Презентація "Засоби індивідуального захисту"










Eye and Face Protection
Potential Incidences of Eye/Face Hazards
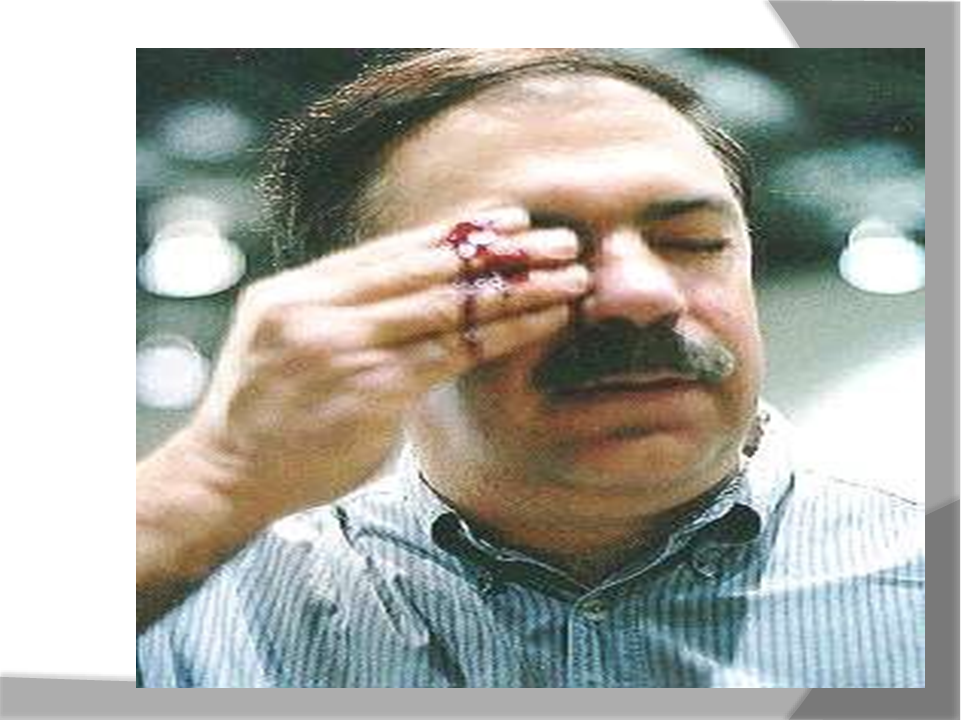
Object Striking Eyes
Dusts, Powders, Fumes, and Mists
○  Small particles of matter can enter your eyes and damage them. Operations such as grinding, chiseling, sanding, hammering, and spraying can create small airborne particles
Small particles of matter can enter your eyes and damage them. Operations such as grinding, chiseling, sanding, hammering, and spraying can create small airborne particles
Contact with Chemicals
Toxic Gases, Vapors, and Liquids
○ Toxic chemicals in the form of gases, vapors, and liquids can damage your eyes. Always read the appropriate MSDS before working with any hazardous material.
○ Always check with your supervisor or safety manager to learn the type of eye or face protection you will need to use in order to work safely
Eye and Face Protection
Potential Incidences of Eye/Face Hazards
Swinging Objects
○ Large objects such as:
1. swinging chains, cables and ropes;
2. tools that are thrown or fall;
Thermal and Radiation Hazards
 ○ Operations such as welding, metal cutting, and working around furnaces can expose your eyes to heat, glare, ultraviolet, and infrared radiation
○ Operations such as welding, metal cutting, and working around furnaces can expose your eyes to heat, glare, ultraviolet, and infrared radiation




Eye and Face Protection
Elimination or Control of Hazards
Safe Work Practices
○ Read and follow all warnings and precautions that may be found on equipment and hazardous materials
○ Do not throw tools or participate in horseplay
○ Keep sharp or pointed objects away from your eyes
