МЕТОДИЧНІ РОЗРОБКИ 1КУРС СЕМЕСТР English for Information Technology
Book 2 Unit 1
Working in IT
Практичне заняття №3-4
Tема: IT workplace rules. Modals of obligation
Мета заняття: ознайомити студентів з новим лексичним матеріалом з теми “IT working place rules”. Навчити вживати modal verbs and imperatives в усному мовленні та письмі. Розвивати навички діалогічного мовлення, слухання; вміння аналізувати інформацію на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою IT working place rules
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: Discussion: IT working place rules
- Language: Modal verbs and imperatives
- Vocabulary: IT operations and working environment
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Students work in small groups and discuss the questions: Do you have any rules in your workplace or college? Do you think they are good or not? Why?
2. Reading and vocabulary
2.1. Pre-reading. Ask students for some examples of IT security rules.
2.2. Reading for gist. Students read the memo on p. 8 (English for IT Part 2 p. 8) and check if their examples are mentioned.
2.3. Vocabulary. Students find the words to match the definitions in ex. 3. They compare the answers in pairs, then check as a class.
Keys: 1 chief information officer, 2 security, 3 data, 4 password, 5 network, 6 alphanumeric, 7 characters, 8 colleagues.
3. Grammar
3.1. Presentation 1. Students underline the words used to express rules. Ask them what these verbs are called (modal verbs). Then ask students to match the modals to the meanings:
- it’s very important to do it (must, have to);
- it’s very important not to do it (mustn’t, can’t);
- it’s a good idea to do it (should);
- it’s not a good idea to do it (shouldn’t);
- it’s required (need to);
- it’s not necessary (don’t have to);
- it’s allowed/possible (can).
Drill the pronunciation if necessary.
3.2. Presentation 2. Write on the board: Keep your password secret. Don’t use common words. Ask: Who are these sentences addressed to? Explain that this form is called imperative. Ask: What form is the verb in the first sentence (bare infinitive, basic verb). What do we add to a sentence to make it negative?
3.3. Practice. Refer students to the table on p. 8 and ask them to work in groups. They should write positive and negative sentences about rules in the classroom using modals and imperatives. Monitor, elicit a few examples from the class and give feedback on the language.
3.4. Freer practice. Students discuss the activities in ex. 5 p. 9 using the learnt grammar.
4. Listening:
4.1. Listening for gist. Students listen to Track 5 and answer the questions:
- How does Lateefa feel about the rules in workplace? (She doesn’t like them.)
- Does she like her manager? Why or why not? (No, because he sets a lot of strict rules that are probably unnecessary.)
4.2. Listening for details. Students listen again and complete the table in ex. 6, then compare in pairs. Check as a class.
Keys
Dos: ask the support technician to update the software, work from home.
Don’ts: make personal phone calls, install software.
5. Speaking
Ask students to work in small groups and write a list of technology-related rules in their workplace or place of study. Then regroup the students and ask them to discuss these rules: Are they necessary? Which would you like to change? Why?
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
Speaking:
Ask students to work in pairs. Tell student A to look at the information on p. 9, and student B look at the information on p. 69, and follow the instructions. Monitor and give feedback on the language. Let them swap their roles and do the exercise again. Ex. 8, p. 9 (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology 2).
Watch two video about the rules in the workplace. Ask students if these rules could be applied to IT sphere. Tell them to write a short summary (10-12 sentences). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pdSEN4H68NQ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XIIW7lhEdzQ
Book 2 Unit 1
Working in IT
Практичне заняття №5-6
Tема: Meetings. Making suggestions, agreeing, disagreeing. Business matters
Мета заняття: ознайомити студентів з новим лексичним матеріалом з теми “Meetings”. Навчити вживати expressions how to make suggestions, agree and disagree в усному мовленні та письмі. Розвивати навички говоріння, слухання, аналізу інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Meetings.
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: How to conduct a meeting . Setting up the meeting agenda
- Language: Making suggestions, agreeing and disagreeing. Modal verbs, maybe, might be, perhaps for making suggestions.
- Vocabulary: Structure of a meeting. Preparing the agenda, making suggestions, agreeing and disagreeing.
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Ask students to work in small groups and discuss the questions:
- Do you ever go to meetings? What kind?
- What happens during a meeting in an organisation?
- Have you ever been to such a meeting? If yes, share your experience.
2. Vocabulary
Students work in small groups and explain the meaning of the words in ex. 2 p. 10 (English for IT Part 2). They may use a dictionary if necessary. Make sure they know the meaning of the words and drill the pronunciation.
3. Listening and Functional language
3.1. Listening for gist. Books closed. Students listen to Track 06. They should say what two items are on the agenda. After listening, they check with the agenda in ex. 3 p. 10.
3.2. Listening for details. Students listen again and answer the questions in ex. 3.
3.3. Functional language. Elicit a few examples of phrases the speakers used to make suggestions (students may open the audio script and find them). Also they should find the agreeing/disagreeing phrases that make the responses more polite. Elicit and write the verbs patterns on the board: could/should + V, how about/what about + V-ing.
3.4. Functional language practice. Students work in pairs and think of suggestions similar to those in teleconference in ex. 3. They should take turns to make and respond to suggestions. They should use the modal verbs and expressions from the table on p. 10.
4. Reading and Vocabulary revision
4.1. Reading for gist. Ask students to read the job advertisement on p. 11 and say if they would like to work for this company or not. They should give reasons.
4.2. Students complete the gaps in the advertisement with the words from the box (ex. 1 p. 11).
4.3. Post-reading and vocabulary practice.
Student A look at the information on this page, student B look at the information on p. 69. They role-play a meeting about replacing the old equipment (ex. 6 p. 10).
5. Writing
5.1. Students look through the advertisement again and answer the question in ex. 3 p. 11 (Answer: 2).
5.2. Students work in groups and write their own job advertisements using the pattern they identified in ex. 3. Then they swap their advertisements. Elicit a few answers from the class: Which company would you like to work for? Why?
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
Speaking: Role-play the interview on p. 11. Prepare the questions about the job and the company. Role-play the interview. Swap the roles and conduct the interview using the same company description and job advertisement. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology 2).
Writing: Look at the advertisement in ex. 1. Write a job advertisement for IT job you would like to have or your current job. Use the pattern of agreeing/ disagreeing and suggestions. Share your results with a partner.
Book 2 Unit 2
IT systems
Практичне заняття №1
Tема: System specifications. Large and small numbers
Мета заняття: ознайомити студентів з новим лексичним матеріалом “System specifications”. Навчити вживати large and small numbers in IT в усному мовленні та письмі. Розвивати навички діалогічного мовлення, слухання та аналізу інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу по темі System specifications.
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
1. Function: Hardware specifications, multimedia types, OS installation
2. Language: large and small numbers, practice
3. Vocabulary: Internal components, peripherals and storage
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Ask students: What is the difference between peripherals and internal hardware? Let them name as many as they can. Can they install any?
2. Vocabulary
2.1. Students work in pairs and do ex. 2 p. 12 (English for IT Part 2). Check as a class.
2.2. Tell students to listen to a technician describing a motherboard to a trainee. They should look at the photo (ex. 3) and match the words in the photo. Check the answers.
Keys: 1E, 2A, 3B, 4F, 5D, 6C, 7G.
2.3. Students work individually and match the prefixes to the numbers (ex. 4 p. 13). Check as a class and drill in pronunciation.
Keys: 1 tera-, 2 giga-, 3 mega-, 4 kilo-, 5 nano-, 6 micro-, 7 mega-*, 8 quad-, 9 dual-
*Looks like there is a mistake in the book, as 3 and 7 are the same. One of them should be 0.001 (milli-).
3. Listening:
3.1. Listening for gist. Students listen to an IT manager and assistant. They should say what problem they are discussing. (There is a problem with the delivery, what has been delivered is not exactly what they ordered.)
3.2. Listening for details. Students listen again and correct the delivery slip in ex. 6 p. 13.
5. Speaking
Ask students to work in pairs and write specifications for a computer. Then tell them to ask and answer questions about their partner’s computer. Remind them to think of the following items: processor speed, memory, hard drive size, screen resolution.
Example
A: How fast is the computer? B: It is 3, 32 megahertz.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
Tell students to refer to IT Glossary and read the Section System Specifications. Read the definitions and translate the new vocabulary. Pay special attention to the use of following terms: multimedia types, OS installation, peripherals, large and small numbers, decimals, using decimals values and prefixes (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology 2).
Tell students to suggest specifications for different people (see ex. 9). Tell them to use the following example: I do not think admin staff needs a fast processor. They only need it for word processing and emailing.
Then let them read the suggested specifications to other students.
Book 2 Unit 2
IT systems
Практичне заняття №2
Tема: Graphical user interface operations. Imperatives
Мета заняття: ознайомити студентів з новим лексичним матеріалом з теми “Graphical user interface operations”. Навчити вживати expressions how to give instructions, imperatives and softteners в усному мовленні та письмі. Розвивати навички усного мовлення, слухання та аналізу інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Graphical user interface operations.
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: Interface operations, matching words to screenshot functions
- Language: giving instructions, softeners, sequencers, imperatives
- Vocabulary: describing screenshots, matching words to actions
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Students work in pair and revise the vocabulary related to hardware specifications, multimedia types, OS installation. Present objectives and expected results of the lesson.
2. Vocabulary
2.1. Tell students to read ex.2 p. 14 (English for IT Part 2) and match the indicated words to the A-L in the screenshot. Let students read the screenshot collocations and drill the pronunciation.
Keys: 1A, 2L, 3F, 4G, 5B, 6K, 7J, 8C, 9I, 10E, 11D, 12H
2.2. Ask students to work in pairs and match the actions to their results (a-g). (ex. 3). Drill the pronunciation.
Keys: 1b, 2f, 3a, 4e, 5d, 6c, 7g.
3. Listening and Functional language
4.1. Listening for gist. Students listen to a help desk technician talking to ac IT user and answer the questions in ex. 4 p. 15.
Answer: The technician wants to know the install date.
