Транспорт»). (Додаток. Заняття1 )
12. Різні види проектних робіт до теми « Домашні помічники моєї матусі», «Мій тато – домашній майстер" або «Чарівні фіксики»). (Додаток )
Для виконання проекту необхідно мати необхідні матеріали для оформлення роботи: довідкову літературу, словники, забраження певних видів техніки, журнали, брошури, малюнки, листівки тощо.
Поступово вихованці повинні навчитися самостійно знаходити потрібну інформацію і звертатися по допомогу до керівника тільки у тих випадках, коли вони самі не можуть знайти відповідь на запитання. Діти також мусять навчитися планувати свої дії і самостійно вирішувати, які матеріали їм знадобляться для виконання завдань проекту і де вони їх можуть знайти.
Результати застосування проектної технології - міцне та глибоке засвоєння знань, підвищений рівень самостійної роботи, високий рівень науковості в знаннях вихованців, вміння працювати в групі, проводити групове обговорення, згуртування дитячого колективу, мотивація колективних досягнень.
Прогнозований результат досвіду:
- сприяє розвитку об'ємно-просторового мислення та уяви;
- використовувати навчальний і додатковий матеріал у розвитку мовлення та володіння мовою в подальшому житті, розширення уявлень про оточуючий світ, техніку, побутові прилади, споруди, космос, технічне конструювання й моделювання;
- знати і використовувати технічну термінологію, надавати певну інформацію, формувати власне Мовне Портфоліо англійською мовою,;
- вміння захищати проект та доводити його до завершення;
- оволодіти досвідом пошукової діяльності, створення найпростіших технічних моделей, знання назв складових технічних моделей англійською мовою, створення власних технічних проектів, що забезпечує розвиток мовних, інтелектуальних і пізнавальних здібностей волі, пам’яті, уваги, уяви, інтелекту, розвиток конструкторських здібностей;
- сформувати у дітей такі риси характеру як працьовитість, активність, доброзичливість, толерантність, колективізм, самостійність, почуття патріотизму, гуманізму, інтернаціоналізму, уміння працювати в колективі.
Використання знань про проектну діяльність не є самоціллю, це засіб досягнення атмосфери творчості та мотиваційної спрямованості на підвищення професійного рівня.
ДОДАТОК
План - конспект заняття 1
Керівник гуртка : Кобріна К.В.
Гурток : «Англійська мова в технічному світі»
Основний рівень, I рік навчання
Тема заняття. Життя суспільства. Засоби пересування. Монолог. Повідомлення з теми.
Мета заняття:
навчальна : тренувати навички монологічного та діалогічного мовлення, читання, аудіювання, письма, активізувати лексичний та граматичний матеріал, зокрема вживання прийменників, повторити раніше вивчені лексичні одиниці, граматичні структури, виготовити колективну роботу колаж «Подорож. Засоби пересування» ;
розвиваюча: розвивати логічне мислення, увагу та зорову пам'ять, спостережливість, удосконалювати фонетику та артикуляцію звуків, усні комунікативні уміння з опорою на наочність, вміння висловлювати свої враження;
виховна: виховувати культуру співбесіди серед гуртківців, взаємоповагу та інтерес до англійської мови, культуру спілкування, виховувати зацікавленість у розширенні своїх знань та вживати вивчений навчальний матеріал в життєвих ситуаціях.
Методи: словесні, наочні, практичні.
Тип заняття: закріплення отриманих знань, вмінь та навичок.
Форми роботи: групова, колективна, індивідуальна
Міжпредметний зв’язок з українською мовою та географією.
Обладнання: плакати, демонстраційний матеріал, роздатковий матеріал, посібники, муз. супровід, матеріали для творчості.
Очікуваний результат: вихованці гуртка закріплять знання з теми, отримають практичне застосування набутих знань на практиці. Колективна робота - колаж «Подорож. Засоби пересування».
Хід уроку
I Вступна частина
- Організаційний момент
- Привітання
- Фонетична зарядка
Бесіда ( використання ілюстрації)
What day is it today? What date is it today? What season is it now ? What is the weather like today ?
Вірш « What is travelling for?»
What is travelling for me?
It is the shining sun. the sea;
The golden sand which look like beads;
The blue-eyed sky and tender breeze.
What do I see when close my eyes?
A milk-white ship with two red strips;
The limpid clouds at the dawn
And sun. that rises all alone…
And when the twilight falls from height.
The night appears from heaven’s gate.
I see the moon in magic light.
And stars. that sparkle at the night.
That’s what I’m looking for in dreams.
And they are my inspiring beams!
I want to see it. to behold
And travel all over the world!
- Мотивація навчальної діяльності.
T. Many people like to travel. What do you think, why do people travel?
In general you will speak about travelling you learn some new things about travelling and perhaps new words and words combinations on the theme..
T:What are you going to do in summer ? (We are going to travel)
T:Which ways of travelling is the fastest one?
T:What ways of travelling do you prefer ?
T:What ways of travelling do you know ?
II Основна частина
- Оголошення теми та мети заняття.
Сьогодні на занятті ми розглянемо види подорожі. З’ясуємо переваги та недоліки кожного виду транспорту? Як слід збиратися до подорожі?
- Актуалізація опорних знань
Мовленнєва розминка
Робота в парах
Ask and answer. What can you see?
( повторення лексичного матеріалу)
coach
plane car bicycle bus train horse/donkey/camel
on foot skateboard scooter motorbike underground/metro
hovercraft steamboat ferry canoe raft cruise ship
yacht ship helicopter airplane
hot-air balloon private jet riverboat
Ігри «Snowball» , «Microphone»
( розвиток монологічного мовленння)
Перш ніж вирушити у подорож ми збираємо валізи. Ми також маємо валізи. Що ви будити брати у подорож? Який одяг вам знадобиться? Поділ на 2 групи: «Одяг». «Необхідні речі».
Team 1 : I should take a blouse, shorts, sunglasses, a hat, a dress, trousers, sandals, a T- shirt, a skirt, …
Team 2 : I should take a travel documents, a passport, a ticket, …
3.Робота з роздатковим матеріалом.
Card 1

4. Закріплення отриманих знань, вмінь та навичок .
Групова робота.
Які види подорожі вам відомі та яким видам ви надаєте перевагу? Які переваги та недоліки у цих видах подорожі? Поділ на групи та обговорення видів подорожі.
T : What method of travelling do you prefer? Why?
Discuss your projects with your group mates and choose the most interesting one for the presentation in the group.
Group 1: Travelling by car.
Group 2: Travelling by plane.
Group 3: Travelling by train.
Group 4: Travelling by bus.
Group 5: Travelling on foot.
So I would like to know how you remember different means of transport.
Робота з опорною схемою «Mind map» .
What things do you associate with the world «travelling»?
Card 2
|
You don’t have to stand in line for tickets or look at bus schedules. |
||||
|
It can take me to just about any place I want to go |
||||
|
You can get to any place at any time |
||||
|
You can take as much luggage as you want. |
||||
|
You are free to go where you want whenever you want |
||||
|
It helps avoid crowded public transport |
||||
|
It gives us freedom |
||||
|
You can travel when you want and to where you want without thinking about tickets and timetables. |
||||
|
It’s fantastic to speed along the road. |
||||
|
It’s usually the fastest way to travel |
||||
|
you do not get stuck in traffic, it is free and it keeps you fit. |
||||
|
because it is a fast way to travel and you can look out at the beautiful countryside.
Suggested Answer My favourite means of transport while on holiday is the car because I don’t have to stand in line for tickets or look at bus schedules. A car can take me to just about any place I want to go. You can get to any place at any time.You can take as much luggage as you want.You are free to go where you want whenever you want. It is more comfortable .It helps avoid crowded public transport. |
5 .Фізхвилинка (рухлива)
- Виготовлення колажу «Подорож. Засоби рересування»
- Презентація зразка.
- Аналіз послідовності виконання роботи.
- Інструктаж т/б перед початком роботи.
- Виготовлення калажу.
- Презентація роботи.

