«The Internet as a tool for teaching and learning English»
Робота присвячена використанню технологій у сучасній школі.
In this work we will discover how an app can make it easy for kids to do research at home with the family in the real world – an app that encourages kids to ask good questions and have the feeling that they can investigate things by themselves.
It will help ensure that they can engage online with government, business and the broader community in a productive and mutually beneficial way. Developing digital citizenship is thus vital to ensure that young people can participate in society online, using digital media to fulfill their civic duty, and that they can take full advantage of the empowering potential of technology.
1
«The Internet as a tool for teaching and learning English»
|
Петренко Яніна Сергіївна, вчитель англійської мови вищої кваліфікаційної категорії,вчитель-методист Височанської спеціалізованої загальноосвітньої школи І-ІІІ ступенів з поглибленим вивченням англійської мови ім. Героя Радянського Союзу О.Л. Пшенички Харківської районної ради Харківської області
|
CONTENTS SUMMARY
|
INTRODUCTION………………………………………………..………………….3 SECTION 1. THEORETICAL BASES OF THE INTERNET USAGE IN EDUCATION…………………………………………………..…………………….5
1.4. Blended Learning……………………………………………………..……..10 SECTION 2. THE IMPLAMENTATION OF THE INTERNET TOOLS IN EDUCATION……………………………………………………………….………11 2.1. Programme eTwinning and Its Role …………………………………………11 2.2. Tools…………………………………………………………………………….13 CONCLUSION………………………………………………………..……………22 REFERENCES……………………………………………………………………..24 APPENDIX ………………………………………………………………………....25
|
INTRODUCTION
The digital shift is transforming almost every aspect of our lives, with changes happening at a pace that is hard to keep up with. Everyone - workers, students, citizens – has to acquire the new skills and capabilities necessary to make full use of the possibilities and opportunities now open to us. Not only is there a need for digital skills for nearly all jobs. Everyone needs at least some basic digital skills in order to live, learn, communicate, and participate in society.
Education has a crucial role to play here. We need young Europeans to have the right competences to enter and stay in the labour market, but we also need them to be engaged, independent citizens. This means that beyond enabling them to become digitally literate, we have a duty to ensure they can rely on a moral compass when navigating the online world.
Nowadays, most of us access online content from many different devices, such as smartphones, tablets and computers. Many of us produce online content too. Either way, the Internet is a fantastic place to learn, play, interact and explore.
Our aim is also to encourage creativity and a positive use of the Internet. This will not only help children and young people develop their digital skills but also empower them to grow and shape their world in a safe, creative way. There is no ‘One Size Fits All’ solution. We should work on flexible solutions and concepts that are appropriate for the age of the child.
A plethora of gaming, educational and interactive apps are available that successfully target children and young people. However, children are also the most vulnerable consumers. We need to be able to protect young users from emerging risks, such as exposure to advertising, excessive online purchasing in virtual worlds, and in-app purchases. Engaging industry across the value chain is central to tackling the growing challenges that are arising as the result of new technology and new user patterns.
All of these contribute to making the Internet a place where children can have positive experiences.
In this work we will discover how an app can make it easy for kids to do research at home with the family in the real world – an app that encourages kids to ask good questions and have the feeling that they can investigate things by themselves.
It will help ensure that they can engage online with government, business and the broader community in a productive and mutually beneficial way. Developing digital citizenship is thus vital to ensure that young people can participate in society online, using digital media to fulfill their civic duty, and that they can take full advantage of the empowering potential of technology.
SECTION 1. THEORTICAL BASES OF THE INTERNET USAGE IN EDUCATION
- Key Competences of XXI Century
What are competences? Competence can be defined as ‘a complex combination of knowledge, skills, understanding, values, attitudes and desire which lead to effective, embodied human action in the world in a particular domain’. Being competent therefore means being able to effectively apply a combination of knowledge, skills and attitudes to successfully react to a situation or solve a problem in the real world.
The term ‘competence’ was originally used in the professional context in France in the 1970s to refer to what employees need beyond qualifications to act effectively in a range of work. In the 1980s, competence-based approaches started to be developed in various countries for vocational education and training. Since then, the concept of competence-based education has been extended to general education, as is explained further below.
Key competences can be expressed and understood in different ways, according to each national context. Competences can be both subject-based as well as transversal in nature. In addition to national definitions and frameworks, various international competence frameworks exist, including the European Union’s Recommendation on Key Competences for Lifelong Learning, the UNESCO framework, Partnerships framework, and others.
The European Framework includes the following 8 Key Competences, which are considered essential for the personal fulfillment and development, active citizenship, social inclusion and employment of all individuals.