 ○ Follow your supervisor's or safety manager's suggestions and recommendations for working safely
○ Follow your supervisor's or safety manager's suggestions and recommendations for working safely








Eye and Face Protection
Care of Eye Protection Equipment
Clean your eye protection equipment. You can usually use mild soap and water
Never use abrasive soaps, rough paper, or cloth towels
Keep PPE in good working condition If damaged, replace as soon as possible
Store your eye protection equipment in a sanitary, cool, dry area away from moisture
Read the manufacturer's directions and warnings before using any eye protection equipment
 If you have any questions concerning your eye protection equipment, talk with your supervisor or safety manager
If you have any questions concerning your eye protection equipment, talk with your supervisor or safety manager
Head Protection
Why is Head Protection Important? In and around your head are:
Your eyes, with which you see
Your ears, with which you hear
Your nose, with which you smell
Your mouth, with which you eat and speak
Your brain, with which you think
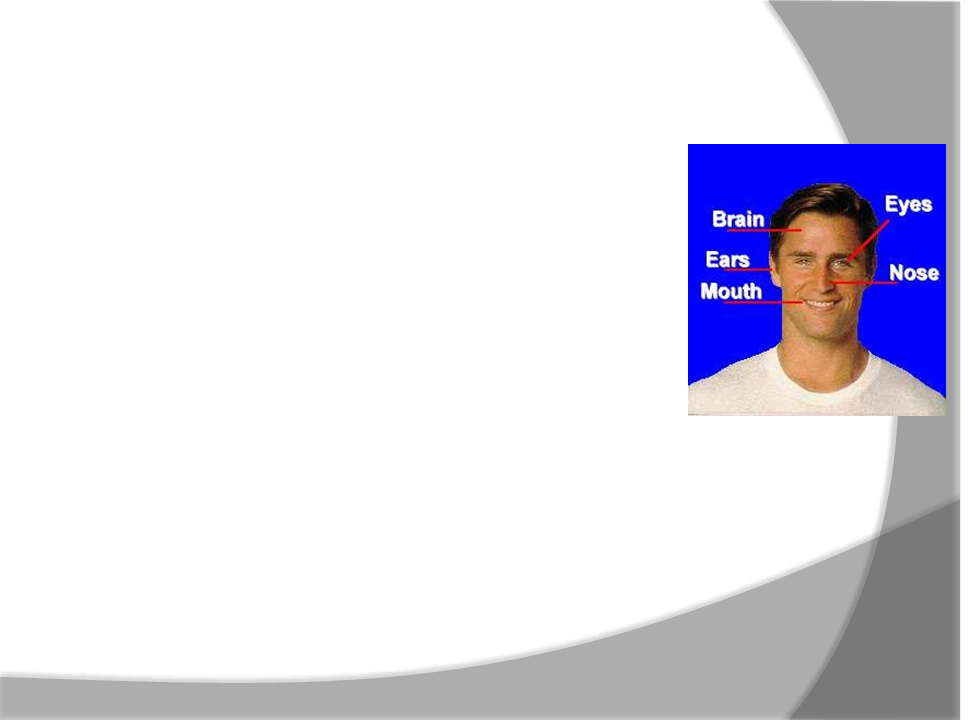 Injuries to the head are very serious. For this reason, head protection and safety are very important .
Injuries to the head are very serious. For this reason, head protection and safety are very important .

Head Protection
Potential Incidences of Head Hazards
Impact
○ Falling or flying objects
○ falling or walking into hard objects
○ injuries include neck sprains, concussions, and skull fractures
Electric Shock
○ Live exposed electric wires
○ Injuries include electrical shocks and burns Drips