4.2. Functional language. Students listen again and do ex. 5.
Keys:
1 Can you scroll up to the top?
2 Just select ‘Manage’.
3 Just right-click where it says ‘Disk 0’.
4 Choose ‘Properties’ from the menu.
5 Choose the ‘Details’ tab.
6 Select ‘Install date’.
4.3. Tell students to read instructions and answer the following questions:
- What verb form does the speaker use to give instructions?
- How does he make the instructions sound more polite?
- What words does he use to show the order of steps?
Refer the students to the table on p. 15.
4. Speaking:
Ask students to work in pairs and do the following task:
Take turns acting as an IT help desk technician and an IT user. Explain to a partner how to follow the steps for each action using the prompts and sequencers (ex. 7 p. 15).
Monitor and give feedback on the language.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
Writing: tell students to refer to ex. 9 and write an email describing steps for the actions using the information from ex. 7 (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Let them read the emails to a partner.
Go to the website and read more definitions of GUI. Add news term and definitions to your vocabulary.
https://www.merriam-ebster.com/dictionary/graphical%20user%20interface
Unit 2 Book 2
IT systems
Практичне заняття №3
Tема: Multimedia hardware. Sentences with two objects
Мета заняття: ознайомити студентів з новим лексичним матеріалом з теми “Multimedia hardware”. Навчити вживати sentences with two objects and prepositional verbs в усному мовленні та письмі. Розвивати навички говоріння та читання, вміння аналізувати інформацію на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу по темі Multimedia software.
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
1. Function: Multimedia hardware, function and installation
2.Language: sentences with two objects, prepositional verbs practice
3.Vocabulary: multimedia equipment, application and definition
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Tell students to work in pairs. Prepare pictures with some of the items from ex. 2 -. 16 (English for IT Part 2). Ask: Who might use each of the items? What might they use them for?
2. Lead-in and Vocabulary
Tell students to work in small groups and answer the questions in ex. 1. Then let them label the photos with multimedia equipment and explain what these items are used for (ex. 1-2 p. 16).
3. Reading and vocabulary
3.1. Reading for gist. Tell students to read the email quickly and answer the questions:
- What does Kamal want to do? (Connect his laptop to a projector.)
- What’s the purpose of Natasha’s email? (She gives him instructions how to do that.)
3.2. Ask students to match the words from email in ex. 4 to the words a-h with similar meanings in ex. 5. They compare in pairs, then check as a class.
Keys
Ex. 5: 1d, 2c, 3b, 4f, 5g, 6a, 7h, 8e.
4. Grammar
4.1. Students complete the prepositional verbs in ex. 6.
Ex. 6: 1 to, 2 into, 3 from, 4 from.
4.2. Students look at the sentence Insert the plug into the socket. Ask: How many objects are there? What are they? Elicit the structure by asking students to complete the gaps: verb + object of verb + ______ + object of ______. Then they check with the table on p. 17.
4.3. Practice. Students complete the instructions using two objects where appropriate (ex. 7).
5. Writing (Freer practice)
5.1. Tell students to write an email explaining how to transfer photos from a camera to a computer. Give instructions about the necessary steps (ex. 8) and elicit some forms of greetings and signing off. Students use the prompts in ex. 9.
5.2. Ask them to read their emails to the class and give feedback.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
Reading: Ask students to work in pairs, read the email in ex. 4 and mark the following features: the greeting, a paragraph, signing off. Tell them to think about other forms of greetings and signing off in emails. Then each pairs should share their findings with the group.
Watch the video about multimedia hardware and ask students if they fully agree or disagree with the lecturer’s ideas? Write a short summary (10-12 sentences).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pKUCRt-npNw
Unit 3 Book 2
Data communication
Практичне заняття №2-3
Тема: Networks. Relative clauses
Мета заняття: ознайомлення студентів з різноманітністю мереж та лексикою з теми Network, з граматичною темою Relative clauses; введення речень з relative clauses у мовлення студентів; формування навичок говоріння, читання та слухання; оволодіння студентам іноземною мовою як засобом спілкування і здійснення в цьому процесі виховання, навчання та розвитку особистості студента.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1.Function: Discussion: types of network (star, mesh, bus and ring).
2.Language: relative clauses.
3. Vocabulary: network terminology.
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Students work in small groups. They should look at the picture and discuss the questions.

- Which of these devices do you use in your daily life?
- Do you think they are on a network? Is it wired or wireless?
- Are these devices secure? What security features do they have?
- Do you use VPN for visiting VK or other websites?
2. Vocabulary I (Jon Marks. Check your English Vocabulary For Computers and Information Technology. Third Edition p. 22)
Students will in the gaps with the given words. Check as a class and drill the pronunciation.
LAN intranet Local log onto network card satellite server terminals WAN (Wide Area Network)
LAN is pronounced "lan", and stands for 1_________________ Area Network. In a typical LAN, there is a central network 2_________________ which supports a number of 3_________________. Users have to 4_________________ the network server. Pages of information that can be viewed within a LAN are called an 5_______________ . A number of LANs connected to each other via 6_________________ or other form of communication are called a 7_________________. To be used as network terminals, each computer needs to have a 8_________________ installed.
Keys: 1 Local, 2 server, 3 terminals, 4 log onto, 5 intranet, 6 satellite, 7 WAN, 8 network card
3. Reading and grammar.
3.1. Students read the web page (p. 22 (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book) and do ex. 2.
3.2. Ask students to read the web page again and find the references to the words given in ex. 3 p. 22. Ask them to label the types of network in ex. 4.
3.3. To check students’ understanding of relative clause, write the phrase There are 2 kinds of networks that are in common use and elicit the answers to the questions:
- Where is main clause of the sentence?
- What pronoun do we use to give more information about the thing/idea?
3.4. Read the grammar point and ask students to do the exercise.
In defining relative clauses, we use:
- pronoun who/that in order to give detailed information about the person we're talking about: I met a man who teaches IT at university.
- pronoun which/that in order to specify the object we are talking about: I've got an old camera.
- pronoun where to specify the place we're talking about: They took us to a restaurant where we could eat sea food.
- pronoun whose to specify the person or thing that is the owner of something: I saw a TV program about a man whose comedy career started in 1925.
- pronoun when/that to specify the date of the described event or action: 7969 was the year when the first man walked on the Moon.
3.5. Ask students to look through the text on p. 22 and find relative clauses. They should do the following:
- Answer the question, What relative pronouns do we use in the text to give details?
- Write your own sentences using the relative pronouns from the text.
3.6. Controlled practice. Ask students to choose the correct option.
- The internet is a network where/which covers the world.
- A GPS is a device that/who shows your location.
- He’s the person which/who looks after the servers.
- Mary is the person who/which manages our network.
- He’s the man who/which was promoted at work.
- VPN is a network who/that gives the possibility to use Internet anonymously.
- Wi-fi is a type of network that/who doesn’t use cables.
Keys: 1 which, 2 that, 3 who, 4 who, 5 who, 6 that, 7 that
3.7. Freer practice. Students work in pairs and do ex. 7 p. 23.
Example: A: What’s a CPU? B: It’s a chip that controls the computer.
4. Reading
4.1. Pre-reading. Ask students, What types of network do you know?
4.2. Reading for gist. Students read the text Types of Network (https://www.javatpoint.com/types-of-computer-network) and check what types of network are mentioned there.
A computer network is a group of computers linked to each other that allows the computer to communicate with another computer and share their resources, files, and programs. There are 4 types of network:
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
LAN – Local Area Network
Local Area Network is a group of computers connected to each other in a small area such as building. LAN is used to connect two or more personal computers through a communication medium such as twisted pair, coaxial cable, etc. It is less costly as it is built with inexpensive hardware such as hubs, network adapters, and ethernet cables. The data is transferred at an extremely faster rate in Local Area Network. Local Area Network provides higher security.
PAN – Personal Area Network
Personal Area Network is a network arranged within an individual person, typically within a range of 10 meters. People use smartphone, laptop, mp3 player and PlayStation.
There are two types of Personal Area Network:
- Wireless Personal Area Network: Wireless Personal Area Network is developed by using wireless technologies such as WiFi, Bluetooth. It is a low range network.
- Wired Personal Area Network: Wired Personal Area Network is created by using the USB.
MAN – Metropolitan Area Network
Government agencies use MAN to connect to the citizens and private industries. In MAN, various LANs are connected to each other through a telephone exchange line. It can be used in a college within a city.
WAN – Wide Area Network
A Wide Area Network is a network that covers a large geographical area such as state or country. The internet is one of the biggest WAN in the world. A Wide Area Network is widely used in the field of Business, government, and education.
4.3. Students read the text and answer the questions.
- What type of network is used over small areas?
- How many types are mentioned in the text?
- What hardware does LAN use?
- Does LAN provide high security?
- Is PAN wireless or wired?
- What network does the government use to connect to private industries?
- What network covers a large area such as country?
5. Listening
5.1. Listening for gist. Students to listen the track about a new service and answer the questions (ex. 8 p. 23, Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book). Give them some time to look through the questions before listening.
5.2. Listening for details. Students listen again and do ex. 9 p. 23.
Завдання для самостійної роботи:
- Exercise 13 (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book 2), p.23
- Exercises 5-6 (John Hughes & Jon Naunton) Business Result. Intermediate. Second Edition), p. 88-89.
Використана література:
- Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book 2.
- John Hughes & Jon Naunton. Business Result. Intermediate. Second Edition.
Режим доступу: https://www.javatpoint.com/types-of-computer-network
Book 2 Unit 3
Data communication
Практичне заняття №5
Тема: Zero and first conditionals
Мета заняття: ознайомлення студентів з IT-функціями мобільних пристроїв та використанням їх у різних сферах обслуговування, формування іншомовних навичок і вмінь, оволодіння студентам іноземною мовою як засобом спілкування і здійснення в цьому процесі виховання, навчання та розвитку особистості студента по за темою Mobile computing – zero and first conditional
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: discussing the usage of mobile and сustom devices
- Language: zero and first conditionals
- Vocabulary: mobile computing
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Tell students to do the following.
Imagine that you are traffic wardens. Work in pairs. Write a list of problems (2-3) that a traffic warden can have during their work using electronic devices.