III Заключна частина
- Підведення підсумків заняття .
Thank you very much for your active and hard work at the lesson. It’s very pleasant to work with you.
- Рефлексія.
План - конспект заняття 2
Керівник гуртка : Кобріна К.В.
Гурток : «Англійська мова в технічному світі»
Основний рівень, I рік навчання
Тема заняття. У творчій майстерні. Робот.
Мета заняття:
навчальна :повторити раніше вивчені лексичні одиниці, граматичні структури, закріпити вивчені лексичні одиниці в усному та писемному мовленні, навчити вихованців презентувати власні проектні роботи та виготовити ялинкову прикрасу ;
розвиваюча: розвивати логічне мислення, увагу та зорову пам'ять, спостережливість, удосконалювати фонетику та артикуляцію звуків, усні комунікативні уміння з опорою на наочність, вміння висловлювати свої враження;
виховна: виховувати культуру співбесіди серед гуртківців, взаємоповагу та інтерес до англійської мови, культуру спілкування, виховувати зацікавленість у розширенні своїх знань та вживати вивчений навчальний матеріал в життєвих ситуаціях.
Методи: словесні, наочні, практичні.
Тип заняття: узагальнення умінь та навичок.
Форми роботи: групова, колективна, індивідуальна
Міжпредметний зв’язок з українською мовою та працею.
Обладнання: плакати, демонстраційний матеріал, проектні роботи гуртківців, роздатковий матеріал, посібники, модель – зразок іграшки, муз. супровід, матеріали для творчості.
Очікуваний результат: вихованці гуртка закріплять знання з теми, отримають практичне застосування набутих знань на практиці, удосконалять вміння виготовлення поробок та презентації роботи.
Хід заняття
I Вступна частина
- Організаційний момент
- Привітання
- Фонетична зарядка
Бесіда ( використання ілюстрації)
-What season is it now? - Is it cold? -Is it frosty? -Do you like winter? -What date is it today?
Вірш «Seasons»
Гра - мікрофон « Robot »
Виконання пісні «Head and shoulders»
- Мотивація навчальної діяльності.
II Основна частина
1.Мовленнєва розминка
Актуалізація опорних знань
Гра «Ball»
Вживання лексичного матеріалу: beautiful, pretty, handsome, good-looking, attractive, ugly, tall, short, long, big, small, plump, slim, fair, eye, blue, brown, green, grey, nose, straight, turned up, curly, look like, red, yellow, face, blouse, jumper, pullover, jacket, skirt, shirt, T-shirt, dress, uniform, shorts, trousers, shoes, boots, trainers.
привабливий - beautiful,
гарний - pretty
потворний - ugly,
товстий - plump,
око - eye,
ніс - nose,
блакитний - blue,
сукня - dress,
сапоги - boots,
кросівки - trainers,
близка - blouse,
світлий fair,
обличчя - face
2. Презентація проектних робіт вихованців гуртка.
( розвиток монологічного мовленння)
3.Робота з роздатковим матеріалом.
Card
Tall - small
Dark - fair
Pretty - ugly
Short - long
Black - white
Thin - plump
4. Повторення та систематизація знань.
Бесіда
- How many boats/ rockets / bikes can you see? Count, please.
- What colour is the train/ plane/ car?
- What has he got?
- What has she got?
Робота в парах
Ask and answer. What can you see?
5. Робота з граматикою
Вживання речень у теперічньому часі Present Simple Tense та граматична структура have got/ has got.
Закріплення вивченого матеріалу на практиці.
Listen and complete.
- Виготовлення поробки.
- Презентація зразка вироба.
- Аналіз послідовності виконання роботи.
- Інструктаж т/б перед початком роботи.
- Виготовлення вироба.
- Виставка дитячих робіт.
7 .Фізхвилинка (рухлива)
8. Гра «Guess»
1. Who is it? (face)
2. What is her hair? (long)
3. What has the boy on? (uniform)
4. What is it? (shorts)
5. What is it? (dress)
6. What is it? (boots)
7. Is it a cap or a hat? (hat)
8. What is it? (blouse)
9. What colour is a dress? (blue)
10. What is it? (eye)
- Фізхвилинка
III Заключна частина
- Підведення підсумків заняття .
- Рефлексія.
LESSON 3
Theme. Favourite websites.
Objectives: by the end of the lesson the pupils will be able to :
- develop their reading, listening, writing and speaking skills on the topic;
- practice their communicative skills in pair and group work;
- enrich and activate their vocabulary;
- develop their knowledge about websites;
- develop logical and creative thinking.
PROCEDURE
I. INTRODUCTION
T. We are living in the world of modern technologies. The most important invention which shook the world is the Internet. It is a computer system that allows millions of computer users around the world to get and exchange information. While surfing the net you can visit websites. They are very popular with young people. A website is a place on the Internet where you can find information about something. There is a great variant of them on the Internet. Today we are going to speak about the types of websites and their importance. You will be able to try to make a simple home page while listening to a web designer. Also you are going to fill in the main home page of your local town.
II. WARMING UP
Work in pairs.
T. Read the addresses and decide which of the following are: email addresses?
website addresses? Explain your choice.
- www.google.com.
- annmiller@freemail.co.uk.
- Steve_go@registeredsite.com.
- www.ebay.co.uk.
- www.channel12/competition.net.au.
- http://facebook.com.
III. MAIN PART
- Reading
Pre – reading
Task 1
T. Look at the logos. Which is : a search engine? a social network site?
a shopping site? a travel site? an online auction site? an encyclopaedia? a film site?
T. Which are your favourite websites? What is each about?
Task 2
T. Which of the sentences are true about websites? Decide in pairs. Read and check.
1. YouTube is a social networking site where people upload videos with their pets.
2. IMDB is a social networking site for young children.
3. Expedia.com is a website based in the UK for hotel reservations.
4. Facebook is a website where users must register before using the site.
While – Reading
T. Read the text and fill in the following words:
WIKIPEDIA , Expedia.com , Amazon.com , IMDB , Facebook , Ebay , Google .
WEBSITES
My favourite websites are Facebook and YouTube. I like Facebook because it’s a social networking site which I use to connect with my friends. As for YouTube, it’s another favourite site of mine where people upload videos such as funny things their pets do, their favourite songs or clips from TV programmes and films.
- _______________, the Internet Movie Database is an online database of information related to movies, TV shows, actors, video games and fictional characters featured in visual entertainment media.
- _______________ is an Internet – based travel website based in the US. It books airline tickets, hotel reservations, car rentals, cruises, holiday packages and various attractions and services.
- _______________ is a social networking service and website. Users must register before using the site, after which they may create a personal profile, add other users as friends and exchange messages. Users may join common- interest group organized by workplace, school or college.