 ○ Toxic liquids such as acids, caustics, and molten metals can irritate and burn the head/scalp.
○ Toxic liquids such as acids, caustics, and molten metals can irritate and burn the head/scalp.






Head Protection
Proper use and care of hard hat
Always wear your hard hat while you are working in areas where there are potential head hazards
Adjust the suspension inside your hard hat so that the hat sits comfortably, but securely on your head
 Inspect the shell of your hard hat for cracks, gouges, and dents. Inspect the suspension system for frayed or broken straps. If your hard hat needs to be repaired, have it repaired immediately or ask your employer for a new one
Inspect the shell of your hard hat for cracks, gouges, and dents. Inspect the suspension system for frayed or broken straps. If your hard hat needs to be repaired, have it repaired immediately or ask your employer for a new one
Place plastic (non-metal) reflective tape on hat if working at night
Never paint, scratch or drill "air holes" in your hard hat
Never carry personal belongings such as cigarettes, lighters, or pens in your hard hat



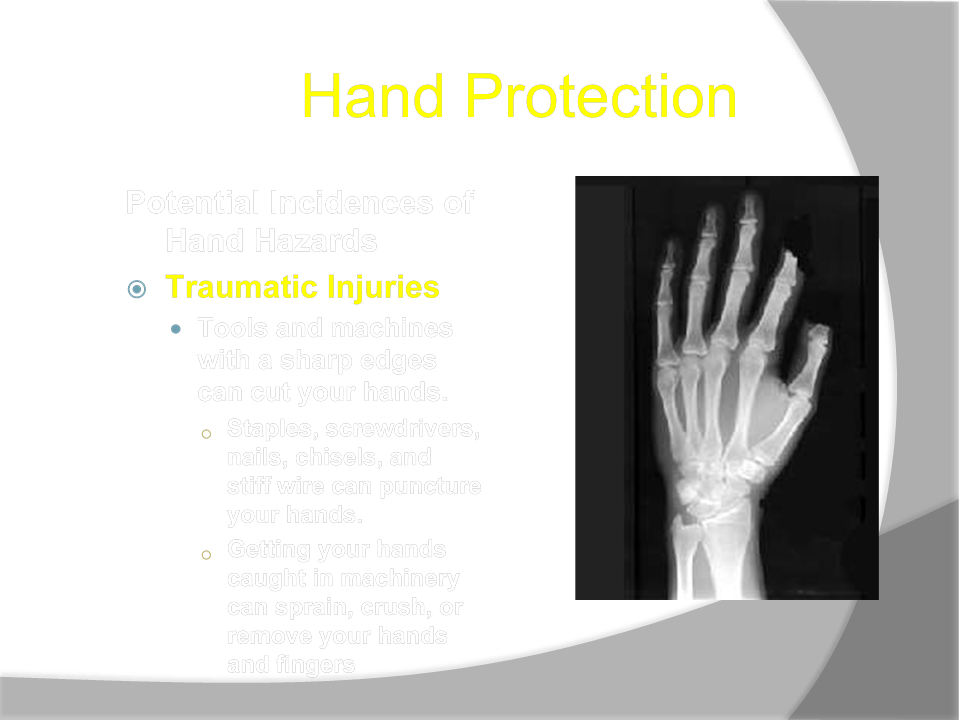
Hand Protection
Potential Incidences of Hand Hazards
Contact Injuries
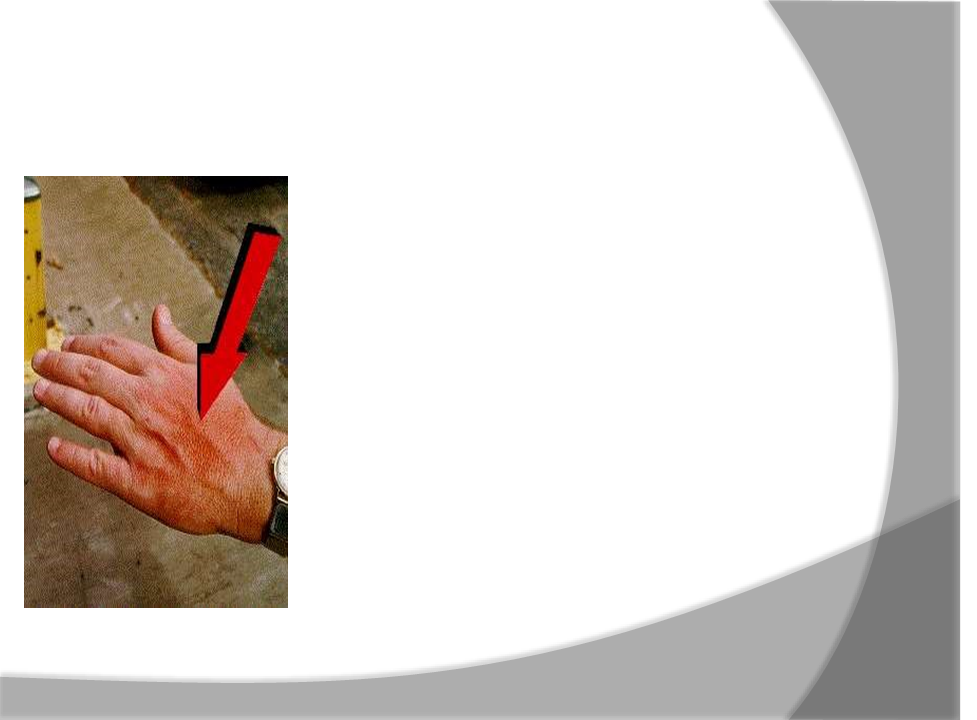 Coming into contact with caustic or toxic chemicals, biological substances, electrical sources, or extremely cold or hot objects can irritate or burn your hands
Coming into contact with caustic or toxic chemicals, biological substances, electrical sources, or extremely cold or hot objects can irritate or burn your hands
○ WARNING: Toxic substances are poisonous substances that can be absorbed through your skin and enter your body.