Suggested answers:
- Slow internet connections
- Slow battery of the phone
- Damaged device
2. Grammar
Test-Teach-Test Technique
2.1. Presentation 1. Write the sentence on the board: If you drop an electronic device, it breaks. Ask students the following questions:
- Does it always break? (Usually.)
- Is it the result of an action or situation? (Yes.)
- Where is the main clause? (…it breaks.)
- Can we change the order of clauses? (Yes.)
- Should we use a comma between clauses? (Yes, when the if-clause comes first.)
2.2. Practice 1. Ask students to do ex. 6 p. 24 (English for IT, Part 2). They work individually, then compare their answers in pairs. Check as a class.
Keys: 1 doesn’t know, uses; 2 is, signs; 3 changes, updates; 4 needs, sends.
2.3. Presentation 2. Write the sentence on the board: If we have a problem, we’ll send a message. Ask students the following questions:
- Do we always have a problem? (No.)
- Can we have a problem in the future? (Yes.)
- Is it a result of a future action? (Yes.)
- What tenses do we use in both clauses? (If + present simple, will + V.)
2.4. Controlled practice 2. Ask students to do the following exercises.


2.5. Free practice 1. Students work in pairs and do the following task:
Imagine that you are traffic wardens and have some problems at work. Write a list of them, and then suggest solutions using Zero and First conditionals.
Example:
If you don’t charge your device, it stops working during the rush-hours. If you don’t have camera, you won’t know where the illegally parked cars are.
2.6. Freer practice 2. Elicit a few other professions from students. They should work with a new partner, discuss what problems they can have at work and make a list of solutions using the conditionals. Monitor and give feedback on the language.
Unit 3 Book 2
Data communication
Практичне заняття №6
Тема: Email and Business matters
Мета заняття: ознайомлення з новою лексикою, написання електронного листа; формування іншомовних навичок і вмінь, оволодіння студентам іноземною мовою як засобом спілкування і здійснення в цьому процесі виховання, навчання та розвитку особистості студента за темою Email and Business matters.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: writing an email
- Language: articles (a and the)
- Vocabulary: email components and electronic communications systems
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Students work in pairs and discuss the questions.
1. How often do you use email?
2. Which do you prefer: instant messaging, face-to-face communication, or telephone communication? Why?
2. Vocabulary
2.1. Ask students if they know what these mean: carbon copy, blind carbon copy. Then they read the following passage and check their answers.
Carbon Copy (CC) – people who receive the email for their own information, but who are not expected to reply. When you press “reply all,” all of these addresses receive your response.
Blind Carbon Copy (BCC) – people who receive the email but are not listed as recipients. Senders use the BCC section if they don’t want recipients to know who else has received the email. They do not receive “reply all” responses.
2.2. Students work individually and complete the gaps (Jon Marks. Check your English Vocabulary For Computers and Information Technology. Third Edition). Check as a class.
Sending an attachment
attach browse field inboxes open send size
You can send almost any file as an attachment. 1_______________ through the folders on your computer until you find the file you want to attach. Click on 2 “_______________”. The file will appear in the attachments 3_______________. Then click 4 “_______________”, and wait while the file uploads. Add more files if you wish. When you have finished adding files, click 5 “_______________”.
Some email 6_______________ will only receive attachments up to a certain 7_______________ with one email, for example 10MB. If you need to send a lot of very big attachments, it's sometimes necessary to spread them over a number of separate emails.
Keys: 1 browse, 2 open, 3 field, 4 attach, 5 send, 6 inboxes, 7 size
3. Writing
3.1. Students look at the email and answer the questions: true or false. (Jon Marks. Check your English Vocabulary For Computers and Information Technology. Third Edition p. 59)
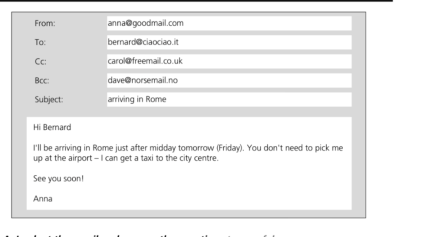
1. The recipient is Anna.
2. The sender is Anna.
3. Bernard knows that Carol knows when Anna will be arriving in Rome.
4. Bernard knows that Dave knows when Anna will be arriving in Rome.
5. You can say that Anna Cc-ed her email to Carol.
6. You can say that Anna Bcc-ed her email to Dave.
7. The subject line is empty.
8. The style of the email is formal.
9. Cc stands for carbon copy and Bcc stands for blind carbon copy, but the full terms are almost never used.
10. Carbon copies were a method of making copies of documents typed on typewriters.
Keys: 1F, 2T, 3T, 4F, 5T, 6T, 7F, 8F, 9T, 10T
|
3.2. Preparation. Students do the following: |
|
|
Write a number (1-6) to put these parts of an email to a friend in the right order. |
|
|
……… |
Closing – Write back soon and tell me about your family. |
|
……… |
Your name – Lucinda |
|
……… |
Opening greeting - Hi Jo |
|
……… |
Body of email – I go to my local high school. It's great because I've got loads of friends there and ... |
|
……… |
Closing greeting – Best wishes |
|
……… |
Introduction and reason for writing – My name's Lucinda. Let me tell you a little about myself and my family. ... |

3.2. Check your understanding: gap fill. Students work individually and complete the sentences using the sentence ends in the box.
and computers and her dog, Cookie go roller-skating
are Jo and Steph to Marco to the café and use the Wi-Fi
1. Sara sent an email ______________________________.
2. Sara lives in London with her family ______________________________.
3. Sara likes studying maths ______________________________.
4. Sara’s close friends ______________________________.
5. After school Sara and her friends go ______________________________.
6. Sara likes to play hockey and ______________________________.
Keys: 1 to Marco; 2 and her dog, Cookie; 3 and computers; 4 are Jo and Steph; to the café…; 6 go roller skating.
3.3. Students work individually and do the following task:
Write an email to your new pen friend. Tell them about the latest news. (This can be done as homework.) Then they can peer-check each other’s emails.
4. Grammar.
4.1. Presentation. Write the sentences on the board, After school I often go to a café, with my friends. The café has got Wi-Fi so we can chat online, and then we usually go home to do homework.” Ask students the following questions:
- In which sentence do we mention the word “café” for the first time?
- Which article do we use to mention “café” for the first time?
- Which article do we use with the word “café” in the second sentence?
- Do we know what café is it?
4.4. Controlled practice. Ask students to complete the sentences with articles a/an/the.
1. Yesterday, I ordered __ sandwich and __coffee for lunch. ___ sandwich wasn’t very tasty, but ___ coffee was good. 2. Near my town, there is __ old castle. Behind __ castle, there is ___ lovely lake. 3. "I met __ interesting girl at the party last night. She was from Vietnam." "Really? I’ve never met __ girl from Vietnam before." 4. "I sent you __ sms and __ email. Did you receive them?" "I got ___ sms, but not ___ email. 5. Jack has __ new job. He works as __ tour manager ___ for music band. I’d like to have __ job like that!
Keys: 1 a, a, the, the; 2 an, the, a; 3 an; a; 4 an, an, the, the; 5 a, a, a, a.
4.5. Freer practice
- Divide the students into groups of three or four.
- Give each group a copy of the game board (Articles board game from TeachThis, https://www.teach-this.com/parts-of-speech-activities-worksheets/articles), dice and counters. Students will also need a pen and paper for keeping score. Nominate one student in each group to be the time keeper.
- The players place their counters on the start square. The players then take turns to roll the dice and move their counter along the board.
- When a player lands on a 'True or false?' square, they complete the statement with the correct article (a, an, or the) and read it to the group. If the player is able to do this correctly, they score a point. If not, they must move back to their previous square.
- If the statement is correct, the other group members guess whether it's true or false for the player. The player then reveals the answer. The students who guessed correctly each score one point.
- When a player lands on a 'Talk about...' square, they complete the 'Talk about...' sentence with the correct article for one point. If the player doesn't complete the sentence correctly, they must go back to their previous square.
- If the sentence is correct, the player then talks about the topic for 30 seconds for an extra point.
- When a player reaches the finish, the game ends and the points are added up. The student with the most points wins the game. If at any point, the students are unsure of the correct article, they can ask you to adjudicate.
|
Finish |
Talk about...
32....trip you plan to take. |
True or false? 31. I have never been to .... Philippines. |
Talk about... 30. .... important problem facing .... world. |
True or false?
29. I love to visit coast. |
Talk about...
28....useful invention. |
|
|
True or false? 27. I would like to live in .... countryside. |
||||
|
True or false? |
Talk about... |
True or false? |
Talk about... |
True or false? |
Talk about... |
|
21. I had .... cold last month. |
22....most expensive thing you've ever bought. |
23. I usually meet my friends at .... weekend. |
24. something you like to do in .... evening. |
25. I once ran in .... marathon. |
26. what you were doing .... hour ago. |
|
Talk about... 20. what .... teachers at your school are like. |
|
||||
|
True or false? 19. I eat junk food more than twice week. |
Talk about... 18. the last time you went to cinema. |
True or false? 17. I have .... older brother/ sister. |
Talk about... 16....new language you would like to learn. |
True or false? 15. I use .... Internet every day. |
Talk about... 14. something interesting you've done in .... last week. |
|
|
True or false?
13. I live in .... apartment. |
||||
|
True or false? |
Talk about... |
True or false? |
Talk about... |
True or false? |
Talk about... |
|
7. I have seen .... ancient monument. |
8....person you know very well. |
9. I have been to USA. |
10. how much .... umbrella costs. |
11. I never listen to .... radio. |
12. what .... student on your right is wearing. |
|
Talk about... 6....most beautiful place you have visited. |
|
||||
Unit 3 Book 2
Data communication
Практичне заняття №7
Тема: Business matters
Мета заняття: повторення і закріплення вивченої лексики та граматики; формування іншомовних навичок і вмінь, оволодіння студентам іноземною мовою як засобом спілкування і здійснення в цьому процесі виховання, навчання та розвитку особистості студента за темою Business matters.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Ask students the following questions:
1. Are there any companies you would like to work for?
2. Would you like to start your own company? Why or why not?
3. What kinds of businesses might have trouble surviving in the future?
2. Reading and speaking
2.1. Pre-reading. Ask students to think about problems that staff can have working in an architecture company and how they can improve the communication system of a company.
