Методичні розробки 1курс English for Information Technology
Практичне заняття № 1,2
Мета заняття: Ознайомити з новою граматичною категорією злічувальних та незлічувальних іменників та їх використання з how much, how many, a few, a little, a lot of, some. Навчити використовувати новий лексико-граматичний матеріал у монологічному мовлені. Розвивати навички читання, сприйняття на слух, говоріння та письма за темою: E-commerce.
Час заняття: 180 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
- Function : E-commerce companies, features and description
- Language : talking about quantity: how much, how many? A few, a little
- Vocabulary : practice saying business types, B2B, B2C, C2C, e commerce
1. Warm-up activity:
Organize the class in pairs. Ask students to give names of different types of data storage, then ask them to recommend suitable kind of data storage to family, company or organization (revision task of unit 4.3, ex.2 p.32):
- What kind of data storage would you recommend to small business? - I’d recommend a hard drive. - I would not recommend magnetic tape.
2. Speaking:
Use three photos from the textbook as a prompt for a short discussion. Work in pairs and let them speak about advantages and disadvantages of on-line shopping. Ask them to compare the online price of a product. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). ex.1.p. 35)
Do not get involved in the discussion of advantages and disadvantages of online shopping. Then do ex.8, practice and consolidate the lexical material.
3.Listening:
Give students the time to read the sentences before listening. (track 29)
Ask them to read the script on p.74 and listen again. Point out the use of
- Do you think? - I do not think. To ask or give opinions.
Note that will is used for predictions. Refer to page 40 where will is used for plans. Practice using in pairs.
4. Language:
Point out the use of much, a little from exercise 2. Ask students to demonstrate example sentences to demonstrate meaning (ex.2. English for IT, Part 1).
The focus is on countable and uncountable nouns. Ask students to do the exercise on their own and then compare their answers in pairs (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). p.37, ex.3.)
Keys: (1 A lot of, many 2 Some 3 much 4 a lot of 5 a little)( from TB).
5.Listening:
(Track 30) Ask students to listen to just phrases first. Point out to the syllables in English (not a lot of time, only a little money, a few computers).
Make sure stress the words and syllables correctly.
6. Vocabulary:
Match the types of business in the box to the correct column (ex.6, English for IT, Part 1). When reviewing the answers point out where we commonly use the acronyms B2B, B2C,C2C. Ask students to practice them in pairs.
Explain about the M-commerce which is new but growing. In some countries, for example, you can buy train or airline tickets, ringtones, music and movies, as well as ‘on-the-go services’ (for example, information about tourist sites, restaurants and the location of toilets or the nearest police station).
Let them suggest the real life situations with the examples of commonly used acronyms B2B, B2C, C2C.
Writing:
Ask students to write on the topic:
-What are the advantages and disadvantages of shopping online?
Let them use the table to make notes and then make sentences. (ex.8). Go round the class and check students’ work.
Ask students to be ready to present their ideas to the group.
ADITIONAL PRACTICE:
Speaking: Inform the students that this activity provides them a chance to compare their ideas about advantages and disadvantages of shopping online. Ask them to do it in small groups.
Check how well they use the comparative form of adjective which they saw in Unit 2 (gaps. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). Vocational English Course Book1.)
Watch video on the U-Tube about E-commerce. Give your comments and opinions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxSDHBdsWqA&t=61s7.
Практичне заняття № 2
Tема: E-commerce features
Мета заняття: Ознайомити студентів з лексичними одиницями сполучних слів (linking words) та використовувати їх для зв’язаного мовлення. Розвивати навички на вміння читання та сприйняття на слух англомовного тексту з використанням лексично-граматичного матеріалу юніту за темою E-commerce features.
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1.Function : Talking about e-commerce features
- Language : Practicing linking words
- Vocabulary : practice students’ understanding of the meanings of the words: account, check out, debit/credit, card, order.
Основна частина
1. Warm-up activity:
Listen and repeat these phrases:
- open an account 2 go to the checkout 3 put an item in the basket 4 browse the website 5 choose an item 6 check the order.
Ask students to use them to describe the steps in buying product or service.
2.Speaking:
Ask students to make a list of the features of the website in small groups. Features include: a system for making purchases including:
- a basket where you put your chosen products),
- information about products, including the ability to look inside the book and read a sample, price and delivery times, stock situation (in stock, out of stock and quantity of stock),
- advertisements for other related products both at the top and at the bottom, and a request for customer feedback.
Then ask them to do the activity at their choice using the phrases from ex.1. Make sure they use the sequencing words firstly, secondly, than, later. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). Vocational English Course Book1, p.38, ex.1.)
3. Vocabulary:
Go through the 8 sentences to make sure that students understand the meaning of the following words: account, check-out, credit/debit card, order, shopping cart. Then ask students to do the activity on their own before comparing answers in pairs ( Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). Vocational English Course Book1, p.39, ex.6.)
Match the first part of the sentences (1-8) to the second one (a-f).
Keys: (2 a 3 f 4 g 5 c 6 b 7 h 8 d ) (from TB)
4.Reading:
Ask students to read quickly and check understanding the key new vocabulary reach, set up, customer, interface, reliable. Then ask them to complete the text with the missing words. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). Vocational English Course Book1, p.39, ex.5.)
Keys: (1 so 2 but 3 and 4 or) (From TB)
5. Language
Go through the example sentences with students to make sure they understand the differences in meaning between them. Ask students to make example sentences using and, but, so and or to show that they understand their meaning.
They can do this in the context of their work or studies (for example):
- I’m studying English but not Chinese. I’m studying so I can get a job.
- I’m working on Wednesday and Thursday but not on Friday.
- I’m working on Saturday so I can finish the project.)
6. Speaking:
Ask students to go to an e-commerce website they like and talk about it.
Suggested answers :
- I like the Amazon website. It has a lot of products but I think it is easy to find things.
- You can buy books, CDs or videos. I like music, so I use it a lot.
- I often download music but I don’t buy CDs.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
Put students in small groups and ask them to design an e-commerce website for a product or service which interests them.
For example, it could be for leisure or recreational facilities where they live, or second-hand goods. They can do this either on paper or on a computer. They could then present their website to another group.
Watch video and learn more about E-Commerce features. Share your opinion and ideas with a partner. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ADurpo5VX8
Практичне заняття № 3
Tема: Transaction security
Мета заняття: Ознайомити студентів з граматичною конструкцією майбутнього часу та навчити використовувати її для монологічного та діалогічного мовлення та письма. Розвивати навички на вміння читання та сприйняття на слух англомовного тексту з використанням лексично-граматичного матеріалу заняття за темою Transaction security.
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина. Making a roll-call in the group
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
- Function : transection security: dealing with the threats. Discussing potential threats.
- Language : Future: will + Infinitive talking about the plans for the future
- Vocabulary : reading emails and trying to deal with the vocabulary queries.
Основна частина
1. Warm-up activity:
Work in small groups. Discuss what are the potential security threats to online shopping? Share your ideas with the group.
2.Reading:
Before students try to answer the questions, give them two or three minutes to read through the email.
Ask them to read the email, and underline the words used to express security threats. Deal with any vocabulary queries and ask students to answer the questions in pairs.
Keys: (1 four 2 a firewall 3 the web application protection firewall (WAF) 4 the secure socket layer (SSL) 5 password leaks 6 encrypted backup). (From TB). (English for IT, Part 1, ex.2, p.40).
3.Speaking:
A. Work in small groups. Talk about your school, college or organization’s plans or your plans for the future. Ask and answer each other questions:
Example: - We will open a new office in Baku.
-When will you open it?
- Next year.
B. Ask students to do this activity in pairs and then to check their answers with another pair.
4. Writing:
Ask students to use the information in the completed diagram in Exercise 5 and the email in Exercise 2 for this activity. Ask them to prepare their recommendations in pairs and then to present them to other pairs or to the whole class. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). Vocational English Course Book1, p.41, ex.6.)
Suggested answer :
- We will set up a network with a firewall and routers to restrict the inbound traffic. We will give limited access to WAN and external email and we will give unlimited access to LAN, internal email and messenger to all users.
- We will install an application that restricts access to and from the internet. We will set up backup solutions for the company database. Finally, we will install an application to prevent the storage of unauthorised files on.
5.Speaking:
Give students the following task:
- You are setting a new computer workstation with a network installation. Your client wants to use the set up for online purchases and bank dealings securely. Talk about what security solutions you will install. Present your solutions to the group.
ADDIOTNAL PRACTICE
Use the Interactive Glossary, Section 1- TRANSACTION SECURITY (in the English for IT. See Supplement). Ask students to read the definitions of new terms and examples of their derivatives. Ask them to translate these definitions. Let them make five sentences using new glossary.
Ask students to watch the video and learn more about the importance of transactions security.
Video: Security, identity and data integrity are of growing concern, especially when it comes to online transactions and payments. Find out more about transaction security. Share your ideas and acquired knowledge with a partner.
https://www.globalvoicegroup.com/online-transaction-security-video/
Практичне заняття № 4,5
Тема заняття: Online transactions та Business matters
Мета заняття: закріпити лексичний матеріал юніту та заохотити використання нових слів у монологічному та діалогічному мовленні. Розвивати навички сприйняття на слух, говоріння та письма з використанням лексично-граматичного матеріалу за темою Online transactions.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина. Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
- Function : making online presence for clients
- Language : practicing phrases to organize ideas in a presentation
- Vocabulary : preparing proposal template for online presence
Основна частина
1. Warm-up activity:
Before reading, check if the students know the meaning of the words in the box (p.42. English for IT, Part 1). Practice speaking.
2. Vocabulary:
A. Draw students attention to useful phrases. Tell them they are important for organizing ideas in a presentation. Go through the phrases one by one and play particular attention to intonation and word stress. Ask students to repeat phrases.
B. Then ask them to read the dialogue and compete the sentences. Go round the class and deal with questions individually. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). Vocational English Course Book1, p.42, ex1)
Keys: (1 completes 2 First 3 web 4 payment 5 gateway 6 bank 7 rejection 8 confirmation 9 customer 10 accounts) (English for IT, TB).
3. Listening: (Track 33)
Play the recording so students can check their answers.
4. .Speaking:
Complete the flowchart of the online purchasing process. Students will need to refer to the dialogue in Exercise 1 to do this activity. Encourage them to write short notes and not full sentences
For example: customer places order, not The customer will place an order.
Ask students to compare their answers with a partner before explaining them to a different partner.
Use these phrases:
-customer registers and opens account; customer places order;
seller’s server confirms availability; seller’s server sends a response;
customer checks out and completes the payment instruction;
payment gateway confirms customer’s ability to pay;
customer receives order confirmation.
Then explain it to your partner. (ex.2 p.42. English for IT, Part 1).
5. Speaking:
A. Read through the rubric and make sure students understand the context. Tell them that they are going to present a plan for an e-commerce solution for Document Ltd. (English for IT, Part 1, p.43)
B. Put students in small groups and ask them to discuss the five questions. These are all open questions and students will need to use their own ideas to answer them. Ask them to make notes about their ideas in the proposal template.
These questions will help you:
- What type of E-commerce will Document Ltd offer?
- What E-commerce technologies will Document Ltd use to attract customers?
- What security solutions will the company set up in order to protect both the customer and the company?
- What tools and features will the company website have?
- How will the customer complete transactions
6. Writing:
Prepare and deliver a presentation for the marketing director of Document Ltd.
- Draw students’ attention to the useful phrases. Tell them that the phrases are important for organising ideas in a presentation.
- Go through the phrases one by one and drill them, paying particular attention to intonation and word stress.
- Try to make students as comfortable as possible using the phrases so that they will be more likely to use them in their own presentations. Note that going to and will are used to talk about future plans.
ADITIONAL PRACTICE
Speaking:
- Encourage students to use the phrases from the Language section in their presentations. Give them a time limit of two to three minutes. If time is short, they can do the activity in small groups. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (1). Vocational English Course Book1, ex.2 p.43).
Watch video about online transaction process. Share your ideas with a partner
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ADurpo5VX8
Unit 8 book1
IT security and safety Практичне заняття № 1
Тема: Security solutions
Мета заняття:
Ознайомити студентів з використанням граматичних конструкцій для вираження можливості в теперішньому та майбутньому. Розвивати вміння роботи в парах, вести групову бесіду. Сформувати лексичний мінімум для спілкування та обговорення за темою "Security solutions".
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття:
Ознайомлювальна частина.
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Talking about security threats and solutions.
2. Language: Expressing possibility (You may have a virus on the computer).
3. Vocabulary: Types of security threats. Security system.
Основна частина:
1. Warm-up activity:
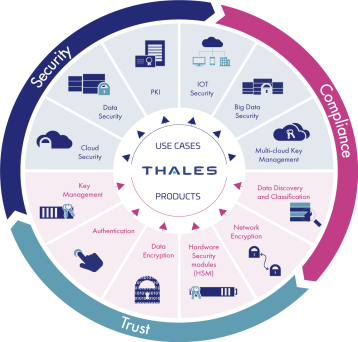
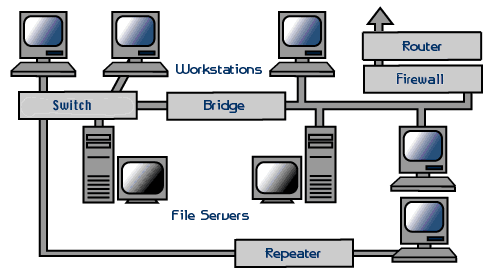
Fig.1 Security solutions [1]
A.: In pairs, students look at Fig.1 and try to give a short description for each segment, and then in group discuss their assumptions.
B.: Answer the questions.
1. Which popular viruses do you know?
2. Which security app do you use?
3. Name three popular security solutions you use?
4. What kind of viruses do you know?
5. Have you ever got the virus? How did you deal with it?
6. What can you say about:
worms, trojans, a browser hijacker, piggybacking?
7. What do you use to protect your computer from cyber attacks?
2. Speaking:
Activity is done with the closed books. Students suggest as many terms as they can about security threats and attacks.
In addition to the terms in the reading text, students may suggest some of the following:
zombies (a computer connected to a network that has been compromised by a hacker, a virus or a Trojan);
phishing (type of social engineering attack often used to steal user data);
viral websites (a website receiving an abnormally large amount of web traffic); bluesnarfing (a type of hacking attack that uses a Bluetooth connection to gain access and steal data from a wireless device).
3. Reading: Pre-teach: before reading explain the meaning of the following words: malicious, infect, spread, replace, gain unauthorized access and commercials.
Then go through the eight descriptions to check that students understand them and then label the diagram in Activity 2 on page 60.
Keys: 1 – virus, 2 – spyware, 3 – worm, 4 – hacker, 5 – browser hijacker, 6 – malware attack, 7 – adware, 8 – Trojan.
4. Speaking 2: Ask students to talk about stories of computer attacks they have heard from friends or read about in newspapers (using the terms from Activities 1 and 2).
Pay their attention to using Present Perfect when talking about experience (e.g. I`ve had a virus on my laptop).
If students have no experience about computer attack, you may offer them to surf the Internet and find the information about famous cyber attacks, make some notes and discuss the found information in group.
5. Speaking 3: Work in groups of three or four: discuss what can be done to stop the problems, mentioned in the previous Activity.
In order to help students to formulate solutions the following questions may be asked:
1. Should you download software from a non-verified source?
2. Is it necessary to check the system on a regular basis?
3. Do you need to make sure that your antivirus is updated daily?
4. Is it safe to buy things online through unknown websites?
5. Is it important to scan the incoming email for malware?
Ask students to give full answers, not just Yes or No.
6. Vocabulary1: Before doing the matching activity ask students it they can provide the explanations of the given terms themselves.
After checking the answers, go through the words and phrases to practise the stressed syllables. (1- firewall, 2 – antivirus software, 3- authentification, 4- username, password and biometric scanning, 5 - encryption).
Keys:2a, 3c, 4b, 5d.
7. Listening 1: Play the recording straight through once to give students the opportunity to get a general understanding of the conversation. Ask them what Ludek`s problem is (His laptop is not working), then play the recording again.
If necessary stop the recording in the middle, so the students could make notes and write the answers:
1. Because nothing seems to work.
2. Because he hasn`t backed it up.
3. He thinks the computer has (spyware or some other) malware on it.
4. Because an antivirus program may not catch everything.
5. Because it will protect the computer from hackers and piggybackers.
6. He will scan Ludek`s system with his anti-spyware software.
Ask students to go to page 77 so they can read through the dialogue while listening a third time. As revision, ask them to underline the ways Ales gives advice (You should install a good spyware doctor program. And why don`t you protect your WLAN access with a password).
8. Using the language 1: Ask students: How we can express possibility in English? Then give them an explanation as follows:
We use may and might to say that something is possible, but not certain:
They may come by car. (= Maybe they will come by car.)
They might be at home. (= Maybe they are at home.)
Possibility in the Present and in Future
We can use both may and might to express a possibility or make a prediction. For example,
Tom might win this game. He’s been playing very well recently.
We may go out later. I’m not sure.
Do you think the company might hire more people next year?
There is a small difference in the level of probability. May usually expresses a 50% possibility, while an action with might normally means a slightly lower possibility, e.g. 40%. For example,
It may rain later on. We’d better take an umbrella. (50% probable)
It might rain later on, but I don’t think it will. (40% probable)
Might is also a bit more informal than may and is more common in spoken English. [2]
Ask students to make up 5 sentences using may/might, considering the security safety topic.
9. Speaking 4: Tell students that this discussion reviews the use of should for asking for and giving advice and also gives them the opportunity to use may and might in the context of protecting their computers.
Students work in pairs and practise giving advice to a non-IT expert on protecting their computer.
Example:
Non-IT expert: What should I do to stop.... ?
Expert: You should …It may/might
Make sure both students in each pair get the opportunity to play the part of both the non-IT expert and the expert.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE:
Watch the video “Top 10 Web Application Security Solutions” [3]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=thLsfAGj_GY&ab_channel=EnterpriseManagement360
A. Answer the questions:
1. Which security solution is better choice when deciding who can have access to your app at any given time?
2. What does the abbreviation “WAF” stand for?
3. What are the advantages of the “WhiteHat Security”?
4. Which application would you choose to protect your business?
5. Which application has AI?
B. Make a comparison table of the apps.
Example:
|
Name of the app |
Main features |
Weakness (if any) |
|
|
|
|
Unit 8 book 1
IT security and safety.
Практичне заняття № 2
Тема: Workstations health and safety
Мета заняття: Формувати комунікативні навички та сприймати на слух аудіо, вміти коментувати та давати аналіз даної інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Workstations health and safety
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Identifying a safe working environment: how to sit at a computer, also discussing computer do`s and don`ts.
2. Language: Using should/shouldn`t when providing advice and recommendations.
3. Vocabulary: Office rules for IT security and safety.
Основна частина
Завдання
1. Warm-up activity:
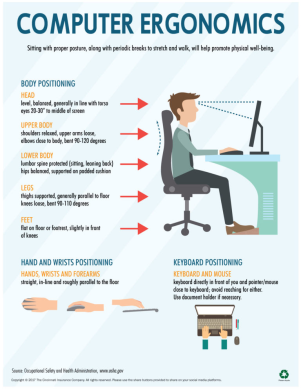
Fig. 2. Computer Ergonomics [4]
Work with the partner: look at the picture and read the recommendations about computer ergonomics. Discuss them with another pair and tell if you follow these rules.
2. Speaking 1: Pre-teaching: ask students to name the body parts, which are the most vulnerable when working with a computer (feet, arms, hands, back, fingers, eyes, shoulders, neck, legs). Write the, down on a board, so you could write the problems with these body parts in the next step.
Ask students to look at the illustration on the page 62 and suggest some of the following problems: headaches, sore eyes, back pain, a stiff neck, pain in the arms and fingers (an example of RSI, which stands for Repetitive Strain Injury).
3. Vocabulary1: Work in group. Ask students to read the advice and deal with any vocabulary questions they may have. Then they match the phrases with the correct part of the illustration in pairs.
Keys: 1d, 2e, 3h, 4f, 5b, 6g, 7c, 8a.
4. Speaking 2: After students have discussed the three questions in pairs, ask them to report back to the whole class on what they said.
5. Speaking 3: Students practice giving instructions to each other, using the following key words: chair, keyboard, footrest, desk, monitor.
Example:
A: What is the best way of typing?
B: Make sure you keep your wrists straight, your upper arms close to your body, and your hands at or slightly below the level of your elbow.
6. Reading 1: Pre-teach the words power surges, cleaner and polish. Students read the list of rules for using the computer in pairs. While discussing each rule, students should tell whether they follow it or not.
With the partner discuss the importance of such rules.
Pay attention to new vocabulary:
Scandisk is a utility that checks and repairs file systems.
Power surges are when there is an unexpected increase in power (for example, as a result of electric storms).
Unauthorised software is software the organisation has not given permission to use.
7. Vocabulary 2: Tell students that this activity practices and checks some key verb-noun collocations. They can do the activity in pairs or individually.
Keys: 2d, 3c, 4a/b, 5a/b.
8. Speaking 4: Ask students to think of and write at least four rules for computer use. They may suggest some of the following ideas:
Take a break every thirty minutes.
Don`t let your computer get too hot.
Use cleaning tools appropriate for computers.
Wipe your screen with a damp cloth only.
Ask IT support for assistance before opening a computer.
Follow maintenance recommendations.
Secure all cables.
8. Speaking 5: Work in pairs. What is the most important rule students can give about computer use? Practice giving advice to each other.
Example: Always..../You should ....
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE:
Watch video about workstation ergonomics. [5] Make notes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MTL8EBBH69o&ab_channel=MartelaGroup
Using your notes write a 5-8 sentences guidelines for setting the workplace correctly.
Практичне заняття № 3
Тема: Security procedures
Мета заняття: Ознайомити студентів з новим лексичним матеріалом за темою Security procedures. Сформувати навички надання письмових рекомендацій щодо правил користування комп’ютерною технікою в компанії або офісі, використовуючи граматичні конструкції для вираження заборони або для надання рекомендацій, а також повторення матеріалу щодо ступенів порівняння прикметників та вживання Present Simple.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Explaining network and system security.
2. Language: Expressing prohibition: mustn`t, shouldn`t, and not be allowed/permitted.
3. Vocabulary: Security procedures: data transfer, security incidents, security breach.
Основна частина
Завдання
1. Warm-up activity: 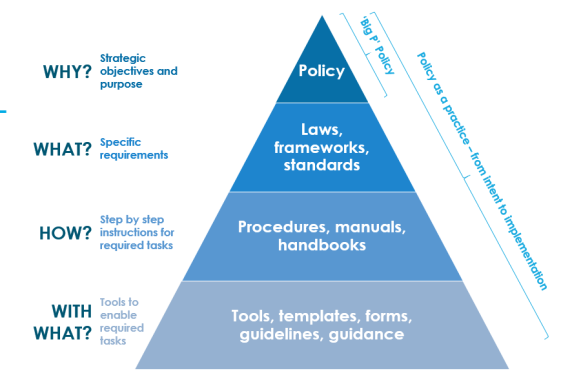
Fig.3. Security policy [6]
Students look at the picture and answer the questions.
1. How many stages does the security policy include?
2. Give a brief description of each stage, using the explanation from the picture.
3. Do you agree with the order of these stages? If no, what would you change?
2. Speaking 1: Ask students what security procedures they are familiar with and share it with a group. Students may suggest the following procedures: installing anti-virus software, creating a firewall, using passwords, backing up files.
Discuss which of them is the most effective.
3. Reading 1: Encourage students to do the matching activity without trying to understand every word in the text. Point out that current in the first paragraph means up-to-date in this context.
Keys to exercise: 1 Safety security requirements, 2 Password recommendations,
3 Email and network usage, 4 Data transfer and backup, 5 Reporting IT security incidents.
4. Vocabulary 1: Offer students to record the given word combinations to practice usage of collocations about security procedures.
Keys to exercise: 2b, 3c, 4a, 5f, 6e.
5. Speaking 2: Ask students to discuss the two questions in pairs and make sure they use the superlative form (for example, The most (or least) important thing is only installing software that management has approved). Remind students to use Present Simple to talk about habits (for example, People sometimes do not report incidents).
6. Usage of language 3: Read the explanations and examples of expressing prohibition with class. Do not teach the formation of the passive form; just teach these two items as set phrases. Point out that you refers to people in general.