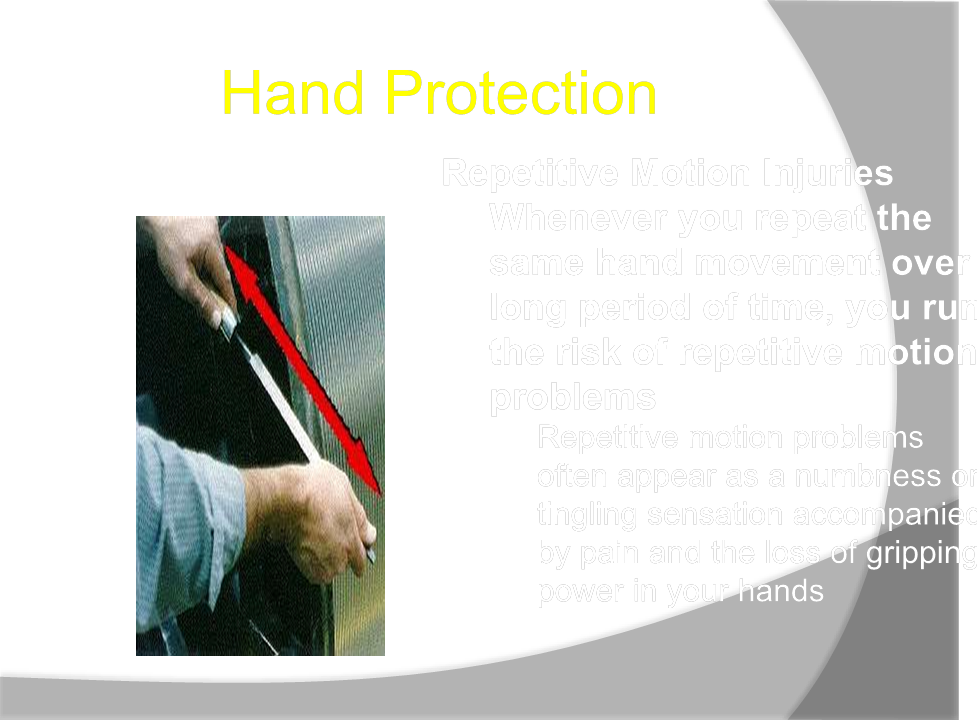
Hand Protection
Proper Fit and Use of PPE
 Select and use the right kind of glove for the job you are going to be performing
Select and use the right kind of glove for the job you are going to be performing
Check fit, always use correct size
Make sure chemical resistant to chemical being used
Inspect your gloves before you use them
Remove any rings, watches, or bracelets that might cut or tear your gloves
Look for holes and cracks that might leak
Replace gloves that are worn or torn
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ARM PROTECTION
ARM PROTECTION
Gauntlets for workers handling corrosive substances, such as acids and caustics, shall be made of natural rubber, synthetic rubber
or pliable plastic material resistant to corrosion.
Gauntlets for protecting workers against the action of toxic, irritating or infectious substances shall:
(1) cover the forearm as much as possible,
(2) have a close fit at the upper end and
(3) not have the slightest break. Gloves torn during use shall be replaced immediately
GAUNTLETS – gloves, w/c are closed-fittings to the hands
Safety Belts, Life Lines and Safety Nets
1) ![]() Workmen working in unguarded surface above open pits or tanks, steep slopes, moving machinery and similar locations, or working from unguarded surfaces six (6) meters (20 ft.) or more above water or ground, temporary or permanent floor platform, scaffold construction or where otherwise exposed to the possibility of falls hazardous to life or limb, shall be secured by safety belts and life lines. In situations where safety belts and life lines in guarded platforms and scaffolds or temporary floors are not feasible, safety nets shall be provided and installed.
Workmen working in unguarded surface above open pits or tanks, steep slopes, moving machinery and similar locations, or working from unguarded surfaces six (6) meters (20 ft.) or more above water or ground, temporary or permanent floor platform, scaffold construction or where otherwise exposed to the possibility of falls hazardous to life or limb, shall be secured by safety belts and life lines. In situations where safety belts and life lines in guarded platforms and scaffolds or temporary floors are not feasible, safety nets shall be provided and installed.
2) Window washers or cleaners working outside buildings six (6) meters (20 ft.) or more above the ground or other surfaces unless protected from falling by other means, shall use safety belts attached to suitable anchors.
3.) Workmen entering a sewer, flue, duct, or other similarly confined places shall be provided and required to wear safety belts with life lines attached and held by another person stationed at the opening ready to respond to agreed signals.
4.) ![]() Workers who are required to climb and work on top of poles six (6) meters or more shall use safety belts. On top of structures where there is no place to strap a safety belt, a messenger line shall be installed for strapping the safety belt or life line.
Workers who are required to climb and work on top of poles six (6) meters or more shall use safety belts. On top of structures where there is no place to strap a safety belt, a messenger line shall be installed for strapping the safety belt or life line.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Foot Protection
Proper Fit and Use of PPE
![]() Select and use the right kind of footwear for the job you are going to be performing. Footwear should meet or exceed the standards set by ANSI (ANSI
Select and use the right kind of footwear for the job you are going to be performing. Footwear should meet or exceed the standards set by ANSI (ANSI
Z41-1991) Proper fit
Correct protection for job task
Inspect your footwear before you use them
Look for holes and cracks that might leak
Replace footwear that are worn or torn
When working with chemicals
hose your footwear with water to rinse away any chemicals or dirt before removing your footwear
Store footwear in a clean, cool, dry, ventilated area
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