2.2. Reading. Ask students to read the profile p. 27 and make a list of the equipment and software they are using. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book 2)
2.3. Post-reading and speaking. Ask students to discuss and decide the hardware and software needed to meet all the requirements.
3. Writing
3.1. Ask students if they know what a proposal (in business) is (a plan or suggestion, especially a formal or written one, put forward for consideration by others – from Oxford Languages dictionary). Draw their attention to the structure of a proposal suggested in 1.3 p. 27. Students work in groups and brainstorm ideas on what each part of their proposal will include. Monitor and help with ideas if necessary.
3.2. Ask students to write their proposals (in groups) and then to present it to the class and comment on each other’s works Give feedback on the language, point out some good examples and correct the mistakes if necessary.
Unit 4 Book 2
Administration
Практичне заняття №3
Тема: Databases
Мета заняття: Формування комунікативних навичок говоріння, читання, письма, сприйняття на слух аудіо та відео, вміння коментувати та аналізувати дану інформацію на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Databases.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
1. Function: General information about databases: what do they look like and what they are used for.
2. Language: Revision of recent grammar structures. Construction by + -ing to express how to do things.
3. Vocabulary: Related to databases (a form, a table, a report).
Основна частина
1. Warming-up

Fig. 2. List of popular databases [4]
Students look at the picture and tell whether they know those databases. They should try to explain what are they used for. Then they work in pairs or small groups and discuss the following questions:
1. What database programs do you know?
2. What do people use those databases for? Give some examples. (Ex. 1 p. 30 English for IT Part 2.)
2. Listening
2.1. Listening for gist. Students match the vocabulary relating to databases with three screenshots from Microsoft Access. To do this they listen to a database administrator explaining the structure of a company database to a trainee (ex. 2 p. 30).
Keys: 1b, 2c, 3a.
2.3. Listening to details. After listening to the recording for the second time, students should choose the option that best describes what the database keeps track of and explain why (ex. 3 p. 30, the answer is A).
Pay attention to the new vocabulary: orders, stock and accounts.
3. Vocabulary
3.1. Presentation. Students work in small groups and complete the manual with the words in the box (ex. 4 p. 30). Then students can refer to the audio script on page 75 to check their answers, as well as the meaning of the vocabulary.
Keys:1 objects, 2 record, 3 fields, 4 unique, 5 primary key, 6 form, 7 report, 8 retrieve a record, 9 query the database.
3.2. Practice. Students work in pairs to practise the vocabulary from the previous task and decide which field is an appropriate primary key (a unique name for better search in database). Check first that students know the vocabulary in each description.
Pay attention to the given example, it is necessary to provide the reason for the answer.
Keys: Good primary keys are: 1 Membership number, 2 Barcode, 3 Case number/National identity card number.
4. Speaking
In pairs, students choose tables, fields and primary key for each situation described in ex. 6 p. 31. When finished, they compare their answers with another group and discuss any differences.
If it is possible, students can make a table for each database in Excel.
Students change their partners; discuss and compare their answers (or tables if any).
5. Grammar
5.1. Presentation. Write the following sentence on the board: By running a report, we can print a list of customers. Ask students to choose which is the underlined phrase used for: a) to give reason, b) to explain how to do something, c) to give some additional information (the answer is B).
5.2. Practice. Refer students to the table on p. 31 and then ask them to make up 5-6 sentences about Databases, using the “by+-ing” structure.

5.3. Freer practice. Students ask and answer questions about how to do several tasks involving databases using the language from the Language box. An example is provided as a model (ex. 8 p. 31).
Suggested answers
1 You can do that by retrieving a record, querying the database or running a report.
2 You can do that by using the ‘sum’ function (in formula).
3 You can do that by using a primary key.
4 You can do that by running a report.
6. Speaking
6.1. Students work in pairs and discuss possible solution for each problem in ex. 9 p. 31. Encourage them to use the learnt grammar and vocabulary.
Suggested answers
By using OCR, your company will save time on data entry.
By using a database, you only have to enter data once.
By running reports from a database, you won`t need to copy and paste data into word processing documents. The data will be ready for print.
6.2. Elicit some ideas from different pairs and ask the class to comment on them. Give feedback on the language.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE:
Make a table in Excel as follows. Give 5-6 examples.
|
Basic Operation for Software |
How it can be done (by+-ing) |
|
|
|
Book 2 Unit 4
Administration
Практичне заняття №4
Тема: System administration
Мета заняття: Ознайомити студентів із основними обов’язками системного адміністратора з презентацією нового лексико-граматичного матеріалу. Удосконалити навички сприйняття на слух аудіо для подальшого коментування та аналізу. Розширити словниковий запас студентів за темою: System administration.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
1. Function: Talking about stereotypes of a system administration and the real duties and responsibilities of Sysadmin.
2. Language: Showing the order of events using while, before and after. Writing semi-formal letters.
3. Vocabulary: Reset, deploy, permission, logs, backups.
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
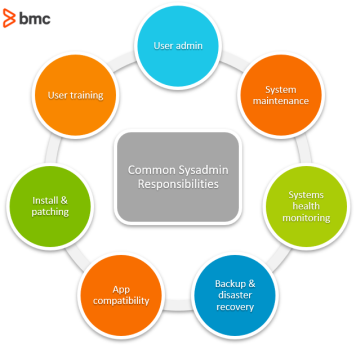
Fig. 3. Common Sysadmin Responsibilities [5]
Students look at the picture and try to explain the described Sysadmin`s duties. Then answer the following questions:
1. What do you think the Sysadmin`s duties are?
2. What stereotypes about system administrator do you know?
3. Do you think this profession is important? Why?
4. Have you ever asked system administrator about help? If yes, can you tell about that situation?
2. Vocabulary
2.1. Students work in pairs. After reading the definition of “system administrator”, they place the tasks provided in the box taking into account whether they fit the definition in the table (ex. 1 p. 32 English for IT, Part 2). If necessary, explain some vocabulary or ask students to use a dictionary.
Keys:
|
A system administrator`s task |
Not a system administrator`s task |
|
Deploy new software, looks after network security, sets up user accounts, updates software across an organisation |
Designs databases, works on a help desk, writes software to sell it other companies |
2.2. Students work in pairs. They should choose a job title from p. 4 for each task in ex. 1 p. 32 and explain their choice.
Keys:
designs databases - database administrator,
works on a help desk - help desk supervisor,
writes software to sell it other companies - software developer.
3. Listening
3.1. Listening for gist. Students listen to a system administrator asking a technician about the status of the company`s computer systems. On this first listening students are asked the two questions in ex. 3 p. 32. (Answers: 1. No, it isn`t. 2. There are several departments).
3.2. Listening for details. Students listen again and tick the correct column in the table in ex. 4 p. 32 to indicate whether the task worked fine, there was a problem, or whether it was not mentioned. Before listening, give some time to read the table. Students can check their answers with the audio script on page 75.
4. Vocabulary
4.1. In pairs, students match words from the table in the Activity 4 with their meanings (ex. 5 p. 32).
Keys: 1 reset, 2 deploy, 3 permission, 4 logs.
4.2. In pairs, students complete the collocations and phrasal verbs that they heard in the audio and try to explain their meanings (ex. 6 p. 32).
Keys: 1 smoothly, 2 crash, 3 running again, 4 out of, 5 out, 6 smoothly.
5. Grammar
5.1. Presentation. Write the example sentences from the Language box on p. 33 on the board with gaps for the words showing the order of events (e.g. ____ you reinstall the OS, beck everything up). Ask students to complete the gaps with before, while, or after (don’t tell students that these sentences are from the book). For the last sentence, ask: Who is resetting the password? Who should log in? (A user, you, etc.) Is it the same person? (Yes.) Then students check their answers with the table on p. 33.
As in the previous section, gerunds are the language focus here but this time they are used in conjunction with time words: while, before and after. Make sure students are aware that punctuation is important with these words: the commas in the example cannot be substituted with full stop, which is common mistake.
Showing the order of events
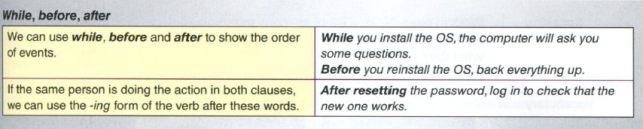
5.2. Practice 1. Students use these prompts and write sentences with while, before, or after (ex. 7 on p. 33). They will have to work out which action occurs first or whether they occur simultaneously in order to decide which word to use.
Keys:
1 While you install/While installing an operating system, the computer may reboot several times.
2 Before you deploy/Before deploying major software upgrades, (you need/have to) train users.
3 After you replace/After replacing the hard drive, everything will go smoothly.
4 After someone forgets a password, (you need/have to) reset it.
5.3. Practice 2. Students listen to five extracts from conversations and write the action that should happen first in each case (ex. 8 p. 33). The aim is to develop awareness of the effect of the time conjunction on the order of events.
Keys: 2 partition the hard drive, 3 check the schedule, 4 get access to machine, 5 ask if it`s OK/ask for permission.
5.4. Practice 3. Ask students to provide a couple examples of the order of the simple task
Example: starting working on the computer:
First you switch it on, while computer is downloading, check the Internet cable. Before finishing the work make sure to save all the documents. After shutting all the windows, switch off the computer.
5.4. Pronunciation. Student mark the intonation of the five extracts from conversations in the previous activity on the audio script (ex. 9). Intonation generally rises at the end of yes/no question and falls at the end of statements.
5.5. Freer practice. In pairs, students use prompts to produce instructions for their partner. They will have to think logically about which action comes first (ex. 10).
Suggested answers:
1 Before you finish work for the day, could you check the logs? After you check the logs, you can finish work for the day/
2 After you start work tomorrow please check out the database problem.
3 While you`re in the server room, could you check the network cables?
4 After the new designer arrives, could you set permissions on his computer?
6. Speaking
Students use prompts to talk about some precautions related to systems administration (ex. 11). Giving precautions is a function of before + clause/gerund.