1. Communication in the mother tongue
2. Communication in foreign languages
3. Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology
4. Digital competence
5. Learning to learn
6. Social and civic competences
7. Sense of initiative and entrepreneurship
8. Cultural awareness and expression
These key competences are all interdependent, and the emphasis in each case is on critical thinking, creativity, initiative, problem solving, risk assessment, decision taking and constructive management of feelings.
Why is competence-based education needed? The need for students to develop competences at school has increasingly gained importance, and has recently become prominent in education systems worldwide thanks to social and economic motivations, as well as developments in educational research. The need to improve the quality and relevance of the competences which learners acquire before leaving formal education has been widely recognised, particularly in view of Europe’s high youth unemployment. Knowledge and basic skills are necessary, but no longer sufficient to meet the complex requirements of today’s social demands in an ever more competitive global economy.
In an increasingly digital world where functional skills-based professions are in decline, competence oriented education has particular relevance. Educational research, such as John Dewey’s social perspective on learning and constructivist learning theories also emphasise the importance of competence development within a social learning context, where learners are engaged in active learning in real life situations.
How are education systems responding to this need? Most EU countries have introduced the concept of key competences and learning outcomes into their national curricula or official steering documents for compulsory education during the last decade.
1.2. List of the Advantages of Technology in Education
A. Promotes independent learning in students. The internet is a treasure trove of information. Practically anything you need to know can be found online. Although there is a question of the credibility of the source and the data provided, it can still serve as an educational resource for students. Even without assistance from parents and teachers, students can just look up their lessons online. Unlike regular textbooks, electronic books and web-based content are updated in real time, feeding students with the most current information they can get their hands on, helping them become more knowledgeable even outside the classroom setting.
B. Prepares students for the future. From the way technological advancements are going, it is obvious that the future will be digital and technology-focused. If students are well-versed on using technology to collaborate and communicate as early as now, they will not have trouble fitting in, competing and finding jobs in the future. Being familiar with using at least one form of technology at an early age will help them become comfortable using it, and eventually develop other skills necessary to handle other innovative devices and processes.
C. Has the potential to lower textbook and tuition prices. With resources more accessible and in great abundance, the cost of textbooks is likely to decrease. It is also possible that students may no longer need to buy a textbook, if it is converted into digital format. The actual books can stay in the classroom, while the content is saved on a student’s computer. Tuition will also decrease when learning is done online, rather than inside the classroom. By taking out the factors that contribute to a higher tuition fee, such as utility bills and transportation allowance of teachers, the overall cost of education will be lower.
D. Allows teachers to create an exciting way to educate students. Gone are the days when the only tools for teaching are limited to books, a blackboard or whiteboard, and a chalk or markers. With technology integrated to education, teachers can now incorporate images, videos and other graphics when delivering lessons. Specific websites, apps and programs will also enable teachers to vary how they provide instructions. This creates an exciting learning environment and promotes interest in education in general. Other tools available for teachers include Smart Boards (interactive whiteboards), email Skype, and PowerPoint.
E. Encourages development of new teaching methods. Rather than spend an hour or so talking while the students listen, or have them read an entire chapter in silence, teachers and professors now have the option to use advanced teaching methods, such as podcasts, blogs and social media. When working with a particular group or one-on-one, teachers can take advantage of web conferencing technologies other online communication tools. Technology also presents universal tools that enable teachers to educate all types of students, including those who are struggling or have special needs. These include voice recognition, text-to-speech converter, translator, volume control, word prediction software and other assistive technologies.
1.3. List of Disadvantages of Technology in Education
A. Results in a lack of interest in studying. Because everything is now accessible online or through data saved in a computer or mobile devices, students are likely to develop poor studying habits and a lazy attitude towards education. Some of them may even think they can skip school because they can find answers and lessons online. Who needs teachers when you have internet and Google, right?
This can also lead to students forgetting the basics of studying. They would rather rely on computers and the internet, instead of their books and the input from their teachers. Most of them will misspell words because they often use spell checkers. Rather than solve mathematical equations the traditional way, they would seek assistance from computers or look for the answers directly through search engines. When it is time to take the tests in the classroom and without any form of technology, students are likely to fail.
B. Makes students vulnerable to potential pitfalls. While computers prove to be an invaluable educational tool, it can also be a source of problems. This is especially true for students who lack the skills needed to maximize a device’s functionalities. Technical problems and computer malfunctions can cause loss of assignments and other materials, resulting in high levels of stress that students would rather not experience. Difference in internet speeds and a device’s capabilities can also lead to certain difficulties that will de-motivate students. Add to this other things that they will discover online, which are completely unrelated to school and education, and they will be distracted to no end.