- _______________ is the world’s largest online retailer. It started as an online bookstore but soon diversified selling DVDs, CDs, software, video games, electronics, apparel, furniture, food and toys.
- _______________ is an online auction and shipping website in which people and businesses sell a broad variety of goods and services worldwide.
- _______________ is a free, collaborative, multilingual encyclopedia. It has become the largest and most popular reference work on the Internet.
- _______________ specializes in Internet Search and cloud computing. It hosts and develops a number of Internet-based services and products.
PRACTICE
Reading Comprehension
T. Match the websites (1 – 8) with the definitions (a – h) :
1. YouTube. A) a shipping website where a great variety of goods and
services worldwide are sold;
2. IMDB. B) a website where a personal profile is created and messages
are exchanged by users;
3. Expedia.com. C) a website with TV shows, movies, video games and
fictional characters featured in visual media;
4. Facebook. D) a website where videos with funny things of pets,
favourite songs, films are uploaded by people;
5. Amazon.com. E) a website with the largest and most popular general
reference work on the Internet;
6. Ebay. F) a website where DVDs, CDs, software, video games,
electronics, apparel food and toys are sold;
7. WIKIPEDIA. G) a website specializes in Internet Search with a number of
Internet – bases services and products;
8. Google. H) a travel website where airline tickets are booked, hotel
reservations, car rentals and cruises are made.
2. Vocabulary Practice
T. Fill in the correct word(s) from the list below. Use the words only once:
networking, visual entertainment, retailer, common-interest, multilingual, search, online, services, upload, Internet – based.
1. …………………. site.
2. ………………….. videos.
3. ………………….. database.
4. …………………... travel.
5. …………………… groups.
6. online ……………………
7. ……………………. encyclopedia.
8. Internet ………………………….
9. Internet – based …………………
10. ……………………. …media.
3. Listening
T. Listen to a web designer describing how to make a simple home page. Make notes about his recommendations using the headings below.
|
NAME ………………………………….. |
|
LINKS ………………………………….. |
|
ICONS ………………………………….. |
|
OTHER FEATURES …………………… |
|
…………………………………………… |
|
CONTACT ………………………………. |
|
|
Tapescript
Because it’s so easy to use the Internet these days, virtually anyone can think to themselves ‘let’s set up a website’. Maybe you want a home page for friends to look at, or how about advertising your local club? Perhaps you could even start an e – business and become a dot com millionaire. Before you begin, make sure you know why you want a website and what it’s going to be for. It’s also important to choose a good name early on and get an address for the web page. It should be a name that’s easy to remember and the best ones are generally those which say what the site does or which get your attention.
Take the site www.milliodollarhomepage.com. Alex Tew, the student who came up with it, chose a name that said what it was about and it was also interesting because most people want to know anything that mentions money. Another reason people visit sites is because they want information. So, I strongly recommend that you include links to other sites. These need to be up – to – date and useful.
You might think that links to other sites will send people away but in fact if you can help users they will keep coming back to yours. Also, don’t forget that links can take the form of words that you click on or they can be icons which are more visual and make the site colourful.
People also often ask me about things like having pictures and music. That’s OK but it’s also worth remembering that the more features and effects you have, the harder it will be to find what you want and it may take a long time to load the site. Visitors will get bored if they have to wait every time they click on another page. It’s a good idea to give a contact e-mail so you can get feedback from visitors to the site.
Listening Comprehension
T. Match a beginning ( in A) to an ending (in B):
A.
|
1. Let’s ________________ . |
|
2. How about ___________________ . |
|
3. Perhaps ____________________ . |
|
4. Make sure you know ________________ . |
|
5. It’s also important _____________________ . |
|
6. It’s should be a name that’s __________________ . |
|
7. I strongly recommend _________________________ . |
|
8. Don’t forget that _______________________ . |
|
9. It’s also worth ________________________ . |
|
10. It’s a good idea to ______________________ . |
B.
|
a) that you include links to other sites; |
|
b) why you want a website; |
|
c) remembering that the more features and effects you have …; |
|
d) links can take the form of words that you click on; |
|
e) you could even start an e- business; |
|
f) advertising your local club? |
|
g) set up a website; |
|
h) give a contact email; |
|
i) to choose a good name; |
|
j) easy to remember. |
4. Speaking
Task 1. Pair Work
T. Discuss it in pairs. Do you agree with the speaker’s recommendations? What do you think makes a good website? Present your ideas to the class.
Task 2. “Just a minute” game
T. A minute can seem very long when you have to talk about something. Work in groups of three. Mix up the cards and put them face down on the table. Take it in turns to pick up a card and talk for a minute about the topic on the card. If a member of the group runs out of things to say, then someone else in the group can take up the subject.
Cards
|
Talk for a minute about: |
|
1. the difference between Facebook and YouTube; |
|
2. the reasons of success of some websites; |
|
3. the most interesting website for you and why; |
|
4. the difference between Expedia.com and WIKIPEDIA; |
|
5. while setting up a website what type of it would you choose; |
|
6. the most popular websites among teenagers and why; |
|
7. the most helpful websites while doing your homework; |
|
8. your favourite website and why. |
Task 3. Group Work
T. Your local town wants to set up a website to let people know about its news and events. On the main home page there is space which you should fill in order to represent what the site is about and help to attract lots of visitors. What are you going to fill in this page? Let’s divide into groups of three and discuss the topic.
IV. ENDING THE LESSON
1. Memory game
2. Homework
LESSON 4
Theme. Everyday technology.
Objectives: by the end of the lesson the pupils will be able to :
- talk about everyday technologies;
- develop their reading, writing, listening and communicative skills;
- learn and use vocabulary related to various aspects of the topic;
- develop their imagination;
- communicate with each other in pairs and groups.
PROCEDURE
I. WARMING UP
T. Look at the keywords. What do you know about these inventions?
computer network, e-mail, instant-messaging, mobile phone, telephone, telegraph.
Pair Work
T. Work in pairs and complete the information with the keywords.
1. 1844 The first 1) _______ message is sent in the USA using the Morse Code.