Suggested answers:
1 Before upgrading some software, check that no one is using it!
2 Before remote accessing someone`s computer, you should ask permission/let them know what you`re doing.
3 Before switching off a server with users` computers networked to it, check that they`re not using the network/accessing the server.
4 Before deploying new software, give the users training with it.
7. Writing
Students should write a semi-formal letter to a user as a system administrator using the prompts from ex. 12.
Give students the following structure of a semi-formal letter [6]:
|
Feature |
Example |
|
The surname should be used when addressing people |
Dear Mrs.Thomas, Dear Mr Jones, |
|
Opening remarks |
I am writing to tell you … It was very kind of you … It is very kind … I am writing to request … |
|
Semi-formal or neutral style is characterized by |
|
|
Closing remarks |
Thank you very much for your … I am looking forwad to … I would be very grateful if you could … |
|
When signing off the letter |
Yours truly’, ‘Sincerely yours’ and ‘Yours faithfully’ With best wishes’, ‘Cordial regards’, ‘With best personal regards’ and ‘With regards’ |
Alternatively, you can jumble up the functions and features in the first column and ask students to match them to the phrases in the second column.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE:
For students already working in or studying IT, ask them to write an email giving a procedure related to their work or recent studies. The email should incorporate language from the Language box.
Unit 1 Book 2
Working in IT
Практичне заняття №1
Tема: Describing IT Related Jobs and Duties
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина. Checking the group’s presence
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: IT related jobs and duties. Workplace rules
- Language: Expressing frequency, adverbs of frequency, time expressions
- Vocabulary: Introductions: Questions about jobs and companies
1.Warming-up
Students work in pairs. Then should make a list of IT jobs they know and explain the responsibilities of each job.
2. Listening and vocabulary
2.1. Listening for gist. Students do ex. 2 p. 4 (English for Information Technology Part 2) and complete the people’s jobs. Check as a class.
2.2. Listening for details + vocabulary. Students listen again and complete the collocations in ex. 3 p. 5. Check as a class and drill the pronunciation.
Keys: 1 a team, 2 a problem, 3 for, 4 after, 5 software, 6 the problem, 7 databases, 8 databases, 9 specifications
3. Speaking
Ask each student to choose an IT job. Then they work in pairs and interview each other about their jobs:
- Tell me about your current job.
- What are your duties?
- What IT jobs would you like to do/would not like to do? Why?
When speaking, they should use the new collocations.
4. Listening
4.1. Listening for gist. Students listen to track 03 where an IT employee is telling his new manager about his job. Ask students to answer the question, What do you think the employee job is? (Ex. 8 p. 5).
4.2. Listening for details. Ask students to listen again and tick the things that usually happen, then put the phrase in the correct order (ex. 9-10).
5. Grammar
5.1. Draw a horizontal line on the board. Write never, 0% at the beginning of the line and always, 100% at its end. Ask students to put the expressions from ex. 10 in the order that is right in their opinion.
5.2. Check as a class. Ask students to look at the sentences with the adverbs of frequency. Ask: Does the adverb go before or after the verb?
5.3. Refer students to the table on p. 5.
5.4. Students work in new pairs. One student describes a job in IT using adverbs of frequency, the other one should guess the job. Then they switch roles.
5.5. Give feedback on the language and correct the mistakes if necessary.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
1. Use the Interactive Glossary, Section 1 - IT Related jobs and duties (in the English for IT, Supplement). Ask students to read the definitions of the new terms and examples of their derivatives. Ask them to translate these definitions. Let them make five sentences using the new vocabulary.
2. Visit the site with the description of IT jobs. Find out more about the sphere of IT jobs and responsibilities, add them to the list. Share your ideas and findings with a partner. Write a short summary of the text (10-12 sentences).
https://brainporteindhoven.com/int/for-you/work/jobs/jobs-in-it?gclid=EAIaIQobChMI59-brLv28gIVy-h3Ch3jlw6VEAAYASAAEgIa2vD_BwE
Unit 1 Book 2
Working in IT
Практичне заняття №2
Tема: IT Organizations. Present Simple. Adverbs of frequency
Мета заняття: ознайомити студентів з новим лексичним матеріалом з теми “IT Organizations”. Навчити вживати Present Simple questions в усному мовленні та письмі. Розвивати навички діалогічного мовлення, слухання та читання; вміння вести бесіду в групі, аналізувати інформацію на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою IT Organizations
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: Talk about what IT companies do. Company profile
- Language: Present Simple questions,
- Vocabulary: IT Business and products. Company activities
Основна частина
1. Warming-up (revision)
Revision of lexical-grammatical material of the previous lesson. Ask students to work in pairs and talk about IT-related jobs, practise using adverbs of frequency and time expressions.
2. Reading and Vocabulary
2.1. Pre-reading. Students work in new pairs, choose a technology company and list the activities it carries out.
2.2. Reading for gist. Ask students to look at the pictures and names of the companies on p. 6 (English for IT Part 2) and try to predict what these companies do. Then they read the companies’ profiles and check their predictions.
2.3. Reading for details. Students read the profiles again and answer the questions in ex. 3.
Keys: 1 IBGroup, 2 IBGroup, Digital World, 3 Futachiba, 4 Digital World, 5 IBGroup.
2.4. Vocabulary. Students work individually and match the words with their (ex. 2 p. 6, English for IT Part 2). Check as a class.
Keys: 1 provider, supplier; 2 manufacturers; 3 facilities; 4 products; 5 cloud computing; 6 clients; 7 launch.
2.5. Post-reading. Students underline 5 types of software in the company profiles, then work in small groups and answer the questions in ex. 4 p. 7.
3. Listening and grammar
3.1. Listening for gist. Tell students that you’re going to listen to a conversation between two people who work in different IT companies. They should say what kind of company the woman words for and what she does (The company develops apps for Apple and Android devices.)
3.2. Listening for details. Students listen again and complete the gaps in ex. 6 p. 7.
3.3. Grammar. Students look at the sentences they’ve completed. Ask them the following questions: What auxiliary verbs do we use to make questions in the present simple? Which do we use for he/she/it? Which do we use for I/you/we/they? What’s their position in the question? What’s the position of the question word?
3.4. Student check their answers with the table on p. 7.
4. Freer practice
4.1. Students work in groups. Give them the following assignment: You are preparing a magazine article about the local IT companies. Write at least six questions for a questionnaire to find out what each company does. Use the present simple (ex. 9).
4.2. Students from different groups compare their questionnaires. Give feedback on the language.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
Speaking
A. Ask students to think about the answers to questions in questionnaire in ex. 9. Then they should work in pairs, ask and answer the questions. Repeat with a new partner.
B. Students work in pairs. Ask them to answer the following about the product launch:
- What is a product launch? Why is it a good idea?
- Which companies hold big product launches? What kind of events do they hold?
C. Tell students to watch the video about IT organizations and provide comments of the lecture: https://www.coursera.org/lecture/itil-4-exam-preparation/module-3-organizations-people-and-information-technology-video-1-of-2-yAPUC
Unit 2 Book 2
IT systems
Практичне заняття №4-5
Tема: Operating systems. Expressing reason and purpose. Business matters
Мета заняття: ознайомити студентів з новим лексичним матеріалом з теми “Operating systems”. Навчити вживати reason and purpose expressions and grammar structures в усному мовленні та на письмі. Розвивати навички діалогічного мовлення, читання та аналізу інформації на основі лексико-граматичного матеріалу по темі Operating systems.
Час заняття : 90 хвилин
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: Re-installing operating systems in the correct order
- Language: expressing reason and purpose, grammar structures
- Vocabulary: matching words and definitions, OS and PS
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Ask students what they know about open source software and proprietary software. How often do people use it and why?
2. Vocabulary
2.1. Tell students to work in pairs and put the steps in reinstalling the operating system in the correct order (ex. 1 p. 18 in English for IT Part 2).
Keys: 1 Before…, 2 First…, 3 In the BIOS…, 4 This time…, 5 Near the start…, 6 During…, 7 Near the end…
2.2. Ask students to find the words that match the definitions in ex. 2. Check as a class and drill the pronunciation.
Keys: 1 restart, 2 partition, 3 operating system, 4 BIOS, 5 licence, 6 user accounts, 7 reboot, 8 process, 9 back up, 10 licence terms.
3. Functional language
3.1. Presentation. Students underline the words and phrases in ex. 1 used to express reason and purpose, then check with the table on p. 18.
3.2. Practice. Students work in pairs, match the sentence halves and complete the sentences in ex. 3.
Keys
1. Back up everything for safety.
2. Put the DVD in the drive so that the process can start.
3. Press ‘F2’ while rebooting the computer to enter the BIOS.
4. During the installation process, the computer will ask you some questions because it needs to know some information, such as where you are.
5. You might want to partition the hard drive to use the different partitions for different purposes.
6. Change the boot drive to the optical drive so that the computer restarts from the operating system DVD.
3.3. Freer practice. Students do the following task.
Work in pairs and role-play the situation: student A is an IT technician, student B is an IT user. Ask and answer questions using the following prompts:
Back up everything; put DVD in the drive; reboot the computer; you might want to partition the hard drive, etc. (ex. 4). Give reason for your advice. Then swap roles. Practice using the purpose and reason collocations.
4. Listening:
Tell students to listen to a spokesmen of a big operating system company giving a speech: Why open source is a bad idea. Ask students to make a list of reasons given by the speaker that explain why PS is better idea. Compare as a class.
5. Writing
Tell students to write an email to a manager explaining which operating system to use: OS or PS? They should give reasons of their choice for each of the systems. Ask them to use the language box on p. 18 and the information about writing emails on p. 17.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
Reading: Ask students to work in pairs and answer the following questions:
- What do you think about open source software? Think about the cost.
- What are the advantages of proprietary software? Make a list. Give reasons why OS is better than PS.
Read the web article and check your answers. (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2) p.19).