C. Negative views on technology. Consumerism has taught us that technologies, from computers to mobile devices, are widely viewed as tools to entertain rather than educate. Textbooks, on the other hand, are seen as tools for learning. So, between a tablet and a textbook, students are likely to gravitate towards learning when reading a book, while they are likely to use a tablet to play games or spend time on social media.
D. Raise instructional challenges. For professors and teachers to stay abreast with technology, they may need to be retrained. Those who have been teaching all their lives using traditional methods may not be very susceptible to the changes being applied. They may even see it as a threat to their job security and shun technology altogether. In fact, a majority of teachers believe that constant use of digital technology is affecting a student’s attention span and his ability to persevere when a challenging task is thrown his way. Although such belief is subjective, scholars, experts and teachers all agree that technology has changed the way students learn.
E. Can diminish overall value of in-person education. Although research on online learning did not establish a direct link to how personal interaction affects a student’s performance, data gathered did show that those who enrolled in online courses have higher chances of failing, dropping out of classes, and are less likely to benefit from them. This may have something to do with the fact that lessons delivered online or through digital resources lack the face-to-face interaction between teacher and student that provides a more personal experience.
Conclusion
Integrating technology in education has its advantages and disadvantages, but proper implementation might help keep the drawbacks to a minimum.
1.4. Blended Learning
The terms "blended learning", "hybrid learning", "technology-mediated instruction", "web-enhanced instruction", and "mixed-mode instruction" are often used interchangeably in research literature. Although the concepts behind blended learning first developed in the 1960s, the formal terminology to describe it did not take its current form until the late 1990s. One of the earliest uses of the term appears in a 1999 press release, in which the Interactive Learning Centers, an Atlanta-based education business, announced a change of name to EPIC Learning. In 2006, the term became more concrete with the publication of the first Handbook of Blended Learning by Bonk and Graham. Graham challenged the breadth and ambiguity of the term's definition, and defined "blended learning systems" as learning systems that "combine face-to-face instruction with computer mediated instruction.
With reference to blended learning in education, it has been defined as: ‘a combination of technology and classroom instruction in a flexible approach to learning that recognises the benefits of delivering some training and assessment online but also uses other modes to make up a complete training programme which can improve learning outcomes and/or save costs’ (Banados, 2006: 534).
So blended learning is an education program (formal or informal) that combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods. It requires the physical presence of both teacher and student, with some element of student control over time, place, path, or pace. While students still attend "brick-and-mortar" schools with a teacher present, face-to-face classroom practices are combined with computer-mediated activities regarding content and delivery. Blended learning is also used in professional development and training settings.
SECTION 2. THE IMPLAMENTATION OF THE INTERNET TOOLS IN EDUCATION
2.1. Programme eTwinning and Its Role
How can teachers develop students’ key competences? The main recommended approach to teaching key competences is through the provision of interactive learning environments in which learners can engage in practical, inquiry-based tasks. These learning environments, which promote collaborative and multidisciplinary learning, are increasingly technology enhanced.
Projectbased learning is a particularly well suited method for the development of pupils’ competences, as several key competences can be addressed simultaneously in a cross-curricular manner.
It is for this reason that eTwinning projects can be a successful channel for the development of pupils’ competences. The eTwinning action is an initiative of the European Commission that aims to encourage European schools to collaborate using Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) by providing the necessary infrastructure (online tools, services, support). Therefore, teachers registered in the eTwinning action are enabled to form partnerships and develop collaborative, pedagogical school projects in any subject area with the sole requirements to employ ICT to develop their project and collaborate with teachers from other European countries (at least two teachers from two different European countries are needed).
The primary workspace for the eTwinning action, is the eTwinning Portal (www.etwinning.net) and it is available in twenty-five languages. Teachers registered in the eTwinning action, also called eTwinners, find each other, communicate, share resources and collaborate through the eTwinning platform.
While project-based learning encourages pupils to be active and responsible for their own learning, activities need to be supported by scaffolding and by explicit instruction from the teacher where relevant. In particular, learners need support to develop their ability to learn independently; the so-called ‘learning to learn’ competence. Schools should consider learners’ social and emotional wellbeing and allow learning to be more self-directed.
Wittgenstein, the great linguistic philosopher wrote “the limits of my language are the limits of my world”. This is all the more important now in a world of quick communication, surface analysis, the three-minute sound bite of information.
Communication in foreign languages broadly shares the main skill dimensions of communication in the mother tongue. It is based on the ability to understand, express and interpret concepts, thoughts, feelings, facts and opinions in both oral and written form (listening, speaking, reading and writing) in an appropriate range of societal and cultural contexts (in education and training, work, home and leisure) according to one’s wants or needs. Communication in foreign languages also calls for skills such as mediation and intercultural understanding. An individual’s level of proficiency will vary between the four dimensions (listening, speaking, reading and writing) and between the different languages, and according to that individual’s social and cultural background, environment, needs and/or interests.