To express prohibition you can use: [7] |
Examples: |
|
▪ It is prohibited to .. |
Parking is strictly prohibited between these gates. |
|
▪ You aren’t allowed to ... |
Students aren't allowed to come too late to school |
|
▪ You mustn’t ... |
Drivers mustn't park their cars here |
|
▪ You aren’t permitted to ... |
People aren't permitted to throw rubbish here |
|
▪ You shouldn`t ... |
You shouldn`t download films at work. |
7. Listening 1: Play the recording and ask students just to listen. Then play the recording again and ask students to repeat the sentences. Walk around the class to make sure there are no problems with pronunciation.
8. Speaking 3. Work in small groups. Tell students that they can refer back to the text in Exercise 2 on page 64 and to the text in Exercise 5 on page 63 for help with this activity. If students have difficulties with discussion ask them to make a research in the Internet about the rules and recommendations about computer regulations in company or University by their choice.
9. Writing 1: Students in small groups write a document listing the regulations you talked in the previous task. Use these headings:
Personal use of computers
Health and safety
Security
Reporting problems
If there is not enough time, set this activity as homework.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE:
Using the following document [8] http://docushare3.dcc.edu/docushare/dsweb/Get/Document-48/
as an example, make a short list of the most important security measures and procedures. Write them down as a memo for students.
Unit 8 book 1
IT security and safety
Reporti09lng incidents
Мета заняття: Ознайомити студентів із процедурою доповіді щодо інцидентів, пов’язаних з ІТ безпекою. Коментувати та давати аналіз інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою: Reporting incidents
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Talking about security incidents: their kinds and how to report about them.
2. Language: How to write a short report on a security incident.
3. Vocabulary: Types of security incidents: changing printer settings, downloading a movie at work, installing unauthorised software, illegal file sharing and reporting process.
Основна частина
Завдання
1. Warm-up activity
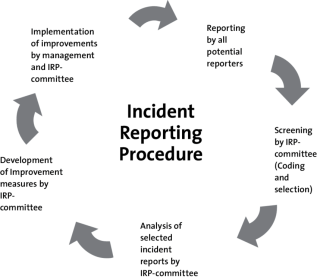
Fig.4. Incident Reporting Procedure [9]
Students look at the picture and express their opinion about the order of the Incident Reporting Procedure. (For example, I think the first stage should be Reporting by all potential reporters, because it is essential to get all the information about the incidents)
2. Speaking 1: Students answer the questions:
1. Have you ever reported a security incident?
2. What was it about?
3. Whom did you report it about?
4. Were there any recommendations about the incident?
2. Reading 1: Ask students to read the reports and say if any of them refer to incidents that are similar to what you talked about in Exercise 1. Pay student`s attention to the structure of the report (e.g. Date, Report for, Report prepared by, Incident, Recommendations).
3. Speaking 2: Write ‘I think’ on the board with two examples (for instance, I think the teacher incident is the most serious one. The printer settings change is the least important incident, I think)
Stronger student may be able to explain their choice by adding ‘because’ and explaining the reason.
Example:
Student 1: I consider being the least serious incident D, because it didn`t result in damage to company`s property or reputation.
Student 2: In addition, the incident was reported about and manager took measures to prevent it in the future.
4. Writing1: Students write a short report to the IT supervisor on the most serious incident and give some recommendations on how to deal with the incident. Use the following structure. Tell students they should write two or three sentences for lines ‘Incident’ and ‘Recommendations’.
|
Incident report |
|
|
Date: |
|
|
Report for: |
|
|
Report prepared by: |
|
|
Incident: |
|
|
Recommendations: |
|
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE:
Watch the video about how to write Incident Reports in Five Easy steps [10]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LXMvHkTDVHE&ab_channel=PrudentialSecurity%2CInc.
Write down the tips on writing Incident report and discuss them in your group.
Unit 8 book 1
IT security and safety.
Практичне заняття № 5
Тема: Business matters
Мета заняття: Закріпити лексичний матеріал за темою IT security and safety, в контексті написання доповіді щодо інформування з приводу інциденту щодо порушення безпеки на робочому місці, з використанням граматичних конструкцій з попередніх практичних занять (Present Simple, Expressing prohibition, Giving recommendations, Superlatives Adjectives)
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Review and report on a computer set-up in an office, both in terms of health and safety and computer security.
2. Language: Apply the language students have learnt and practiced on the previous pages of the Unit 8.
3. Vocabulary: Workstation health and safety, security procedures and reporting incidents.
Основна частина
Завдання
1. Warm-up activity: Students answer the questions:
1. What is the network security?
2. What is health and safety in a workplace?
3. What security and safety systems weakness do you know?
4. How can workstation health and safety be improved?
2. Reading: Before students do the activity, ask them to look at the two illustrations and identify one problem in each; this will help them to get the idea of what they supposed to do. Then ask them to make notes as a system safety coordinator about the problems of the IT systems in QuickFix Ltd.
When making notes focus on things like:
|
Network security problems |
Health and safety in the workplace problems |
|
Firewall, anti-virus software, email and browser filter, back p for data or cloud storage, filtering software, username and password protection |
food and drinks on workstations, the sort of office furniture hanging cables from ceiling, fan on the floor, dartboard in dangerous position near filing cabinet |
2. Speaking: Within ten minutes preparation, in pairs, students make notes to present the report after the inspections and providing proper recommendations to another group. The presentation should be no longer than one minute for each part.
Student A: talk about health and safety in the workplace.
Student B: talk about network security.
You can use the following table for key points of your report
|
Problem |
Recommendation |
|
Cables are not correctly positioned |
Call the tech support and position the cables correctly. |
|
|
|
|
Food and drinks on workstations |
Organize the place for lunch, at least 200 meters from the workstation |
|
|
|
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE : Watch the video about Ethical hacking and learn more about malware, viruses and trojans.