Speaking: Tell students to work in small groups. As a technician in advertising company, you received an email from a manager who asks for advice. Decide which software to use: open source OS or proprietary OS, or some of each? Then explain your decision to the class (see ex. 5 p.19)
Watch the video describing operating systems and tell the class about the new features and information that you learned from this video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mXw9ruZaxzQ
Unit 3 Book 2
Data communication
Практичне заняття №1
Тема: Internet browsing. Present Simple vs. Present Continuous
Мета заняття: формування навичок монологічного та діалогічного мовлення студентів на рівні речення, слухання іншомовного мовлення; ознайомлення з новою лексикою; оволодіння студентам іноземною мовою як засобом спілкування і здійснення в цьому процесі виховання, навчання та розвитку особистості студента за темою Internet browsing.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
- Function: describing browser problems.
- Language: present simple and present continuous; stative verbs.
- Vocabulary: components of a browser, talking about browser problems.
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
Ask students the following questions.
- Which websites do you visit most often?
- Which browser do you prefer? Why?
- What should a good website have?
2. Vocabulary (Jon Marks. Check your English Vocabulary For Computers and Information Technology. Third Edition).
2.1. Ask students to match the activities 1-10 with the internet features a-j. Then check their answers and drill the pronunciation of the new words.
1. Keep a public diary of your journey through South America
2. Lose lots of money
3. Find out about the First World War
4. Download songs
5. Listen to music in real time
6. Check your email from any computer
7. Find links to other websites
8. Exchange messages in real time with friends or colleagues
9. Check the latest exchange rates
10. Read new articles about a subject that interests you
a. webmail
b. online music store
c. instant messaging
d. online radio
e. portal
f. blog
g. online encyclopedia
h. currency converter
i. e-zine
j. online casino
Keys: 1f, 2j, 3g, 4b, 5d, 6a, 7e, 8c, 9h, 10i
2.2. Students should work in small groups and answer the question, What do you do on the internet? using the features and activities from ex 1.
2.3. Ask students to match the browser toolbar buttons 1-11 with the function a-k.
1. Back
2. Forward
3. Stop
4. Refresh1 / Reload2
5. Home
6. Search
7. Favourites1 / Bookmarks2
8. Media
9. History
10. Mail
11. Print
a. Shows a list of the websites you have visited recently.
b. Opens the media bar, accessing internet radio, music, video etc.
c. Displays the page you were on before.
d. Shows the latest version of the page.
e. Opens the search panel.
f. Displays the page you were on before using the Back button.
g. Displays the page you have set as your home page.
h. Prints the current page.
i. Stops a page from downloading.
j. Displays the web addresses you have chosen as your favourites.
k. Shows email options.
Keys: 1c, 2f, 3i, 4d, 5g, 6e, 7j, 8b, 9a, 10k, 11h
2.4. Students work in pairs and do the following task:
Cover the list of the functions with your hand. Choose a toolbar button, but don’t tell your partner which one you’ve chosen. Explain its functions to your partner from memory. Your partner should guess which button you’re describing. Then switch roles.
3. Watching
3.1. Pre-watching. Students look at the picture, explain what it means and what problems it shows.

3.2. Watching for gist. Students watch the video How to Fix Internet browsing problems (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VZ18BChfszE) and tick the browser problems that the tech expert mentions:
Slow browser
Errors on the page
Browser getting hijacked to a site you weren’t going to
Browser infected by spyware or adware
Problems with video streaming
Keys: all except the last one (problems with video streaming)
3.3. Watching for details. Students watch the video again and in pairs put the following steps of troubleshooting in the correct order.
A Click on Internet Options
B Click the Advanced tab on top in the same window
C Click Delete files and then OK
D Open Internet Explorer
E Click Tools from the top menu
F Click Apply and OK
G Uncheck Enable third-party browser extension
Keys: D E A C B G F
4. Speaking
4.1. Students read the article, then work in pairs and discuss whether they’ve had similar problems and how they solved them.
Slow performance and page loads
You should already be running the latest version of your browser, but just check anyway: Help then About Google Chrome from the Chrome menu; About Firefox from the Firefox menu in Firefox for macOS; Help then About Firefox from the browser menu in Windows;
Is an extension dragging down the performance of your browser? Disabling add-ons one by one is something you can try to see if it has any effect—More Tools then Extensions from the Chrome menu; Add-ons from the Firefox menu;
If it’s not an extension that’s slowing everything down, it might be a corrupted cache of data. You can easily blitz these temporary files and give your browser a fresh start—you’ll have to log in everywhere again, so keep those passwords handy.
In Chrome, open up Settings from the menu then pick Clear browsing data. In Firefox, you want Preferences from the menu, then Privacy & Security and Clear Data.
If you’re still experiencing problems, uninstall and reinstall your browser—if a clean reinstall doesn’t work, something besides the browser might be affecting performance. That something could be malware, which we discuss in more detail below.
Chrome, Firefox have a single reset settings option. In Chrome, Restore settings to their original defaults is at the bottom of the main settings pane; in Firefox, choose Help then Troubleshooting Information from the menu to find the reset option.
Too many pop-up windows
Use whatever antivirus software you have installed to run a thorough scan for problems, and for an extra sweep, run a no-install, on-demand scanner (like Microsoft Safety Scanner or ClamWin Portable).
Pages don’t work as intended
Check your browser extensions and settings, clear out the cache. These options are under Site settings in Chrome settings; Privacy & Security and Permissions in Firefox settings; If you’re having problems with one site in particular, see if it works in another browser.
4.1. Students work in the same pairs. They choose one of the problems and make a dialogue following the troubleshooting steps above.
Example:
A: Hello, Mark. I have a problem with the network. Can you give me some advice?
B: Yes, sure. Could you explain what’s wrong with the network?
A: The internet is slow and the pages don’t load quickly.
B: I think you should check the version of your browser, whether it’s new. What browser do you have?
A: Chrome, and I have the newest one.
B: Perhaps your browser has too much cache. I guess you should go to Settings and choose Clear browsing data. This might help.
A: Thank you!
B: You are welcome.
5. Grammar
Test-Teach-Test technique
5.1. TEST: to check students’ understanding of how to use the present simple and continuous, write the phrase I work in an IT Department. This week I’m managing the department because my manager is away on the board and elicit the answers to the questions:
1. What tenses do we use in these sentences? (Present Simple, Present Continuous.)
2. Why is the verb work in the present simple? (It’s a regular action.)
3. Why is manage in the present continuous? (It’s temporary.)
TEST: to check students’ understanding of stative verbs, write the phrase I understand that now on the board and elicit the answers to the questions:
1. Does the sentence describe an action or state? (State.)
2. What other state verbs do you know? (like, love, know, etc.)
3. Do we normally use stative verbs in the present continuous? (No.)
Ask students to read and explain the use of tenses, ex. 5 p. 20 (Why do we use I’m having trouble in the present continuous? You mean in present simple? I need in present simple?
5.2. TEACH: look at the picture and answer the questions:
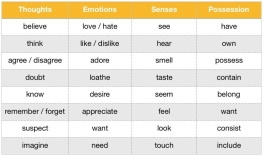
- What category of verbs is shown?
- What characteristics of verbs are shown?
- Are they stative verbs or action verbs?
5.3. Practice: Ask students to do ex. 8 p. 21 (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book).
5.4. Test control: Ask students to do the ex. 11 p. 9 (Virginia Evans. Grammarway 3.) 
5.5. Freer Practice: Ask students to work in pairs. They role-play a telephone conversation using the learnt grammar (Ex. 9 p. 21 in Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book)
5.6. Give feedback on the language.
Завдання для самостійної роботи:
- Exercise 12 (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book 2), p. 21
- Exercise 5 (John Hughes & Jon Naunton) Business Result. Intermediate. Second Edition), p. 9.
Використана література:
- Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book
- How to Fix Browsing Problems. Режим доступу: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VZ18BChfszE
- Virginia Evans. Grammarway 3
Unit 3 Book 2
Data communication
Практичне заняття №4
Тема: Mobile computing
Мета заняття: ознайомлення студентів із IT функціями мобільних пристроїв та використанням їх у різних сферах обслуговування; розвиток навичок читання та слухання; формування іншомовних навичок і вмінь, оволодіння студентам іноземною мовою як засобом спілкування і здійснення в цьому процесі виховання, навчання та розвитку особистості студента за темою Mobile computing.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
- Function: discussion: the usage of mobile and сustom devices
- Language: zero and first conditionals
- Vocabulary: mobile computing
Основна частина
Students work in pairs and discuss the questions.
1.What features do you have on your mobile phones? What do you use them for?
2.What mobile phone functions are important for you?
3.What are the advantages and disadvantages of mobile phones?
2. Vocabulary (Jon Marks. Check your English Vocabulary For Computers and Information Technology. Third Edition)
2.1. Students do the following tasks.
- Consult a dictionary and choose the best word.
- I need to charge up my mobile phone battery. Have you seen my __________?
- charger b. recharger c. charging machine
- When you send a text message, the __________ function can help you write it more quickly.
- predicting text b. predictive text c. text predictor
- If you don't want to dial a number by mistake, turn on the __________.
- keypad locker b. keypad lock c. locker of keypad
Keys: 1a, 2b, 3b
- Which one is not possible?
- I'll call her on my…
a. mobile phone b. cell phone c. moving phone d. cellular phone
- A mobile phone can't work without a…
a. SIM card b. sim card c. sim chip d. similar card
- Don't forget to send me…
a. a text message b. a text c. an SMS d. a phone message
- When I arrive, I'll…
- text you b. textualise you c. send you an SMS d. send you a text
Keys: 1c, 2d, 3d, 4b
2.2. Students match the devices 1-8 with the places a-h where they would find them.
1. cash dispenser / cash machine / ATM
2. barcode reader
3. magnetic strip
4. MP3 player
5. photocopier
6. telex machine
7. video camera
8. mainframe computer
a. at a supermarket checkout
b. connected to a pair of headphones
c. in an office in 1975
d. in an office, school or copy shop
e. in the hands of a tourist
f. in the headquarters of a large company
g. on the back of a credit card
h. outside a bank
Keys: 1h, 2a, 3g, 4b, 5d, 6c, 7e, 8f
2.3. Drill the pronunciation of the new words. Then students should work in pairs and explain some of the words above in other words. One students explains, the other one should guess. Then they swap roles.