Essential knowledge, skills and attitudes related to this competence: Competence in foreign languages requires knowledge of vocabulary and functional grammar and an awareness of the main types of verbal interaction and registers of language. Knowledge of societal conventions, and the cultural aspect and variability of languages is important. Essential skills for communication in foreign languages consist of the ability to understand spoken messages, to initiate, sustain and conclude conversations and to read, understand and produce texts appropriate to the individual’ needs. Individuals should also be able to use aids appropriately, and also learn languages informally as part of lifelong learning. A positive attitude involves the appreciation of cultural diversity, and an interest and curiosity in languages and intercultural communication.
eTwinning plays its role not only in helping young people develop digital skills, but in promoting fundamental values and citizenship in the classroom. In the anti-radicalisation agenda that the European Commission presented earlier this year, we identified eTwinning as one of the main tools to help promote inclusive education and common values.
Direct contacts between people are crucial in developing mutual respect and intercultural understanding. And teachers are well placed to detect early signs of radicalisation in pupils and help address them. eTwinning projects allow teachers and students faced with similar challenges to share experiences and learn from each other.
eTwinning provides a powerful learning experience, offering students the opportunity to participate in collaborative learning projects. eTwinning projects combine all important elements of digital citizenship: respecting and learning about others through cooperation and problem solving, peer-learning in a safe and flexible online environment and learning about using online tools in a safe and responsible way.
2.2. Tools
The digital society provides opportunities for interacting, learning, working, being.
Everyone has a sense of belonging, as much as everyone needs to feel they belong somewhere. This is especially true for young people, who are shaping their personality traits in adjustment to the group (and society) they belong to.
Participation in the digital domain is no longer a question of “have” or “have not”, as we have seen before, but rather of “can” or “cannot”. If digital participation depends on access and use, it even more so depends on attitudes. Participation has different gradients, from lurking to advocacy. You can participate just by browsing through the net, or you can have a voice (and a strong one).
Young people are prolific producers of digital content: they take and share pictures, videos, multimedia, texts, and opinions. Being producers rather than consumers allows digital citizens to contribute to the landscape of the digital society and to understand it better.
Digital tools and means are, as well, used to advocate for ‘transparency’ in policy making, by allowing citizen to get together in new forms. I am protected – and I protect Citizens are by definition protected by the country they belong to. Protection is also part of the rights that people have when being online. Technologies offer opportunities – and risk. While risk does not inevitably imply harm, harm can be detrimental to the enjoyment of digital citizenship.
Therefore, policy makers, educators, parents must implement specific strategies to ensure children’s rights to protection, without curtailing their rights to participation.As in the real world, certain protective measures need to be established. Children and young people should also have room to experiment and learn from their mistakes, without every click or like being tracked or traced. They should be encouraged to respect and safeguard the right of others.
Web 2.0 is the current state of online technology as it compares to the early days of the Web, characterized by greater user interactivity and collaboration, more pervasive network connectivity and enhanced communication channels.
One of the most significant differences between Web 2.0 and the traditional World Wide Web (WWW, retroactively referred to as Web 1.0) is greater collaboration among Internet users, content providers and enterprises. Originally, data was posted on Web sites, and users simply viewed or downloaded the content.
Increasingly, users have more input into the nature and scope of Web content and in some cases exert real-time control over it.
Elements of Web 2.0
- Wikis: Websites that enable users to contribute, collaborate and edit site content. Wikipedia is one of the oldest and best-known wiki-based sites.
- The increasing prevalence of Software as a Service (SaaS), web apps and cloud computing rather than locally-installed programs and services.
- Mobile computing, also known as nomadicity, the trend toward users connecting from wherever they may be. That trend is enabled by the proliferation of smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices in conjunction with readily accessible Wi-Fi networks.
- Mash-ups: Web pages or applications that integrate complementary elements from two or more sources.
- Social networking: The practice of expanding the number of one's business and/or social contacts by making connections through individuals. Social networking sites include Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Google+.
- Collaborative efforts based on the ability to reach large numbers of participants and their collective resources,suchas crowdsourcing, crowdfunding and crowdsource testing.
- User-generated content (UGC): Writing, images, audio and video content -- among other possibilities -- made freely available online by the individuals who create it.
- Unified communications (UC): The integration of multiple forms of call and multimedia/cross-media message-management functions controlled by an individual user for both business and social purposes.
- Social curation: The collaborative sharing of content organized around one or more particular themes or topics. Social content curation sites include Reddit, Digg,Pinterest and Instagram.
So let us learn how to use 2.0 web tools effectively through eTwinning projects.
- Kahoot! is a free game-based learning platform, as educational technology.