Fig. 5. Ethical Hacking [11]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SrqzaR8ZrII&ab_channel=TutorialsPoint%28India%29Ltd [12]
Перелік використаної літератури в методичному керівництві до підручника English for Information Technology (Part 1) UNIT 8
|
Практичне заняття |
Використані джерела |
|
Практичне заняття № 1 Тема: Security solutions |
1. Security solutions [Електронний ресурс]. – 2021. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.thalestct.com/Solutions/Enterprise-Security/. 2. Probability [Електронний ресурс] // British Council. – 2021. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/english-grammar-reference/probability. 3. Top 10 Web Application Security Solutions [Електронний ресурс] // Enterprise Management 360. – 2020. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=thLsfAGj_GY&ab_channel=EnterpriseManagement360. |
|
Практичне заняття № 2 Тема: Workstations health and safety |
4. Get in Position for Workstation Comfort & Safety [Електронний ресурс] // Saginaw Bay Underwriters. – 2017. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://sbuins.com/get-in-position-for-workstation-comfort-safety/. 5. Workstation ergonomics [Електронний ресурс] // MartelaGroup. – 2012. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MTL8EBBH69o&ab_channel=MartelaGroup. |
|
Практичне заняття № 3 Тема: Security procedures |
6. What’s in a Name? Deconstructing and Defining ‘Policy’ [Електронний ресурс] // NSW Government. – 2019. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.digital.nsw.gov.au/article/whats-name-deconstructing-and-defining-policy. 7. Expressing Prohibition [Електронний ресурс] // My English Pages.com. – 2021. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.myenglishpages.com/english/communication-lesson-prohibition.php. 8. Violence in the workplace [Електронний ресурс] // Delgado Community College. – 2013. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: http://docushare3.dcc.edu/docushare/dsweb/Get/Document-48/. |
|
Практичне заняття № 4 Тема: Reporting incidents |
9. Feasibility of centre-based incident reporting in primary healthcare: The SPIEGEL study [Електронний ресурс] // Cor J Kalkman. – 2011. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/ncident-Reporting-Procedure-IRP-as-a-Plan-Do-Act-Check-cycle_fig1_49731594. 10. Training Time With Terry - Write Incident Reports in Five Easy Steps [Електронний ресурс] // Prudential Security, Inc.. – 2018. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LXMvHkTDVHE&ab_channel=PrudentialSecurity%2CInc. |
|
Практичне заняття № 5 Тема: Business matters |
11. Ethical Hacking [Електронний ресурс] // Depositphotos. – 2021. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://ua.depositphotos.com/stock-photos/ethical-hacking.html. 12. Ethical Hacking - Malware, Viruses and Trojans [Електронний ресурс] // Tutorials Point (India) Ltd.. – 2018. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SrqzaR8ZrII&ab_channel=TutorialsPoint%28India%29Ltd. |
Практичне заняття №4
Тема: Customer service.
Мета заняття: Сформувати необхідні практичні навички говоріння , читання, письма, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео, вміння коментувати та давати аналіз даної інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Customer service , які застосуються для вирішення проблем при обслуговуванні споживачів.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Solving customer service problems;
2. Language: The present perfect: Has(s)he switched off the computer?
3. Vocabulary: Phonecalls.
Основна частина
Завдання
1. Warm-up activity: Ask students to look at the picture and answer the questions: 1. What do people working for the customer service usually do to deal with the people who are having difficulties with a particular problem? 
2. Look at the picture and find words describing the qualities of the people working for the customer services.
3.What should people from the customer sevices do to help people?
2. Speaking: A: Look at the illustration and say how the man is feeling (frustrated, fed up, angry or stressed). 
B: Look at the cartoon again. How do people react when there is a problem with their computer? Why?
(People often get angry or stressed because they have a problem with their computers and their time is being wasted. It is up to IT colleagues to help non-IT experts out in these situations and to reduce stress levels).
3. Listening ► 46 A: Play the recording with books closed so your students can get a general understanding of the situation.
B: Give students a minute to read the questions and then play the recording “A phone call to a company IT help desk” again so they can answer them. Ask them to choose the correct answers a, b or c to the questions. Then let them listen again to check your answers. 1 b 2 a 3 c 4 c 5 b
4. Listening: This activity focuses specifically on phrases students can use when dealing with a colleague’s computer problem. Listen and complete the technician’s sentences in ex.3, p.58. Play the recording several times if necessary.
1 help 2 see 3 sure 4 Please 5 luck
5. Pronunciation: Listen and repeat the technician’s sentences.
6. Writing: Work in pairs: rite a short dialogue (8-10 lines) between IT helpdesk technician and a colleague about a software or hardware problem. Use phrases from ex.3. A time limit is ten minutes.
7. Reading: Work in pairs. Read your dialogues to the rest of the group.
8. Optional : Speaking: Role-play the dialogues.
Практичне заняття №5
Тема: Business matters.
Мета заняття: Навчити комунікативних навичок говоріння , читання, письма у сфері роботи підтримки клієнтів та вирішення із проблем із технікою он-лайн; сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео, вміння коментувати та давати аналіз інформації, отриманої від клієнтів,використовуючи лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Fault diagnosis.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Understanding and Solving customer service problems;
2. Language: The present perfect: Has(s)he switched off the computer?
3. Vocabulary: Fault diagnosis questions and answers.
Основна частина
1. Warm-up activity: Answer the questions:
1. What does the ticket mean?
2. What is it used for?
2. Reading: You work as an IT help desk technician. You are responsible for these tickets from colleagues in your company. Read through the tickets to understand the problems. Answer the question: What are the problems?
3. Writing: Choose one of the Help Desk tickets from ex.1. Write questions for the fault diagnosis and possible solutions.
Example:
Fault diagnosis question: Is there an error message on your screen? What does it say?
Possible solutions: Have you tried restarting your computer?
Suggested answers :***
Ben: Fault diagnosis questions: Is there an error message? Is your printer on? Is there paper in the feeder? Are you connected to the network? Possible solutions: Load paper in the feeder. Check your network connections. Wait for IT support to arrive and solve the problem. Check the cable connections and the socket. Check if the paper is jammed. Clare: Fault diagnosis questions: Do you have a password and a username? Do you have a wireless modem? Is your wireless modem switched on? Where are you? Have you changed your password recently? Have you tried to log in unsuccessfully three times? Possible solutions: Restart your computer. Switch your modem on. Go to the main office – you are outside the coverage area. Wait, the server is under maintenance. The server is down. The cables may be damaged. IT support will reset your password for you. Your account has been locked – IT support will unlock it for you. Simone: Fault diagnosis questions: Have you dropped your computer? Where do you keep your computer? Possible solutions: Your fan is loose. IT support will collect your computer and fix the problem. Please bring your computer to IT support. Please back up your files, log out and wait for IT support – you will receive a temporary laptop. Please move your computer so that it has space all around it.
4. Speaking: A: Work in pair. Tell students that they are going to have another opportunity to practise dealing with problems over the phone. You may also want to write key phrases on the board or a piece of paper for students to use while you are making their calls (for example, Hello, this is … . Don’t worry. Thank you. You’re welcome. Goodbye. Bye. Good luck.) The students playing the non-IT colleagues should sound angry and stressed at the beginning and the students playing the help desk technicians should make sure they calm down their colleagues during the phone call. If it is practical, you may use their mobile phones to carry out this activity or at least sit back to back so you cannot look at each other.
B: So, Role-play the conversation about the problems. Student A is the help desk technician and Student B is the colleague.
Preparing for the next unit:
Unit 8 is about IT security and safety, so find a news story about a threat to IT
security involving a virus for the next class.
Unit 6: Network systems.
Практичне заняття №1
Тема: Types of network.
Мета заняття: Сформувати комунікативні навички говоріння за темою «Типи Мереж» ,тренувати навички читання, письма, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео, вміння коментувати, давати рекомендації, аналіз та обґрунтування інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Types of network.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Explaining networks;
2. Language: Giving reasons. E.g.: I’d recommend a Dell computer because it’s cheaper.
3. Vocabulary: Types of network system: LANs, WANs and VPNs,
POP, internet routers and modems, network switches, CCTV…
Основна частина
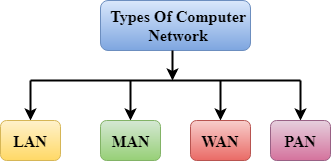
1. Warm-up activity:
A.: Look at the picture and answer the questions:
1. What can you see in the picture?
2. Is it related to the title o f the unit?
3. Can you define the words LAN, MAN, WAN, PAN in it?
4. Where can we use these solutions?
5. Where can they operate?
Key: LANs= Local Area Networks; WANs= Wide Area Networks; VPNs= Virtual Private Networks; MANs= Metropolian Area Network;Solutions can be used for different types of situations: the home, small business and large corporations. LANs operate over a limited geographical area whereas WANs operate over a broad area ( for example, a region). VPNs use the internet to provide remote office connections. MANs are computer networks that connect computers within metropolitan areas, which could be a single large city, multiple cities and towns or any given large area with multiple buildings. MAN is lager than LAN but smaller than WAN. The term metropolitan implies the size of the network, not the demographics of area that it serves; do not have to be urban areas. PAN=Personal Area Network, interconnecting electronic devices( computers, smart phones, tablets and personal assistants) within an individual personal workplace, providing data transmission. Here one master device takes up the role of gateway.
B: Think of examples of these four types and tell to the group.
What is B2C?
What is B2B?
What is C2C?
What is m-commerce?
C: Tell us the kind of information about a product or service you can find on a commercial website (for example, price, and availability, information about the product and other related products, and method of payment).
2. Speaking: Answer the questions using the following vocabulary: to use organization’s intranet/social networks/the internet; to get information and communicate with colleagues; to access the networks from the PCs and mobile devices such as phones and iPads.
1. What computer networks do you use in your work or studies?
2. What do you use the networks for?
3. How do you access the networks?
2. Listening: Ask students first to read the situation and the four questions.
Answer the question: What sort of network do you think Katharina will suggest to Agatha?
Now, tell them to cover the questions and play the recording once so they get a general understanding.
Then play the recording again so they can answer the four questions.