2. 1874 A.G. Bell has the first successful 2) ________ conversation.
3. 1969 The first computer 3) _________ links universities in the USA.
4. 1972 The first 4) _________ is sent. The message explains how to use the @ symbol.
5. 1983 Motorola make their first 5) ________ . it measures 25cm* 8cm!
6. 1991 The World Wide Web is developed and surfing the Net becomes possible.
7. 1996 6) ________ is invented. You can now chat to your friends on your computer.
Keys: 1) telegraph 2) telephone 3) network 4) e – mail 5) mobile phone
6) instant – messaging.
II. MAIN PART
1. Presentation
T. Inventions and their usefulness or importance is a common topic nowadays. Talk about different inventions and decide which three you could not live without or which have changed our lives most.
T. The most common ways of giving an opinion in spoken English are as follows (table).
|
I think that … |
|
I believe that … |
|
In my opinion … |
|
To my mind … |
|
From my point of view … |
2. Speaking
T. Work with a partner. Match the words in the columns to make everyday inventions. What do you use each invention for?
|
dish |
control |
|
washing |
dryer |
|
remote |
wave |
|
micro |
washer |
|
lap |
printer |
|
mobile |
top |
|
laser |
cleaner |
|
cam |
nav |
|
vacuum |
camera |
|
hair |
phone |
|
digital |
machine |
|
sat |
corder |
Keys: 1) dishwasher – a machine that washes dishes;
2) washing machine – a machine for washing clothes;
3) remote control – a piece of equipment that you use for controlling a machine, such as a television or stereo system, from a short distance away;
4) microwave – an oven that cooks food very quickly by passing electricity through it, instead of using heat;
5) laptop – a small computer that you can carry with you;
6) mobile phone – a small phone that you can carry around with you;
7) laser printer – a type of printer that you use with a computer, using light from a laser to make very clear letters and pictures;
8) camcorder – a small camera used for recording pictures and sound onto videotape;
9) vacuum cleaner – a piece of electrical equipment that cleans floors by sucking up dirt;
10) hairdryer – a piece of electrical equipment used for making your hair dry after you have washed it;
11) digital camera – a camera that takes and stores pictures in the form of electronic signals;
12) satnav - satellite navigation: a system for finding the best way to a place using information from satellites. It is often found in cars.
3. Writing
T. Write the words in the box under the correct heading.
|
broadband, charger, coverage, device, dishwasher, flash drive, hairdryer, keyboard, laptop, laser printer, network, plug , touch screen, vacuum cleaner, washing machine, wireless
|
|
Computer and phone hardware |
Internet or phone connection |
Electrical household equipment |
|
|
broadband |
|
Keys:
|
Computer and phone hardware |
Internet or phone connection
|
Electrical household equipment |
|
charger; device; flash drive; keyboard; laptop; laser printer; touch screen |
broadband; coverage; network; plug; wireless |
dishwasher; hairdryer; vacuum cleaner; washing machine |
4. Group Work. Brainstorming
T. Everybody will take a sheet of paper and find a partner asking the questions to your classmates. Come here
Ask each other:
A: Do you have a definition of the word …?
B: Do you have the word that means …?
E.g. 1) Do you have a definition of the word broadband?
2) Do you have the word that means …
- a type of connection to the Internet that allows you to receive or send a lot of information very quickly.
|
broadband, changer, coverage, device, flash drive, keyboard, network, plug, touch screen, wireless |
1. A machine or piece of equipment that does a particular thing;
2. When a set of similar things are connected to each other, for example computers or mobile phones;
3. A screen on a computer or mobile phone that you touch in order to choose what you want to do next;
4. A piece of equipment used for giving power to a battery;
5. A piece of equipment with numbers and letters, used for putting information into a computer;
6. A small piece of equipment which stores information and that you can carry around with you;
7. A type of connection to the Internet that allows you to receive or send a lot of information very quickly;
8. This technology communicates using electronic signals, not with wires;
9. The strength of the signal to your mobile phone from your network;
10. An object used to connect a piece of equipment to an electricity supply.
Keys: 1 device, 2 network, 3 touch screen, 4 changer, 5 keyboard, 6 flash drive, 7 broadband, 8 wireless, 9 coverage, 10 plug.
5. Oral Practice. Discussion
T. Work with a partner. Discuss these questions:
1. Do you prefer mobile phones with touch screens?
2. Do you think keyboards will be replaced by touch screens and voice – operated technology?
3. Have you got any wireless technology at home or at school? What is it?
4. Have you got a flash drive? What do you use it for?
5. Which are the biggest and best mobile phone networks where you live?
6. What is mobile phone coverage like in the area where you live?
7. Have you got a broadband Internet connection at home or at school? How fast is it?
8. Do you know whether the plugs in your country are similar to or different from plugs in your country are similar to or different from plugs in other countries?
6. Listening
T. Listen to somebody giving instructions. What exactly are the instructions for?
OK, first make sure the computer is plugged in and then switch it on. On my computer you have to press a button on the right. You don’t need to keep pressing, just press once. Wait for the computer to start up. Mine usually takes a couple of minutes. Then click on the bottom right corner of the screen, where you can see the time and date. Just click once. Click the right button, not the left. Then you can see a calendar and a clock. It shows you where to change the day and time and you click there. It’s really easy. Once you’ve got the day, date and time you want, just press ‘accept’. Or you can click in the right corner again and the window on the screen closes. And that’s all you have to do!
Keys: The instructions are for setting the day, date and time on a computer.
8. Developing Writing
T. Imagine that your mobile is switched off and the battery is dead. What different steps do you need to take to call a friend? Work individually and write instructions.
E.g. Plug in the charger and connect the phone.
III. ENDING THE LESSON
Developing Speaking
T. Work with a partner. Read your instructions to your partner and compare them. Are they the same?
Video Game Consoles
Video game consoles are used mostly for playing video games, why “mostly”, because modern consoles, like Xbox One or Playstation 4 and others, can do much more for entertainment such as watching movies, listening music, internet surfing, etc. All video game consoles from the first ones like Atari 2600 to the latest, such as Xbox One, PS 4 or Wii U should be connected to television.