Kahoot! is typically used for formative assessment, to monitor each student’s progress towards learning objectives, identify strengths and weaknesses, and to identify areas where the students would benefit from more one-to-one teaching, more challenging learning opportunities, or a review of foundational knowledge for that subject.
More experienced users also integrate kahoots into their curriculum to introduce new topics, increase retention of new facts, revise before exams, challenge classrooms around the world, survey opinions, gather insights, facilitate discussion, or to reward and re-energize learners.Kahoot! is designed for social learning, with learners gathered around a common screen. In a typical classroom environment, this will be a smartscreen, interactive whiteboard, or a computer monitor.Influenced by the "bring your own device" trend, Kahoot! aims to support a wide range of web browsers and mobile devices through its web interface, including Android 4.0 or later and all modern web browsers.
The Kahoot! pedagogy is based on creating a trusted learning space, encouraging a loop from "learner to leader".
In a classroom environment, the typical "learners to leaders" loop is normally as follows:
- The teacher introduces a topic using a kahoot designed to prompt debate, critical thinking and active learning. He or she normally supplements the kahoot with instructional images and video.
- Once the leader or teacher has introduced the topic, they play a kahoot designed for formative assessment, to assess and improve upon students' understanding of the topic.
- The teacher leads the class in other activities, discussions and related quizzes to consolidate students' knowledge. In some cases the class may play the same quiz multiple times in "Ghost Mode" to reinforce learning through repetition.
- The teacher then asks students to create their own quizzes on the same or related subject.
- Students research, build up knowledge and gather or create relevant content, and then create their own quizzes using this content.
- The students, or groups of students, are then empowered to become leaders as they play their quiz back to classmates.
- Teachers can assess students' understanding and approach based on the quality of their content, structure of the kahoot and how they have explained the correct answers to their peers.
- Animoto is a cloud-based video creation service that produces video from photos, video clips, and music into video slideshows.
- Kizoa can be an incredibly powerful tool for both students and teachers.Online Video Maker using Photos, Videos and Music, Add Text, Special Effects, and Transitions. Share via Email, Blogs, Facebook, and Youtube, Burn onto DVD or download as a video file. Everyone who uses Kizoa for educational purposes has the opportunity to benefit from a free lifetime Premium VIDEO membership.
They believe that technology is essential to learning and that this tool should be accessible to everybody regardless of what level of education you are in.
http://www.kizoa.com
- Glogster
Glogster is a cloud-based (SaaS) platform for presentation and interactive learning. It allows users to mix all kinds of media on a virtual canvas to create multimedia posters, and access a library of engaging educational content created by students and educators worldwide. Glogster encourages interactive, collaborative education and digital literacy.
The Glogpedia library is a constantly-growing collection of over 21,000 top-quality glogs, hand-picked based for accuracy and presentation, and categorized by 80 subjects under 9 disciplines according to the currciculum. Glogster users can nominate glogs to be considered for inclusion in the library by clicking a button at the top of any public glog.
Glogpedia content is intended for use in place of or alongside conventional curriculum texts, for example as interactive research material or to engage learners with a new topic. Users can also save editable copies of glogs to their own dashboards, and adapt them to their own needs.
5. VoiceThread
VoiceThread is a pre-K through 12th grade network where students develop the “Four Cs” that will underpin a lifetime of learning: critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and creativity.
With VoiceThread, group conversations are collected and shared in one place from anywhere in the world. All with no software to install. A VoiceThread is a collaborative, multimedia slide show that holds images, documents, and videos and allows people to navigate slides and leave comments in 5 ways - using voice through a Facebook Fan Page (with a mic or telephone), text, audio file, or video (via a webcam). Share a VoiceThread with friends, students, and colleagues for them to record comments too. Users can doodle while commenting, use multiple identities, and pick which comments are shown through moderation. VoiceThreads can even be embedded to show and receive comments on other websites and exported to MP3 players or DVDs to play as archival movies.

6. Padlet is an Internet application that allows people to express their thoughts on a common topic easily. It works like an online sheet of paper where people can put any content (e.g. images, videos, documents, text) anywhere on the page, together with anyone, from any device. Think of it like a multimedia friendly, free-form, real-time wiki.

7.QR CODE/ QR READER
http://goqr.me
QR codes are a great way to interact with your clients, students or visitors. They provide a really compact way of sharing information or educating your customers or visitors.
One of the advantages of using QR codes for these types of situations and applications is that the cost of creating of content is minimal, and the cost of sharing that information is negligible, since content can be hosted on free sites like YouTube or Facebook.
8. TAXEDO
http://www.tagxedo.com
Tagxedo turns words -- famous speeches, news articles, slogans and themes, even your love letters -- into a visually stunning word cloud, words individually sized appropriately to highlight the frequencies of occurrence within the body of text.