2.4. Students work in pairs and do the following task:
Think about people in these jobs. How might a mobile device be useful to them? (Ex. 2 p 24, Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book).
2.5. Students complete the flowchart with steps a-f in the correct order. Then they should say whether the technicians work will change if the technician has a mobile device.

3. Listening
3.1. Listening for gist. Ask students to read the question and listen to the track to answer it, What function helps technicians to find the clients quickly?
3.2. Listening for details. Students listen again and answer the following questions.
1. How can technicians use new tablet computers?
2. How will tablets improve their flexibility?
3. What was the problem in the old system?
4. Reading and Vocabulary.
4.1. Pre-reading. Students look at the picture on p. 25 (Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book), work in pairs and answer the questions:
- What is she doing?
- What’s her job?
- How can a mobile device help her?
4.2. Reading for gist. Students read the advertisement and check their predictions.
Keys: She is a traffic warden. A mobile device can help her be safe and more productive.
4.3. Reading for details. Students read again and answer the questions:
- Who is the advertisement for: consumers or businesses? (Businesses.)
- Are the company’s devices only for traffic wardens, or for other people as well? (They can be customized for any situation and used by other people as well.)
- How does the device improve traffic wardens’ productivity and safety? (The devices have cameras and GPS so wardens can take photos of illegally parked cars. Also, they can transmit cars’ registration numbers to a central database so wardens save their time; report the warden’s location to the control centre, and send a message to signal about a dangerous situation.)
4.4. Vocabulary. Students work individually, read the advertisement and use the context to match the words to their definitions (ex. 10). Check as a class and drill the pronunciation.
Читання (https://www.healthitoutcomes.com/solution/healthcare-mobile-computing ) - optional
Read a short paragraph about mobile computing in healthcare and answer the questions.
MOBILE COMPUTING
Mobile devices can save time, reduce errors, and real time data access at the point-of-care. With mobile computers, healthcare providers have access to patient information on-demand and at any location in the facility. In general, these point-of-care computing solutions include tablets, laptops, smartphones, mobile carts, handheld scanners, and RFID readers. All of these mobile devices are essential to the larger category of mHealth solutions.
Mobile devices like tablets and laptops offer providers easy access to EHR/EMR systems, allowing doctors to diagnose patients quickly and have patient information available to them immediately. Handheld scanners, barcode scanners, barcoded wrist bands, RFID tags, and other identification applications allow for quick and easy identification of patients and medications. These technologies ensure proper medication dispensing and also provide patient security and safety.
Many of these mobile devices are housed in mobile carts, allowing for quick and easy access to tools, additional battery power for all devices, and enhanced mobility. All of these mobile computing technologies allow healthcare providers to access and record patient data in real time at the point-of-care, ensuring the highest quality healthcare possible.
- What role does mobile computing have in medical care?
- What does mobile computing help doctors to do?
- What devices can be used for healthcare solutions?
- What do barcode scanners, barcoded wrist bands, RFID tags allow doctors to identify?
- Are doctors able to record patient’s data in real time?
5. Grammar.
5.1. Presentation. Write two sentence on the board:
1. So if there is a problem, the control centre knows exactly where the warden is and who to contact.
2. If we have a problem, we’ll send you a message.
Ask students:
- Is the first sentence about a situation in the future, or something that usually happens? (Something that usually happens). What about the second one? (A situation in the future.)
- In the first sentence, what tense do we use in the first part? What about the other part? (Present simple in both parts.)
- In the second sentence, what tense do we use after if? (Present Simple.) What verb form do we use in the other part? (will + V.)
Then students look at the grammar table on p. 24 and the one below and check their answers.
1. FIRST CONDITIONAL
We use the first conditional to express something that will probably happen in the future.
If Paul gets the job, he will move to London.
|
IF CLAUSE MAIN CLAUSE |
|
Present Simple Future Simple (will + infinitive) . Modal verbs (Can / May / Must + infinitive) Imperative |
2 ZERO CONDITIONAL
We use the zero conditional for general truths or natural laws.
If you don’t water plants regularly, they die.
If you heat ice, it turns into water.
|
IF CLAUSE MAIN CLAUSE |
|
Present Simple Present Simple |
5.2. Practice 2. Students match the sentences and join them with if (John Eastwood. OPG Intermediate p. 347 ex. C).
1 You lose your credit card. A I can't sleep.
2 You get promoted. B You get a warning letter.
3 I drink coffee late at night. C You have to ring the bank.
4 You don't pay the bill. D Your salary goes up.
5 I try to run fast. E The alarm goes off.
6 Someone enters the building. F I get out of breath.
► If you lose your credit card, you have to ring the bank.
- ……………………………………………………………………………….
- ……………………………………………………………………………….
- ...................................................................................
- ……………………………………………………………………………….
- .......................................................................................
Keys: 1C, 2D, 3A, 4B, 5F, 6E
5.3. Practice 3. Students should work in pairs and comment on the situations. Use if + the present simple, will/can + V. (John Eastwood. OPG Intermediate p. 347 ex. B).
Examples:
? It might rain. If it does, everyone can eat inside.
If it rains, everyone can eat inside.
? The children mustn't go near Nick's dog. It'll bite them.
If the children go near Nick's dog, it'll bite them.
1 Rachel might fail her driving test. But she can take it again.
2 United might lose. If they do, Tom will be upset.
3 The office may be closed. In that case Mark won't be able to get in.
4 Nick may arrive a bit early. If he does, he can help Tom to get things ready.
5 The party might go on all night. If it does, no one will want to do any work tomorrow.
6 We buy some tablets soon, so we’ll save money.
7 Is Matthew going to enter the race? He'll probably win it.
5.4. Freer practice. Regroup the students. They work in pairs and do ex. 7 p. 25. They should use conditional sentences when discussing.
5.5. Point out some good examples of the language and correct the mistakes if necessary.
Завдання для самостійної роботи:
- Exercise 1-2 (John Hughes & Jon Naunton. Business Result. Pre-intermediate. Second Edition), p. 125.
Використана література:
1. Olejniczak M. English for Information Technology (2). Vocational English Course Book 2.
2. John Eastwood. Oxford Practice Grammar Intermediate.
3. Jon Marks. Check your English Vocabulary For Computers and Information Technology. Third Edition
4. Healthcare Mobile Computing. Режим доступу: https://www.healthitoutcomes.com/solution/healthcare-mobile-computing
Unit 4 Book 2
Administration
Практичне заняття №1-2
Тема: Spreadsheets and formulae. Past Simple
Мета заняття: Ознайомити студентів із основними формулами та математичними діями для роботи в таблицях Excel. Навчити вживати вивчений лексичний матеріал в усному мовленні з використанням відповідних граматичних конструкцій (Present and Past Simple, Zero Conditional). Навчити студентів коментувати та давати аналіз даної інформації за темою Spreadsheets and formulae.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за наступними питаннями:
1. Function: Talking about how people use spreadsheets generally and about students’ own experiences with spreadsheets using Past Simple.
2. Language: Past and Present Simple. Zero conditional.
3. Vocabulary: Basic vocabulary of arithmetic, spreadsheet formulae.
Основна частина
1. Warming-up
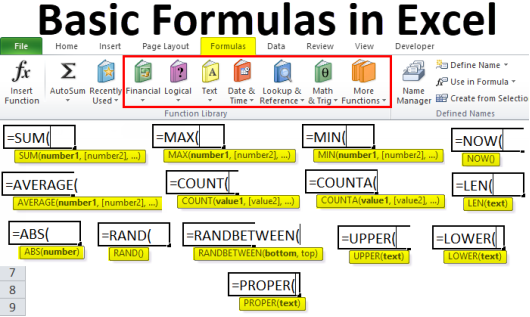
Fig. 1. Basic formulas in Excel [1]
1.1. Students look at the picture and try to guess what each formula is used for. If there is problem with some formulas, offer students to find information about them on the Internet (or use this Activity as a part of homework).
1.2. Students work in groups and discuss the following questions.
1. What do people use spreadsheets for?
2. Do you use spreadsheets? What for?
3. What do you find difficult/easy about using them?
2. Vocabulary
2.1. After discussing students’ experience of using spreadsheets, ask them about the basic arithmetic operations they know (e.g. plus +, minus (subtract)-, multiply by *, divide by /) as part of preparation for the next Activity.
2.21. Students match some basic sums written as words with the equivalent sums in symbols to obtain the basic vocabulary of arithmetic, a necessary step towards being able to say spreadsheet formula (ex. 2 p. 28 English for IT Part 2).
Point out that the way that some of these sums are written by hands is different from how they are typed in Excel, for example, ‘/’ is used instead of ‘÷’ and ‘*’ (asterisk) – instead of ‘x’.
Keys to Exercise: 1c; 2b, 8 minus 2 is 6; 3d, 8 times 2 is 16; 4a, 8 plus 2 is ten.
2.3. Students work in pairs. They should write down a number of sums of their choice, and then say it randomly to a partner, who says the answer.
For example: A: What is 7 minus 5?
B: 2. If you divide 10 by 2.5, what do you get?
A:4
2.4. Students listen to a trainer explaining a spreadsheet to a trainee and match the words to the items on the screenshot of a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
Before listening, they may work in small groups and discuss the meaning of the following words: cell, column, formula, row, value, worksheet. Pay attention to pronunciation.
Keys: 1F, 2E, 3A, 4B, 5C, 6D. The formula adds up some numbers.
2.5. Students work in pairs and practise saying formulas. Student A looks at the information on p. 29 and reads it to Student B; Student B writes it down then Student A checks it. Then Student B looks at the information on p. 70 and reads it to Student A; Student A writes it down then Student B checks it (ex. 5 p. 29).
Example:
Student A: equals, capital letters SUM, open brackets, select the column from 1 to 11, close brackets, and press Enter.