![]()
The Atari 2600 Nintendo Wii U


Playstation 4 Microsoft Xbox One
Nowadays to play a game on consol you need to buy it in internet games distribution service and download it via internet connection. Previous consoles used other storage devices such as cartridges, chip cards, floppy disks and optical disks.
Why video game consoles are needed for as everyone can play video games on computers? It’s very difficult question and for many years a lot of gamers all over the world have been arguing. Gaming computers are more powerful and universal devices and they are rather expensive. Consoles are cheaper than PCs and good for people who wants to sit on comfortable sofa and enjoys video game or plays multiplayer game with a friend sitting nearby.
Portable battery chargers
Every portable device such as smartphone, tablet, laptop or camera has a battery so it may discharge in the most important moment. In such situation you may use portable battery charger.
The most popular portable charger is so-called “powerbank”. Powerbank consists of several built-in batteries that can be charged from network or a USB port. More number of batteries in a powerbank means higher capacity of it so it can be used longer before recharge.

Powerbank charging a smartphone
If you travel a lot, especially hiking for long distances where there’s no electric power network, portable solar charger is your variant. All you need to charge your discharged smartphone or camera is sunny weather.

Portable solar charger
eReaders
Despite the fact that movies and video games are extremely popular, many people still prefer reading books. But paper books can be very large and heavy and it may not be very convenient to read them outdoor. In such situation eReader is a way out. It is compact and light device which can contain hundreds and thousands of books. Some of them may have more function, for example playing music and videos.
 There are 2 type of eReaders: LCD screen eReaders and e-paper (also e-ink) eReaders. The first ones are like tablets but have less functions, therefore you can use them not only for reading books. Due to LCD backlight you may read in completely dark room, but it also causes your eyes get tired.
There are 2 type of eReaders: LCD screen eReaders and e-paper (also e-ink) eReaders. The first ones are like tablets but have less functions, therefore you can use them not only for reading books. Due to LCD backlight you may read in completely dark room, but it also causes your eyes get tired.
eReader with LCD screen
 On the other hand there is an e-paper eReader which doesn’t have any backlight. Its only function is reading books. As there is no backlight, this device can’t be used in dark room, it needs external light, so it’s almost harmless for human eyesight. E-paper simulates the page of the real book.
On the other hand there is an e-paper eReader which doesn’t have any backlight. Its only function is reading books. As there is no backlight, this device can’t be used in dark room, it needs external light, so it’s almost harmless for human eyesight. E-paper simulates the page of the real book.
E-paper eReader
However, none of eReader can simulate the smell of new book and feel of touching and turning over the pages of real book.
Photo and video cameras
Photo cameras are used to take photos. Nowadays most of cameras are digital, it means that shots are saved in memory storage and there is no need to use photo film. The same is for video cameras which records videos. Both are multifunctional devices, that is you can film using photo camera as well as you can take photos using video camera.

Photo camera

Video camera
Somebody may say “These devices are useless because I have both of them in my smartphone!”. But have you seen any photographer or camera operator using smartphone. NO. As if you want to get a photo or a video in good quality you should use good photo or video camera. And there is a good proverb “Every special device is better than multifunctional one”.
A laptop, often called a notebook or "notebook computer", is a small, portable personal computer so it can be used outdoor. Modern laptops can fulfill all functions that stationary PCs do. But laptops are less powerful so if you want to play new video game and enjoy high-quality graphic on large monitor, laptop is not your choice.

Laptop
Laptops are very convenient when you travel for a long distance or you have to work at holidays. It’s irreplaceable during studying performing laboratory works, correcting reports, giving presentation and so on. However laptops have the same problem as all mobile devices – battery. Modern laptop with high-capacity battery (which is rather expensive) can work for 8-10 hours, afterward it should be connected to power network.
So, laptop is full value computer with its advantages and disadvantages. And it’s up to you what to choose small portable laptop or high-performance PC with large monitor.
Smartphones
 A smartphone is a mobile phone which combines features of a personal computer. Smartphones, which are usually pocket-sized, typically combine the features of a cell phone, such as the abilities to phone and receive voice calls and create and receive text messages, with those of other popular digital mobile devices like personal digital assistants (PDAs), such as an event calendar, media player, video games, GPS navigation, digital camera and digital video camera. Every smartphone can access the Internet and can run a variety of programs called applications. Nowadays all smartphones have touchscreens, which enables the user to use a virtual keyboard to type words and numbers and press onscreen icons to activate "app" features.
A smartphone is a mobile phone which combines features of a personal computer. Smartphones, which are usually pocket-sized, typically combine the features of a cell phone, such as the abilities to phone and receive voice calls and create and receive text messages, with those of other popular digital mobile devices like personal digital assistants (PDAs), such as an event calendar, media player, video games, GPS navigation, digital camera and digital video camera. Every smartphone can access the Internet and can run a variety of programs called applications. Nowadays all smartphones have touchscreens, which enables the user to use a virtual keyboard to type words and numbers and press onscreen icons to activate "app" features.
Modern smartphones
Smartphone is the most universal and multifunctional device of all. Ability to access mobile Internet (EDGE or 3G which is still unavailable in Zaporizhzhya) allows you to stay online everywhere. But smartphones have one serious disadvantage that is high power consumption due to large screen, Internet connection and huge amount of usable functions. It means that you need to charge your smartphone every day. And if your smartphone discharged you would even lose the opportunity to make a call and it may happen in the most unsuitable moment. But it is a small pay for such handy device.
After the first space flight of Yuri Gagarin many children wanted to become astronauts and iterate his heroic achievement. However, being an astronaut is still a dream for lots of kids. But do you know what is necessary to become an astronaut? What education and knowledge is needed to this profession? How do astronauts train and what do they do during their space flights. So let’s have a short observation of such questions. I believe it’ll be interest for you. OK, let it roll!
Astronauts in Training
The most exciting day for anyone who wants to travel into space is the day he or she is selected to be an astronaut candidate. Then the real work begins. It can take up to two years of training to become a fully qualified astronaut. Candidates must learn the basics of the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station. They must also learn how to be a part of a team by flying the NASA T-38 training jets.

Two potential astronauts are training in T-38 jet. These trainings make pilots and mission specialists think quickly in changing situations, and prepare them for rigors of spaceflight.
Astronauts also take classes. They must learn many things besides science. They also learn about medical procedures. Many times, they have to give speeches, so they take public speaking classes. In order to be prepared for any emergency, astronauts take survival training.
If you are going to be a crew member on the International Space Station, you will also have to take language classes. You will need to communicate with foreign colleagues and Mission Control Center.
Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility (макет космического корабля)
In order for astronauts to a feel for what they will be doing in space, they practice on life-sized models. These models are called “mock-ups”. The Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility (SVMF) is where they practice. In the SVMF, astronauts practice using the Space Shuttle Orbiter (многоразовый орбитальный шаттл) and parts of the International Space Station. In these mock-ups, astronauts will learn how they will move about.


Mock-up facilities where astronauts practice what they will be doing in space.
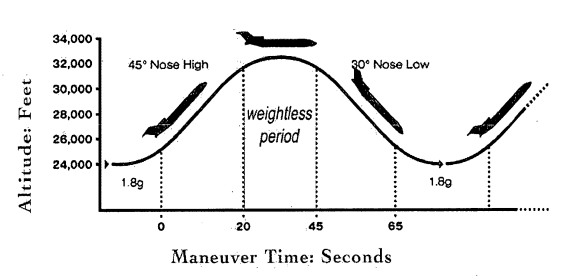
Preparing for Microgravity
How do astronauts practice for being in space? There are many things to learn about being in the almost weightless condition known as microgravity. And there is a way how microgravity can be imitated on Earth. For this purpose KC-135 is used. This plane is also known as the Weightless Wonder or Vomit Comet. It provides about 20-25 seconds of zero gravity. For this brief amount of time, astronauts fell weightless. Sometimes, even experienced astronauts get sick in the KC-135. That is where it gets one of its names.
The Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (гидролаборатория)
To practice extravehicular activity (работа в открытом космосе), or space walks, astronauts go underwater. The astronauts use the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (NBL), a huge “swimming pool”. The NBL is 62 meters in length, 31 meters in width and 12 meters in depth. The pool holds 22.7 million liters of water. Astronauts float in the water while they practice on full-sized models of space vehicles. They may spend up to seven hours at a time under water.