CONCLUSION
In the world of this 21st Century, the literacy of the digital age cannot be neglected. With the command of this literacy comes the confidence and empowerment. We can no longer divide the happening of the digital and physical worlds they are intertwined at every level and what happens in one has enormous effects in what happens in the other. Which is the real world? The digital cannot be separated from the physical and to try to do so is to create a false division between the two.
A major advantage of the Internet is the ability to access all types of information from library resources all over the world, including magazines, books, newspapers and journal publications, instantaneously. This information increases the learning potential by providing students with the latest information. It also expands the resources of a smaller library tremendously. Students using search engines can find information quicker and more tailored to their specific needs.
As a disadvantage, educators may consider this information overload. With all of the information available to students, they may find it difficult to choose which information is most important to a topic and also when to stop looking. In addition, the validity of Internet sources varies considerably from website to website, which means students can very easily acquire inaccurate or out-dated information online.
When it was first invented, the Internet was merely a place to store and locate information. It was static and non-interactive in that website visitors could only read content.
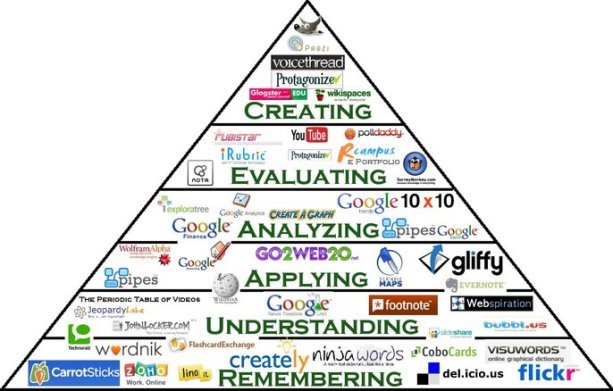
Web 2.0 is about revolutionary new ways of creating, collaborating, editing and sharing user-generated content online. It's also about ease of use. There's no need to download, and teachers and students can master many of these tools in minutes. Technology has never been easier or more accessible to all.
What’s the benefit of using Web 2.0 tools in teaching and learning? Because Web 2.0 tools allow users to collaborate to generate/upload content, it is an excellent means to engage learners and help foster a community of learning in your course.
In summary, when selecting an appropriate Web 2.0 tool, ask yourselves these questions: Does the tool help learners achieve the objectives? Does it enhance their learning experience? Does it engage all of them and allow learner-learner interaction? Does it require extensive user-training? What is the cost of the tool? How likely is it to disappear in a semester or two? As long as you consider the above factors, Web 2.0 tools can be a useful addition to your course design.
Розглянуто проблему використання web 2.0 технологій у освітньому процесі. Зазначено, що застосування на заняттях та в позакласній діяльності розширює можливості навчального процесу, забезпечує нові шляхи подання інформації, урізноманітнює шляхи для випробовування власних ідей та проектів. Наведено приклади технологій, що сприяють формуванню життєвих навичок XXI століття.
Автор Я.С. Петренко
REFERENCES
- Alexander, B.( 2006) A New Wave of Innovation for Teaching and learning.
- Bonk, Curtis J. & Graham, Charles R. (2004) The Handbook of Blended Learning: Global Perspectives, Local Designs.
- Byram, M.(1989) Cultural studies and Foreign Language Education. Cleveton, Multilingual Matters.
- Common European Framework of Reference for languages: Learning, teaching,assessment. Strasbourg.Council of Europe.(2001).
- Do Web 2.0 tools really open the door to learning? Practices, perceptions and profiles of 11–16 year old students. (2009) Learning, Media and Technology, Volume 34, Issue 2: Learning and social software – researching the realities.
- European language portfolio: proposals for development. Strasbourg.Council of Europe. (1997).
- Language learning for European citizenship: final report of the Project. Council of Europe.(1997).
- Laver, J &Hutcheson, S. (1972) Communication in face-to-face interaction. Harmondsworth, Penquin.
- Malmberg, P. (1989) Towards a better language teaching: a presentation of the Council of Europe’s language projects. Uppsala, University of Uppsala.
- Tomlinson, Brian & Whittaker, Claire. (2013).Blended Learning in English.Language Teaching: Course Design and Implementation. London. British Council.
APPENDIX
50 2.0 Web Tool Sites for Education
19 Pencils - 19Pencils is the easiest way for teachers to discover, share and manage web-based educational content with students. A teacher can create quizzes, websites, track students, and more.
ACMI Generator - This is a great site for older students for digital storytelling and creating a storyboard scene with a script.
Animoto - Create wonderful looking slideshows that includes, video, images, music, and more.
Aviary Education - A safe private environment to use Aviary's suite of online tools for: audio, video, and image editing.