Student B: =SUM(A1;A11)
3. Use of language (grammar revision and function)
3.1. Remind students the key points of Present and Past Simple usage, as well as Zero Conditional. Optionally, you can draw this table on the board.
Present and Past Simple, Zero Conditional revision [2].
|
Present Simple |
Example |
|
Always true |
Two plus two is four |
|
Permanent situations |
I check the formulas every time |
|
Short actions now |
He types equals, writes formula, opens the brackets and inserts data. |
|
Zero conditional (general truth) |
If you divide 4 by 2, you get 2 |
|
Past Simple |
Example |
|
Finished actions or events in the past |
Did you check the formula in the spreadsheet? Yes, I did. |
|
Remember: |
|
|
Regular verbs (e.g. check, correct) usually add -ed |
I corrected the mistake in formula. |
|
Irregular verbs (e.g. be, write, find) have their own past simple forms |
I found the mistake and rewrote the formula. |
Alternatively, you may leave out some information from the table and ask students to complete it. For example: Regular verbs usually add ____. ________ verbs have their own past forms.
Ask students to make up 2-5 sentences using new grammar structure.
3.2. Students read the audio script 17 on page 75 and say which tenses are used. They complete the sentence from ex. 6 on page 29 and discuss the answer in small groups.
Keys: The past simple and present simple are used. Present simple, past simple
3.3. Ask students to make up 2-5 sentences using new grammar structure in order to describe the problems they faced in the past and how did they solved them.
Example: (problems: wrong format of the data, wrong formula, didn`t put “=” before formula, chose the wrong formula etc.)
Q.1. What problem did you have when you tried to complete the spreadsheet in Excel?
A.1. I did not get any result, because of the wrong format of the data.
Q.2. What did you do with that?
A.2. I corrected the format and applied the formula one more time and got the right result.
4. Listening
4.1. Pre-listening. Ask students to describe problems they’ve had with spreadsheets, pay their attention to using the correct tense while they describe the problem.
4.2. Students should listen to Track 18 and say what all speakers have in common. (They all have problems with spreadsheets.)
4.3. Students listen again and complete the table to show the past and present actions.
Keys: 2 saved a spreadsheet (in the main folder); can`t find it; 3 designed a spreadsheet; it doesn`t work; 4 typed a date (into cell); it shows a number
4.4. Post-listening. Students work in pairs and match the explanations and solutions to the problems in ex. 8 p.29.
Keys: a2, c4, d3.
5. Speaking
5.1. Then students use the information from ex. 8 to make up a dialogue and role-play the situations and solutions. Choose two strong students to model the first conversation using the example as a starting point.
5.2. Students work in pairs and take turns to describe an IT problem (it’s better to choose a problem with a spreadsheet) that happened to them, and the solution. Then they may switch partners and discuss new problems.
5.3. Give feedback on the language. Point out some good examples and correct some mistakes.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE:
Watch the video How to Create a Table in Excel (Spreadsheet Basics) [3]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IACzM_mzstk&ab_channel=HowTo-byNatalie
Using the example make your own table about your personal budget, taking into account that the Currency, Expense category and Type of expenses will be different for you.
Unit 4 Book 2
Administration
Практичне заняття №5
Тема: Peripherals and tools. Past Continuous
Мета заняття: Ознайомити студентів із особливостями використання Past Continuous та Past Simple для вирішення проблем, що виникають при роботі з комп’ютерною технікою. Сприяти формуванню комунікативних навичок та навичок роботі в групі при обговоренні лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою: Peripherals.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence.
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
1. Function: Talking about peripherals, their types and functions. Explaining how problems occur.
2. Language: Past Continuous. Past Simple revision
3. Vocabulary: Types of peripherals: network attached storage, touchpad, stylus, graphics tablet and stylus, touch screen, headset, multifunction printer.
Основна частина
1. Warming-up

Fig. 4. Types of Peripheral Devices [7]
Students look at the picture and try to name as many peripherals as they can. Then students may be asked to make a list of 3 peripheral devices which are not shown on the picture. Then they describe each item to a partner, so he/she can guess what it is.
2. Vocabulary
2.1. In pairs, student match photos of peripherals to descriptions of what the peripherals do (ex. 2 p. 34 in English for IT, Part 2). Note that all-in-one devices are also referred to as multifunction devices (MFD) and multifunction printers, and that these also come in sizes that will fit on a desk.
Keys: A1, B5, C7, D2, E4, F3, G8, H6.
2.2. In the same pairs, students decide whether the devices in Activity 2 are output or input. Write I or O as appropriate next to each. Some devices can be both or neither (ex. 3 p. 34).
Keys: 1 neither; 2I; 3I; 4I; 5I,O; 6O; 7 I,O; 8O.
3. Listening
Students listen to an assistant systems administrator explaining a problem to his manager and complete the table (ex. 4 p. 34). Explain that in progress means happening. Students listen only once, then compare their answers in pairs or small groups. Check as a class. (Answer: The accountant was trying to save a spreadsheet to the NAS device. 1 got an error message; 2 couldn`t connect to it (from anywhere); 3 maybe a problem with the network cable).
4. Grammar
4.1. Write on the board: The printer ran out of ink while I was using it. Ask: How many actions are described in this sentence? (Two.) Did they happen at the same time or one after the other? (At the same time.) Which one was shorter and interrupted the longer action? (Ran out of ink.) Refer students to the Language table on p. 35. The second point in the table, about interrupted actions, should be emphasised as this is the point practiced in later activities.
Past Continuous. Past Simple revision

4.2. Practice. Students use the prompts provided in ex. 5 p. 35 to explain problems to their partner. Before beginning the activity, choose two students and elicit a conversation similar to the following:
A: Albert, I`ve got a problem. Could you help me?
B: Sure, what`s the matter?
A: Well, the printer`s jammed. This morning I was printing a report when it stopped suddenly. Half of the report didn`t print properly.
This model can be written on a board as a model answer.
For weaker students, allow some time before role-playing to write the sentences with the prompts using the past simple and past continuous, then check as a class.
4.3. Freer practice (writing). Students should write a semi-formal letter to a company`s IT Support Office explaining one of the problems from the previous Activity. They can use the letter structure from the previous lesson.
4.4. Students work in small groups. They should swap their letters and discuss how to solve each problem. Monitor and give feedback on the language.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE:
Read some unknown facts about computers and peripherals [8]
https://www.quora.com/What-are-some-unknown-facts-about-computer-peripherals
Try to find at least 5 mind-blowing facts for further discussion in the group.
Unit 4 Book 2
Administration
Практичне заняття №6
Тема: Administration. Business matters
Мета заняття: Закріплення лексико-граматичного матеріалу за темою Administration в контексті обговорення проблем, пов’язаних із системним адмініструванням, та надання рекомендацій щодо їх вирішення. Удосконалення навичок написання рекомендацій з використанням граматичних конструкцій із while, before, after.
Час заняття: 90 хвилин.
Зміст заняття
Ознайомлювальна частина
Checking the group’s presence
Опитування студентів за такими питаннями:
1. Function: Discuss and propose solutions to some IT problems related to the unit topics.
2. Language: Apply the language students have learnt and practiced on the previous pages of the unit 4.
3. Vocabulary: Revision of the vocabulary from Unit 4.
Основна частина
1. Speaking
1.1. Students read the scenario on p. 35 (English for IT, Part 2). Then they should work in small groups, choose four of the problems, and complete a log with those problems and actions taken (ex. 2 p. 35). (For space reasons, it may be better for them to use a copy of the log in their own notebooks).
1.2. Students work with a new partner and explain the problems from the “action taken” column in their logs, using the language from earlier in this unit.
2. Follow-up writing
Students write an email to the system administrator as requested in the scenario in Activity 1, explaining the problems they encountered and how they solved them (ex. 4 p. 35). After that, you can collect and check their emails, or ask them to do peer-checking and then collect the works yourself.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE: Read the information about “Databases vs Spreadsheets” https://blog.airtable.com/database-vs-spreadsheet/. [9] and make a comparison table of both of them. In the end, write a conclusion about which one is the best to use at the University for studying purposes.
Перелік використаної літератури в методичному керівництві до підручника English for Information Technology (Part 2) UNIT 4
|
Практичне заняття |
Використані джерела |
|
Практичне заняття № 20-21 Тема: Spreadsheets and formulae. Past Simple |
1. Basic Excel Formulas [Електронний ресурс] // EDUCBA. – 2021. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.educba.com/basic-formulas-in-excel/. 2. The Simple Tenses [Електронний ресурс] // Perfect English Grammar. – 2007. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/ 3. How to Create a Table in Excel (Spreadsheet Basics) [Електронний ресурс] // HowTo-byNatalie. – 2021. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IACzM_mzstk&ab_channel=HowTo-byNatalie. |
|
Практичне заняття № 22 Тема: Databases |
4. Different types of Databases and Cloud Native Databases [Електронний ресурс] // Navdeep Singh Gill. – 2019. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.xenonstack.com/blog/databases. |
|
Практичне заняття № 23 Тема: System administration |
5. Sysadmin: Role, Responsibilities, Job Description & Salary Trends [Електронний ресурс] // BMC blogs. – 2019. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.bmc.com/blogs/sysadmin-role-responsibilities-salary/#. 6. How to Write a Semi-formal Letter [Електронний ресурс] // IntoEnglish. – 2019. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://in2english.net/2019/03/20/how-to-write-a-semi-formal-letter/. |
|
Практичне заняття № 24-25 Тема: Peripherals and tools. Past Continuous |
7. Types of Peripheral Devices [Електронний ресурс] // YourTechOutlet. – 2021. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://yourtechoutlet.com/collections/peripherals. 8. What are some unknown facts about computer/peripherals? [Електронний ресурс] // Quora. – 2020. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://www.quora.com/What-are-some-unknown-facts-about-computer-peripherals. |
|
Практичне заняття № 26 Тема: Business matters |
9. Database vs. spreadsheet: which is better? [Електронний ресурс] // For the record. – 2020. – Режим доступу до ресурсу: https://blog.airtable.com/database-vs-spreadsheet/. |

про публікацію авторської розробки
Додати розробку