Astronauts use the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory to practice extravehicular activities.
Morning Routine in Space
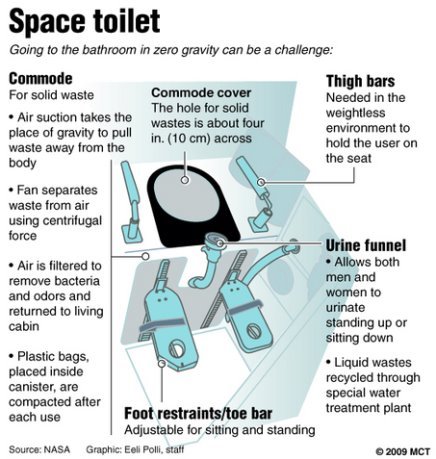
Astronauts living and working in space have the same hygiene needs as people on Earth. They wash their hair, brush their teeth, shave and go to the bathroom. However, because of the microgravity environment, astronauts take care of themselves in different ways.
Astronauts wash their hair with a "rinseless" shampoo (шампунь который не надо смывать) that was originally developed for hospital patients who were unable to take a shower.
Many astronauts have a personal hygiene kit. The kit contains the personal hygiene items each astronaut has chosen to take. Personal preferences, such as the brand of toothpaste, are accommodated if possible. Dental hygiene is basically the same as on Earth.
Because of microgravity, the space station toilet is more complex than what people use on Earth. The astronauts have to position themselves on the toilet seat using leg restraints. The toilet basically works like a vacuum cleaner with fans that suck air and waste into the commode. Each astronaut has a personal urinal funnel (воронка для мочеиспускания) that has to be attached to the hose's adapter (приемный шланг). Fans suck air and urine through the funnel and the hose into the wastewater tank.

Washing of hair on International space station
Eating in Space
Imagine going camping for more than a week with several of your close friends. You would make sure you have plenty of food and the gear (кухонный инвентарь) to cook and eat it with. The food would have to be stored properly and be nonperishable (непортящийся) to avoid spoilage. After finishing your meal, or at the end of your camping trip, you would then pack all your gear and dispose of your trash properly just before the ride home.
Astronauts basically do the same thing when they go to space. Preparation varies with the food type. Some foods can be eaten in their natural forms, such as chocolate cakes and fruit. Other foods require adding water, such as macaroni and cheese or spaghetti. Of course, an oven is provided in the space station to heat foods to the proper temperature. There are no refrigerators in space, so space food must be stored and prepared properly to avoid spoilage, especially on longer missions.
Spices, such as ketchup, mustard and mayonnaise, are provided. Salt and pepper are available but only in a liquid form. This is because astronauts can't sprinkle salt and pepper on their food in space. The salt and pepper would simply float away. There is a danger they could block air vents, pollute equipment or get stuck in an astronaut's eyes, mouth or nose.

Eating in microgravity can be very different than eating on Earth.
Astronauts eat three meals a day: breakfast, lunch and dinner. Nutritionists ensure the food astronauts eat provides them with a balanced supply of vitamins and minerals. Calorie requirements differ for astronauts. For instance, a small woman would require only about 1,900 calories a day, while a large man would require about 3,200 calories. An astronaut can choose from many types of foods such as fruits, nuts, peanut butter, chicken, beef, seafood, candy, chocolate cakes, etc. Available drinks include coffee, tea, orange juice, fruit punches and lemonade.
As on Earth, space food comes in disposable packages. Astronauts must throw their packages away when they have finished eating. Some packaging actually prevents food from flying away. The food packaging is designed to be flexible and easier to use, as well as to maximize space when packing or disposing of food containers.
Working in Space
Astronauts perform many tasks as they orbit Earth. The space station is designed to be a permanent orbiting research facility. Its major purpose is to perform world-class science and research that only a microgravity environment can provide. The station crew spends their day working on science experiments that require their input, as well as monitoring those that are controlled from the ground. They also take part in medical experiments to determine how well their bodies are adjusting to living in microgravity for long periods of time.
Working on the space station also means ensuring the maintenance and health of the orbiting platform. Crew members are constantly checking support systems and cleaning filters, updating computer equipment: doing many of the things homeowners must do to ensure their largest investment stays in good shape. Similarly, the Mission Control Center constantly monitors the space station and sends messages each day through voice or email with new instructions or plans to assist the crew members in their daily routines.
Exercising in Space
Exercise is an important part of the daily routine for astronauts aboard the station to prevent bone and muscle loss. On average, astronauts exercise two hours per day. The equipment they use is different than what we use on Earth. Lifting 100 kilograms on Earth may be a lot of work. But lifting that same object in space would be much easier. Because of microgravity, it would weigh much less than 100 kilograms there. That means exercise equipment needs to be specially designed for use in space so astronauts will receive the workout needed.


Crew members must exercise every day to prevent bone and muscle loss.
Free Time in Space
Living in space is not just all work and no play. Astronauts like to have fun, too. If you're staying on the International Space Station for a few months, it is certainly okay to look out the window, play with your food or tease your crewmates once in a while. Fun is an essential ingredient to the quality of life.
Astronauts need a break from their busy schedules when they are orbiting Earth. Days or even months of hard work are certain to cause stress among space workers. That is why flight planners on Earth schedule time each day for astronauts to relax, exercise and have some fun. Station crew members even manage to have fun while working. Experiments in space sometimes involve ordinary toys and how microgravity affects them.
A popular pastime while orbiting Earth is simply looking out the window. Inside the International Space Station, crew members have numerous windows they can look out. Astronauts often comment on their fascination and awe (восхищение и трепет) as they look at Earth spin beneath them with its multiple shades and textures. Sunsets and sunrises are also very spectacular, occurring every 45 minutes above Earth's atmosphere.
Aboard the space station, crew members have many opportunities to relax and play. Like most people who work full time, astronauts get weekends off. On any given day, crew members can watch movies, play music, read books, play cards and talk to their families. During their off time, they certainly take time out to play games and generally have a good time.


Sleeping in Space
After a long day at work, nothing is better than a good night's sleep! Just like on Earth, in space a worker goes to bed at a certain time, then wakes up and prepares for work again. There are a few differences though. Space has no "up" or "down," but it has microgravity. As a result, astronauts are weightless and can sleep in any orientation. However, they have to attach themselves so they don't float around and hit into something. Space station crews usually sleep in sleeping bags located in small crew cabins. Each crew cabin is just big enough for one person.
Generally, astronauts are scheduled for eight hours of sleep at the end of each mission day. Like on Earth, though, they may wake up in the middle of their sleep period to use the toilet, or stay up late and look out the window. During their sleep period, astronauts have reported having dreams and nightmares. Some have even reported snoring in space.