Ask students to turn to the audio script on page 75. Play the recording again to focus on how the two women greet each other (for example, It’s good to see you again. How are you?)and how they get down to business (for example, So how can I help you?).
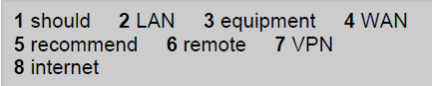
3. Reading: Read the email where Katharina makes a series of recommendations to Agatha on how she should set up her online flower shop, do the activity and then compare your answers in pairs.
4. Use of language: Giving reasons using the word “because’. We use because to say something was the reason for an action or situation. (We can start a sentence with because).
Examples: I had a glass of water because I was thirsty;
Because I have a headache, I’m going to stop work.).
A: Make your own sentences using because.
B: Now make up sentences using the given word combinations: buy a new computer/mobile phone, move apartment, sell my old car, go to Australia for a holiday).
C: Optional task: You may also revise the use of so to talk about results, which was introduced in Unit 5. Make up 3-5 sentences of your own.
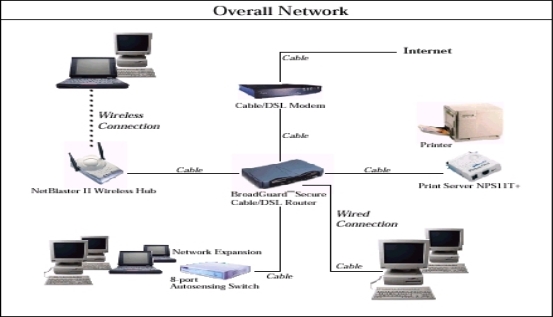
5. Speaking: A: Look at the three network solutions illustrated on the page 45. What are the differences?
B: Now read the definitions of the illustrations and match them with the three network solutions:
Network solution 1 (Picture 1)_______; Network solution 2 (Picture 2)________; Network solution 3 (Picture 3)_________ .
Illustration1 shows the kind of network you find in a family home, where both the parents and children use the computers and the games console. The network connects two desktop computers, one printer and one game console. The devices are connected to the internet via a hub or switch. It is a very simple network and it is efficient only for a few users.
Illustration 2 shows a network for a large company. There are servers that transfer data over the network. Users can access the network from home or from anywhere. This kind of network can transfer a lot of data.
Illustration 3 shows a network set up in a small company. The network devices are a switch, a router, a wireless access point, laptops, printers, scanners, PCs, PDAs and CCTV cameras. The devices are connected via a wireless connection.
C: Learn to tell about the above mentioned Network solutions (as homework).
6. Speaking: A: Answer the following questions:
1. Which network solution would you recommend for a large corporation?
2. Which network solution would you recommend for an organization?
3. Which network solution would you recommend for a small business?
4. Which network solution would you recommend for a family home?
Carry out the activity in groups of three so each person has the opportunity to present one solution to the group.
B: Extra activity with a stronger class: tell us how you would improve the three networks. (You could research this at home or in groups and prepare short presentations).
7. Writing: A: Write three to five sentences describing your network solution you use at work or at home. Which of the three solutions in 4 is it like? Why?(If time is short, you can do this activity for homework).
Example or suggested answer: At home, we have three computers. Our network is similar to Solution 1. We connect the desktop computer to the internet via a modem. The two laptops have a wireless connection to the internet via a router. We only connect the printer to the desktop computer. We also use other devices such as cameras and mobile phones to download pictures and music.
B: Present your Network Solution to the group.
Optional task: Speaking: Ask students to split the Overall Network Solution into the smaller areas as it was in the illustrations above, and describe them spitted or as a whole.
Практичне заняття №2
Тема: Networking hardware.
Мета заняття: Cформувати навички говоріння , читання, письма, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео, вміння коментувати та давати аналіз повідомлень співрозмовника стосовно роботи та взаємодії з IT Help Desk у вирішенні проблем з приладами мереж їх ремонту , навик висловлювання пропозицій на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Networking hardware.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Describing and fixing network hardware;
2. Language: Making suggestions: Why don’t you call the IT Help Desk?
3. Vocabulary: Network hard ware, problems with hardware.
Основна частина
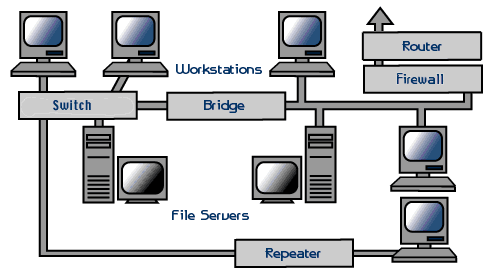
1. Warm-up activity: A.: Ask students to look at the picture at p. 46 and
answer the questions in pairs or small groups:
1. Which of the items do you know?
2. What are they?
3. What do they do?
(a modem, an expansion card, a router (with an antenna) and a network server).
2. Speaking: Do these activities with books closed.
A: Work in pairs/small groups. Make up a list of all the networking hardware you can think of.
B: Compare your list with another pair/ small group.
C: Look at the list of words and try to describe what each item does in your own words.
3. Vocabulary: A: Look at the picture
Then look at the list of the given words and try to describe what each item does in your own words.
B: Match the words with the descriptions in pairs.
!!!! Learn two more notions with their definitions: A computer protocol is the system of regulations that describe how something is done. Bandwidth speed refers to the speed at which information can be transmitted through a network.
![]()
*** (For home task: Lean all the definitions by heart, because they are included into the unit test, progress test, final test, module test and the Moodle exam test).
4. Pronunciation: A: Play the recording and just to listen to it. Mind about the stressed syllables in the words of more than one syllable: modem, repeater, router, gateway, wireless, access point, network connectors, network interface card. Then play the recording again and repeat the words after the speaker.
B: Close your book. Play the recording again and with the books closed write down the words after the speaker, then open your books and check your spelling.
5. Reading: Students are going to read a dialogue in which Boris asks Ahsan, an IT expert, for help with his computer set-up.
First, students should read the dialogue and then complete the sentences with the words in the box.
(As an alternative practice: play Track 36 with books closed first and then answer the questions to check general understanding.
1. What is Boris’s problem?
2. How many recommendations do you hear?
Then open your books and complete the dialogue with the words in the box.).