Boom Writer - BoomWriter is a supremely engaging creative writing website that has students reading, writing and assessing content in ways they’ve never done before!
Classtell - A nice site for teachers to create an educational website.
Diigo - Social bookmarking for teachers where they can create free student accounts.
Dropbox - A great way to share and collaborate on documents on a number of different electronic devices.
Edmodo - A wonderful safe/secure learning environment for teachers and students. A nice all-in-one solution for education.
Educaplay - A excellent way to create interactive multimedia educational activities.
Every1Speaks - A learning platform where students learn through collaborative enquiry-based learning.
Gaggle - A excellent suite of online learning tools for filtered: emailing, messaging, forums, and more.
Glogster - Creating collaborative and interactive posters in this safe environment. A wonderful and very popular web 2.0 tool.
GoAnimate - A terrific way to create custom animations with an educational portal.
Google Apps for Education - Does it really get much better than this?
Gnowledge - A wonderful site to create collaborative online quizzes, share resources, view others quizzes, and more. Excellent tech support and tutorial videos as well.
Grockit Answers - A great teaching tool to create a Q/A session for any YouTube video.
Kidblog - A fantastic way to create a safe environment for students to blog in. Everything is controlled by the teacher as a moderator.
Kerpoof - Lots of educational activities can be found here such as: make a movie, draw a picture, and more.
Kubbu - A free site for teachers to create games, quizzes, or crosswords and then share them with students and view/analyze their results.
Little Bird Tales - A wonderful free site for digital storytelling that allows kids to record and narrate their story.
Live Binders - Is an excellent site for creating an online binder to collect and share resources with others.
MentorMob - One of my favorite new sites for curating the web into learning "playlists." This is an innovative way to teach a lesson, unit, or any given topic.
Mixbook - A great site for digital storytelling in a safe environment. Educators get a discount on printed books.
Musicshake - Legal, copyright, free music for every student in your school - created by students, right from a browser.
Myths & Legends - One of the best free sites around for digital storytelling in a safe environment with lots of characters, themes, and objects to choose from.
PhotoPeach - An excellent site for creating slideshows and creating and managing student accounts.
PikiFriends - A fun safe environment for online pen pals for middle school and high school students.
Pixton - A great way to motivate students by creating digital stories using this comic creator.
PresentationTube - A nice windows app for creating presentations out of PowerPoint slides.
Prezi - A excellent site for creating zooming slideshows and presentations.
Primary Access - A free suite of online tools for students and teachers to create digital movies, storyboards, and other activities.
Primary Wall - A real-time collaboration tool that allows students and teachers to create a page of online sticky notes. Great for mind mapping and brainstorming!
Skype in the Classroom - A great collaboration tool for classrooms to video or audio chat with other educators and students.
SideVibe - Turn bookmarked web content into blended classroom lessons.
SlideRocket - All you need is a Google Apps account to use this free tool to creating stunning presentations.
SpellingCity - One of the best sites around for teaching and learning Spelling and Vocabulary. A very user-friendly and engaging site to use.
Storybird - A fantastic site to inspire students to read & write through the use of digital storytelling.
StoryJumper - A great site for digital storytelling where students can incorporate their own art, publish online, share with others, or order a print copy.
SymbalooEDU - A wonderful way to organize educational sites into one location for students.
Triptico - A great free tool for teachers to help create, share, and edit interactive lessons.
ToonDoo Spaces - Create a private and safe environment for digital storytelling through the use of an online comic.
VoiceThread - One of the most popular web 2.0 sites around for creating dynamic and interactive slideshows and presentations. Also, another great tool for digital storytelling.
Webspiration - From the creators of Inspiration comes this excellent web portal for creating mind maps, brainstorms, outlines, and more.
Weebly - Create a free class/student blog or website.
Wolfram Alpha - There is now an educational portal for Wolfram's computational search engine. This portal contains dynamic textbooks, lesson plans, widgets, interactives, and more.
Yacapaca - A nice free all-in-one solution for schools for creating quizzes, surveys, assessments, and more.
YouTube for Schools - Access 1000s of YouTube videos in a controlled environment without having to worry about comments.
Zimmer Twins - A great site for digital storytelling with an educational portal.
Zoho Wiki - A nice site for educators to create online interactive content.
2.0 Web Tools II
Communication/Collaboration:
Cobblearning: free Edublogs for teacher’s class blog
Edmodo – Vitural classroom…. Powerful tool!!! Collaborate, communicate, research, assess, share, etc. with students and teachers
- Remind – Reminders are sent to parents and students.
- Portfoliyo – Send parents reminders from a computer.