Crew members sleep in a sleeping bag located in a crew cabin.
Automobile [ˈɔːtəməbiːl] systems
Literally the history of all ground transport vehicles began with the wheel invention. But times have changed, the pace of living has speeded up and today we cannot manage without automobiles, buses, trolleybuses, as transport is playing bigger and bigger part in our daily life.
Automobiles are irreplaceable and every year their quantity all around the world grows up. Automobiles have become high-speed transport therefore we are able to cross huge distances, provide cargo transportation in short time and get to the most inaccessible places of the world.
The word “automobile” means motor-powered trackless road vehicle. This term includes car (легковой автомобиль), lorry (грузовой автомобиль), bus, trolleybus and even armored fighting vehicle (бронетранспортёр) but it doesn’t include farm tractor (сельскохозяйственный трактор) and motor-cycle.
There is great variety of automobiles but all of them have almost the same construction. Modern automobiles consist of 15 – 20 thousands of details, 150 – 300 of which are the most important and valuable. An automobile is the result of combined work of a number of systems. Each system, though primarily independent, is influenced by the effect of other systems interacting with it. So let’s consider main automobile systems:
- Power plant (двигатель);
- Drive train (трансмиссия, то есть механизм передачи);
- Steering system (система управления);
- Braking system (тормозная система);
- Suspension (подвеска);
- Electrical (электрическая система);
- Ignition (система зажигания).
Power plant
A vehicle which comes under the class - automobile must produce its own power sufficient enough to initiate and maintain movement. The power is produced from within the automobile, usually from a compact engine placed either in the front or rear. In most of the cases the engine is an internal combustion type (двигатель внутреннего сгорания) that converts chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy. This conversion is done inside a piston cylinder arrangement where controlled explosion of fuel-air mixture is done which produces a very high pressure inside. This high pressure drives the piston (поршень) out from the cylinder. The linear displacement of the piston is converted to rotary motion with the help of a reciprocating motion mechanism (механизм обеспечивающий возвратно-поступательное движение). The output from the engine is available through a shaft.
The classification of various types of power plants used in vehicles is as follows: 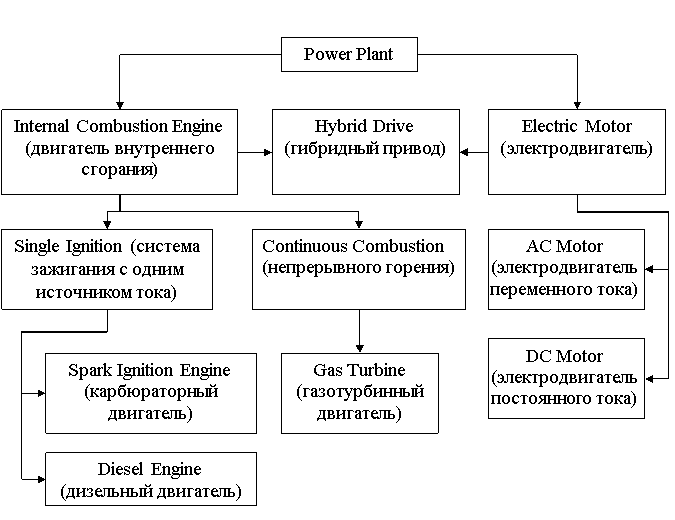
Every type of power plant has its features as well as advantages and disadvantages. Nowadays the internal combustion engines are most commonly used power plants. However, the technology of electric motors and hybrid drives are rapidly developing and some day there may be a monopoly of electric automobiles.
Drive train
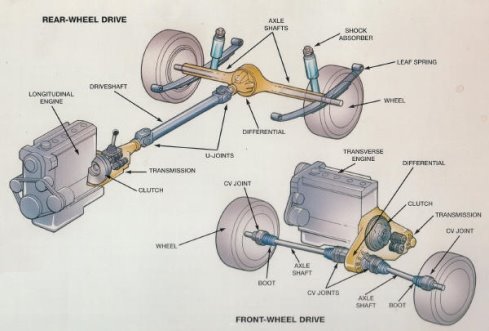
Power is produced by the engine and transferred to the wheels to drive the vehicle. Drive train helps to transfer power produced from the engine to the wheels with the help of intermediate linkages (промежуточных передач). The set of linkages between the engine and the wheels constitute the drive train. It includes the clutch (сцепная муфта), the gearbox (коробка передач), the universal joints (шарнирные муфты) and the drive shaft (вал трансмиссии) and the differential arrangement (дифференциал).
The function of the clutch is to provide gradually increasing amount of power to the shaft, while the engine output remains fixed. Let us understand it this way. Vehicle requires more power when it just starts to roll (it needs to overcome inertia). But at this point of time the speed is very low. As the engine is connected to the wheels rigidly through gears, the engine also moves slowly. A slow rotating engine produces little power which is not sufficient to accelerate. Engine can produce more power if it runs at high RPMs (оборотах). In order to couple an engine running at high speed and a gear system running at low speed, we introduce a clutch which connects the engine and the gear non-rigidly.
Usually the clutch has two stacked plates which slide against each other if pressed. The amount of slip (проскальзывания) depends on the amount of pressure applied. If slip is more, then the power transmitted is less.
The gearbox helps to multiply or divide the available torque (крутящий момент) at several fixed ratios. This is important because the vehicle needs more torque while accelerating and less during constant speed cruising. When the vehicle begins to roll from rest, highest amount of torque is required which can be obtained with the help of a set of reduction gear.
Steering system
To control a moving vehicle we need a steering system. It manipulates the direction of wheel rolling so as to drive the vehicle in that direction. Generally in most vehicles the front wheels (or the front axle) are steered and the rear wheels follow it. But there are vehicles where steering is done on all four wheels or both the axes too. Steering is done with the help of a tie rod (рулевая поперечная балка) attached to both the wheels as shown in the figure below:
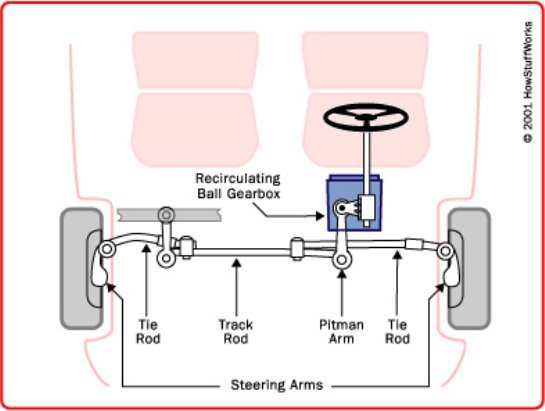
The steering wheel is the only control that a driver of an automobile operates to maneuver the vehicle. The underlying operations may be different in how the steering is achieved for a particular vehicle and it is not needed for a driver to understand the full details.
Braking system
To slow down or to completely stop a vehicle one needs braking system. Brakes absorb the kinetic energy and dissipate or store it in some other form (usually heat or electricity).
Types of brakes:
-
Mechanical:
- Drum and internal shoe brake (барабанно-колодочный тормоз) - is a brake that uses friction caused by a set of shoes or pads that press against a rotating drum-shaped part called a brake drum.