7. Listening and pronunciation: A: Listen and check your answers;
(Self-preparation practice:
1: Listen and repeat after the speaker sentence by sentence using a pause.
2: Read simultaneously with the speaker.)
B: Work in Pairs: Role-play the dialogue with a partner.
8. Use of langusge: This section introduces two new ways to make suggestions or recommendations:
Why don’t you …? ;
And how about…? How about (sth/doing sth)…? / What about …?.
You could also review You should …, which was presented in Unit 4 for making a recommendation or giving a piece of advice / some advice.
You can use or add some more positive and negative responses, for example, Great idea!
OR: I don’t think that’s a very good idea etc.
9. Listening and Pronunciation: A: Play the recording once and just listen to it; identify the stressed words in the questions. Play the recording again and repeat the questions after the speaker.
B: Read the question to your partner and let him answers the questions, then switch the roles.
10. Vocabulary: You may do the exercise individually or in pairs. Complete these sentences with the words (=prepositions) in the box. p.47, ex.8.
![]()
11. Speaking: Answer the question: What problems do you have with networks? Make a list of. Think about speed, compatibility, hardware and software
(****Pay attention that in your discussion you should mention such notions as speed, compatibility, hardware and software and problems can be caused with/by) (Compatibility problems, Speed problem, Software problems, Hardware problems…)
E.g.: Speed problems can be caused by the types of network devices, computer hardware, software and especially the protocols used….
For weaker students: Read the definitions and match them with the given types of problems: Speed problems, Software problems, Compatibility problems.
________can be caused by the types of network devices, computer hardware, software and especially the protocols used. The devices must support the network specifications or the network speed will be impacted negatively.
_______can be related to both the hardware and the software used in the network set-up.
__________ may relate to a network not supporting particular software, too much or too little protection on the firewall settings, software with missing data or errors in software interaction with other software in the system.
Now, Speak about the problems from your list.
11. Speaking: You have to discuss solutions to the problems you’ve just discussed. Use the questions from the dialogue in Exercise 5 (e.g.: What can you suggest?) to ask for suggestions. You should also suggest solutions to the Four Key Problems listed above.
Example:
A: This software doesn’t work with this… .
B: Why don’t you … ?
The Four Key Problems:
Speed problems:
Compatibility problems:
Hardware problems:
Software problems:
****For Weaker students: You may use these questions to help you suggest solutions for the above mentioned problems:
Why don’t you buy a better modem? You shouldn’t connect so many devices to the network._ How about checking that the capacities of the router and the network adapter are compatible? _How about resetting the router? How about upgrading the modem? You should update the drivers. _Why don’t you reinstall the software? How about closing some other applications? Why don’t you change the firewall settings?