- WikiSpaces – Place to share resources and students can publish work
- Smore: online flyers… that can be shared on the web. Make a QR code for an event. Very professional looking and easy to use.- Voki - Jazz up a PBL Task Page, Class Blog &/or Web page. (Personalized speaking avatars)
- Tackk - online creation tool... seamless login via Edmodo
- Canva - Great visual tool for logos, invitations, cards, etc.
- Linoit.com – A place to collaboratively brainstorm and post learning.
- Padlet (was called Wallwisher) – Similar to Linoit. - - It is the digital example of sticky notes on a wall. SO many ways to use with students.
- Stormboard - similar to Padlet... more for MS/HS
- Google Docs – Forms, Spreadsheets, documents, presentation… great place to store and collaborate with others
- OneDrive - Online Microsoft docs - Word, Excel, PowerPoint, OneNote
- Blendspace AKA Edcanvas Example of How to Use for a Flipped Classroom Example for Reading
- Thinglink Math Example
- Weebly – free Web sites
- Spicynodes - Webbing and sharing information
- Stoodle - collaboration tool
- Mozilla's Popcorn Maker - Popcorn Maker helps you easily remix web video, audio and images into cool mashups that you can embed on other websites. Drag and drop content from the web, then add your own comments and links —all within your browser. Popcorn Maker videos are dynamic, full of links and unique with every view. How to video
- Kaizena - feedback tool for teachers and students
- Dash81 - communication and collaboration tool... similar to TodaysMeet
- PADLET
Sign-ups and Lists:
Online Storage: Stop using a flash drive!
Edmodo - Library Feature
Skill Practice/ Assessment Tools:
SkillsTutor - Online homework, one-on-one tutoring, pre-tests, test prep, differentiation, remediation…. Free to CCSD teachers.
ScootPad – Online homework…. Save trees! Practice and learn CCGPS for students… set up classs and keep up with student productivity and progress.
Socrative – (See below in BYOD)
RCampus – Rubric Maker
JogNog Quick Quizzes – How to blog post
Bubblr – Interactice quizzes using YouTube clips (Background information)
Classtools.net - Connect Four - review game
Five FAST Formative Assessment Tools
Team Maker
BouncyBalls - - classroom management - balls bounce based on level of noise in the classroom.
Teaching Tools:
LearnZillion – ELA and Math videos for instructions, remediation, enrichment, homework help, etc.
Discovery Learning AKA United Streaming
Brightstorm – Time-saving homework helpful videos
VirtualNerd - Math instructional Videos
Math Playground – Math videos
Study Jam – Science and Math videos
Brain Pop (Subscription per school)
** Researched Based Tools by Subject
Brainingcamp – Math videos $
Narrable - Everything has a story.
Curriculet - Interactive Reading and research tool
NEWSELA - reading and current events
Read Write Think - Lots of interactive tools for students to use and teachers can model.
Math Antics - math videos, free options
Shmoop YouTube Channel - Math instructional videos
ClassBadges - - reward students with badges (Edmodo can give badges too.)
- Share My Lesson (The American Federation of Teachers’ new online community Share My Lesson offers teachers free access to the resources and knowledge of their peers across the country. Featured are nearly 260,000 teaching resources, a monthly resource calendar, free games and activities mapped to the Common Core and discussion forums. Teaching resources are divided by grade, subject and rating and include activities, puzzles, games, lesson plans, posters, assessments and more.)
Word Clouds: (125 Ways to Use in a Classroom) (170 Ways to Use)
Wordle – word clouds
Tagxedo – Shape, word cloud
You Are Words – student picture with descriptive words
Flashcards/ Vocabulary Practice (Frayer Model)
FlipQuiz (Review game)
More links to help with vocabulary development
Behavior Management:
Group and Name Gene
Flipped/ BYOD Classroom:
Socrative – formative assessment during instruction – students use their device to submit information Example: Teacher Blog
Also look under the titles Teaching Tools and Screencasting on this page.
Screencasting/ Tutorial Creation
Jing * download required
Assessment
Socrative [Socrative 2.0 Overview Video]
Snapshot in Edmodo
iPad Resources (Check Out iPad Resource Page in this web site)
NearPod app
Teach – Knowmia
EXTRA LINKS:
101 Web 2.0 Tools for Teachers
10 Tools for the 21st Century Teacher
Web 2.0 Tools for Students and Teachers
David Kapuler’s Bucket List of Online Education Resources
Web 2.0 Tools for MATH Teachers
Web 2.0 for Social Studies Teachers
Five Online Tools for Lesson Planning
2013 Free Education Technology Resources eBook
Researched Based Tools by Subject
Classroom 2.0 – 100 Tools for Teachers
Web 2.0 Tools for a BYOT/D Classroom
Blooms App list - Google Sheet
Sites that are helpful for Educators


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