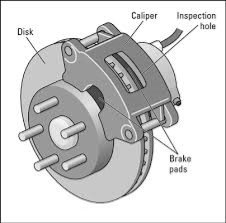
- Disc brake (дисковый тормоз) – is a wheel brake which slows rotation of the wheel by the friction caused by pushing brake pads against a brake disc with a set of calipers.
-
Electrical:
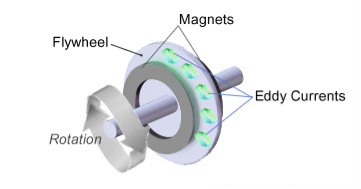
- Eddy current brake (тормоз на вихревых токах) consists of a conductive metal disk (flywheel), which moves through the magnetic field of a magnet, either a permanent magnet or an electromagnet. When it moves past the stationary magnet, the magnet causes a resistance force on the metal which opposes its motion, due to circular electric currents called eddy currents induced in the metal by the magnetic field.
- Regenerative (рекуперативный тормоз) - in electric and hybrid cars, the regenerative brakes charge the main battery during braking, effectively extending the vehicle's range between charges.
- Others.
Suspension system
It provides the vehicle a smooth ride even when the wheels go over uneven terrain. This is achieved by damping of the vibrations that get transmitted to the chassis (ходовая часть) through the wheels. Thus a suspension system is employed between the wheel (axle) and the chassis. All types of suspension systems absorb the energy when aт impact tries to set the suspension in motion. The absorbed energy may be dissipated or converted to other form. By providing a smoother working condition, the suspension enhances the life of all components which are mounted on the chassis that are the drive train, the engine and all boltings.
A suspension system also helps to improve the fuel efficiency by maintaining a continuous contact of the wheels with the road and thereby preventing rolling slip.
There are various types of suspension systems in wide use in the automobile industry. They are:
- Telescopic fluid filled suspension (подвеска на амортизаторах);
- Leaf spring suspension (рессорная подвеска);
- Torsion spring suspension (торсионная подвеска);
- Hydroelastic suspension (упругая гидравлическая подвеска);
- Electromagnetic suspension (электро-магнитная подвеска)
- etc.

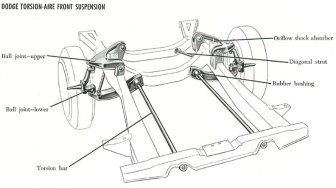 Leaf spring suspension Torsion spring suspension
Leaf spring suspension Torsion spring suspension
All the above mentioned suspension types differ only by construction. Their working principle is same, that is to absorb/dampen the incoming vibration.
Electrical system
All modern vehicles rely heavily on electrical systems: be it running the engine, stability or cruise control or for lighting or air conditioning. Certain vehicles even completely convert the engine output to electricity and then use that electricity to drive a motor for motion (Diesel train engines).
The electrical system on a modern automobile is tightly integrated with the engine, steering and suspension system. It draws power from an alternator (AC) (генератор переменного тока) or dynamo (DC) (генератор постоянного тока) which is coupled with the engine. The power thus produced is either directly used for various activities or is stored in a suitable battery pack for future use.
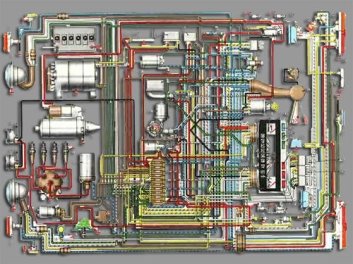
Automobile electric system. It’s complicated, isn’t it?
In spark ignition engines (карбюраторные двигатели), this system also takes care of maintaining the spark (искра) and its timing. A high voltage sub-circuit is used for operating the spark plug (свеча зажигания). This system also powers and maintains the Electronic Stability Programme (ESP) which combines the suspension, braking and engine control.
Ignition system
The ignition system creates an electric spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture in the cylinder’s combustion chamber. Because the ignition system is so crucial to the proper running of your vehicle, it is one of the most important things to be checked during a car service.
The ignition system consists of:
- The battery, which feeds electrical current to the ignition coil.
- The ignition coil, which transforms the 12 volts from the battery into the thousands of volts required to initiate the spark.
- The distributor, which sends the high voltage from the coil to the spark plugs, controlling the timing to ensure they spark at the right time.
- The spark plugs, which fit into the head of the engine cylinders and ignite the fuel when the piston is at the top of its compression stroke.
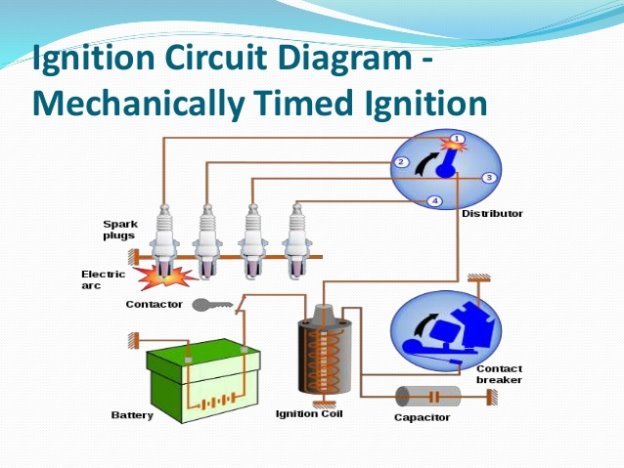
It all begins in the ignition coil, which takes the relatively weak power generated by the battery and turns it into a spark strong enough to ignite air-fuel mixture. What we refer to as the coil is actually a combination of two wire coils — the primary and the secondary. The primary coil or “winding” carries the low voltage from the battery and the secondary coil transforms it into high voltage before sending it to the distributor.
The distributor takes the high voltage electricity generated by the ignition coil and sends it through the rotor — a spinning part that makes contact with each of the spark plug wires. The spark plug wires deliver the voltage to their connected spark plugs in each cylinder of your engine, igniting the air-fuel mixture during the combustion stroke. This process repeats thousands of times per minute, powering your car.
There are three different types of ignition systems. These include:
- Point-type ignition system (контактная система зажигания) – the traditional ignition system, which we’ve defined above.
- Electronic ignition system (электронная система зажигания). Similar to the point ignition system, its difference lies in the distributor component. Instead of a distributor, the electronic system has something called an armature (сердечник), a pickup coil (воспринимающая кашушка) and an electronic control module ( электронный модуль управления). Electronic ignition systems were a response to the quest for greater mileage and reduced vehicle emissions in the modern driving environment. Because the spark created by an electronic ignition system is greater than point type, less fuel is needed with each stroke.
- Distributorless ignition system (безконтактная система зажигания). This type of ignition system gets rid of the distributor altogether, instead firing the spark directly from the coils to the spark plug. The timing is controlled electronically by the ignition control unit (ICU) and engine control unit (ECU).


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