Практичне заняття №2
Тема: Networking hardware.
Мета заняття: Cформувати навички говоріння , читання, письма, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео, вміння коментувати та давати аналіз повідомлень співрозмовника стосовно роботи та взаємодії з IT Help Desk у вирішенні проблем з приладами мереж їх ремонту , навик висловлювання пропозицій на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Networking hardware.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Describing and fixing network hardware;
2. Language: Making suggestions: Why don’t you call the IT Help Desk?
3. Vocabulary: Network hard ware, problems with hardware.
Основна частина
1. Warm-up activity: A.: Ask students to look at the picture at p. 46 and
answer the questions in pairs or small groups:
1. Which of the items do you know?
2. What are they?
3. What do they do?
(a modem, an expansion card, a router (with an antenna) and a network server).
2. Speaking: Do these activities with books closed.
A: Work in pairs/small groups. Make up a list of all the networking hardware you can think of.
B: Compare your list with another pair/ small group.
C: Look at the list of words and try to describe what each item does in your own words.
3. Vocabulary: A: Look at the picture
Then look at the list of the given words and try to describe what each item does in your own words.
B: Match the words with the descriptions in pairs.
!!!! Learn two more notions with their definitions: A computer protocol is the system of regulations that describe how something is done. Bandwidth speed refers to the speed at which information can be transmitted through a network.
![]()
into the unit test, progress test, final test, module test and the Moodle exam test).
4. Pronunciation: A: Play the recording and just to listen to it. Mind about the *** (For home task: Lean all the definitions by heart, because they are includedstressed syllables in the words of more than one syllable: modem, repeater, router, gateway, wireless, access point, network connectors, network interface card. Then play the recording again and repeat the words after the speaker.
B: Close your book. Play the recording again and with the books closed write down the words after the speaker, then open your books and check your spelling.
5. Reading: Students are going to read a dialogue in which Boris asks Ahsan, an IT expert, for help with his computer set-up.
First, students should read the dialogue and then complete the sentences with the words in the box.
(As an alternative practice: play Track 36 with books closed first and then answer the questions to check general understanding.
1. What is Boris’s problem?
2. How many recommendations do you hear?
Then open your books and complete the dialogue with the words in the box.).

7. Listening and pronunciation: A: Listen and check your answers;
(Self-preparation practice:
1: Listen and repeat after the speaker sentence by sentence using a pause.
2: Read simultaneously with the speaker.)
B: Work in Pairs: Role-play the dialogue with a partner.
8. Use of langusge: This section introduces two new ways to make suggestions or recommendations:
Why don’t you …? ;
And how about…? How about (sth/doing sth)…? / What about …?.
You could also review You should …, which was presented in Unit 4 for making a recommendation or giving a piece of advice / some advice.
You can use or add some more positive and negative responses, for example, Great idea!
OR: I don’t think that’s a very good idea etc.
9. Listening and Pronunciation: A: Play the recording once and just listen to it; identify the stressed words in the questions. Play the recording again and repeat the questions after the speaker.
B: Read the question to your partner and let him answers the questions, then switch the roles.
10. Vocabulary: You may do the exercise individually or in pairs. Complete these sentences with the words (=prepositions) in the box. p.47, ex.8.
![]()
11. Speaking: Answer the question: What problems do you have with networks? Make a list of. Think about speed, compatibility, hardware and software
(****Pay attention that in your discussion you should mention such notions as speed, compatibility, hardware and software and problems can be caused with/by) (Compatibility problems, Speed problem, Software problems, Hardware problems…)
E.g.: Speed problems can be caused by the types of network devices, computer hardware, software and especially the protocols used….
For weaker students: Read the definitions and match them with the given types of problems: Speed problems, Software problems, Compatibility problems.
________can be caused by the types of network devices, computer hardware, software and especially the protocols used. The devices must support the network specifications or the network speed will be impacted negatively.
_______can be related to both the hardware and the software used in the network set-up.
__________ may relate to a network not supporting particular software, too much or too little protection on the firewall settings, software with missing data or errors in software interaction with other software in the system.
Now, Speak about the problems from your list.
11. Speaking: You have to discuss solutions to the problems you’ve just discussed. Use the questions from the dialogue in Exercise 5 (e.g.: What can you suggest?) to ask for suggestions. You should also suggest solutions to the Four Key Problems listed above.
Example:
A: This software doesn’t work with this… .
B: Why don’t you … ?
The Four Key Problems:
Speed problems:
Compatibility problems:
Hardware problems:
Software problems:
****For Weaker students: You may use these questions to help you suggest solutions for the above mentioned problems:
Why don’t you buy a better modem? You shouldn’t connect so many devices to the network._ How about checking that the capacities of the router and the network adapter are compatible? _How about resetting the router? How about upgrading the modem? You should update the drivers. _Why don’t you reinstall the software? How about closing some other applications? Why don’t you change the firewall settings?

Практичне заняття №3
Тема: Talking about the past.
Мета заняття: Сформувати та навчити комунікативним навичкаv говоріння, читання, письма, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео, вміння коментувати та давати аналіз подіям, які відбулися у минулому, використовуючи структури Past Simple інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Talking about the past.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Using the past tense to talk about the education or careers to date (for example, I got a job in 2006.)
2. Language: Past Simple: When did they launch_ the network? The Past Simple with regular and irregular verbs. Time expressions.
3. Vocabulary: Networking sites.
Основна частина
1. Warm-up activity: A.: Ask students to look at the picture and answer the questions( you may use some of them- 3 or for , or more):

1. What can you see in the picture?
2. Can you name the networking sites on it?
3. What are they used for?
4. What do you know about networking?
5. What functions does networking have?
6. What networking sites do you know?
7. What are the features and purpose of the networking sites you use?
8. What is the difference between Twitter, Facebook, and MySpace?
***Twitter is a micro-blogging service that sends short written messages to people who follow you, while Facebook and MySpace are a social networking sits.
2. Reading: A: Ask students to look at some years (on the board) and say them (for example, 2006: two thousand and six; 2012: twenty twelve; 1955: nineteen fifty-five). Do the exercise in pairs.
1995, 2016, 2000, 2120, 1901, 1900, 1989, 2001…..
B: Answer the questions: How much do you know about the history of networking? Can you match these events 1-4 to the dates a-d in ex.1, p.48?
![]()
Nouns to talk about the start of something: launch, start, creation, beginning.
3. Speaking: Work in pairs or small groups for this activity. Look, how we use the verb spend to talk about time (for example, I spend about an hour a day talking to friends on the phone.).
A: Answer the questions: What social networks do you use? How much time do you spend on them?
Example: I use… . I spend about ….to….. .
B: Extra activity: Do a short survey on each other’s use of social networks. You can report your results to the whole class, for example, We use Facebook but Jose doesn’t. Ken spends two hours a week on Twitter.).
4. Reading: You are going to read a short biographical text about someone’s IT career. Read the text aloud and then answer the five questions (ex.3, p.48).

Optional:(Prepare your own biographical text/short report/ about your background (leave/left school, enter/entered the university, and about your career prospects, and then present it to the group (job you are going to have, position you are going to occupy/have/get, company you are going to work for…).
5. Use of language: We use Past Simple tense to talk about finished actions in the past
She created the network in December 2008(a single, finished action in the past).
We use time expressions: yesterday, (three days/ minutes; a minute/a day/ a month/a year….) ago, in January 2019/ on Monday, last Monday/ last week.
We use did in questions: Did she create_ the network in December 2008?
We use did not (= didn’t) in negative sentences: She didn’t create_ the network in December 2008.
6. Pronunciation: Play the recording once just to listen to it. Pay attention to the stressed words in the sentences. Then play the recording again and repeat the sentences after the speaker. Answer these questions.
7. Speaking: This is a short activity to practice asking and answering questions about the past. Practice asking and answering questions about what you did yesterday and last week in your work or studies. (You may use the (regular) verbs: study, work, look, watch, test, enjoy, cook, complete, finish, create, start, launch,…etc.).
Example:
A: What did you do last week?
B: I worked on the new network.
8. Speaking: Work in pairs. Task A: Make up a list of typical leisure activities appropriate for students (for example, go/went to the beach/gym/theatre, meet/met friends, do/did nothing, visit/ visited my family, go/went on excursion, attend/attended classes/lectures etc.).
Task B: Talk about what did you do on your day-off?
Example:
A: what did you do on your day-off?
B: I went to the gym.
Task C: Use the words to describe the order of the actions you did on your day-off:
First, I … . Then I… . After that, I ... . Finally, I … .
9. Use of language: Past simple 2, Regular and Irregular verbs.
There is the difference between regular verbs’ endings (-ed) in the Past Simple and irregular verbs, for example, saw –the Past Simple of the verb see. Can you suggest any further irregular verbs to be added to the list? Look at the Language section : Past simple 2, p.49, Read them then learn.
You should start making your own lists of irregular verbs. You may group them any way you like in order to memorise them better.
Example:
Begin began begun
Become became become
Come came come
Run ran run
…..bring brought brought
Buy bought bought
Teach taught taught
Catch caught caught….
Give gave given
Forgive forgave forgiven etc.
OR You may learn the irregular verbs from the list below. (It is better and highly recommended to learn all three forms of them, because you’ll need them in the further study of tense forms).

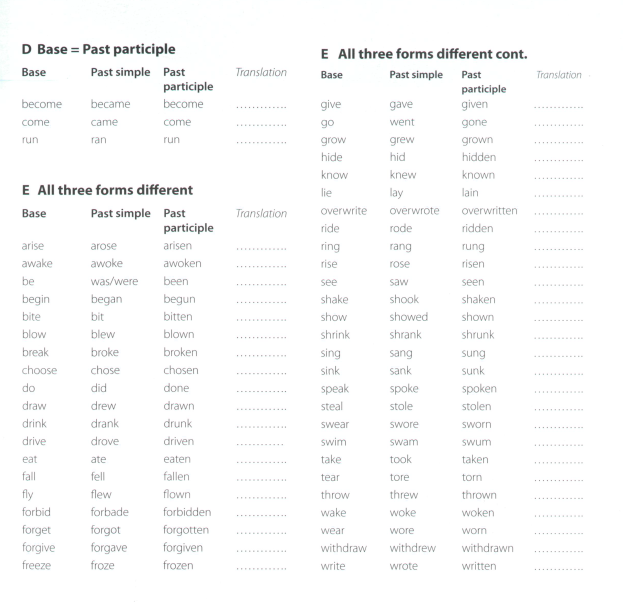
10. Writing: Ask students to read the text in Exercise 3 on page 48 again and use it to help them to make similar sentences about theirselves. Ask them to prepare their own biographical text about their background (leave/left school, enter/entered the university, and about their own ( computer) education and/or work up until now or their career- prospects, and present to the group (job they are going to have, position they are going to occupy/have/get, company they are going to work for…).
11. Speaking: Tell students to ask and answer questions about their education and/or work. Look at the following question cues (on the board) to help students get started.
when / go / university or college?
what / study / at school?
when / start / work?
where / start / work?
Практичне заняття №4
Тема: Network range and speed.
Мета заняття: Сформувати навички говоріння про можливості мереж , читання, письма, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео, використовуючи числа у поєднанні з термінами мереж, вміння коментувати та давати аналіз даної інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Network range and speed
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Talking about network capabilities;
2. Language: Numbers in Network terminology;
3. Vocabulary: Network terminology. Speeds and ranges.
Основна частина
1.Warm-up activity: A.: Ask students to look at the picture and answer the questions:
1. What can you see in the picture?
2. What can you say about depicted items in it? What are they?
3. What do we use them for?
Opional:
Pre-reading task: Ask students to answer the question in pairs encourage them to use the Internet in case they are not sure or don’t know the meanings ( give them 5 min to find the one does it the fasters is a winner) :
1. How can you describe speed?
2. What is range?
3. What do represent network range?
4. What is a kilobit?
5. What is a megabit?
6. What is a gigabit?
7. What do Dial-up connections use to connect to the Internet?
8. What does DSL stand for?
9. What does WLAN stand for?
10. What is latency?
Open class feedback
Then ask them to read and check their answers comparing with the definitions (Later, definitions should be learnt by heat):
Speeds are described in bits, kilobits (a second), megabits and gigabits. They describe network speed.
Range is the distance of network coverage, so distance units represent network range. (in metric (in metres) or feet units of measurement)
Speeds and ranges (for example, twelve kilobits a second and 7,000 metres).
A bit is the basic binary digit.
A kilobit is a thousand bits.
A megabit is a million bits or a thousand kilobits.
A gigabit is a thousand million bits or a thousand megabits.
Dial-up connections use phone networks to connect to the internet.
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line and is a way of transmitting data using phone networks.
WLAN stands for Wireless Local Area Network.
Latency is the time delay in moving data across a network.
Ask them if they are correct with their definitions.
2. Listening: A: Tell students:”You are going to listen to a dialogue in which Sam gives Karoline information about network speeds and range. Before you play the recording, look through the definitions above once again. Play the recording with books closed first to listen to the dialogue without trying to write in the missing words”.
B: Then play the recording again, pausing to let them write in their answers.

Optional practice: A: Listen and repeat sentence by sentence after the speaker with books closed.
B: In pairs, practice reading the dialogue, then switch the roles.
C: Learn the dialogue to role play it.
3. Listening and Pronunciation: Play the recording just to listen to the phrases.
Pay attention that you can say a or per second/minute and that both words are usually not stressed, so they sound very similar. Play the recording again and repeat the phrases.
4. Speaking:( The speeds and ranges are abbreviated but that when spoken, they should be pronounced fully. In written English, you can also abbreviate feet to ft and metres to m).
A: Ask your students to say these speeds and ranges.ex.3,p 50:
Key:

B: Writing: Ask students to write down four speeds and ranges and dictate them to their partner, the switch roles.
5. Reading: Before reading let them look up the words limited (as in limited range), strength (as in strength of signal), architecture (in this case, meaning the physical surroundings and not network architecture) and bandwidth in the dictionary. The text they are going to read is a technical text and they should read it for general understanding and not worrying about the meaning of every word they do not understand.
Ask them to read the text and answered the questions. Then deal with any outstanding vocabulary queries (for better understanding it is quite a good practice to translate the text into the mother tongue and it is highly recommended to learn this information properly so to pass an oral part of the exam well ).

Практичне заняття №5.
Тема: Business matters.
Мета заняття: Сформувати вміння та навички говоріння , читання, письма, використовуючи структури Past Simple для опису дій минулих літ та колишніх видів діяльності на робочому місті, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео матеріалів, вміння коментувати та давати аналіз інформації , що базується на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Business matters.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Talking about past activities at work (for example, On Wednesday, I attended a training session…);
2. Language: Revision: Past Simple: When did they launch_ the network? The Past Simple with regular and irregular verbs. Time expressions.
3. Vocabulary: Network terminology: bits and bytes, gigabit, social networking site. Speeds and ranges. a UK-based supermarket chain, audio/video servers, Cat6 cables, types of network cable.
Основна частина
1. Warm-up activity: A.: Read the terminology words:
modem, repeater, router, gateway, wireless, access point, network connectors, network interface card, a computer protocol, bandwidth speed. audio/video servers, Cat6 cables, types of network cable.
Can you explain what they are, their functions and where they can be used?
B: 1.What do you know about CISCO?
2. What do you know about TESCO?
Key: TESCO is a UK-based supermarket chain, audio/video servers, which are servers that can handle audio and video, and Cat6 cables, which are a type of network cable.
2. Reading: Karam and Natasha work for ComHelp company. The company provides IT services to customers. Karam and Natasha work in different areas of the city. Every week they write a report for their boss. Read their notes.
NOTICE: Notes are not full sentences, and we often use the past simple in diary entries or reports like the one Karam and Natasha write for their boss.
3. Writing: Complete the table in ex.1, p51 with notes about yourselves, what you did last week at work or study. Just write notes using the past simple, not full sentences.
4. Writing: Tell your students to write a report using full sentences, based on their notes. Reind them about the linking words they have been taught: and, but, so and because. In case they did several tasks or activities the same day of the week you may add: First, then, after that, at the end of the day, finally….
Example: 1. Last week I… . On Monday I …. and …so…
.2. . Last week I… . On Monday, fist I …then…. and …so…, because… but… .After that I… . At the end of the day I…. .
5. Speaking : Tell the students that they are going to role-play a conversation between a boss and an employee, which will give them the opportunity to practise questions and answers in the past simple. A question the boss can begin with (for example, Why didn’t you come to the office on …?) and the answer (Because I …). Both Student A and Student B get the opportunity to play the boss but the information on pages 68 and 78 is just for the employee role.
Task: Role- play the following situation: Explain to your boss why you were not in the office.
Preparing for the next unit Unit 7. It is about IT support, so you should come prepared by finding out what procedures their organisation has for dealing with computer problems that non-IT experts have.
Unit 7: IT Support.
Практичне заняття №1
Тема: Fault diagnosis.
Мета заняття: Сформувати комунікативні навички говоріння , читання, письма, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео матеріалів за темою Fault diagnosis.,та вміння коментувати та давати аналіз даної інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу щодо висвітлення нещодавніх подій з використанням Present Perfect у контексті обслуговування клієнтів.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Making a roll-call in the group.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Understanding faults;
2. Language: The present perfect to talk about recent actions in the context of customer service: Has (s)he switched off the computer? Have you checked the cable connections? I’ve unplugged the computer.
3. Vocabulary: Fault diagnosis questions and answers.
Основна частина
1. Warm-up activity A.: Ask students to answer the questions:
1. What technical problems with their computers can people face at home or at work?
2. What should people do to solve the computer hard ware problems?
3. Can you explain what a blank screen mean?
4. What is the installation problem?
5. Can you explain the problem of “Drive fragmentation”? What is it? And what should we do to remove the problem?
B: Now ask them read and check whether they have been right with your answers:
You get a blank screen when there is nothing visible on the screen. You can have installation problems when putting new software onto a computer (for example, when there is not enough space for the program on the computer or when a computer upgrade is required first). Drive fragmentation is when the computer performs less efficiently because data is stored on the hard disk in different places. When this happens, you need to defragment the hard disk.
2. Speaking: Work in pairs. Ask students to make a list of computer hard ware problems. Compare it with another partner. They may use Useful vocabulary: incompatibility between hardware devices ; drive or disk fragmentation; result in poor performance; power cuts or power surges; out of ink/toner ; problems with devices; a printer; a mouse ; dirty; have/has flat batteries; cannot communicate with a device; loose cables; connection conflicts between devices.
3. Reading: You are going to listen to a dialogue in which Maryam, a non-IT expert working in the Human Resources Department, calls Haider at the company IT help desk to ask for help about a problem with her computer.
A: Read the dialogue and then discuss in pairs:
1. What did Maryam and Haider talk about?
2. What were the problem and solution?
B: Vocabulary: Complete the sentences with the words in the box.

Keys : 1 switched 2 type 3 worked 4 checked 5 tight 6 found 7 disconnected/unplugged 8 go 9 working 10 unplugged/disconnected
4. Listening: Play the recording so to check your answers in Exercise 2. Then play the recording a second time. Focus on phrases used to introduce themselves over the phone (for example, Hello and This is …) and present the following expressions: How can I help you? Don’t worry. OK, give me a sec. You’re welcome. Have a good day.
Extra activity: Role-play the telephone conversation between Maryam and Haider using the phrases identified from the dialogue, which you could write down. If mobile phones are available, you can use them for the conversation to make it look more natural. (First: use the phrases, then learn and role play the complete dialogue).
5. Pronunciation ► 42 Play the recording and just listen to the verbs. Pay attention to the three different ways the -ed ending can be pronounced (for example, checked [t], unplugged [d], disconnected [id]). Then listen and repeat the verbs.
Extra activity: Read the following verbs: finished, opened, searched, looked, installed, recommended (you may add some more to your list), categorise them according to the pronunciation of the -ed ending in each.
-[t]; -[d]; -[id].
6. Use of language: The present perfect to talk about recent actions (actions that have happened in the past and have a result in the present):
Look at the following sentences from Exercise 2:
Have you checked the cable connections?
I think I’ve found the problem.
I’ve unplugged the computer.
Answer the questions:
Are these sentences about the past or the present?
Are they completed?
Do they have a result now?
Do we know when the action happened?
Is there the time of the action mentioned in the sentences? (ago, that time, in 2003).
We use the present perfect tense to talk about recent actions (an action that has happened in the past and has a result in the present).
e.g.: You have checked the cable connections.
We use the present perfect tense to talk about recent actions (an action that has not happened in the past and has a result in the present).
e.g.: She hasn't finished the report.
We use the present perfect tense to ask about recent actions (an action that has happened in the past and has a result in the present)
e.g.: Has she switched off the computer? Short answers: Yes, she has. /No, she hasn't.
Have you checked the cable connections?
We use have/has + the past participle of the verb. To form the past participle of regular verbs, we add -ed. to a regular verb.
Now go through the sentences in the Language box. Start building up a list of
irregular verbs that both the past simple and the present perfect have been introduced.
Example: go–went–gone, buy–bought–bought, be–was–been, set up–set up–set up. (You might add the following verbs to your list of the irregular verbs).
Make up 3-5 sentences of your own using the verbs: finish, open, search, look, install, recommend, clean, switch, check, disconnect, unplug, type, find, do, run, see, make, be, have, work…
7. Use of language: The activity will help you practise asking questions in the present perfect. You can work individually or in pairs. Compare the questions with have or has and correct form of the verb in brackets ex.5, p. 53.
Key:
1 Have, run 2 have, had 3 Have, charged 4 Has, opened 5 Has, entered 6 Have, changed 7 Have, checked 8 Have, installed, uninstalled 9 Has, updated
8. Use of language: Before doing the activity, go through all the items to make sure you understand the verb–noun collocations (for example, upgrade the operating system, reinstall the application). Use contracted forms in this activity to practice forming affirmative and negative sentences using the present perfect.
Example: the screen/go/blank
The screen’s gone black. (has gone).
Key;
1 The charger’s stopped working. 2 I haven’t upgraded the operating system. 3 She hasn’t installed the updates. 4 They’ve reinstalled the application. 5 She hasn’t been able to fix the problem. 6 I’ve defragmented your drive.
8. Pronunciation: Play the recording. Listen and repeat the questions in ex.5, p.53. Copy the intonation in the questions. Make up your own answers to the questions.
9. Speaking: Revise the key phrases from the dialogue in Exercise 2 and use these phrases in your phone conversations. Before you carry out the activity, take one or two minutes’ preparation time to think about what you are going to say. If it is practical, use your mobile phones to carry out this activity or at least in pairs sit back to back so you cannot look at each other, but only listen to.
Student A: Turn to page 69.
Student B: Turn to page 79.


про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку
